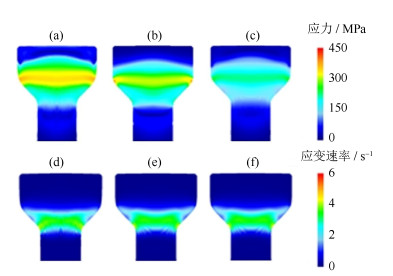
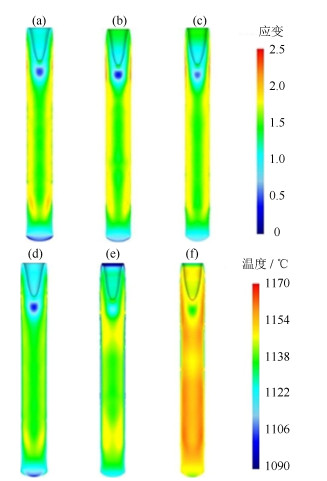
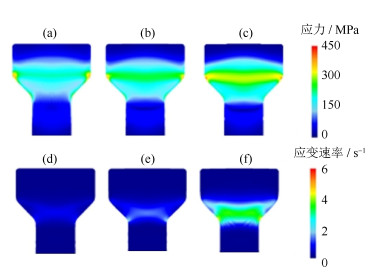
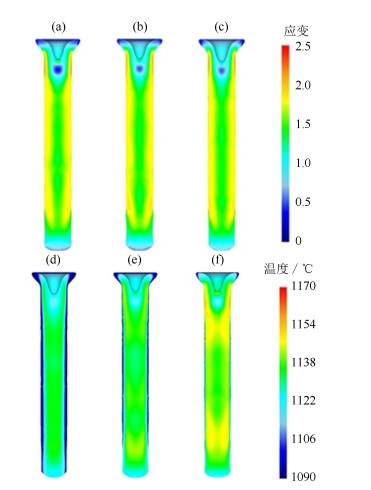
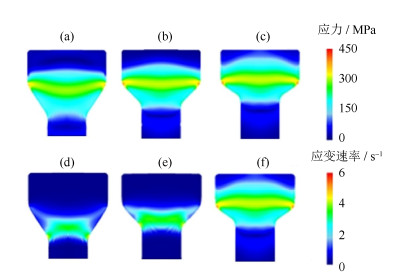
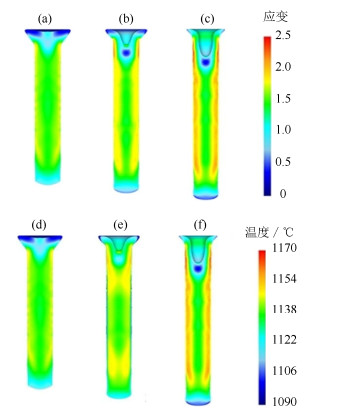
Finite element simulation and experimental verification on hot extrusion of a novel nickel-base P/M superalloy
-
摘要: 采用有限元模拟的方法对一种新型镍基粉末高温合金热挤压工艺进行了优化设计,分析讨论了几种主要参数对热挤压结果的影响,并通过热挤压实验验证了有限元模拟的可靠性。结果显示,在热挤压过程中,坯料初始温度对应力和温度影响显著,对应变速率和应变无明显影响;挤压杆速度是调整应力和应变速率的重要参数;采用较小的模角(小于45.0°)可以使应力、应变速率、应变和温度分布的均匀性大幅度提高,有效避免挤压棒材开裂和保证显微组织均匀性。由模拟结果推出的主要热挤压参数为:坯料初始温度1100℃,挤压杆速度40 mm·s-1,模角40.0°。将推荐的参数用于热挤压实验,结果证明了有限元分析结果准确,热挤压参数合理。Abstract: The finite element method was used to optimize the hot extrusion process of a novel nickel-based powder metallurgy superalloy in this paper, the influences of finite element parameters on hot extrusion were analyzed and discussed, and the reliability of finite element simulation was verified by extrusion experiment. The results show that, the initial temperature of billet has a significant effect on the stress and temperature during hot extrusion process, but has no obvious influence on the strain rate and strain. The speed of extrusion stem is an important parameter to control the stress and strain rate. The uniformity of stress, strain rate, strain, and temperature can be greatly improved by using smaller die angles (< 45.0°), which can effectively avoid the cracking of extrusion bar and ensure the uniformity of microstructures. The main hot extrusion parameters are recommended as following: the initial temperature of billet is 1100℃, the speed of extrusion ram is 40 mm·s-1, and the die angle is 40.0°. It is proved that the parameters applied to the hot extrusion experiment based on the finite element analysis are accurate and reasonable.
-
硼化锆(ZrB2)陶瓷具有高熔点、低密度、高硬度、高导热率、低热膨胀系数以及良好的抗腐蚀与耐摩擦磨损性能等特点[1–3]。ZrB2还具有较高的导电率,可通过线切割、电火花等常用加工方法进行加工,因此其加工性较好[4]。基于以上良好的物理与化学性能,ZrB2陶瓷材料被广泛应用于高温领域,比如航空航天,特别是新型超高速飞行器领域[5]。然而,纯ZrB2陶瓷材料强度和断裂韧度较低,这一缺点限制了其进一步发展。为改善ZrB2陶瓷材料这一问题,研究者们向ZrB2基体中添加第二相,例如ZrSi2[6]、HfB2[7]、SiBCN[8]以及ZrC[9]来提高其力学性能。HfN具有高硬度、高熔点和良好的抗氧化性,已被添加到TiB2和TiCN陶瓷基体中,用以改善其力学性能[10–11]。然而,添加HfN对ZrB2基陶瓷材料的微观组织和力学性能影响的研究并不多见。
ZrB2基陶瓷材料的烧结通常选用粉末冶金技术,在制备ZrB2基陶瓷材料时加入金属添加剂可以提高其相对密度和降低烧结温度[12]。Monteverde等[13]在制备ZrB2–B4C陶瓷材料时指出,Ni能够降低ZrB2–B4C陶瓷材料的烧结温度,并有利于其相对密度的提高。然而,金属添加剂的含量(质量分数)要适中(通常为4%~10%),金属添加剂含量太低,不利于陶瓷材料的致密化,金属添加剂含量过高,将会降低陶瓷材料的硬度[14–15]。Jing等[12]在制备ZrB2–HfC陶瓷材料时加入质量分数为8%的Ni作为金属添加剂,并得到了高相对密度的ZrB2陶瓷材料。基于以上分析,本文以HfN为增强剂,Ni为金属添加剂,通过真空热压烧结工艺制备了ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料,研究了HfN含量(质量分数)对ZrB2基陶瓷材料微观组织和力学性能的影响。
1. 实验材料及方法
实验用ZrB2粉(上海巷田纳米材料有限公司)和Ni(上海允复纳米科技有限公司)粉的平均粒度均为1 μm,HfN粉(上海超威纳米科技有限公司)的平均粒度为0.8 μm,其纯度均在99%以上,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的组分及配比如表 1所示。各组粉末材料按照规定配比称量后放入球磨罐中,并加入适量的无水乙醇,球磨介质为直径5 mm的WC硬质合金球,原料粉末球磨48 h后,放入真空干燥箱中进行干燥。干燥好的材料经200目的网筛过筛后,装入石墨模具中压制成标准素坯,之后将素坯放进真空热压烧结炉中烧结。烧结温度、保温时间和烧结压力分别为1750 ℃、30 min和30 MPa。
表 1 ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的组分及配比(质量分数)Table 1. Compositions of ZrB2–HfN ceramic materials% 编号 ZrB2 HfN Ni ZH1 87 5 8 ZH2 82 10 8 ZH3 77 15 8 将烧结后的样品在电火花线切割机床上切成3 mm × 4 mm × 30 mm的试样条,并对其进行研磨和抛光,使其达到测试标准。利用阿基米德排水法测试相对密度;使用CREE-8003G电子式材料试验机测试材料的抗弯强度,跨距为30 mm;采用HVS-30数显维氏硬度计测试材料硬度,载荷为196 N,保压时间为15 s;通过压痕法计算材料的断裂韧性,计算公式如式(1)所示。所有测量结果均是至少5个测试结果的算术平均值。利用扫描电镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)观察材料的抛光面和断口形貌;用X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction,XRD)和能频谱仪(energy disperse spectroscope,EDS)分别分析材料的物相和元素组成。
$${K_{{\rm{IC}}}} = 0.203{\rm{Hv}} \cdot {a^{1/2}} \cdot {\left( {\frac{c}{a}} \right)^{ - 3/2}}$$ (1) 式中,KIC为材料断裂韧性,Hv为维氏硬度,2a是压痕对角线长度,2c是包含2a在内的裂纹总长度
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的物相分析
图 1为添加不同质量分数HfN的ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料X射线衍射图谱。由图可见,材料主要由基体相ZrB2和增强相HfN组成,这表明在烧结过程中没有发生明显的化学反应。此外,X射线衍射检测到的Ni峰不明显,这是因为Ni质量分数较低,并且在烧结温度为1750 ℃的烧结过程中,Ni金属在陶瓷材料中溶解析出,金属离子在高温下运动加剧,导致金属Ni在陶瓷材料中弥散分布[16]。另外,高温下金属Ni容易与ZrB2陶瓷发生反应,但是在X射线衍射图中并没有发现反应产物,这也是因为加入的金属Ni含量较低,且在烧结过程中,金属Ni在陶瓷材料中弥散分布。
图 2为添加不同质量分数HfN的ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的抛光面形貌图以及对应的能谱图。由图 2(a)~图 2(c)可见,不同HfN含量的ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料抛光面上均有黑色相(点A处)、浅灰色相(点B处)和深灰色相(点C处),且随着HfN质量分数的增高,浅灰色相逐渐增多。为了进一步确定各相的组成,对图 2(c)中各相(点A、点B、点C)进行能谱分析,结果如图 2(d)~图 2(f)所示,其中黑色相(点A)中有较多的Zr元素,并有少量的Hf和Ni元素;浅灰色相(点B)中有较多的Hf元素,少量的Zr和Ni元素;深灰色相(点C)中包含较多的Zr、Hf和Ni元素。
![]() 图 2 ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的抛光面扫描电子显微形貌以及对应图 2(c)中不同位置的能谱分析图:(a)ZH1显微形貌;(b)ZH2显微形貌;(c)ZH3显微形貌;(d)图 2(c)A点能谱;(e)图 2(c)B点能谱;(f)图 2(c)C点能谱;Figure 2. Surface SEM images of the ZrB2–HfN ceramic materials and the corresponding EDS: (a) ZH1 SEM image; (b) ZH2 SEM image; (c) ZH3 SEM image; (d) EDS of point A in Fig. 2(c); (e) EDS of point B in Fig. 2(c); (f) EDS of point C in Fig. 2(c)
图 2 ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的抛光面扫描电子显微形貌以及对应图 2(c)中不同位置的能谱分析图:(a)ZH1显微形貌;(b)ZH2显微形貌;(c)ZH3显微形貌;(d)图 2(c)A点能谱;(e)图 2(c)B点能谱;(f)图 2(c)C点能谱;Figure 2. Surface SEM images of the ZrB2–HfN ceramic materials and the corresponding EDS: (a) ZH1 SEM image; (b) ZH2 SEM image; (c) ZH3 SEM image; (d) EDS of point A in Fig. 2(c); (e) EDS of point B in Fig. 2(c); (f) EDS of point C in Fig. 2(c)由上述X射线衍射分析结果可知,在热压烧结过程中没有发生明显的化学反应,且烧结后ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的成分主要为ZrB2和HfN。因此,黑色相主要为ZrB2,浅灰色相主要为HfN,深灰色相主要为ZrB2、HfN以及金属Ni。由上述能谱分析可以看出,Ni元素在不同物相中均有分布,这与X射线衍射分析得到的Ni元素在陶瓷材料中分布广泛一致。此外,由图 2可知,在抛光面上存在有凹坑(如图中圆圈和方框所示)。Song等[17]在研究HfC添加相对TiN和TiB2陶瓷材料影响时指出,在烧结过程中形成的气孔通常为球形,因此,可以推测出圆圈所示的凹坑是在烧结过程中形成的气孔,方框所示的凹坑为研磨抛光过程中材料表面晶粒的剥落。由图 2(c)可见,当HfN质量分数为15%时,存在较多气孔。这主要是由于当HfN质量分数为15%时,试样中出现了HfN晶粒的聚集(如图 2(c)中浅灰色相),导致ZrB2–HfN陶瓷内部各组分分布不均匀,在烧结冷却阶段,出现微孔洞。
2.2 ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的微观组织分析
图 3为添加不同质量分数HfN的ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料断口形貌。由图可见,ZH1陶瓷材料的晶粒粗大,晶粒尺寸约为5~10 μm,粗大晶粒的生成对材料力学性能的提高极为不利;ZH2陶瓷的晶粒细小且分布均,晶粒尺寸约为2~5 μm,这表明质量分数为10%的HfN能有效抑制晶粒的长大。随着HfN质量分数增加到15%,ZH3陶瓷材料中出现了部分粗大晶粒,造成了微观组织的不均匀。这主要是由于当HfN质量分数为15%时,ZH3陶瓷材料中出现了HfN晶粒的聚集(如图 2(c)中浅灰色相),导致HfN在ZH3陶瓷材料中分布不均匀,从而使得HfN不能有效抑制ZrB2晶粒长大,出现了部分粗大晶粒。由上述可知,HfN含量过多或过少都不利于获得晶粒细小且分布均匀的微观组织。在材料的断裂过程中,粗大晶粒易发生穿晶断裂,小晶粒易发生沿晶断裂。结合断口形貌可见,ZH1陶瓷的断裂主要为穿晶断裂,ZH2陶瓷的断裂主要为沿晶断裂,ZH3陶瓷的断裂主要为穿晶断裂与沿晶断裂并存。有文献表明,当穿晶断裂与沿晶断裂共存时,有利于材料力学性能的提高,尤其是断裂韧度的提高[16]。此外,ZH1、ZH2和ZH3陶瓷中均存在凹坑(如图中方框所示)。有文献提到,在烧结过程中形成的孔隙为球形[17],根据图 3中凹坑的形状可以判断这些凹坑不是烧结过程中形成的孔隙。结合图 2物相分析可知,这些凹坑的形状和尺寸与图 2中浅灰色相的形状与尺寸相似,因此凹坑可能是由于在断裂过程中HfN晶粒的拔出形成的。在材料的断裂过程中,晶粒的拔出会消耗大量的断裂能,因此,有利于提高材料的抗弯强度。
2.3 ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的力学性能分析
表 2为添加不同质量分数HfN的ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料相对密度和力学性能。由表 2可知,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的相对密度变化较小,且随着HfN含量的增加而逐渐减小,这主要是由于随着HfN含量的增加,材料中气孔逐渐增多。随着HfN质量分数从5%增加到15%,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料硬度和抗弯强度先增大后减小,当HfN质量分数为10%时,硬度和抗弯强度达到最大值,分别为(16.47±0.24) GPa和(734.48±25) MPa。这主要是因为ZH2陶瓷材料的晶粒细小且分布均匀。Zhao等[18]在研究TiB2–SiC陶瓷材料的微观组织和力学性能时指出,晶粒细小且分布均匀有利于陶瓷材料力学性能的提高。同时,在断裂过程中,晶粒拔出需要消耗较多的断裂能,有利于其抗弯强度的提高。ZH2和ZH3陶瓷材料中存在较多粗大晶粒,这些粗大晶粒的晶界处容易形成应力集中,且粗大晶粒容易在晶界和晶粒体中形成微裂纹等缺陷,因此,粗大晶粒不利于材料力学性能的提高[19]。此外,随着HfN含量的增多,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料断裂韧度逐渐增大,当HfN质量分数为15%时达到最大值,为(5.81±0.15) MPa·m1/2,这主要是由于ZH3陶瓷的断裂模式为穿晶断裂与沿晶断裂并存,有效的促进了材料断裂韧度的提高;当HfN质量分数为10%时,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料断裂韧度值为(5.37±0.15) MPa·m1/2,虽然其值没有达到最大,但是与最大值[(5.81±0.15) MPa·m1/2]相比只下降了7.5%,而与HfN含量为5%的材料断裂韧度值[(4.67±0.22) MPa·m1/2)]相比,提高了15%。综上所述,当HfN质量分数为10%时,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料具有较好的综合力学性能,即硬度为(16.47±0.24) GPa、抗弯强度为(734.48±25) MPa、断裂韧度为(5.37±0.15) MPa·m1/2。
表 2 ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的相对密度和力学性能Table 2. Relative densities and mechanical properties of ZrB2–HfN ceramic materials编号 相对密度/ % 维氏硬度/ GPa 抗弯强度/ MPa 断裂韧度/ (MPa·m1/2) ZH1 99.4 ± 0.2 15.08 ± 0.20 422.96 ± 23 4.67 ± 0.22 ZH2 99.3 ± 0.1 16.47 ± 0.24 734.48 ± 25 5.37 ± 0.20 ZH3 99.1 ± 0.3 14.67 ± 0.23 540.46 ± 21 5.81 ± 0.15 3. 结论
(1)采用真空热压烧结技术,在烧结温度1750 ℃、保温时间30 min、烧结压力30 MPa的烧结参数下,制备了添加不同质量分数HfN的ZrB2–HfN陶瓷。
(2)随着HfN质量分数从5%增加到15%,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的硬度和抗弯强度先增大后减小,断裂韧度逐渐增大。当HfN质量分数为10%时,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的硬度和抗弯强度达到最大值,分别为(16.47±0.24) GPa和(734.48±25) MPa,这主要是由于该ZrB2–HfN陶瓷晶粒细小且分布均匀。当HfN质量分数为15%时,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的断裂韧度达到最大值,为(5.81±0.15) MPa·m1/2,这主要是由于该ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料的断裂模式为穿晶断裂与沿晶断裂共存,有效提高了断裂韧度。
(3)当HfN质量分数为10%时,ZrB2–HfN陶瓷材料具有较好的综合力学性能,其硬度、抗弯强度和断裂韧度分别为:(16.47±0.24) GPa、(734.48±25) MPa和(5.37±0.20) MPa·m1/2。
-
-
[1] Dever J A, Nathal M V, DiCarlo J A. Research on high-temperature aerospace materials at NASA Glenn Research Center. J Aerosp Eng, 2013, 26(2): 500 DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0000321
[2] Alniak M O, Bedir F. Hot forging behavior of nickel based superalloys under elevated temperatures. Mater Des, 2010, 31(3): 1588 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2009.09.020
[3] Wilkinson N A. Technological considerations in the forging of superalloy rotor parts. Met Technol, 1977, 4(1): 346 DOI: 10.1179/030716977803292637
[4] Zhang H B, Zhang K F, Jiang S S, et al. Dynamic recrystallization behavior of a γ'-hardened nickel-based superalloy during hot deformation. J Alloys Compd, 2015, 623: 374 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2014.11.056
[5] Gessinger G H, Bomford M J. Powder metallurgy of superalloys. Int Metall Rev, 1974, 19(1): 51 DOI: 10.1179/095066074790136999
[6] Coyne J E. Microstructural control in titanium-and nickel-base forgings; an overview. Met Technol, 1977, 4(1): 337 DOI: 10.1179/030716977803292745
[7] 马文斌, 刘国权, 胡本芙, 等. 粉末高温合金FGH96中的原始粉末颗粒边界及其对合金拉伸断裂行为的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2013, 18(1): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2013.01.003 Ma W B, Liu G Q, Hu B F, et al. Prior particle boundary and its effect on tensile properties of PM FGH96 superalloy. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2013, 18(1): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2013.01.003
[8] Liu C Z, Liu F, Huang L, et al. Effect of hot extrusion and heat treatment on microstructure of nickel-base superalloy. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2014, 24(8): 2544 DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(14)63381-1
[9] Chen L, Zhao G Q, Yu J Q, et al. Constitutive analysis of homogenized 7005 aluminum alloy at evaluated temperature for extrusion process. Mater Des, 2015, 66: 129 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.10.045
[10] Bai Q, Lin J, Jiang J, et al. A study of direct forging process for powder superalloys. Mater Sci Eng A, 2015, 621: 68 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.10.039
[11] 张明, 刘国权, 胡本芙. 镍基粉末高温合金热加工变形过程中显微组织不稳定性对热塑性的影响. 金属学报, 2017, 53(11): 1469 DOI: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00172 Zhang M, Liu G Q, Hu B F. Effect of microstructure instability on hot plasticity during thermomechanical processing in PM nickel-based superalloy. Acta Metall Sinica, 2017, 53(11): 1469 DOI: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00172
[12] Semiatin S L, Shank J M, Shiveley A R, et al. The effect of forging variables on the supersolvus heat-treatment response of powder-metallurgy nickel-base superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A, 2014, 45(13): 6231 DOI: 10.1007/s11661-014-2572-y
[13] Wu K, Liu G Q, Hu B F, et al. Characterization of hot deformation behavior of a new Ni–Cr–Co based P/M superalloy. Mater Charact, 2010, 61(3): 330 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2009.12.013
[14] Ning Y Q, Yao Z K, Lei Y Y, et al. Hot deformation behavior of the post-cogging FGH4096 superalloy with fine equiaxed microstructure. Mater Charact, 2011, 62(9): 887 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2011.06.004
[15] He G A, Liu F, Si J Y, et al. Characterization of hot compression behavior of a new HIPed nickel-based P/M superalloy using processing maps. Mater Des, 2015, 87: 256 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.08.035
[16] Immarigeon J A, Floyd P H. Microstructural instabilities during superplastic forging of a nickel-base superalloy compact. Metall Trans A, 1981, 12(7): 1177 DOI: 10.1007/BF02642331
[17] Semiatin S L, McClary K E, Rollett A D, et al. Plastic flow and microstructure evolution during thermomechanical processing of a PM nickel-base superalloy. Metall Mater Trans A, 2013, 44(6): 2778 DOI: 10.1007/s11661-013-1675-1
[18] Wu K, Liu G Q, Hu B F, et al. Effect of processing parameters on hot compressive deformation behavior of a new Ni–Cr–Co based P/M superalloy. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528(13-14): 4620 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.02.051
[19] Zhang B J, Zhao G P, Zhang W Y, et al. Deformation mechanisms and microstructural evolution of γ + γ' duplex aggregates generated during thermomechanical processing of nickel-base superalloys // Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Superalloys. Seven Springs, PA, 2016: 487
[20] Semiatin S L, Kim S L, Zhang F, et al. An investigation of high-temperature precipitation in powder-metallurgy, gamma/gamma-prime nickel-base superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A, 2015, 46(4): 1715 DOI: 10.1007/s11661-015-2748-0
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 万霖,张继峰,孙露,邱天旭,申小平. C与Cr含量对粉末锻造Fe–Cu–C–Cr合金组织和物理性能影响. 粉末冶金技术. 2023(06): 508-515 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 林冰涛,何君,刘仲位,王承阳,李明,孙晓霞,周淑秋. 固体火箭发动机用钼镧喷管断口形貌及组织分析. 粉末冶金技术. 2022(01): 80-85 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 刘波,刘军强. 数控机床齿轮Fe-Ni-Cu-C-Mo-V合金粉末锻造研究. 锻压技术. 2022(09): 23-29 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: