Microstructure and mechanical properties of ceramic particle-reinforced powder metallurgy Fe-2Cu-0.6C composites
-
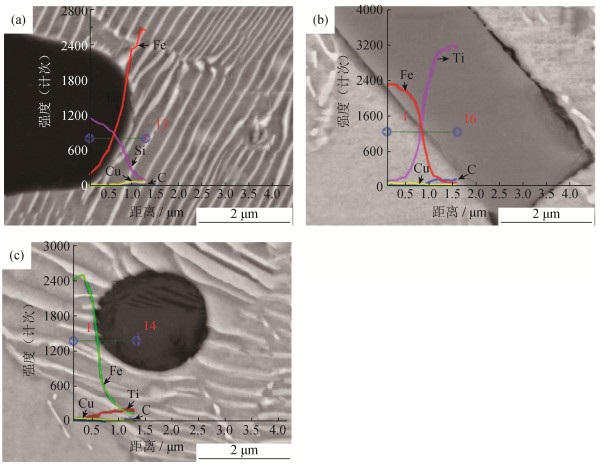
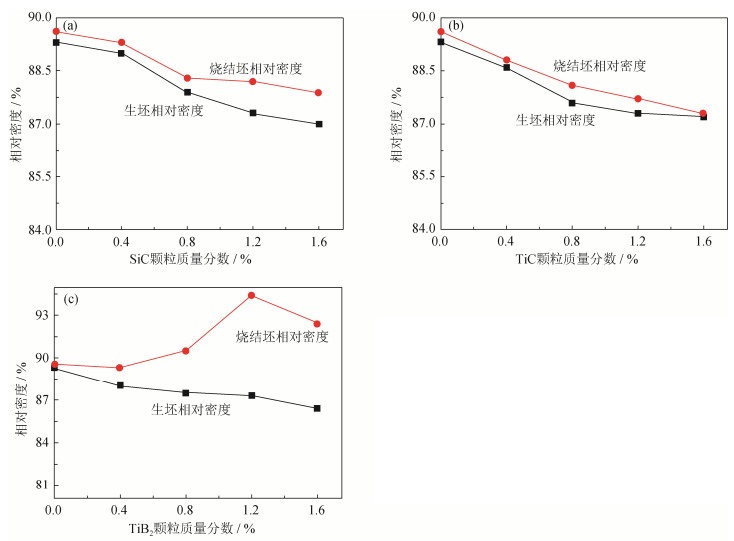
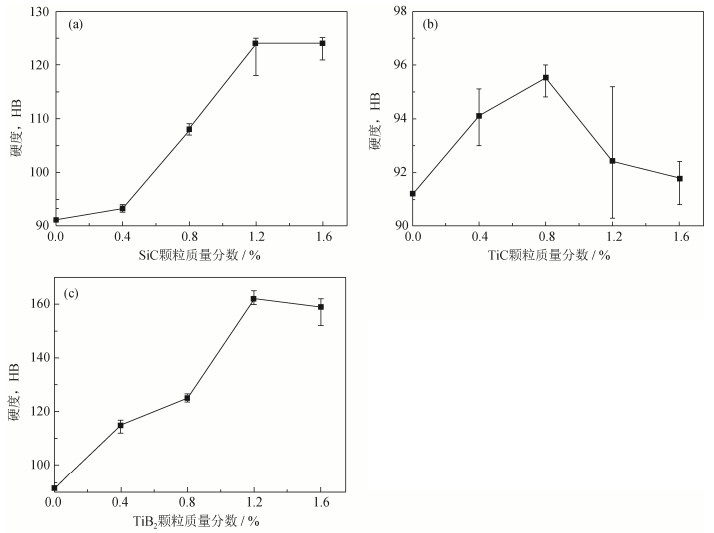
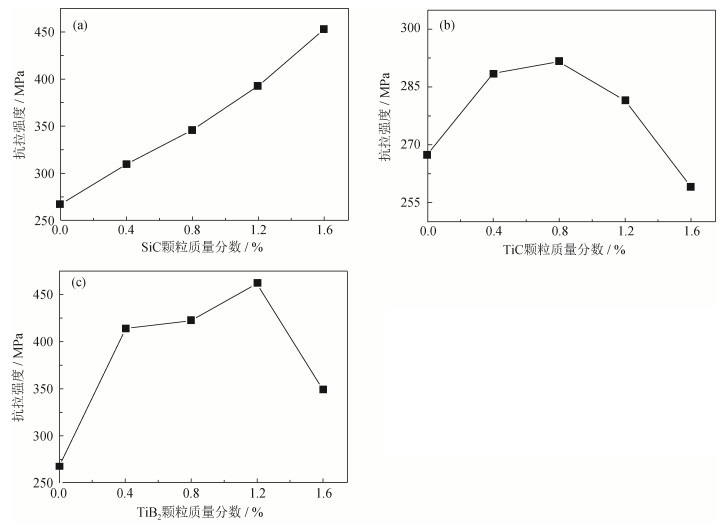
摘要: 采用传统粉末冶金压制/烧结技术,经600 MPa压制、1140℃烧结制备了陶瓷颗粒增强(SiC、TiC及TiB2陶瓷颗粒,质量分数0~1.6%)Fe-2Cu-0.6C低合金钢复合材料,对三种复合材料的微观结构和力学性能进行了研究。结果表明:在烧结过程中,SiC与TiB2颗粒与基体发生反应,故而与基体界面结合良好;当添加质量分数为1.6%的SiC颗粒时,复合材料烧结后的布氏硬度与抗拉强度分别比基体提高了35.9%、69.4%;添加质量分数为1.2%的TiB2颗粒时,复合材料相对密度比基体提高了5.3%,其烧结硬度、抗拉强度与基体相比分别提高了77.9%、72.6%;由于烧结过程中TiC颗粒不与基体发生反应,故而添加TiC颗粒对复合材料的布氏硬度、抗拉强度影响不大。Abstract: Ceramic particle-reinforced Fe-2Cu-0.6C low-alloy steel composites (SiC, TiC, and TiB2 ceramic particles in the mass fraction of 0~1.6%) were prepared by the conventional powder pressing/sintering technology at 600 MPa and 1140℃, the microstructures and mechanical properties of composites were investigated. The results show a good interface bonding between the reinforced particles (SiC and TiB2) and the matrix because of the reaction during sintering. The Brinell hardness and tensile strength of the sintered composites added with 1.6% SiC particles by mass increase by 35.9% and 69.4%, respectively, compared with those of Fe-2Cu-0.6C matrix. When 1.2% TiB2 particles by mass are introduced, the hardness and tensile strength of the sintered composites increase by 77.9% and 72.6%, respectively, compared with those of the matrix. Meanwhile, it is noted that the relative density of the TiB2-reinforced low-alloy steel composite also increases by 5.3%. The addition of TiC particles has little effect on the Brinell hardness and tensile strength of the composites due to no reaction between TiC particles and the matrix.
-
粉末冶金摩擦材料是一种含有金属和非金属的多组元假合金。一般由基体组元、摩擦组元和润滑组元三部分组成[1-2]。与有机摩擦材料相比, 粉末冶金摩擦材料的力学强度高、抗冲击载荷强、摩擦系数稳定、热稳定性高、热传导性好、抗腐蚀能力强, 以及耐磨性能优良, 是现代刹车材料中应用较为广泛的材料之一[3-5]。目前已被应用于各种大型民用飞机、高性能军用飞机、火车、汽车、风电行业以及其它机械制动装置中[6-10]。
相对比于铁基粉末冶金摩擦材料高温下容易产生胶合、摩擦系数波动大、异常磨损明显、噪声大等情况, 铜基摩擦材料因其良好的导热性和自润湿性能, 在干、湿条件下均具备稳定的摩擦性能, 并在高速制动摩擦过程中, 基体与铜结构形成热扩散通道, 能够在相对短的时间内将大量摩擦热散发到环境中, 有效避免了热聚集引起胶粘对制动盘性能造成不利的影响[11]。长期以来, 对铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料的研究主要集中在配方研究和制备工艺对摩擦磨损性能的影响方面, 而刹车速度对铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料的摩擦磨损机理的研究相对较少。本文以铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料为研究对象, 探讨不同的刹车速度对铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料摩擦磨损性能的影响规律, 并对其微观组织进行研究表征, 为新型铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料的深入研究提供参考与理论支持。
1. 实验
1.1 试样制备
实验中所用的材料主要包括电解铜粉、还原铁粉、鳞片状天然石墨, SiO2粉和铬铁等。按表 1的配方分别称取各种粉料, 并在双锥形混合机中混合20~24 h, 将混合均匀的混合料制成压坯, 压坯尺寸为20 mm×15 mm, 厚度大于5 mm。将压坯置于钟罩式加压烧结炉内, 并在氢气保护气氛中进行加压烧结, 烧结温度为850~900℃, 烧结压力为0.3~0.5 MPa, 烧结时间为3.5~4 h。烧结完成后冷却至500℃后再随箱水冷至≤60℃, 出砂。
表 1 铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料化学成分(质量分数)Table 1. Chemical composition of the copper-based powder metallurgy brake materials% Cu Sn Fe SiO2 铬铁 其它 60~70 1~6 6~15 5~10 2~5 10~20 1.2 性能表征
采用JEOL公司的JSM-6390A型扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM)对铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料实验前后的表面形貌进行观测; 采用HRF-150型洛氏硬度计和夏比冲击试验机分别对烧结后粉末层的硬度和冲击韧性进行表征; 在MM-3000型摩擦磨损性能试验台上进行摩擦磨损性能试验, 对偶盘材料为30CrMnSiA。试验前, 摩擦副表面先磨合至摩擦副贴合面积≥80%, 摩擦磨损试验条件及要求见表 2。
表 2 摩擦磨损试验条件Table 2. Condition of friction and wear test编号 惯量/ (kg·m2) 刹车压力/ MPa 刹车速度/ (m·s-1) 刹车转速/ (r·min-1) 次数 1# 0.225 0.66 27.78 2652 10 2# 33.33 3183 10 3# 38.89 3714 10 4# 44.44 4244 10 5# 50.00 4775 10 6# 55.56 5305 10 摩擦试验机记录摩擦吸收功率、刹车力矩与刹车时间关系。根据式(1)可计算出摩擦系数。
$$ \mu = \frac{{2M}}{{\left( {{\gamma _1} + {\gamma _2}} \right) \cdot F}} $$ (1) 式中:μ为摩擦系数, M为力矩(N·m), F为荷重(N), γ1为内圈半径(m), γ2为外圈半径(m)。用电子天平测量试样摩擦试验前后的质量变化; 用千分尺测量试样上6个不同位置处摩擦试验前后的厚度变化, 计算出摩擦试验前后试样厚度差, 求出平均值即试样的线性磨损量。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 微观结构
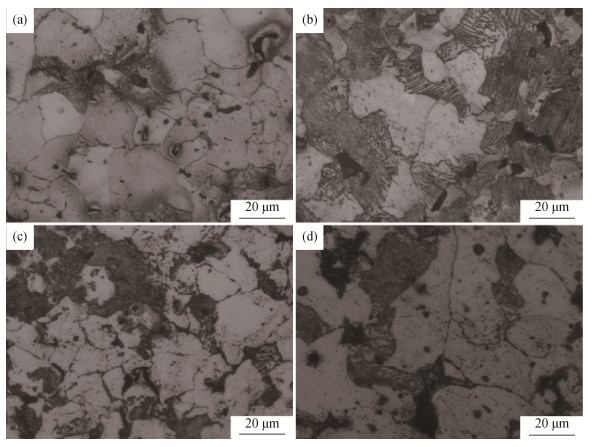
图 1为烧结后铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料表面显微组织形貌。图中黑色的为鳞片石墨, 白色的为铜, 灰色的可能为铁、铬铁或SiO2颗粒。从图可以看出, 大量的鳞片石墨稳定地分布在铜基体当中, 从而保证了刹车过程的平稳性和摩擦系数的稳定性。从图 1 (b)可以清楚地看到大量的灰色颗粒, 其中近似球状的较大颗粒为铬铁(200目, 如箭头所示), 其与基体接触良好, 两者之间观测不到明显的界面[12]; 较小的球状物可能为铁、二氧化硅等颗粒(100目); 这些颗粒均匀地分布在铜基体当中, 铜基体包裹着鳞片状石墨分布在摩擦片表面, 具有稳定的摩擦系数。
2.2 物理性能
铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料的力学性能如表 3所示。从表中可以看出, 摩擦材料的密度较高, 说明摩擦材料中的非金属组元所占体积较小; 材料的洛氏硬度较低, 说明摩擦试验中的对偶磨损相对较小; 材料的抗冲击韧性较大, 表明摩擦组元在材料烧结过程中以机械镶嵌的方式存在基体材料中, 提高了摩擦材料的耐磨性。在高速刹车过程中, 摩擦材料的力学性能确保了其在较大冲击力和较大磨损量条件下的使用。
表 3 摩擦材料的力学性能Table 3. Mechanical properties of friction material密度/ (g·cm-3) 洛氏硬度,HB 冲击韧性/ (J·cm-2) ≥5.72 ≥27 ≥33.5 2.3 摩擦磨损试验
图 2为试样在55.56 m/s刹车速度下的摩擦磨损曲线图。在此刹车速度下, 最大摩擦系数为0.5061, 平均摩擦系数为0.4521;经计算, 离均差率为11.94%, 较小的离均差率说明了铜基摩擦材料具有稳定的摩擦系数。从图中还可以看出, 摩擦系数曲线无明显的振颤现象, 力矩曲线也呈稳定增长趋势, 这也充分表明了该铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料的刹车制动效果平稳, 产生这种现象的原因可能是由于摩擦材料配方中摩擦组元铬铁和铜基体具有良好的润湿性能, 从而提高了摩擦系数的稳定性[12]。
图 3 (a)是在不同刹车速度条件下摩擦磨损性能试验后试样的摩擦吸收功率和摩擦系数曲线图。摩擦吸收功率是指试样在单位时间单位面积内所吸收的功, 它与摩擦面的温度升高有着直接对应关系, 因此影响试样的摩擦系数。从图 3 (a)可以看出, 随着刹车速度增大, 刹车能量升高, 摩擦面的温度进一步升高, 试样的摩擦吸收功率呈近似线性升高。刹车速度从27.78 m/s增加到44.44 m/s, 试样的摩擦吸收功率速率增长最快; 当刹车速度从44.44 m/s增加到55.56 m/s, 试样的摩擦吸收功率增加相对缓慢, 这表明铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料在低速条件下, 吸收的动能可能主要被铜基摩擦材料中的孔隙吸收并传导到空气当中; 当制动速率超过44.4 m/s时, 摩擦材料的吸收动能会被铜基摩擦材料自身所吸收, 并通过高的导热性将吸收能量传导至空气中。从图中还可以看出, 当刹车速度从27.78 m/s增加到44.44 m/s时, 摩擦系数也相对从0.4040增加到0.5071。但随着刹车速率的提高, 试样的摩擦系数出现了明显下降的趋势, 这可能与摩擦材料的摩擦机理和微观结构有关。
图 3 (b)是在不同刹车速度条件下摩擦磨损性能试验后试样的线性磨损率和质量磨损。从图 3 (b)可以看出, 试样的线磨损率随刹车速度的变化与质量损失随刹车速度的变化一致, 都呈上升的趋势。当刹车速度从27.78 m/s增加到33.33 m/s, 试样的线磨损率和质量磨损均较大, 这是由于在较低的速度下, 刹车未进入平稳阶段, 出现了较为明显的磨粒磨损; 当刹车速度从33.33 m/s增加到50.00 m/s时, 粘着磨损起主要作用, 因此线性磨损率和质量磨损都相对较小; 当刹车速率增长至55.56 m/s时, 试样的质量磨损呈明显增长趋势, 这可能是由于在高速条件下, 铜基摩擦材料自身软化造成摩擦组元脱落, 从而质量损耗明显。但由于线性磨损率数据的获得是通过千分尺测量一定面积上的厚度损耗而计算得到的, 因此线性磨损率并不能完全反应出摩擦组元的脱落引起厚度的微小变化, 因而线性损耗率增长不明显。
为进一步研究刹车速度对摩擦磨损性能的影响, 探讨摩擦磨损性能与摩擦面的关系, 采用扫描电子显微镜对在不同刹车速度下试样的摩擦面进行分析。图 4所示为不同刹车速度试验后铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料表面的扫描电子显微形貌。从图中可以看出, 当刹车速度为27.78 m/s和33.33 m/s时, 由于刹车速度较低, 摩擦剪切力较小, 因此摩擦表面温度较低, 且未能形成连续完整的氧化膜, 从而出现了较小面积的剥落且剥落的块状物较小, 其中剥落后较小的硬质颗粒在剪切力作用下从摩擦表面脱落, 在摩擦副之间形成磨粒, 在摩擦表面产生犁沟, 发生磨料磨损和剥层损耗, 其磨损主要是由机械啮合作用造成的; 当刹车速度为38.89 m/s和44.44 m/s时, 摩擦表面较为光滑, 无明显的脱落。这是由于随着刹车速度的增大, 摩擦吸收功率增大, 摩擦面的温度提高, 摩擦剪切力的作用也逐渐增强, 氧化膜趋于平滑连续, 摩擦表面与摩擦副的真实接触面积越大, 其机械啮合作用减弱, 粘着机理起主要作用。随着刹车速度的进一步增大, 摩擦表面在较大剪切力的作用下发生了较为严重的脱落。当刹车速度从50.00 m/s逐渐增大到55.56 m/s, 试样摩擦表面单位面积吸收的能量进一步增大, 温度进一步升高, 摩擦表面在较大剪切力的作用下发生了较为严重的脱落。这是由于摩擦产生的高温引起材料软化, 破坏了形成的氧化膜, 降低了分子键的抗剪切强度, 从而在摩擦面上出现了不同程度的犁沟[13-14]。
3. 结论
(1) 铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料的摩擦磨损性能与刹车速度密切相关。随着刹车速度的增大, 刹车能量急剧升高, 摩擦材料的摩擦吸收功率近似线性增长, 而摩擦系数呈先增大后减小的趋势, 并且铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料的线磨损率与质量磨损随刹车速度增长呈上升趋势。
(2) 在一定的刹车速度下, 铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料摩擦表面的氧化膜愈趋平滑连续。但随着刹车速度的提高, 铜基体自身发生软化, 破坏了已形成的氧化膜, 降低了分子键的抗剪切强度, 从而增大了磨损量。
-
表 1 FHY100.27还原铁粉化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of FHY100.27 reduced iron powder
% C Si Mn P S 氢损(HL) 全铁含量(TFe) 0.010 0.100 0.330 0.012 0.011 0.180 98.570 表 2 陶瓷颗粒增强复合材料体系组成(质量分数)
Table 2 Composition of ceramic particle-reinforced composite system
% 铜粉 石墨 陶瓷颗粒(SiC、TiC、TiB2) 铁粉 2.0 0.6 0.4、0.8、1.2、1.6 余量 -
[1] Efe G C, Ipek M, Zeytin S, et al. An investigation of the effect of SiC particle size on Cu-SiC composites. Composites Part B, 2012, 43(4): 1813 DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2012.01.006
[2] Morris D G, Muñoz-Morris M A. Nanoprecipitation of oxide particles and related high strength in oxide-dispersion-strengthened iron-aluminium-chromium intermetallics. Acta Mater, 2013, 61(12): 4636 DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2013.04.034
[3] Cha L M, Lartigue-Korinek S, Walls M, et al. Interface structure and chemistry in a novel steel-based composite Fe-TiB2 obtained by eutectic solidification. Acta Mater, 2012, 60(18): 6382 DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2012.08.017
[4] Wang H Y, Jiang Q C, Ma B X, et al. Reactive infiltration synthesis of TiB2-TiC particulates reinforced steel matrix composites. J Alloys Compd, 2005, 391(1-2): 55 DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.08.045
[5] Bastwros M, Kim G Y. Ultrasonic spray deposition of SiC nanoparticles for laminate metal composite fabrication. Powder Technol, 2016, 288: 279 DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2015.10.039
[6] Yi D Q, Yu P C, Hu B, et al. Preparation of nickel-coated titanium carbide particulates and their use in the production of reinforced iron matrix composites. Mater Des, 2013, 52: 572 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.05.097
[7] Sulima I, Boczkal S, Jaworska L. SEM and TEM characterization of microstructure of stainless steel composites reinforced with TiB2. Mater Charact, 2016, 118: 560 DOI: 10.1016/j.matchar.2016.07.005
[8] 黄小琴, 左爱文, 王哲, 等. SiC含量对铁基复合材料性能的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2014, 19(2): 271 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2014.02.018 Huang X Q, Zuo A W, Wang Z, et al. Performance of iron-based composites reinforced by different SiC contents. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2014, 19(2): 271 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2014.02.018
[9] Song B, Dong S J, Coddet P, et al. Microstructure and tensile behavior of hybrid nano-micro SiC reinforced iron matrix composites produced by selective laser melting. J Alloys Compd, 2013, 579(10): 415 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925838813014850
[10] Pelleg J. Reactions in the matrix and interface of the Fe-SiC metal matrix composite system. Mater Sci Eng A, 1999, 269(1-2): 225 DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(99)00158-6
[11] Lartigue-Korinek S, Walls M, Haneche N, et al. Interfaces and defects in a successfully hot-rolled steel-based composite Fe-TiB2. Acta Mater, 2015, 98: 297 DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2015.07.024
[12] Efe G C, Zeytin S, Bindal C. The effect of SiC particle size on the properties of Cu-SiC composites. Mater Des, 2012, 36: 633 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2011.11.019
[13] 张一帆, 纪箴, 刘贵民, 等. Al2O3弥散增强Cu基高导电率复合材料的制备及性能研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(5): 346 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.05.005 Zhang Y F, Ji Z, Liu G M, et al. Manufacturing process and properties of Al2O3 dispersion strengthened copper-based composite with high electrical conductivity. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(5): 346 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.05.005
[14] 李荣久. 陶瓷-金属复合材料. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2004 Li J R. Ceramic-Metal Composite Material. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2004
[15] 刘君武, 吕珺, 王建民, 等. 微量SiC颗粒增强铁基合金的摩擦磨损性能研究. 材料热处理学报, 2006, 27(1): 16 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSCL200601005.htm Liu J W, Lv J, Wang J M, et al. Study on tribological properties of sintered ferrous alloys reinforced by SiC particles. Trans Mater Heat Treat, 2006, 27(1): 16 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSCL200601005.htm
[16] Beygi H, Sajjadi S A, Zebarjad S M. Microstructural analysis and mechanical characterization of aluminum matrix nanocomposites reinforced with uncoated and Cu-coated alumina particles. Mater Sci Eng A, 2014, 607: 81 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.03.050
-
期刊类型引用(10)
1. 徐琴,张驰,樊江磊,刘建秀. Cr-Fe粒度对铜基粉末冶金材料摩擦磨损性能的影响. 特种铸造及有色合金. 2024(05): 587-590 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈孝婷,卢纯,莫继良,张庆贺,赵婧. 考虑摩擦升温的铁路列车制动摩擦块高温磨损机制演变. 中国表面工程. 2023(03): 142-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘思涵,耿雪骞,王晔,马运章,陈德峰,张波,曹宏发,齐冀,吕宝佳. Cu基粉末冶金闸片高速制动性能. 粉末冶金技术. 2023(03): 210-217 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 安先龙,王国权,王立勇,陈勇. 铜基粉末冶金摩擦块摩擦磨损特性研究. 机械设计与制造. 2023(12): 209-213+218 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 贾潞. 铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料粘接层失效机理研究. 铁道机车车辆. 2023(06): 111-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘喜双,许雄飞,王秀飞,文国富,尹彩流,冯驰原. 鳞片石墨含量对地铁集电靴用铜基粉末冶金材料性能的影响. 粉末冶金工业. 2021(03): 18-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 任澍忻,陈文革,冯涛,欧阳方明. 粉末冶金制备碳纤维增强铁-铜基摩擦材料的组织与性能. 粉末冶金技术. 2020(02): 104-112 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 韩明,杜建华,宁克焱,李辉,王志勇,邱倩. 温度分布对铜基摩擦材料点蚀损伤的影响. 粉末冶金技术. 2019(01): 18-22 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 姚萍屏,肖叶龙,张忠义,周海滨,贡太敏,赵林,邓敏文. 高速列车粉末冶金制动材料的研究进展. 中国材料进展. 2019(02): 116-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 丁干,王国权,曾圣迪,陈勇,王立勇,雷桐辉. 铜基粉末冶金材料摩擦磨损性能分析. 北京信息科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(04): 61-65+96 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: