-
摘要: 通过测量相同时间、不同温度下制备的W/Ti扩散偶成分和显微硬度,研究了W–Ti合金的扩散特性和机理,计算了W/Ti互扩散系数(单位:cm2·s-1),并利用MS软件对Ti原子数分数为12.5%~50%的W–Ti二元合金的能量、电子结构进行了理论计算。结果表明:W与Ti发生互扩散,其中W在Ti中的扩散速度远高于Ti在W中的扩散速度;在1100~1300℃时,W基固溶体中的互扩散系数公式为2.6×10-5exp(-385.3/kT),Ti基固溶体中的互扩散系数公式为4.1×10-2exp(-285.1/kT),其中,T为扩散温度,k为扩散距离;随着Ti原子数分数的升高,W–Ti合金的β结构稳定性降低。Abstract: The composition and microhardness of W/Ti diffusion couple prepared at different temperatures in the sameholding time were analyzed to study the interdiffusion of W–Ti alloy, the W/Ti interdiffusion coefficients were calculated, and the energy and electronic structure of W–Ti binary alloy in the Ti atomic fraction of 12.5%~50% were calculated by MS software. The results show that the diffusion speed of W in Ti is farhigher than the diffusion speed of Ti in W. The W/Ti interdiffusion coefficient equations (unit: cm2·s-1) at 1100~1300℃ in tungsten and titanium solid solutions are expressed as 2.6×10-5exp(-385.3/kT) and 4.1×10-2exp(-285.1/kT), respectively, T is diffusion temperature, k is diffusion distance; the β phase stability of W–Ti alloy decreases monotonously with the increasing of Ti content.
-
Keywords:
- W–Ti alloy /
- interdiffusion /
- microhardness /
- first-principle
-
W–Ti合金具有良好的热稳定性、低的电子迁移率、高的抗腐蚀性及化学稳定性等优势,特别适合在高温和高电流环境下使用[1-3],因而成为了金属布线扩散阻挡层的主导材料之一。由于制备方法和工艺的不同使W–Ti合金呈现出不同的相结构,而扩散是影响相结构的主要因素,因此研究W和Ti之间的扩散对于制备不同相结构的W–Ti合金具有指导意义[4],但关于这方面的研究较少。本文采用制备扩散偶的方法,将相图、扩散理论和扩散模型相结合,计算得到了1100~1300℃之间W/Ti互扩散系数、互扩散公式及扩散特点。通过W和Ti之间的扩散研究,将进一步明确两者之间的扩散机理,为制备高均匀的W–Ti合金靶材提供理论依据。
1. 实验
将W粉和高纯Ti粉分别在400MPa的压力下冷压成型,以尺寸过200目筛网的多角形粉体作为实验样本,筛分的目的是为了保持粉体粒度分布一致,以消除原始粉体粒度分布对后续扩散结果的影响,试样尺寸为φ21mm×4mm,压坯相对密度80%。把压制好的压坯制成一端为W,一端为Ti的扩散偶,置于惰性气体(Ar)热压烧结炉内烧结成型,升温速度10℃·min−1,烧结温度分别为1100、1200和1300℃,保温时间为1h。完成热处理后,样品随炉空冷。
采用金相显微镜(optical metalloscope,OM)、JSM-6700场发射扫描电镜(field emission scanning electron microscope,FESEM)及能谱分析(energy dispersive spectrometer,EDS)分别进行显微组织形貌观察和成分测量,并从W/Ti界面处分别向W和Ti端进行等距定点成分测量。采用Wilson-tukon2100型显微硬度仪测量不同组织的显微硬度。利用MS软件对Ti原子数分数为12.5%~50%的W–Ti二元合金的能量、电子结构进行理论计算,采用2×2×2的体心立方W超晶胞,晶胞中均含有16个原子,并分别用x(x=2~8)个Ti原子去分别置换超晶胞中的W原子,此时W–Ti合金的名义分子式为W16-xTix(Ti元素的原子数分数为12.5%~50%)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同烧结温度下W/Ti扩散偶组织
图 1为不同烧结温度制备的W/Ti扩散偶显微组织。由图 1可见,扩散偶主要是由四种形貌组成,即Ⅰ区为扩散层,Ⅱ区为扩散过渡区,Ⅲ区为纯Ti区,Ⅳ区为纯W区。随着烧结温度的提高,纯Ti区的晶粒逐渐长大而纯W区的孔隙逐渐减少;同时,扩散层的厚度也逐渐增加,由1100℃时的(15±3)μm增加到1300℃时的(30±3)μm,可见随着温度的升高扩散速度明显加快。
除却温度以外,晶界也是高温下利于扩散的主要主导因素。实验所用原料低杂质钛粉体系,故而一般表面氧化污染引起的扩散阻碍可以忽略,又由于实验温度在Ti的β转变温度之上,故而此时已经具有较为明显的烧结作用[5],此时的β晶粒主要受到所处温度与时间控制[6]。因此,一般只有晶粒达到纳米尺度时,Ti系扩散偶的自扩散系数才具有比较明显的变化[7-9]。由于β晶粒在相变点上很快过热充分长大[10],因而在本实验中,由于晶粒尺寸差异对于实验结果造成的误差在可接受范围之内,这是后续分析的重要前提。
2.2 W/Ti扩散偶的成分差异
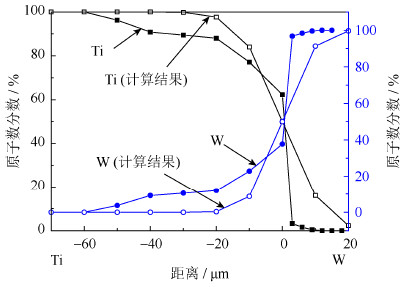
图 2为1300℃时W/Ti扩散偶的线扫描分析,其中浅色部分为纯W区,深色部分为纯Ti区,在纯W区与纯Ti区之间为W/Ti扩散区,宽度在46~62μm之间。由图可知,W/Ti扩散区颜色随着Ti原子数分数的增大而逐渐变深,在纯W区与W/Ti扩散区的界面附近Ti含量迅速下降到零,同时W原子数分数也很快达到最大值。在纯Ti区与W–Ti合金区的界面附近Ti含量缓慢地达到最大值,W原子数分数也同时缓慢地降为零。这表明W原子更容易扩散进入纯Ti中,而Ti原子扩散进入纯W的速度较慢。
图 3为1300℃制备的W/Ti扩散偶结合面附近的成分分布,能够反映扩散层的宽度和所形成W–Ti固溶体的成分。Ti区一侧形成了富Ti固溶体相,W的原子数分数范围在0~37.7%;W区形成了富W相固溶体且Ti原子数分数较少,最高仅为3.2%。不同成分的W–Ti固溶体硬度差别较大,图 4为W/Ti扩散偶结合面附近的显微硬度曲线。从曲线中可以看出,随着W原子数分数的降低,Ti基体区硬度先升高后逐渐下降,这说明,富W固溶体的硬度明显高于富Ti固溶体;纯Ti区的显微硬度为HV0.05(170±5),低于熔炼法制备的纯Ti;纯W区的显微硬度为HV0.05(220±10),略低于高温烧结的纯W棒。
2.3 扩散过程分析
根据W–Ti二元相图[11],当温度高于882.5℃时,纯W和纯Ti的晶格类型均为体心立方,两者的原子半径分别为0.1368nm和0.1460nm。根据Hume-Rothery经验规则[12],两者之间形成无限置换固溶体,因此空位扩散为主导扩散机制。且W原子质量是Ti原子质量的4倍,根据前苏联科学家弗兰克尔1945年提出的空洞理论:温度升高时,晶体中的空位浓度增加,使固体中组元的扩散系数提高。制备温度均高于Ti的晶体转变温度(882.5℃),Ti经过晶体转变以及在压力的作用下产生大量的空位,多于纯W中的空位数量,这导致W原子有更大的几率摆脱晶格的缚束进入纯Ti中,而且W原子进入Ti区能够沿着空位快速地向Ti基体内迁移,降低界面附近的W原子数分数,有助于W原子的进一步扩散,扩散距离达到了37~57μm;保温阶段,虽然Ti原子具有了足够的能量,有很大的活性,但W原子质量大、熔点较高,W原子不容易摆脱晶格的缚束形成大量的空位,仅在压力的作用下产生少量空位,所以Ti原子扩散进入纯W的量较少,扩散距离也很短(5~9μm)。
根据扩散偶计算模型,即无限长棒中的扩散模型计算各温度下不同区域的扩散系数[12]。利用非稳态扩散方程和高斯误差函数可以得到一维无限长棒中扩散方程误差函数,如式(1)~式(4)所示。
$$ \frac{{\partial C}}{{\partial t}} = D\frac{{{\partial ^{\rm{2}}}C}}{{\partial {x^{\rm{2}}}}} $$ (1) $$ C\left( {x,t} \right) = \frac{{{C_{\rm{2}}} + {C_{\rm{1}}}}}{{\rm{2}}} - \frac{{{C_{\rm{2}}} - {C_{\rm{1}}}}}{{\rm{2}}} \cdot \frac{{\rm{2}}}{{\sqrt \pi }} \cdot \int_{\rm{0}}^{\frac{x}{{{\rm{2}}\sqrt {Dt} }}} {{{\rm{e}}^{{\rm{ - }}{\lambda ^{\rm{2}}}}}{\rm{d}}\lambda } $$ (2) $$ erf\left( \beta \right) = \frac{{\rm{2}}}{{\sqrt \pi }} \cdot \int_0^\beta {{{\rm{e}}^{ - {\lambda ^{\rm{2}}}}}{\rm{d}}\lambda } $$ (3) $$ C\left( {x, t} \right) = \frac{{{C_{\rm{2}}} + {C_{\rm{1}}}}}{{\rm{2}}} - \frac{{{C_{\rm{2}}} - {C_{\rm{1}}}}}{{\rm{2}}}erf\left( {\frac{x}{{{\rm{2}}\sqrt {Dt} }}} \right) $$ (4) 式中:C、C1、C2为原子数分数,t为扩散时间,D为互扩散系数,x为扩散距离,λ、β为误差函数值。
将测量得到的Ti原子数分数代入扩散方程误差函数中,通过计算得到各温度下、不同区域的互扩散系数D[13-14],如表 1所示。进一步计算得到扩散激活能、互扩散系数公式见表 2。从表 1中可以发现,随着温度的升高,Ti基固溶体中的互扩散系数远大于W基固溶体中互扩散系数,从而解释了大量的W扩散入Ti层而Ti扩散入W层较少的原因。
表 1 不同温度条件下W-Ti合金中不同区域的互扩散系数Table 1. Interdiffusion coefficients of W-Tialloy in different areas at different temperatures温度/℃ Ti基固溶体互扩散系数/(cm2·s−1) W基固溶体互扩散系数/(cm2·s−1) 1100 5.1×10−11 9.2×10−14 1200 3.2×10−10 9.5×10−13 1300 1.4×10−9 7.5×10−12 表 2 Ti和W基固溶体中的扩散激活能和互扩散系数公式Table 2. Activation energy and interdiffusion coefficient equation of Ti/W solid solution相名称 预扩散系数/ (cm2·s−1) 扩散激活能/ (kJ·mol−1) 互扩散方程/ (cm2·s−1) Ti 4.1×10−2 285.1 4.1×10−2exp(−285.1/kT) W 2.3×10−5 385.3 2.6×10−5exp(−385.3/kT) 注:k—扩散距离,T—扩散温度。 通过式(4)计算得到的W/Ti扩散偶界面元素成分和实测结果(1300℃,1h)如图 5所示。可以看到,计算结果与测量结果基本相当,因而可以依据上述分析对扩散过程进行解析。值得指出的是,计算结果与实际结果尚具有误差,可能是由实际扩散层的差异性以及扩散偶不同部分组织与成分差异引起的。
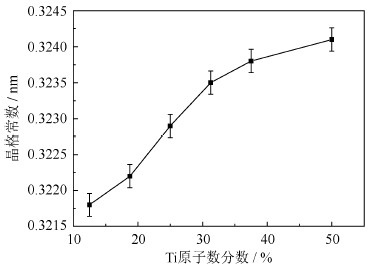
对不同Ti原子数分数的各超晶胞的晶格常数进行了优化,得到的平衡晶格常数如图 6所示。从图中可以看出随着Ti原子数分数的增加,相应β结构晶胞的晶格常数基本以线性关系逐渐增大,这是由于Ti原子的原子半径大于W原子的原子半径所造成的。为了研究Ti原子数分数与β结构W–Ti合金的结构稳定性之间的关系,需进行内聚能(Ecoh)计算,如式(5)所示。
$$ {E_{{\rm{coh}}}} = \left( {{\rm{16}} - x} \right){E_{\rm{W}}} + x{E_{{\rm{Ti}}}} - E $$ (5) 式中:Ecoh为内聚能,E为立方结构W16–xTix合金的总能量,ETi和EW分别为Ti和W的单原子能量。不同Ti原子数分数的W–Ti合金的内聚能计算结果如图 7所示。可以看出,随着Ti原子数分数的增加,合金的内聚能以线性关系逐渐减少,这说明Ti元素的添加降低了β结构的W–Ti合金的稳定性。
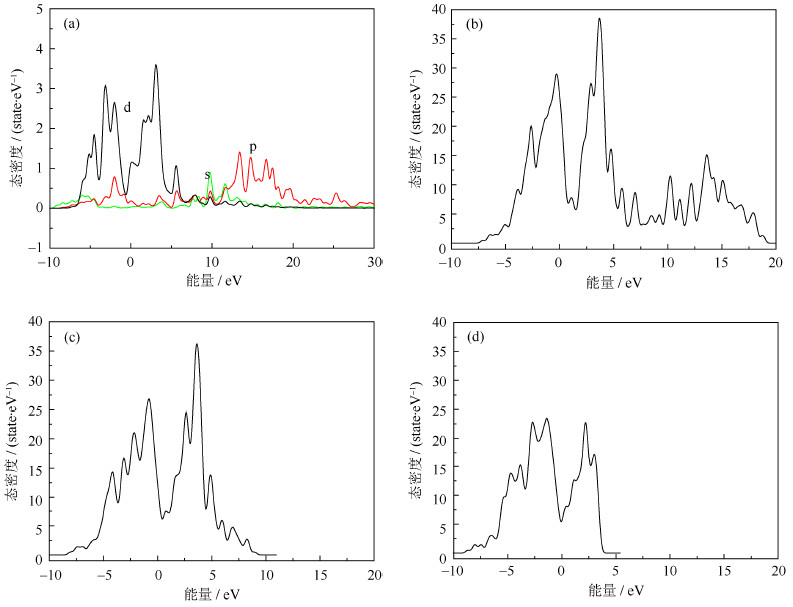
为了研究影响W–Ti合金β结构稳定性的物理本质,本研究计算了β结构W16–xTix合金的态密度分布(density of states,DOS),图 8所示为纯W和β结构W16–xTix(x=2, 4, 8)态密度分布的计算结果,s、p和d为不同的电子轨道。由图 8可以看出,W、W14Ti2、W12Ti4和W8Ti84者态密度分布图的峰形十分相似,且态密度分布图中均存在一个能区分出态密度分布中的低能成键态和高能反键态区域的峰谷,而费米能级均未处于成键态区域,导致了费米能级处态密度N(EF)值相对比较低,这也说明了W–Ti合金β结构的稳定性相对较高。随着Ti原子数分数的增加,W16–xTix(x=2, 4, 8)合金态密度分布图中费米能所处的位置逐渐向峰谷方向移动,成键峰则逐渐向高能方向移动,这说明随着Ti原子数分数的增加,W–Ti合金β结构的稳定性逐渐降低,这与以上内聚能计算结果是自洽的[15]。
3. 结论
(1)建立了W/Ti两相扩散偶模型:由W基和Ti基固溶相构成,采用两个扩散系数来描述不同相区。
(2)在1100~1300℃时,W基固溶体中的互扩散系数公式为2.6×10−5exp(−385.3/kT),Ti基固溶体中的互扩散系数公式为4.1×10−2exp(−285.1/kT),其中k为扩散距离,T为扩散温度。
(3)随着Ti原子数分数的升高,晶格常数逐渐增大,而内聚能逐渐减少,W–Ti合金的β结构稳定性降低。
-
表 1 不同温度条件下W-Ti合金中不同区域的互扩散系数
Table 1 Interdiffusion coefficients of W-Tialloy in different areas at different temperatures
温度/℃ Ti基固溶体互扩散系数/(cm2·s−1) W基固溶体互扩散系数/(cm2·s−1) 1100 5.1×10−11 9.2×10−14 1200 3.2×10−10 9.5×10−13 1300 1.4×10−9 7.5×10−12 表 2 Ti和W基固溶体中的扩散激活能和互扩散系数公式
Table 2 Activation energy and interdiffusion coefficient equation of Ti/W solid solution
相名称 预扩散系数/ (cm2·s−1) 扩散激活能/ (kJ·mol−1) 互扩散方程/ (cm2·s−1) Ti 4.1×10−2 285.1 4.1×10−2exp(−285.1/kT) W 2.3×10−5 385.3 2.6×10−5exp(−385.3/kT) 注:k—扩散距离,T—扩散温度。 -
[1] Berger S. Elastic and plastic strains in Al/TiW/Si contacts during thermal cycles. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 288(2): 164 DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(00)00863-7
[2] Dirks A G, Wolters R A M, Nellissen A J M. On the microstructure-property relationship of W–Ti–(N) diffusion barriers. Thin Solid Films, 1990, 193-194(1): 201 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040609005800288
[3] Bhagat S, hanh, Alfrod T L. Tungsten-titanium diffusion barriers for silver metallization. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 515(4): 1998 DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2006.03.049
[4] Kecskesa L J, hall I W. Microstructural effects inhot-explosively-consolidated W–Tialloys. J Mater Process Technol, 1999, 94(2-3): 247 DOI: 10.1016/S0924-0136(99)00077-1
[5] 刘超, 孔祥吉, 吴胜文, 等. 钛及钛合金金属粉末注射成形技术的研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(2): 150 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.012 Liu C, Kong X J, Wu S W, et al. Research progress on metal injection molding of titanium and titanium alloys. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(2): 150 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.012
[6] 梁宝岩, 王艳芝, 张旺玺, 等. 金刚石含量与粒度对自蔓延高温烧结钛铝碳结合剂/金刚石复合材料组织与形貌的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(1): 35 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.01.007 Liang B Y, Wang Y Z, Zhang W X, et al. Effect of diamond size and content on the phase composition and morphology of Ti2AlC bonded diamond obtained by self-propagationhigh temperature sintering. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(1): 35 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.01.007
[7] 郑淮北, 叶晓宁, 张雪峰, 等. 12%Cr铁素体不锈钢粗晶区组织转变和晶粒长大及析出相分析. 焊接学报, 2011, 32(6): 37 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXB201106011.htm Zhengh B, Ye X N, Zhang X F, et al. Microstructure transformation, grain growth and precipitated phase of 12% Cr ferritic stainless steel in coarse grain zone. Trans China Weld Inst, 2011, 32(6): 37 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJXB201106011.htm
[8] Peng X N, Guoh Z, Qin C, et al. Isothermal beta grain growth kinetics of TC4–DT titanium alloy under two different prior processing conditions: deformed vs. undeformed. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2014, 43(8): 1855 DOI: 10.1016/S1875-5372(14)60145-4
[9] 韩靖, 盛光敏, 秦斌, 等. 钛合金与不锈钢扩散连接研究现状. 机械工程材料, 2007, 31(12): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2007.12.001 Han J, Sheng G M, Qin B, et al. Present status of research in diffusion bonding of titanium alloy to stainless steel. Mater Mech Eng, 2007, 31(12): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2007.12.001
[10] 马英杰, 刘建荣, 雷家峰, 等. 钛合金β晶粒生长规律及晶粒尺寸对损伤容限性能的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(6): 976 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2009.06.009 Ma Y J, Liu J R, Lei J F, et al. β-grain growth and influence of its grain size on damage-tolerance property in titanium alloy. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2009, 38(6): 976 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2009.06.009
[11] Massalski T B, Murray J L, Bennett Lh, et al. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams. New York: American Society for Metals, 1990
[12] 潘金生, 田民波, 仝健民. 材料科学基础. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011 Pan J S, Tian M B, Tong J M. Fundamental of Materials Science. Beijing: Tsinghua Unversity Press, 2011
[13] 陈松, 胡昌义, 杨家明, 等. Ir/Re互扩散研究. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2006, 35(1): 17 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2006.01.005 Chen S, hu C Y, Yang J M, et al. Study on interdiffusion of iridium/rhenium. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2006, 35(1): 17 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2006.01.005
[14] 马权, 刘向宏, 陈自力, 等. Nb/Ti扩散研究. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36 (10): 1745 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185x.2007.10.011 Ma Q, Liu Xh, Chen Z L, et al. The research of Nb/Tidiffusion. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2007, 36(10): 1745 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185x.2007.10.011
[15] 姚强, 邢辉, 郭文渊, 等. Ti–Nb合金β结构稳定性和弹性性质. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(1): 126 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ200801023.htm Yao Q, Xingh, Guo W Y, et al. β phase stability and elastic property of Ti–Nb alloys. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2008, 18(1): 126 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ200801023.htm
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 杨亚飞,姚草根,吕宏军,谢飞,孟烁. 粉末特性对W-Ti[w(Ti)=10%]合金致密度和组织的影响. 宇航材料工艺. 2024(05): 31-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨亚飞,吕宏军,姚草根,李圣刚,王思伦. 制备工艺对W-10Ti合金组织的影响. 宇航材料工艺. 2023(05): 38-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 莫蓉,李晖,孙洪涛,白英丽,陈红. 惰性熔融-红外吸收光谱法测定钨钛合金中氧含量. 广州化工. 2020(01): 95-96+146 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: