Preparation of micro-nano Mo(C, N) powders by low temperature carbothermal and micro-positive pressure of nitrogen
-
摘要: 金属Mo的碳氮化物对改善金属基复合材料的结构性能起到重要作用,而Mo(C,N)固溶体综合了金属及碳氮化物的性能,其改善复合材料结构的效果优于单纯的Mo2C或者MoN粉末。本研究采用机械合金化技术和微正压碳热氮化法,低温下制备微纳米Mo(C,N)固溶体粉末。利用热重分析-示差扫描量热法(thermogravimetric analysis-differential scanning calorimetry,TG-DSC)、X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction,XRD)、扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)分析考察机械力及氮化条件对粉体结构及粒度的影响。结果表明:MoO2粉末和碳粉经9 h高能球磨后,机械力足够使粉末细化,同时能够增加界面能和缺陷,以提供MoC-N化学吸附向微纳米Mo(C,N)固溶体粉末转变所需的激活能,并借此改变Mo原子表面电子的不饱和性,结合微正压N2气气氛,促使混合粉末在碳化阶段Mo与N有效键合;最终,在N2气压力0.2 MPa、850 ℃下制备出了Mo(C,N)微纳米类球形粉未;碳氮化温度低,有效地降低了能耗,节约了成本,有重要的工业应用前景。Abstract: The carbonitride of Mo (Mo2C or MoN) is important to improve the structural properties of metal matrix composites. The solid solution of Mo(C, N) combined the characteristics of metal and carbonitride of Mo shows the better structural properties of metal matrix composites. The micro-nano Mo(C, N) spherical solid solution powders were prepared by mechanical alloying technique and carbothermal method at low temperature and low-pressure of nitriding in this study. The effects of mechanical force and nitriding conditions on the structures and particle sizes of powders were studied by thermogravimetric analysis-differential scanning calorimetry (TG-DSC), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and scanning electron microscope (SEM).The results show that, after high-energy ball mill for 9 h, enough mechanical force can refine the mixture powders of MoO2 and carbon, improve the interface energy, and increase the defects, which can provide the activation energy of MoC-N chemical adsorption to transform to the micro-nano Mo (C, N) solid solution powders. Moreover, it can change the unsaturation of electrons on the surface of Mo atoms and promote the Mo-N bonding when the mixture powders are carbothermal at the condition of micro-positive pressure of nitrogen. Finally, the micro-nano Mo(C, N) spherical solid solution powders are prepared at the N2 pressure of 0.2 MPa and the temperature of 850 ℃; it can effectively reduce the energy consumption and save cost at this low carbothermal temperature, showing the important prospects of industrial applications.
-
金属基复合材料具有强度高、韧性好、耐磨性好、硬度高以及化学稳定性好等优异性能,在能源、汽车、航空航天、轨道交通、微电子制造行业应用广泛[1-3]。国内外学者通过添加适量的过渡族金属碳氮化合物来改善金属复合材料的结构及性能,以达到固溶强化的目的[4-5]。大量研究表明,过渡族金属Mo的碳氮化合物在成键时包含有金属键、离子键以及共价键三种化学键类型,表现出诸多优异的物理性能[6-7]。Mo(C,N)固溶体综合了碳氮化物的性能,在改善金属复合材料结构方面比单纯的Mo2C或者MoN粉末效果更好,因此制备高品质的Mo(C,N)粉末具有重要的研究价值。
制备碳、氮化钼粉末一般采用高温碳化或化学气相沉积法等方法,而Mo(C,N)固溶体粉的制备方法报道极少。文献报道,金属碳氮化物的固溶体粉末一般制备反应温度在1400~1700 ℃左右,其反应温度高,能源消耗大,设备不易控制[8-9]。因此,低温制备Mo(C,N)固溶体粉有重要的应用价值。
近几年来,机械合金化(mechanical alloying,MA)[10-11]作为一种新型制备技术,已经成功制备出了包括许多难熔碳化物等在内的新材料。该方法设备工艺简单、制造成本低,已成为制备纳米粉末的一种重要途径[12]。本研究采用机械合金化技术和碳热还原氮化法相结合,利用高能球磨诱发机械力,使粉末细化的同时增加界面能和缺陷,以提供MoC-N化学吸附向Mo(C,N)固溶体粉末转变所需的激活能,并借此改变Mo原子表面电子的不饱和性,同时结合微正压N2气气氛,促进Mo与N的键合,制备出了Mo(C,N)微纳米类球形固溶体粉。氧化钼碳化和氮化的温度低,有效的降低了能耗,节约成本,有重要的工业应用前景。
1. 实验
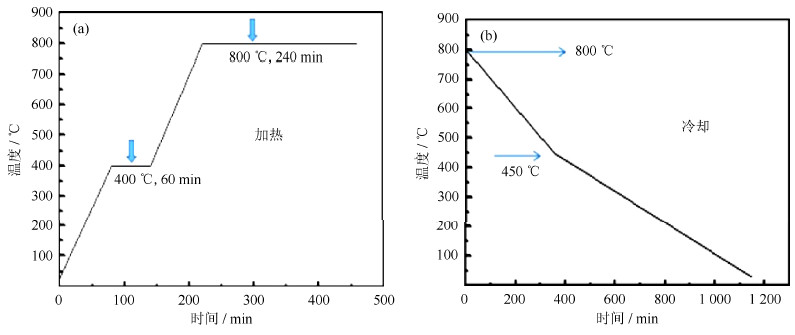
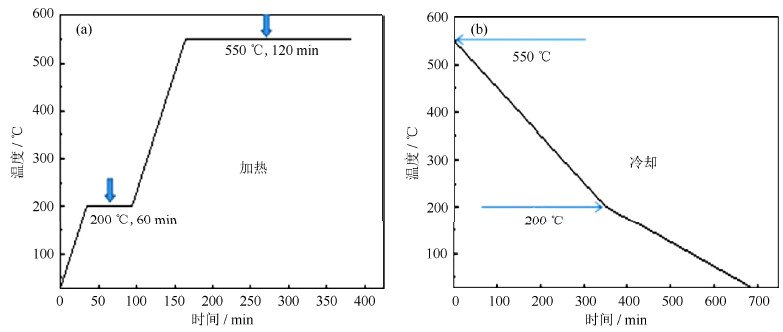
称取适量的钼酸铵置于玛瑙中进行高能行星球磨(球料比10:1,转速300 r/min,球磨10 h)。样品取出后置于管式炉中进行热分解生成MoO2粉末(工艺参数见图 1)。然后按比例将MoO2粉末与碳粉混合,再置于玛瑙中进行高能球磨(球料比10:1,转速500 r/min,球磨3~9 h)。最后将球磨好的样品置入管式炉中N2气氛下进行碳热氮化。N2流量为1000 mL/min,控制炉内气压为正压0.2~0.5 MPa,碳热氮化工艺参数曲线如图 2所示。
实验用原料钼酸铵粉末、C粉(粒度为1 μm)均为分析纯,由重庆化学试剂厂生产。采用YXQM-4L行星球磨机进行机械合金化,采用OTL1200管式炉进行钼酸铵分解和氧化钼碳化、氮化。采用德国STA-409PC热分析仪,升温速率为5 ℃/min,氮气流速为30 mL/min;使用日本JEOL-6490LV扫描电子显微镜观察样品形貌与晶粒;利用D/MAX2500VL/PC型X射线衍射仪进行物相分析(Cu Kα,λ=0.154 nm,扫描速度0.02º /s);使用Jade软件,对衍射峰进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 氧化钼的制备
钼酸铵热分解可能发生的反应如式(1)和式(2)所示。
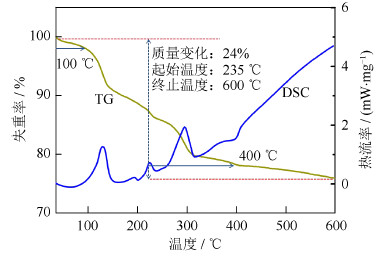
$$ \begin{array}{l} {\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}} \right)_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{M}}{{\rm{o}}_{\rm{7}}}{{\rm{O}}_{{\rm{24}}}} \cdot {\rm{4}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} \buildrel \Delta \over = \\ {\rm{4N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} \uparrow {\rm{ + 2N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} \uparrow {\rm{ + 7Mo}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{ + 10}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} \uparrow \end{array} $$ (1) $$ \begin{array}{l} {\left( {{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}} \right)_{\rm{6}}}{\rm{M}}{{\rm{o}}_{\rm{7}}}{{\rm{O}}_{{\rm{24}}}} \cdot {\rm{4}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} \buildrel \Delta \over = \\ {\rm{6N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{3}}} \uparrow {\rm{ + 7Mo}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}}{\rm{ + 7}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{O}} \uparrow \end{array} $$ (2) 图 3为钼酸铵粉末球磨样品的热重-示差扫描量热分析曲线(thermogravimetric analysis-differential scanning calorimetry,TG-DSC),从DSC曲线中可以看出,在100 ℃到400 ℃之间有几个明显的凸起的峰,表明该阶段试样大量吸热,正好与TG曲线分析结果相对应,是钼酸铵分解阶段。根据TG曲线分析,样品质量在100 ℃左右开始显著变化,在400 ℃左右变化开始趋于平缓。这说明钼酸铵粉末在100 ℃开始分解,在400 ℃左右基本分解成为低价氧化物;到600 ℃左右TG曲线逐渐平缓,反应趋于完成,这说明普通钼酸铵的热分解温度高于600 ℃。
图 4为钼酸铵不同球磨时间扫描电子显微(scanning electron microscopy,SEM)组织形貌。从图中可以观察到粉末颗粒随着球磨时间的增加,其颗粒尺寸逐渐降低,当球磨时间大于10 h后,颗粒尺寸无明显变化,高能球磨效率达到临界值。球磨10 h后的钼酸铵粉末显著细化,热分解后分解得到的氧化钼颗粒更小且分布均匀。
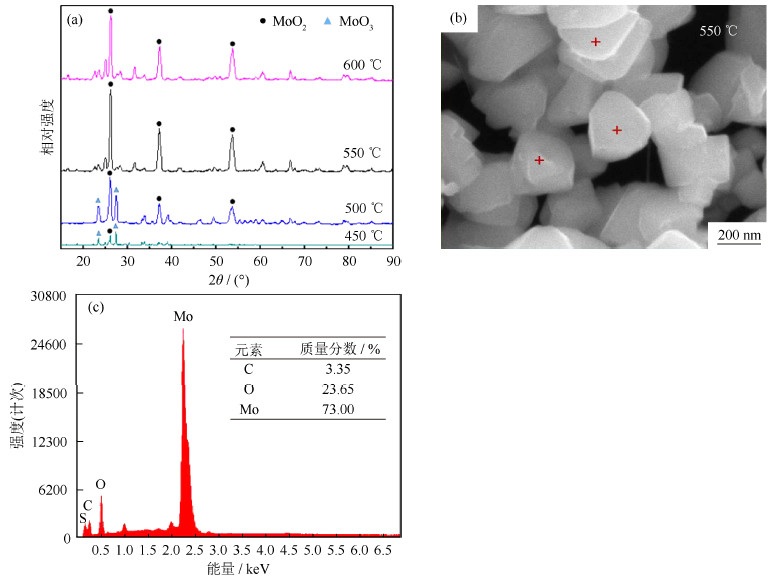
图 5为球磨10 h后的钼酸铵在不同烧结温度下产物的X射线衍射图谱(X-ray diffraction,XRD)、扫描电子显微组织形貌及能谱分析(energydispersive spectrometer,EDS)。从X射线衍射图中可以看出,550 ℃时钼酸铵完全分解成MoO2,说明钼酸铵球磨10 h后,在图 1设定工艺条件下(550 ℃)发生热分解,反应按式(1)进行;图 5(b)和图 5(c)为钼酸铵(球磨10 h)550 ℃烧结后扫描电子显微形貌及能谱分析,从图中可以看出,钼酸铵经10 h球磨后550 ℃烧结可获得平均粒度小于200 nm的类球形粉末,从对应的能谱分析与X射线衍射分析可以确定为MoO2粉末,最终反应温度低于未球磨钼酸铵的热分解温度(图 3 TG-DSC分析)。这说明,高能球磨可使颗粒表面能及内能增大,这部分能量将在热分解阶段将转变为分解所需的能量,使得热分解温度降低。
2.2 碳氮化钼的制备
MoO2和C在氮气气氛下加热可能发生的反应如式(3)所示。
$$ {\rm{2Mo}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}} + {\rm{6C}} + {{\rm{N}}_{\rm{2}}} \uparrow \buildrel \Delta \over = {\rm{2Mo}}\left( {{\rm{C, N}}} \right) + {\rm{4CO}} \uparrow $$ (3) MoO2碳热还原氮化制备Mo(C,N)的反应包含MoO2与C固-固反应和借助于Boudeward反应进行的MoO2与CO气-固反应两种[13-14]。一般来说,式(3)应分为3个阶段:第一阶段为MoO2与C反应,生成MonO2n-1与CmMonO2n-1系列产物;第二阶段生成MoC相;第三阶段是MoC相与C、N原子之间的置换反应,最终形成Mo(C,N)相,这一阶段是通过原子扩散发生的置换反应,置换速度与温度、粉末粒度、N2气压力浓度直接相关,需要的温度高、时间长。
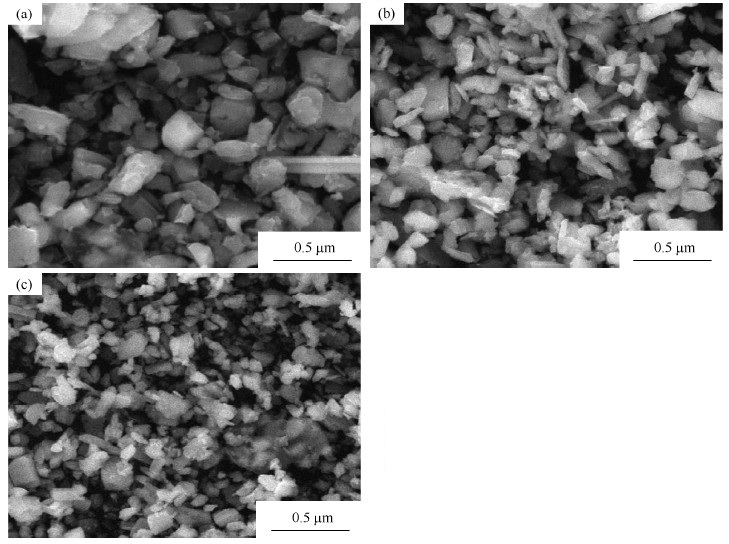
超细及纳米粉末由于其较高的表面能可使反应加速,降低反应速度[15]。本实验利用高能球磨的机械力使大颗粒破碎,从而达到降低粉末粒度,增加其内能的目的。图 6为氧化钼与碳粉经过不同球磨时间后的扫描电子显微组织形貌,从图中可以观察到粉末颗粒随着球磨时间的增加,其颗粒尺寸明显细化。高能球磨能有效降低颗粒尺寸,球磨9 h后的样品的粒度达到了200 nm左右。
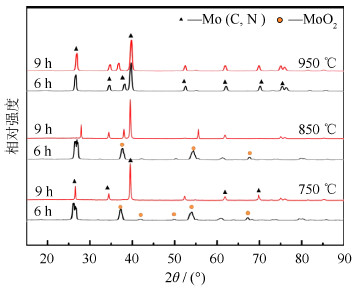
图 7为氧化钼与碳粉高能球磨9 h后不同氮气压力下900 ℃碳热反应的X射线衍射图谱。从图中可以看出,无氮气压力下氧化钼在900 ℃反应后产物主要为MoO2,随着氮气压力的增加,Mo(C,N)相逐渐增多,在氮气压力大于0.2 MPa时,MoO2全部反应生成Mo(C,N)相。这说明微正压下,有利于Mo、C与N的键合,降低键合温度。
图 8为不同球磨时间的氧化钼、碳粉在氮气压力为0.2 MPa、不同温度下碳热反应的X射线衍射图谱。从图中可以看出,球磨6 h样品在950 ℃可完成碳氮化反应获得Mo(C,N)。而球磨9 h样品在850 ℃左右即反应完全获得Mo(C,N)。这说明氧化钼和碳粉的混合粉随着球磨时间的增加,其碳化和氮化所需达到的温度将逐渐降低。这说明足够机械力使粉末产生的界面能和缺陷能提供了MoC-N化学吸附向Mo(C,N)转变所需的激活能,并改变了Mo原子表面电子的不饱和性,从而促进了Mo与C、N的键合作用,降低了反应温度。
图 9为本实验制备所得的Mo(C,N)扫描电子显微组织形貌及对应的能谱图(球磨9 h、850 ℃碳热反应)。从图中组织形貌和能谱分析可知,在既定工艺下制备的粉末为Mo(C,N),粒度为200 nm左右,分散良好。
3. 结论
(1)采用机械合金化技术和微正压碳热氮化法,以钼酸铵、C粉为原料,控制氮气流量为正压0.2 MPa,在低温850 ℃下可制备出Mo(C,N)粉末,其平均粒度为200 nm左右,分布均匀。与传统工艺相比,此项技术具有低能耗、成本低等优点;
(2)高能球磨可以明显的降低粉末粒度,提高其活性,使粉末产生的界面能和缺陷能提供碳热所需的激活能,从而有效降低碳热氮化温度。
(3)微正压氮气气氛有利于MoC-N化学吸附向Mo(C,N)转变,可促进Mo与N的键合。
-
-
[1] Barsoum M W, Yaroschuk G, Tyagi S. Fabrication and characterization of M2SnC (M = Ti, Zr, Hf and Nb). Scripta Mater, 1997, 37(10): 1583 DOI: 10.1016/S1359-6462(97)00288-1
[2] 李燕, 刘宁. 细晶粒TiCN-Co金属陶瓷的显微结构与力学性能. 材料热处理学报, 2008, 29(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSCL200801001.htm Li Y, Liu N. Microstructure and mechanical properties of fine-grained Ti(C, N)-Co cermets. Trans Mater Heat Treat, 2008, 29(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSCL200801001.htm
[3] 肖广涛, 刘颖, 叶金文, 等. (W, Ta) C复合碳化物含量对WC-10Co硬质合金显微结构和力学性能的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2013, 31(5): 355 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2013.05.007 Xiao G T, Liu Y, Ye J W, et al. The influence of different content of (W, Ta) C composite carbide on microstructure and properties of WC-10Co cemented carbide. Powder Metall Technol, 2013, 31(5): 355 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2013.05.007
[4] Li S B, Bei G P, Zhai H X, et al. Synthesis of Ti2SnC from Ti/Sn/TiC powder mixtures by pressureless sintering technique. Mater Lett, 2006, 60(29-30): 3530 DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2006.03.045
[5] 董帝, 王承阳. 钼合金制备工艺的研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(4): 304 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYJ201704011.htm Dong D, Wang C Y. Research progress on preparation technology of molybdenum alloy. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(4): 304 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYJ201704011.htm
[6] Zheng Y, You M, Xiong W H, et al. Valence-electron structure and properties of main phase in Ti(C, N)-based cermets. Mater Chem Phys, 2003, 82(3): 877 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2003.07.008
[7] Meng F A, Liang B Y, Wang M Z. Investigation of formation mechanism of Ti3SiC2 by self-propagating high-temperature synthesis. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2013, 41: 152 DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.03.005
[8] Toth L E. Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides. New York : Academic Press, 1971
[9] Xiang J Y, Liu S C, Hu W T, et al. Mechanochemically activated synthesis of zirconium carbide nanoparticles at room temperature: A simple route to prepare nanoparticles of transition metal carbides. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2011, 31(8): 1491 DOI: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2011.01.022
[10] Benjamin J S. Dispersion strengthened superalloys by mechanical alloying. Metall Trans A, 1970, 1(10): 2943 DOI: 10.1007/BF03037835
[11] 张斌. 机械合金化方法制备碳化物的研究[学位论文]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2005 Zhang B. The Research of Mechanical Alloying Method on Preparing Metal Carbides[Dissertation]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2005
[12] Deng Y, Jiang X Q, Zhang Y H, et al. The effect of Co particle structures on the mechanical properties and microstructure of TiCN-based cermets. Mater Sci Eng A, 2016, 675: 164 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.08.050
[13] Berger L M, Grunerb W, Langholf E, et al. On the mechanism of carbothermal reduction processes of TiO2 and ZrO2. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 1999, 17(1-3): 235 DOI: 10.1016/S0263-4368(98)00077-8
[14] 姜中涛, 刘颖, 陈巧旺, 等. V2O5碳热还原合成碳化钒粉末的反应过程. 粉末冶金技术, 2012, 30(1): 40 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2012.01.008 Jiang Z T, Liu Y, Chen Q W, et al. Reaction process of synthesizing vanadium carbide powder by vanadium pentoxide carbothermal reduction. Powder Metall Technol, 2012, 30(1): 40 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2012.01.008
[15] Urakaev F K, Boldyrev V V. Mechanism and kinetics of mechanochemical processes in comminuting devices: 2. Applications of the theory. Experiment. Powder Technol, 2000, 107(3): 197 DOI: 10.1016/S0032-5910(99)00200-4
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 卫佳乐,白亚平,刘萌萌,李建平. 自生TiB_2-TiC_x/7075Al基复合材料显微组织与力学性能研究. 西安工业大学学报. 2022(03): 276-284 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 谢刚,俞小花,彭如振,王有维. 大气等离子喷涂TiB_2涂层微观结构及性能研究. 轻金属. 2020(08): 27-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: