-
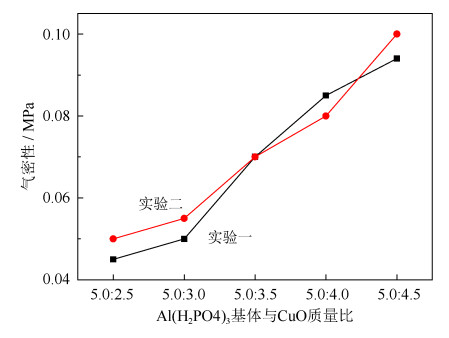
摘要: 以Al(H2PO4)3溶液为磷酸盐胶黏剂基体,研究了MgO、Al2O3、CuO三种固化剂对胶黏剂固化速率、固化温度、固化气密性的影响,分析了高温煅烧前后MgO和CuO对胶黏剂性能的影响。结果表明:MgO活性大,与Al(H2PO4)3基体反应迅速,不适合用作固化剂;以Al2O3为固化剂的胶黏剂密封性能差,Al2O3也不适合用作固化剂;未煅烧CuO作为磷酸盐胶黏剂的固化剂,反应速率适中且密封性能良好,当Al(H2PO4)3基体与CuO质量比为5.0:4.5时,气密性最好,为0.15 MPa(非上限)。Abstract: Al(H2PO4)3 solution was used as the matrix of phosphate adhesive, the effects of curing agents (MgO, Al2O3, and CuO) on the curing rate, curing temperature, and curing airtightness of adhesive were studied, and the influence of MgO and CuO before and after high temperature curing on the adhesive performance was also discussed. The results show that, MgO is not suitable as the curing agent due to the high activity, resulting in the rapid reaction with Al(H2PO4)3 matrix; Al2O3 is also not suitable used as the curing agent because of the low airtightness. Uncalcined CuO as curing agent shows the advantages of moderate reaction rate and good sealing performance. When the mass ratio of Al(H2PO4)3 matrix to CuO is 5.0:4.5, the adhesive airtightness is 0.15 MPa (not upper limit).
-
Keywords:
- adhesive /
- curing agent /
- airtightness /
- curing temperature /
- calcination
-
金属银由于良好的高温抗氧化性、导电性和导热性被广泛应用于电子行业, 微纳级的超细银粉是其当前的主要应用形态。超细银粉按微观形貌主要分为球形、片状、不定形微晶三大类, 其中以超细球形银粉用量最大, 可用于硅太阳能电池导电栅线银浆、片式元器件电极银浆、汽车后档玻璃除霜线银浆等各种厚膜烧结型银浆。目前超细球形银粉的制备以液相化学还原法为主, 可通过抗坏血酸-硝酸银还原体系[1, 2]、水合肼-银氨体系[3]及甲醛-银氨体系[4]制备得到球形或类球形银粉。
通过相转化来制备金属粉末是常见方法之一。李军义等[5]以草酸镍为前驱体, 包覆草酸镁后, 经真空分解烧结、酸洗得到超细球形镍粉。胡敏毅[6]和王岳俊等[7]采用氢氧化铜-葡萄糖为原料, 通过还原沉淀得到氧化亚铜-氢氧化铝, 经过包覆、氢气热还原、酸洗得到单分散的超细球形铜粉。由于银的化合物分解温度较低, 且具有较强的高温抗氧化能力, 可直接在空气气氛下加热分解, 因此热分解法完全可以适用。刘志宏等[8]报道了喷雾热分解硝酸银水溶液方法制备单分散的超细球形银粉, 但存在设备构造复杂、投入大、产物粒度分布宽的缺陷。本文借鉴了包覆-热分解(热还原) 制备超细球形镍粉和铜粉的经验, 以碳酸银为前驱体, 利用并流沉淀法包覆改性碳酸银前驱体, 并通过热分解制备得到超细球形银粉[9]; 采用X射线衍射分析(X-ray diffraction, XRD)、粒度分布统计(particle size distribution, PSD)、振实密度测量和扫描电子显微检查(scanning electron microscopy, SEM) 等表征手段研究了热分解银粉的结晶度、纯度、分散性、填充性及微观形貌; 讨论了硝酸银溶液浓度和甲醇添加对碳酸银前驱体颗粒分散性和粒径的影响, 并分析了碳酸镁与碳酸银包覆比例(摩尔比) 对银粉分散性的影响。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 试验试剂和设备
试验试剂包括硝酸银(金川产)、碳酸铵、硝酸镁、甲醇、聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP, 分子量25 K)、乙酸、油酸、无水乙醇和葡萄糖, 以上试剂均为分析纯。试验设备包括玻璃烧杯(0.5 L、1 L、2 L)、电磁加热搅拌器、可调速蠕动加料泵、pH计(梅特勒)、布氏漏斗、真空泵、可编程高温电热炉(西尼特, TSX1200) 及鼓风烘箱(上海试验仪器101A-3B)。
1.2 试验过程
(1) 前躯体的制备: 将一定浓度的硝酸银溶液(500 mL) 加入到一定量的甲醇中, 按碳酸铵/硝酸银摩尔比1:2配制碳酸铵溶液(500 mL), 在一定温度下以恒定速度将碳酸铵溶液加入到配置好的硝酸银溶液中, 搅拌10 min, 得到含有前驱体碳酸银的浆液, 在浆液中加入适量葡萄糖(以碳酸银摩尔量2%计), 以改善碳酸银表面的包覆适性。
(2) 碳酸银前躯体的包覆: 配制硝酸镁溶液(0.5 mol/L) 和碳酸铵溶液(0.5 mol/L), 按一定的包覆比例确定硝酸镁和碳酸铵溶液的用量, 然后用蠕动泵等速并流滴加硝酸镁和碳酸铵溶液到含前驱体碳酸银的浆液中, 滴加结束后充分搅拌使碳酸镁完全沉淀, 纯水洗涤至电导率小于100μS/m, 滤干, 将滤饼送入恒温电热烘箱干燥, 得到包覆碳酸银样品。
(3) 包覆碳酸银的热分解: 将干燥后的包覆碳酸银物料装入坩埚, 设定升温速度5℃/min, 分别在200、300℃保温, 经热分解得到碳酸银样品。热分解产物经质量分数10%的乙酸酸洗(含质量分数0.5%银粉的PVP分散剂), 搅拌并用去离子水洗涤澄清至上清液电导率小于10µs/m后, 将热分解产物转移到乙醇中分散, 加入质量分数1%的脂肪酸作为分散剂, 吸附、过滤, 再用乙醇将未吸附的脂肪酸洗去, 固液分离并烘干后, 对热分解产物进行表征, 具体试验过程如图 1所示。
1.3 分析与表征
采用日本岛津XRD-5610型X衍射分析仪(Cu Kα, 波长0.15406 nm) 分析银粉的结晶度, 使用JEOL产JSM-6000型扫描电子显微镜观察碳酸银前驱体、包覆产物、热解烧结包覆产物形貌和颗粒尺寸, 利用全自动氮吸附比表面仪(型号3H-2000A) 测定银粉比表面, 通过Bettersize2000型粒度分布仪测定银粉粒度分布, 使用振实密度仪测定银粉振实密度。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 碳酸银前驱体粒径和分散性研究
热分解银粉的形貌、分散性、粒径受到前驱体碳酸银的影响, 沉淀法制备前驱体受到沉淀剂种类、温度、浓度、搅拌速度、加料速度、分散剂种类和加入量的影响[10]。参考文献[11]中沉淀法制备草酸银前驱体的实验条件, 本实验选择沉淀温度为40℃, 硝酸银溶液浓度范围为0.2~1.0 mol·L-1; 沉淀剂没有选择碳酸钠和碳酸钾, 而是使用了碳酸铵, 是因为碳酸铵的pH值低于碳酸钾和碳酸钠, 得到的碳酸银粒径适中, 且没有残余的钾钠杂质离子; 搅拌转速统一设定为300 r/min, 加入沉淀剂溶液的速度为10 mL/min。
分散剂可以显著改善湿法沉淀粒子的分散性, 常见分散剂包括极性较强的阴(阳) 离子型分散剂, 如十二烷基磺酸钠、十二烷基硫酸钠和十六烷基三甲基溴化铵, 以及大分子量的非极性分散剂, 如聚乙烯吡咯烷酮PVP、聚乙烯醇PVA和聚乙二醇PEG。考虑上述分散剂会吸附在碳酸银表面, 阻碍碳酸镁在碳酸银表面沉积包覆, 本实验采用小分子量的甲醇作为分散剂调节溶液表面张力, 减轻碳酸银前驱体颗粒之间的团聚。碳酸银前驱体制备条件如表 1所示, 选择硝酸银溶液浓度和甲醇添加量(甲醇与硝酸银溶液体积比) 作为制备条件的主要因素, 其中, 硝酸银溶液浓度为0.2、0.5、1.0 mol·L-1, 甲醇含量(甲醇在硝酸银溶液中的体积分数) 为0、5%、10%、15%及20%。
表 1 碳酸银前驱体制备条件Table 1. Preparation conditions of silver carbonate precursor编号 硝酸银溶液浓度/(mol·L−1) 沉淀剂溶液浓度/(mol·L−1) 温度/℃ 甲醇含量(甲醇在硝酸银溶液中的体积分数)/% 加料方式 Ag2CO3–1 0.2 0.10 40 10 滴加 Ag2CO3–2 0.2 0.10 40 0 滴加 Ag2CO3–3 0.5 0.25 40 5 滴加 Ag2CO3–4 0.5 0.25 40 10 滴加 Ag2CO3–5 0.5 0.25 40 15 滴加 Ag2CO3–6 1.0 0.50 40 20 滴加 由于碳酸银易于分解, 依靠扫描电镜表征碳酸银的粒径和分散性, 所得碳酸银前驱体形貌及粒径分布如图 2所示。由图可知, 随着硝酸银溶液浓度的增加, 碳酸银粒径逐渐减小; 硝酸银溶液浓度较低的Ag2CO3-1、Ag2CO3-2, 粒径可以达到3~5μm, 其中未加入甲醇的Ag2CO3-2局部有团聚现象, 而加入体积分数10%甲醇作为分散剂的Ag2CO3-1则分散性较好; Ag2CO3-3、Ag2CO3-4及Ag2CO3-5粒径相当, 分散性均良好, 但Ag2CO3-5微观形貌从类球形变为长条形, 这说明甲醇作为分散剂对粒径的生长抑制是各向异性的, 超过一定剂量时, 碳酸银各向异性生长速度的差异将得到较为显著的体现, 从而使形貌发生变化; 当硝酸银溶液浓度增加到1 mol·L-1时, 前驱体粒径急剧变小, 过小的粒径造成严重的自团聚, 即使增加甲醇加入量也无法改善其分散性。
综上所述, 随着硝酸银溶液浓度的增加, 碳酸银前驱体的粒径逐渐减小, 并导致颗粒间的团聚变得严重; 适量的加入甲醇有助于改善前驱体的分散性。当硝酸银溶液浓度为0.1~0.5 mol/L, 甲醇在硝酸银溶液中的体积分数控制在5%~10%是制备碳酸银前驱体的优选条件。
2.2 热分解制备球形银粉
2.2.1 沉淀-包覆碳酸银前驱体
碳酸银前驱体的沉淀-包覆改性属于无机粉末的化学表面改性方法[12], 首先沉淀得到淡黄色碳酸银前驱体的混合溶液, 碳酸银呈悬浮状态, 在并流滴加碳酸铵和硝酸镁后, 碳酸银由淡黄色逐渐变成乳白色, 颗粒逐渐变大, 并最终沉淀, 表明碳酸银颗粒表面被碳酸镁所覆盖。分别取包覆前碳酸银前驱体(图3(a))和表面包覆碳酸镁的碳酸银(图 3(b))的电镜照片来观察形貌变化和包覆效果。碳酸银沉淀为不规则的类球形, 碳酸镁结晶形貌规则, 将图 3中沉淀物结晶的形貌和颗粒尺寸进行对比, 可以判断碳酸银前驱体已经完全被碳酸镁沉淀所包覆, 而且经包覆碳酸镁后沉淀物粒径尺寸显著增加, 碳酸银原始颗粒尺寸约1μm, 而包覆碳酸镁颗粒后尺寸接近5μm。碳酸镁沉淀包覆碳酸银前驱体发生的反应如式(1) 和式(2) 所示。
$$ 2{\rm{AgN}}{{\rm{O}}_3} + {({\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_4})_2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_3} = {\rm{A}}{{\rm{g}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}} + 2{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}_3} $$ (1) $$ {\rm{Mg(N}}{{\rm{O}}_3}{)_2} + {({\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_4})_2}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_3} = {\rm{MgC}}{{\rm{O}}_3} + 2{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{4}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{3}}} $$ (2) 2.2.2 包覆量对银粉分散性的影响
为了研究碳酸镁包覆量对银粉分散性的影响, 配制碳酸镁与碳酸银摩尔为1:1、1.5:1.0、2:1的碳酸铵溶液和硝酸镁溶液, 并以Ag2CO3-3沉淀条件的碳酸银为前驱体, 将不同碳酸镁包覆量的包覆产物进行热分解, 经酸洗、分散, 分析比较银粉粒度分布, 结果如图 4所示。结果表明, 随着包覆量的增加, 热分解后得到的球形银粉的粒度分布峰变窄而且粒径变小, 碳酸镁: 碳酸银摩尔比为2:1时得到的银粉粒度分布与电镜观察前驱体粒径相符, 有效避免了颗粒间的烧结。
2.2.3 热分解-酸洗得到类球形银粉
碳酸银包覆产物经固液分离并干燥后加热分解, 其中包覆产物在300℃热分解后形貌和酸洗后球形银粉形貌如图 5所示, 热分解反应方程如式(3) 和式(4) 所示。碳酸银热分解制备银粉包含两次相变, 首先由碳酸银一次分解成氧化银, 然后由氧化银二次分解成银, 因此热分解工艺分两步进行。将装有物料的坩埚放入可编程电热炉中, 升温至220℃保温1 h进行一次分解, 再升温至300℃保温1 h进行二次分解, 保温结束后冷却至室温, 出料。碳酸银分解为氧化银的理论温度为220℃, 为保证分解完全, 设定其实际分解温度略高于理论分解温度。碳酸镁的理论分解分为两个阶段, 第一阶段脱去结晶水(220~360℃), 第二阶段分解成氧化镁和二氧化碳(360~450℃), 因此在氧化银分解成银的温度下, 碳酸镁尚未发生分解。
$$ {\rm{A}}{{\rm{g}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_3} = 2{\rm{AgO}} + {\rm{C}}{{\rm{O}}_2} $$ (3) $$ 2{\rm{AgO}} = 2{\rm{Ag}} + {{\rm{O}}_2} $$ (4) 表 2是图 5(b)中银粉粒径分布统计, 如表所示, 包覆沉淀物300℃热分解后粒径分布范围为0.463~1.818μm, 其中粒径主要集中在0.731~1.153μm范围内, 占粒径总体的76%, 粒度分布集中度尚可。
表 2 酸洗后热分解球形银粉粒径分布Table 2. Particle size distribution (PSD) of spherical silver powders prepared by thermal decomposition after acid leaching粒径尺寸/μm 粒径分布/% 0.463~0.582 0.93 0.582~0.731 8.26 0.731~0.918 35.67 0.918~1.153 41.70 1.153~1.448 12.70 1.448~1.818 0.73 图 6为银粉X射线衍射图谱, 谱线峰的位置和强度与粉末衍射标准卡片JCPDS 89-3722相对应, 无其他无机杂峰存在, 所制银粉为面心立方晶系, 结晶性能良好, 纯度较高。物相判断银粉中没有杂质, 而且热分解制备得到银粉衍射峰强度高于还原银粉, 表明热分解银粉结晶度高于还原银粉, 这是银粉在热分解过程中晶粒由热驱动生长的结果。使用谢乐公式计算图 6中热分解银粉(111) 面对应的晶粒尺寸为46 nm, 而还原银粉(111) 面对应的晶粒尺寸为28.7 nm。
2.3 包覆–热分解方法制备不同粒径的球形银粉
由于应用领域和使用条件的不同, 银浆对银粉粒径的要求也有很大差别, 因此粒径大小及分布是银粉的重要参数。包覆–热分解法可通过控制前躯体的沉淀条件得到不同粒径大小分布的系列球形银粉。表 3为采用包覆–热分解法制备的三种规格球形银粉(Ag–A、Ag–B和Ag–C), 其粒径范围为0.677~2.346μm。如表所示, 随着银粉粒径的减小, 振实密度降低, 比表面增加, 所吸附的分散剂量增加; 其中, 通过比表面积计算得到的平均粒径和对应的D50偏差不大, 说明所得球形银粉具有良好的单分散特性。
表 3 不同粒径球形银粉物理性能Table 3. Physical properties of spherical silver powders in different particle sizes编号 D10/μm D50/μm D90/μm 比表面积/(m2·g-1) 振实密度/(g·cm-3) 灼减/% 平均粒径/μm Ag-A 1.253 1.751 2.346 0.43 5.52 0.29 1.32 Ag-B 0.844 1.010 1.251 0.61 4.44 0.52 0.93 Ag-C 0.677 0.951 1.304 0.88 4.00 0.75 0.65 3. 结论
(1) 使用包覆-热分解方法可以制备得到单分散的球形银粉, 该方法具有设备简单、投资少、产品分散性好且粒度分布集中的优点。。
(2) 当硝酸银溶液浓度为0.2~0.5 mol/L时, 可以得到粒径为0.5~2.5μm的球形银粉。
(3) 碳酸银分散性可通过添加甲醇进行调整, 甲醇含量(甲醇在硝酸银溶液中的体积分数) 应控制在5%~10%。
(4) 当硝酸银溶液浓度为0.5 mol/L、甲醇体积分数为5%时, 碳酸镁与碳酸银摩尔比2:1制备得到的球形银粉分散性最佳。
-
表 1 MgO煅烧前后对胶黏剂密封性能的影响
Table 1 Effect of MgO on the sealing performance of adhesive before and after calcining
未做高温处理 1200 ℃,煅烧2 h 1500 ℃,煅烧2 h 在室温下,胶料瞬间固化,无法涂刷,放出大量的热量 在室温下,胶料在1 min后完全固化,无法涂刷 胶料在2 min后完全固化,可涂刷2个试件,烧成收缩率大,无气密性 表 2 Al2O3质量分数对胶黏剂密封性能的影响
Table 2 Effect of Al2O3 content by mass on the sealing performance of adhesive
基料与固化剂质量比 胶料状态 气密性 5.0:2.5 在室温下,24 h固化,胶料流动性能好,可涂刷,有裂纹 0 5:3 室温下,24 h固化,胶料流动性能减弱,可涂刷 0.020 MPa 5.0:3.5 室温下,24 h固化,胶料的胶黏性上升,可涂刷 0.053 MPa 5:4 室温下,24 h固化,胶料的胶黏性增大,可涂刷 0.058 MPa 5.0:4.5 室温下,24 h固化,胶料的流动性差,可涂刷,胶黏性强,有裂纹 0 -
[1] 路顺, 林健, 陈江翠. 氧化锆氧传感器的研究进展. 仪表技术与传感器, 2007(3): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2007.03.001 Lu S, Lin J, Chen J C. Progress of research on zirconia oxygen sensor. Instrum Tech Sens, 2007(3): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-1841.2007.03.001
[2] 李重, 向蓝翔, 谢姣容, 等. 钇稳定氧化锆铂电极活化时间对氧化锆氧传感器性能的影响. 材料保护, 2014, 47(10): 39 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLBH201410016.htm Li C, Xiang L X, Xie J R, et al. Effect of activation time on sensing performance of yttria stabilized zirconia-platinum electrode. Mater Prot, 2014, 47(10): 39 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLBH201410016.htm
[3] 陈孜, 张雷, 周科朝. 磷酸盐基耐高温无机胶黏剂的研究进展. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2009, 14(2): 74 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2009.02.002 Chen Z, Zhang L, Zhou K C. Research progress of phosphate inorganic binder for high temperature resistance. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2009, 14(2): 74 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2009.02.002
[4] Wang M C, Zhuang M M, Tao X, et al. High temperature bonding effect of the room-temperature-curing phosphate adhesive for C/C composites. Key Eng Mater, 2016, 680: 179 DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.680.179
[5] 张新荔, 吴义强, 李贤军. 硅酸盐胶黏剂的研究与应用. 化工新型材料, 2014, 42(10): 233 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGXC201410079.htm Zhang X L, Wu Y Q, Li X J. Research and application of silicate adhesive. New Chem Mater, 2014, 42(10): 233 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HGXC201410079.htm
[6] Zhou X, Yang J Z, Su D P, et al. The high-temperature resistant mechanism of α-starch composite binder for foundry. J Mater Process Technol, 2009, 209(14): 5394 DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2009.04.010
[7] 韩爽, 曹先启, 张广鑫, 等. 醇溶性磷酸盐胶黏剂高温粘接性能研究. 化学与黏合, 2017, 39(4): 275 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0017.2017.04.011 Han S, Cao X Q, Zhang G X, et al. High temperature bonding performance of alcohol soluble phosphate adhesive. Chem Adhes, 2017, 39(4): 275 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-0017.2017.04.011
[8] Hao R, Liu J, Wang M, et al. Tensile strength and bonding mechanism of the mullite eramic/ceramic sample joined by phosphate adhesive // Advanced Ceramic Materials Proceedings. Taiyuan, 2012: 571 http://cpfd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CPFDTOTAL-ZGCZ201207011012.htm
[9] 陈正中, 王晨. 无机磷酸盐胶粘剂的研究进展. 化工中间体, 2009, 5(4): 12 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJTY200904007.htm Chen Z Z, Wang C. Development and application of inorganic phosphate adhesive. Chem Intermed, 2009, 5(4): 12 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZJTY200904007.htm
[10] 贺孝先, 晏成栋, 孙争光. 无机胶黏剂. 化学工业出版社, 2003 He X X, Yan C D, Sun Z Z. Inorganic Adhesive. Chemical Industry Press, 2003
[11] 侯运城, 范君怡, 蔡永源. 我国胶粘剂工业现状及应用进展. 热固性树脂, 2009, 24(4): 55 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7432.2009.04.014 Hou Y C, Fan J Y, Cai Y Y. Chinese adhesive industry status and application progress. Thermoset Resin, 2009, 24(4): 55 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7432.2009.04.014
[12] 孙世清, 谢维章. 用热分析方法研究MgO的活性. 硅酸盐学报, 1986, 14(2): 226 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYB198602014.htm Sun S Q, Xie W Z. Study on the activity of MgO by thermal analysis. J Chin Ceram Soc, 1986, 14(2): 226 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXYB198602014.htm
[13] Hipedinger N E, Scian A N, Aglietti E F. Magnesia– phosphate bond for cold-setting cordierite-based refractories. Cem Concr Res, 2002, 32(5): 675 DOI: 10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00725-6
[14] 崔韶丽, 陈宁, 霍冀川. 磷酸铝系晶型转变与控制的研究进展. 人工晶体学报, 2013, 42(1): 93 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2013.01.017 Cui S L, Chen N, Huo J C. Research advance on the crystal transformation and control of aluminum phosphate dystem. J Synth Cryst, 2013, 42(1): 93 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2013.01.017
[15] Zou C, Zhang D H, Li Y, et al. Phase evolution of aluminum-chromium-phosphate binders during heat-treatment. Key Eng Mater, 2007, 336-338: 1280 DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.336-338.1280
[16] 余历军, 雷阎盈, 俞强, 等. 氧化铜–磷酸盐胶粘剂粘接机理的剖析与探讨. 粘接, 1998(6): 5 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NIAN199806001.htm Yu L J, Lei Y Y, Yu Q, et al. Study on adhesive mechanism of inorganic phosphate and copper oxide adhesive. Adhesion, 1998(6): 5 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NIAN199806001.htm
[17] 汤旭相, 李瑞安. 氧化铜及其与磷酸反应产物的研究. 粘接, 1985, 6(2): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NIAN198502001.htm Tang X X, Li R A. Studies on copper oxide and the reactants reacted it with phosphoric acid. Adhesion, 1985, 6(2): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-NIAN198502001.htm




 下载:
下载: