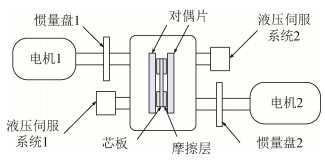
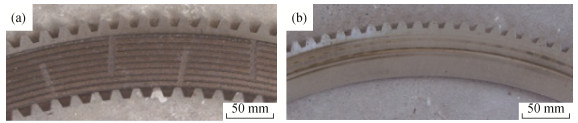
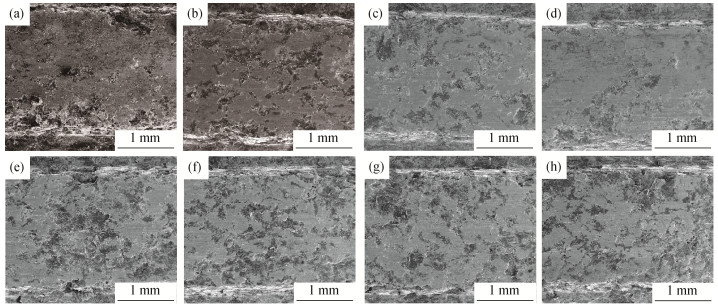
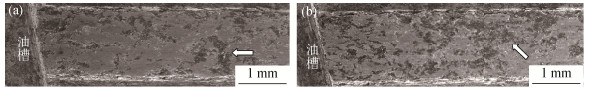
Effect of temperature distribution on pitting damage of copper-based friction material
-
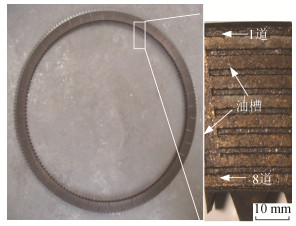
摘要: 通过离合器惯性实验台耐热实验,结合对非均质粉末冶金摩擦层结构模型和温度场的分析结果,研究了特定工况下的铜基粉末冶金摩擦副点蚀损伤现象,分析了温度分布对摩擦材料点蚀损伤的影响。结果表明:湿式铜基摩擦材料在长时间过载或热负荷集中时,由于摩擦表面产生局部高温,摩擦层内部产生较大的温度梯度和热应力,在铜基体与石墨接触区域会产生裂纹并出现铜基体的脱落与转移,发生点蚀;摩擦层上的点蚀程度由外侧向内侧逐渐加重后再减轻,中部点蚀现象最严重;在同一道摩擦层上,距离径向油槽较远区域的点蚀现象严重。Abstract: The pitting damage of copper-based friction material by powder metallurgy was investigated in specific working conditions by the combination of clutch inertia test, the structure model of heterogeneous friction layer by powder metallurgy, and the temperature field of friction layer. The effect of temperature distribution on the pitting damage of friction materials was analyzed. The results show that, the pitting phenomenon occurs because of the temperature gradient and heat stress, resulting from the bonding areas of copper and graphite, when the wet copper-base friction material is overloaded or superheated. The pitting degree of the friction layer is gradually reduced from the lateral to the inside, and the most serious pitting phenomenon appears in the middle. In the same friction channel, the pitting phenomenon is more seriously far away from the radial oil groove.
-
Keywords:
- copper-based friction materials /
- powder metallurgy /
- pitting /
- temperature field /
- oil grooves
-
锆酸钙材料(CaZrO3)具有优秀的抗水化性能、高熔点及良好的抗热震性能[1-5],拥有广阔的应用前景,由于自然界中不存在天然的CaZrO3,研究锆酸钙材料的合成就显得非常必要。制备CaZrO3的方法主要包括高温固相反应法、共沉淀法、溶胶-凝胶法、燃烧法和水热法等[6-8],高温固相法由于工艺简单、生产成本较低和生产量大等优点被人们广泛使用,但这种方法存在烧结温度高、制备锆酸钙致密性差等缺点。为了解决这些问题,研究者们在制备锆酸钙材料过程中向物系添加少量稀土氧化物、Al2O3、SiO2、CuO等添加剂,用于促进锆酸钙在低温下的烧结致密化;这些添加剂虽然可以起到促进锆酸钙材料烧结致密性的作用[9-11],但也会带来外来物质,降低CaZrO3高温使用性能。
CaCO3作为制备CaZrO3的添加剂在高温下分解生成CaO,不会对CaZrO3产生污染;同时,由于CaCO3和制备原料Ca(OH)2分解温度不同,产生CaO晶体顺序不同,可以对CaO晶体质点的扩散产生影响。故本文考虑向锆酸钙材料中添加少量CaCO3微粉,利用分解温度不同,生成CaO晶体顺序不同,促进CaZrO3烧结致密性,降低锆酸钙烧结温度。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 实验材料
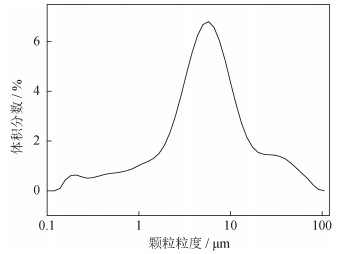
以天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司生产的分析纯Ca(OH)2和天津市光复精细化工研究生产的m-ZrO2为主要原料(平均粒度为7.4 μm和4.5 μm,纯度大于99%),实验中添加的CaCO3微粉为高纯微粉,纯度大于99%,其粒度分布如图 1示。可以看出,CaCO3微粉粒度较小,主要粒度分布在10 μm左右,D50为6 μm,D90为24 μm。
1.2 实验过程及方法
将Ca(OH)2和m-ZrO2按摩尔比1:1称量,等量分成五组,每组混合粉末中依次加入质量分数为0%、2%、4%、6%、8%和10%CaCO3微粉,再用卧式球磨机混合12 h,经过FLS手动四柱油压机在200 MPa压力下将混合粉末压制成ϕ20 mm圆柱试样,再用硅钼棒高温烧结炉在1600 ℃加热并保温3 h后随炉冷却到常温以备性能检测。
烧结前将压好的试样放置在烘箱内110 ℃下保温24 h,取出冷却至常温,测量其高度(L0);试样经高温煅烧,冷却到常温后测量其烧后高度(L1),根据式(1)计算试样烧结前后线变化率(ΔLd)。
$$ \Delta {L_{\rm{d}}} = \left[ {\left( {{L_1} - {L_0}} \right)/{L_0}} \right] \times 100\% $$ (1) 利用阿基米德排水法检测试样煅烧后的体积密度和显气孔率[12]。煅烧后试样经切割、抛光及热处理后,采用扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)观察其组织形貌,使用X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffractometer,XRD)对其进行物相分析。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 烧结性能
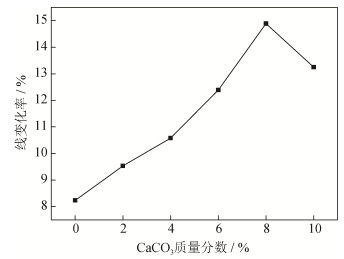
图 2为烧结前后试样线变化率,从图 2可以看到,CaCO3微粉加入会改变试样线变化率。没有添加CaCO3微粉时,试样烧结前后线变化率为8.23%;当添加CaCO3微粉质量分数小于8%时,随CaCO3微粉添加量增大,试样烧结前后线变化率逐渐增大;当加入CaCO3微粉质量分数为8%时,试样收缩率达到最大值,为14.89%;继续增大CaCO3微粉添加量,试样烧结前后线变化率呈降低趋势。
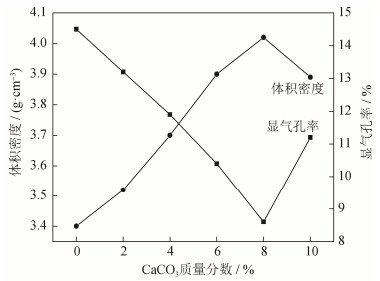
图 3为高温煅烧后制备的锆酸钙体积密度和显气孔率,由图 3可以看到,CaCO3微粉的引入对制备的锆酸钙烧结性能产生影响。当没有添加CaCO3微粉时,制备的锆酸钙体积密度为3.4 g·cm-3,显气孔率为14.5%;随CaCO3质量分数增加,制备锆酸钙体积密度逐渐增加,显气孔率逐渐减小;当CaCO3微粉添加量为8%时,制备锆酸钙的体积密度最大,为4.02 g·cm-3,显气孔率最小,为8.6%;当CaCO3质量分数继续增大时,锆酸钙的体积密度开始降低,显气孔率反增大。
图 4为添加质量分数10%CaCO3制备样品的X射线衍射图谱,从图中可以看出,样品经1600 ℃保温3 h后主要物相为CaZrO3以及少量CaZr4O18。
2.2 材料微观结构
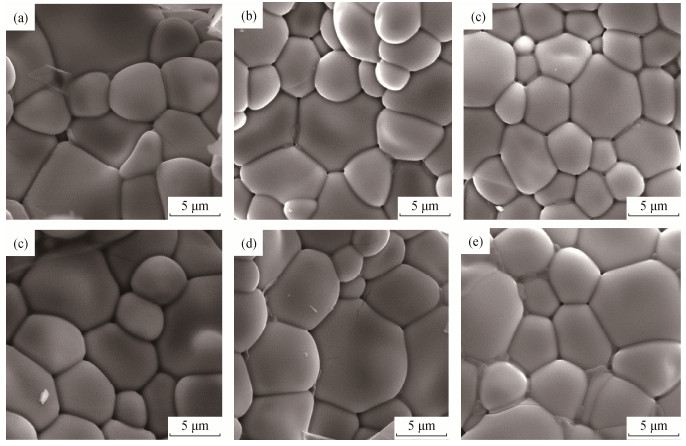
图 5为添加不同质量分数CaCO3微粉的样品在1600 ℃烧后放大10000倍的扫描电子显微组织结构图。从图 5可以看出,CaCO3微粉质量分数小于8%时,随CaCO3微粉添加量的增大,试样致密性逐渐增加,锆酸钙晶粒尺寸逐渐变大,且晶体发育越来越均匀;当CaCO3微粉质量分数为8%时,锆酸钙晶粒尺寸最大,试样中基本无封闭气孔;当CaCO3微粉质量分数继续增大时,样品中出现封闭气孔,致密性变差,锆酸钙晶粒尺寸有变小趋势。
利用图象处理软件对图 5进行定量晶体大小测定,获得锆酸钙的平均晶粒尺寸,见表 1。可以发现,没有引入CaCO3微粉时,样品中锆酸钙晶粒尺寸最小为4.08 μm;随CaCO3微粉质量分数增大,锆酸钙晶粒尺寸逐渐增大;当CaCO3微粉质量分数为8%时,锆酸钙晶粒尺寸达到最大,为5.45 μm;当CaCO3微粉质量分数量继续增大时,锆酸钙晶粒尺寸反而变小。
表 1 样品中CaCO3质量分数与锆酸钙晶粒直径的关系Table 1. Relationship between CaZrO3 particle diameter and CaCO3 addition content by massCaCO3质量分数/% 0 2 4 6 8 10 CaZrO3晶粒直径/μm 4.08 4.43 4.88 5.08 5.45 5.21 2.3 促烧机理
为了分析CaCO3微粉对锆酸钙烧结性能的影响,选取添加质量分数8%CaCO3微粉的试样,分别在500、600、700、800、900、1000及1100 ℃下保温3 h,分析在各个温度下烧后试样物相组成。图 6为试样在不同温度烧结后X射线衍射图谱。可以看出,试样经过500 ℃保温3 h后,物相组成没有太大变化;经过600 ℃保温3 h后,物相中开始有少量CaO出现,这是因为Ca(OH)2分解为CaO温度为580 ℃左右[13];当试样在700、800 ℃保温3 h后,Ca(OH)2质量分数逐渐减少,衍射峰逐渐减弱,CaO质量分数逐渐增大,衍射峰峰强逐渐增强,CaCO3衍射峰强在700 ℃之前逐渐增强,这是因为随烧结温度的升高,CaCO3晶粒发育越来越充分,烧成温度达到800 ℃时,CaCO3衍射峰强开始减弱,说明CaCO3开始分解为CaO;烧结温度为900 ℃时,CaCO3衍射峰逐渐减弱,CaO峰强增加迅速,这是因为CaCO3理论分解温度为850 ℃左右[14],分解生成高活性的CaO微晶均匀附着在Ca(OH)2分解形成CaO晶体表面,从而有利于CaO晶体扩散,可以促进CaO晶体长大,提高了CaO晶体的均匀性和生长致密性;继续升高烧结温度,CaCO3衍射峰强逐渐减弱乃至消失。
当烧结温度达到900 ℃时,物相中开始出现CaZrO3衍射峰,说明开始生成CaZrO3。随烧结温度的提高,CaZrO3衍射峰强增加迅速,一部分原因是因为温度升高,CaZrO3迅速长大,另一部分原因是因为CaCO3分解CaO微晶附着在Ca(OH)2分解形成的CaO晶体表面,促进CaO晶体长大,为高温下CaO和ZrO2反应生成CaZrO3奠定基础。但添加过多的CaCO3微粉时,由于CaCO3在分解过程中产生过量CO2气体逸出形成大量的气体孔洞,不利于质点的迁移,导致烧结性能变差。
3. 结论
(1)添加少量CaCO3微粉有利于锆酸钙烧结致密性。没有添加CaCO3微粉时,烧结温度为1600 ℃,锆酸钙体积密度为3.40 g·cm-3,显气孔率为14.5%;添加质量分数8%CaCO3微粉时,锆酸钙体积密度为4.02 g·cm-3,显气孔率为8.6%。
(2)添加少量CaCO3微粉有利于锆酸钙晶粒长大。烧结温度为1600 ℃,无添加CaCO3微粉时,锆酸钙晶粒尺寸为4.08 μm;添加质量分数8%CaCO3微粉时,锆酸钙晶粒尺寸为5.45 μm。
-
表 1 铜基摩擦材料化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of Cu-based friction materials
% Cu SiO2 Sn 石墨 78 3 4 15 -
[1] Han B L, Lu X C. Effect of nano-sized CeF3 on microstructure, mechanical, high temperature friction corrosion behavior of Ni–W composite coatings. Surf Coat Technol, 2009, 203(23): 3656 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2009.05.046
[2] Majcherczak D, Dufrenoy P, Nait-abdelaziz, M. Third body influence on thermal friction contact problems: application to braking. J Tribol, 2005, 127(1): 89 DOI: 10.1115/1.1757490
[3] Holinski R, Hesse D. Changes at interfaces of friction components during braking. J Automob Eng, 2003, 217(9): 765 DOI: 10.1177/095440700321700901
[4] 符蓉, 宋宝韫, 高飞, 等. SiO2对摩擦第三体形成的作用. 材料研究学报, 2008, 22(1): 31 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3093.2008.01.005 Fu R, Song B Y, Gao F, et al. Effects of SiO2 on the formation of third bodies in friction. Chin J Mater Res, 2008, 22(1): 31 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-3093.2008.01.005
[5] Majcherczaka D, Dufrenor P, Berthier Y, et al. Experimental thermal study of contact with third body. Wear, 2006, 261(5-6): 467 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2005.12.006
[6] 续海峰. 粘着磨损机理及其分析. 机械管理开发, 2007(4): 94 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGL2007S1048.htm Xu H F. Adhesion wear mechanism and analysis. Mech Manage Dev, 2007(4): 94 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSGL2007S1048.htm
[7] 符蓉, 高飞, 牟超, 等. 铜基复合材料干湿条件下的摩擦学行为. 复合材料学报, 2010, 27(1): 79 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FUHE201001015.htm Fu R, Gao F, Mu C, et al. Tribology performance of copper matrix composites under dry and wet conditions. Acta Mater Compos Sin, 2010, 27(1): 79-84 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FUHE201001015.htm
[8] Chu K, Jia C C, Liang X B, el a1. The thermal conductivity of pressure infiltrated SiCp/Al composites with various size distributions: experimental study and modeling. Mater Des, 2009, 30(9): 3497 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2009.03.009
[9] 李园园, 杜建华, 贾成厂. 微/纳米SiO2增强铜基复合材料摩擦学性能的研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2012, 30(5): 353 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2012.05.006 Li Y Y, Du J H, Jia C C. Investigation on tribological properties of micro/nano-SiO2 particles reinforced copper matrix composites. Powder Metall Technol, 2012, 30(5): 353 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2012.05.006
[10] 姚萍屏, 张忠义, 汪琳, 等. 烧结温度对铁基粉末冶金航空刹车材料摩擦磨损性能的影响. 润滑与密封, 2007, 32(6): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2007.06.001 Yao P P, Zhang Z Y, Wang L, et al. Effect of sintering temperature on frictional wear behavior of iron-based powder metallurgy aircraft brake materials. Lubr Eng, 2007, 32(6): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0150.2007.06.001
[11] 王蕊. 粉末冶金凸轮材料摩擦磨损性能研究[学位论文]. 北京: 北京有色金属研究总院, 2017 Wang R. Friction and Wear Properties of Powder Metallurgy Cam Materials [Dissertation]. Beijing: General Research Institute for Nonferrous Metals, 2017
[12] 刘联军, 李利, 吴其俊, 等. 高速直线制动对铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(6): 422 DOI: 10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2017.06.004 Liu L J, Li L, Wu Q J, et al. Effects of high speed linear straight-line braking on Cu-based powder metallurgy friction materials. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(6): 422 DOI: 10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2017.06.004
[13] 刘联军, 李利, 吴其俊, 等. 刹车速度对铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料性能的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2018, 36(2): 83 DOI: 10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2018.02.001 Liu L J, Li L, Wu Q J, et al. Effects of braking velocity on friction properties of Cu-based powder metallurgy friction material. Powder Metall Technol, 2018, 36(2): 83 DOI: 10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2018.02.001
[14] 王大锋, 张波萍, 贾成厂, 等. 超音速火焰喷涂技术制备的双峰WC–CoCr涂层磨粒磨损特性. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(2): 118 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.008 Wang D F, Zhang B P, Jia C C, et al. Abrasive wear behavior of bimodal WC–CoCr coatings sprayed by high velocity oxy-fuel. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(2): 118 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.008
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 路跃,刘国齐,杨文刚,燕鹏飞,马渭奎,李红霞. 烧结助剂对锆酸钙材料性能的影响. 耐火材料. 2023(05): 407-411 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: