-
摘要: 采用熔化极气体保护焊技术(gas metal arc welding,GMAW)制备了Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金,对合金在不同法向载荷(70~190 N)下进行干砂/橡胶轮松散三体磨粒磨损实验。通过X射线衍射分析、扫描电子显微镜观察、能谱分析、磨损失重测试、体视显微镜观察、激光扫描共焦显微镜观察和维氏硬度测量等手段表征了合金显微组织与磨痕特征,研究了合金在不同法向载荷作用下磨损行为的变化。结果表明:堆焊合金显微组织主要由初生奥氏体基体、网状共晶组织及分布于基体上的NbC硬质相组成;合金磨损损失、磨痕深度随法向载荷增大而增大,磨损机制主要为奥氏体基体的微切削及NbC、M7C3的脆性剥落;法向载荷的提高加剧了磨痕亚表面的加工硬化,从而提高了奥氏体基体耐磨性,这导致磨损损失及磨痕深度增长幅度缓慢。Abstract: Fe-Cr-C-Nb hardfacing alloys were prepared by gas metal arc welding (GMAW) method. Loosing abrasive wear tests of dry sand/rubber wheel were carried out on Fe-Cr-C-Nb alloys at different normal loads (70~190 N). Microstructures and wear scar characteristics of alloy were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy disperse spectroscopy (EDS), weight loss test, stereo microscopy, laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM), and Vickers-hardness test to investigate the abrasive wear behavior of alloy in various normal loads. The results show that, the microstructures of Fe-Cr-C-Nb hardfacing alloys are mainly composed of primary austenite matrix, reticular eutectic structure, and NbC hard phase distributed on the matrix. The wear loss and wear scar depth increase with the increase of normal load. The wear mechanism is mainly composed of the micro-cutting of austenite matrix and the brittle flaking of NbC and M7C3. The increase of normal load aggravates the machining hardening of wear scar subsurface, thus improving the wear resistance of austenite matrix and leading to the slow increase of wear loss and wear scar depth.
-
Keywords:
- hardfacing alloy /
- hard phase /
- abrasive wear /
- work hardening
-
磨损作为工件的主要失效形式难以完全避免。据统计,每年有1/3~1/2的能源消耗于摩擦与磨损中,也就是说,机械零件的磨损失效占所有失效形式的60%~80%,这其中的磨粒磨损又占总磨损情况的50%[1]。在农用器具、物料粉磨、冶金矿石等领域,主要且直接的磨损形式均为磨粒磨损,可以说,研究磨粒磨损对于提升机械零件的寿命有着重要的现实意义。针对工件表面的磨损破坏,通常采用堆焊、喷涂等手段在失效位置产生高耐磨性的硬面合金层来进行修复强化[2-3],该方法不仅经济方便,也可有效提高工件服役寿命。传统的Fe-Cr-C系堆焊合金主要依靠其凝固时产生的M3C、M23C6、M7C3、高碳马氏体等高硬度物相来获得一定耐磨性,然而在实际磨损工况中,往往会出现硬度更高的SiC、Al2O3等磨粒[4-5]。近年来,随着各种高新技术的出现,机械设备规格的转型升级必不可少,这使得各类耐磨部件的服役环境更为苛刻,因此,Fe-Cr-C系堆焊合金的耐磨性需要进一步提高。目前真对Fe-Cr-C堆焊合金耐磨性的研究主要集中在合金成分调整和碳化物形态改善上[6-10],关于某种成分合金在特定磨损条件下磨损行为的研究较少[11-12]。
本文利用熔化极气体保护焊技术(gas metal arc welding,GMAW)制备了Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金,采用基于ASTM-G65的干砂/橡胶轮磨损系统,在不同法向载荷(70、100、130、160、190 N)条件下进行Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金磨损试验,通过磨损失重统计和相关磨痕检测,研究了Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金松散三体磨粒磨损行为的变化。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 试样制备
使用自制的Fe-Cr-C-Nb气保护药芯焊丝在Q235钢板母材上进行熔化极气体保护堆焊(CO2保护)。堆焊合金为亚共晶Fe-Cr-C系成分,添加Nb元素主要参与原位合成NbC硬质相,其化学成分如表 1所示。控制焊接电压为30~32 V,焊接电流为280~320 A。使用三层三道摆动堆焊的方法,道间搭接量为1/4~1/3,焊接速度为2.48 mm·s-1,摆动速度为20 mm·s-1,可得到每条焊缝宽度35~40 mm、高度3~4 mm。焊前不预热,并保证道间温度为300~350 ℃。为降低焊后试板内部热应力不均导致的形变,保证相邻两焊道之间的焊接方向相反;为减少裂纹剧烈生长,焊后进行缓冷。尽量在焊接试板中间位置进行机械加工取样,由于磨损实验针对于堆焊合金,使用磨床细砂轮加工71 mm × 25 mm的预磨堆焊合金面,保证表面轮廓算术平均偏差(Ra)小于或等于0.75 mm,最终得到磨损试样规格为71 mm × 25 mm × 13 mm。
表 1 堆焊合金化学成分(质量分数)Table 1. Chemical composition of hard facing alloy% C Cr Nb Mn Si Ni P、S Fe 1.0~2.5 ≤5.0 ≤15.0 ≤2.5 ≤2.0 0.3~0.5 ≤0.035 余量 1.2 实验方法
采用基于ASTM-G65的方法A对堆焊合金进行干砂/橡胶轮磨损实验,实验相关参数如表 2所示,所用实验机设备型号为MLG-130[13],橡胶轮旋转线速度控制在3.15 m·s-1,磨损时间为12.5 min。调整法向载荷变量为70、100、130、160、190 N。选用粒径尺寸为460~540 μm的铸造石英砂作为磨粒,控制其从喷砂嘴泄出的流速为276~288 g·min-1。使用分析天平计量堆焊合金的磨损失重,精确至0.0001 g,每个载荷下进行5次磨损实验计算磨损失重平均值。
表 2 磨损实验相关参数Table 2. Related parameters of abrasive wear test磨粒介质 磨粒粒径/μm 橡胶轮表面材料 橡胶轮表面材料硬度 磨粒流速/(g·min-1) 磨损时间/min 橡胶轮线速度/(m·s-1) 法向载荷(变量)/N 铸造石英砂 460~540 氯丁橡胶 A 60 276~288 12.5 3.15 70、100、130、160、190 堆焊合金的物相组成使用MAXima XRD-7000型X射线衍射仪进行表征,扫描速度为5°·min-1,扫描范围为30°~100°。堆焊合金的显微组织、磨痕微观形貌及磨痕亚表面形貌使用FEI QUANTA 200型扫描电子显微镜配合EDAX Genesis 2000 xms型能谱仪进行观察与分析。使用OLYMPUS LEXT OLS4100型激光共聚焦显微镜配合LEXT分析软件测量磨痕最大深度。此外,在未磨损的堆焊合金预磨面及磨痕上通过Wolpert 401 MVD数显维氏硬度计进行硬度检测,控制载荷2.94 N,保荷时间15 s。
2. 结果及分析
2.1 合金物相分析、显微组织形貌及硬度分析
Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金的X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction,XRD)结果如图 1所示,可检测到的物相有γ-Fe、α-Fe、Fe-Cr、NbC及M7C3型碳化物。图 2为堆焊合金的扫描电子显微(scanning electron microscopy,SEM)组织形貌,可以看到,对于亚共晶成分的Fe-Cr-C系合金,其初生相为奥氏体枝晶,在枝晶基体上分布有不规则形状的白色NbC,而网状共晶组织则分布于奥氏体枝晶间。Nb在熔池反应中首先与C结合生成NbC,随温度下降,对于亚共晶成分Fe-Cr-C系合金来说,将先析出一次奥氏体枝晶,再发生共晶反应生成网状共晶组织(γ-Fe+M7C3)。此外,即便焊后采取了缓冷措施,由于焊后瞬时过冷度较大,奥氏体的扩散型转变在某种程度上被抑制,导致奥氏体晶粒中存在少量的隐针马氏体[14]。
实验测得堆焊合金硬度范围为HV0.3 870.23~924.08,由于大量低硬度奥氏体枝晶初生相的存在,尽管堆焊合金中存在硬度较高的M7C3共晶碳化物和NbC硬质相,其硬度仍然低于石英砂磨粒(HV0.3 1000~1200)[15]。共晶M7C3及NbC对于亚共晶Fe-Cr-C系合金来说是主要的耐磨物相,在磨损时可以有效抵御局部位置石英砂磨粒的侵蚀[16]。
2.2 合金磨损损失变化
对于干砂/橡胶轮磨损系统,橡胶轮与堆焊合金表面的线接触将使得磨痕呈现出具有一定深度的凹坑,这直接导致了堆焊合金表现出明显的磨损损失[17]。图 3为不同法向载荷条件下堆焊合金的磨损失重及磨痕深度。可以发现,随法向载荷的提高,磨粒的法向应力增大,带来更为深刻的切削及幅度更大的碾压作用,这必然导致磨损失重和磨痕深度的增大。然而也可以观察到,磨损失重和磨痕深度随法向载荷的变化趋势是一致的,即增长幅度逐渐降低。这意味着即便磨粒在高法向载荷下倾向于表现出更强的侵蚀性,堆焊合金的耐磨性也相应提高,甚至会减弱磨损损失的增长幅度。
2.3 磨痕微观形貌
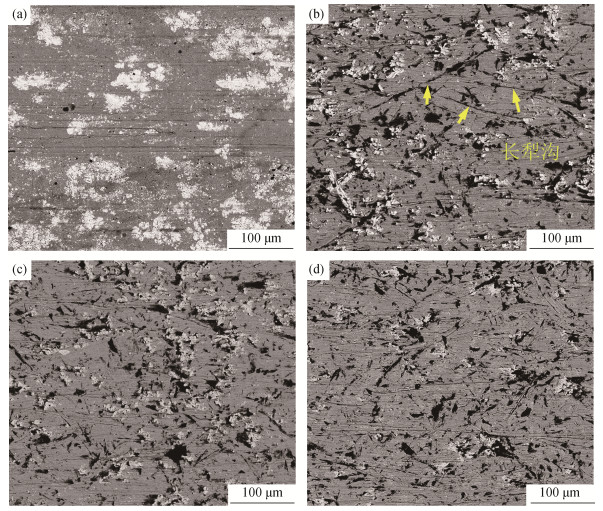
图 4为堆焊合金预磨损面及3个典型法向载荷下(70、130、190 N)磨痕的扫描电子显微形貌。由图 4(a)可知,精细机加工后的堆焊合金预磨面上,大片的白色NbC群落与灰色基体结合较好,仅可以发现少量的平行于机加工方向的细微犁沟及零散的黑色剥落坑。由图 4(b)~图 4(d)可以看到,经过磨损实验后,松散三体磨粒的随机切削及碾压作用导致磨痕上具有大量无方向性的犁沟及黑色剥落坑。
奥氏体枝晶的硬度相对石英较低,且具有较好的塑性和延展性,易被石英磨粒切削出明显的犁沟。由图 4(b)可以看到,当载荷为70 N时,磨痕上存在大量的长犁沟,有些犁沟甚至穿过黑色的剥落坑而极不均匀。高硬脆的NbC作为耐磨相,在抵御磨粒侵蚀时发生了一定的破碎,当奥氏体基体被大幅磨损掉时,NbC将由于无法被有效承载而剥落[18-19]。对于共晶组织来说,由于结构稳定性较差,裂纹易在网状M7C3碳化物间延伸,因此表现出较大的局部脆性剥落倾向。随着载荷的增加,磨粒的法向应力提高,倾向于产生更深刻的切削及碾压。观察图 4(c)和图 4(d)可以发现,磨痕上长犁沟的形成倾向并不随载荷的提高而显著增大,在130 N和190 N时,磨痕上少有如70 N磨痕上长而细犁沟的存在,并倾向于出现大量的小剥落坑,这意味着较软的奥氏体基体对于磨粒的侵蚀开始表现出耐磨性。此外,磨粒法向应力的提高也导致了堆焊合金亚表面内应力的积聚,由于γ-Fe、M7C3及NbC的塑性变形常数和热膨胀系数具有显著差异,相界面处易产生应力集中,因此,对于界面稳定性较差的脆性M7C3和NbC来说,更易发生局部断裂及剥落[20-22]。
2.4 磨痕硬度及亚表面微观形貌变化
预磨面及不同法向载荷条件下磨痕硬度对比如图 5所示。可以发现,在磨损初期,由于磨粒强法向作用及材料严重去除带来的应变使得磨痕发生了显著加工硬化,并表现出远高于磨损前预磨面的硬度值。此外,法向载荷的增大显著提高了磨痕硬度。图 5(b)显示了不同法向载荷下磨痕硬度与磨粒硬度的比值,其变化趋势与硬度结果一致。在磨粒磨损期间,法向载荷的增大提高了硬度比,尤其在130 N载荷时,硬度比已大于1,这意味着在磨损后期,石英磨粒难以对硬化的合金表现出更充分的侵蚀性,因此,从130 N开始,随法向载荷增大,合金在磨损后期的材料去除程度逐渐减弱。
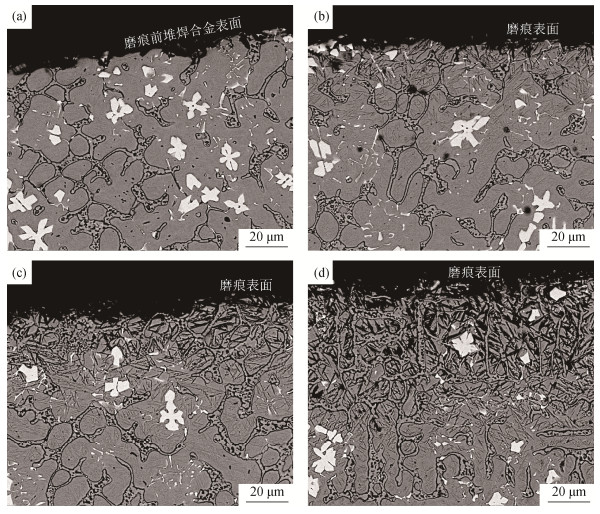
图 6为预磨损面及3个典型法向载荷下(70、130、190 N)磨痕亚表面的扫描电子显微形貌,可以看到,磨痕亚表面产生了典型的针状应变诱发马氏体(strain induced martensite,SIM),这与文献[20]的结果较为一致。γ-Fe的低层错能及奥氏体晶粒中本身存在的隐针马氏体均有利于SIM的形成;在磨损过程中,磨粒的交变应力和奥氏体基体的变形导致在亚表面奥氏体晶粒中形成由堆垛层错和孪晶组成的剪切带,这进一步使得应变诱导的α-马氏体在剪切带交汇处成核并生长[19, 23-24]。由图 6可以看到,随法向载荷增大,磨痕亚表面硬化层增厚,SIM分布愈加密集,这证明了加工硬化程度的提高。磨粒在磨损初期对堆焊合金表现出较强的切削力,随着奥氏体基体不断被磨粒切削形变,其加工硬化也逐渐明显,在磨损后期对磨粒逐渐表现出耐侵蚀性,如图 4(b)所示,在最低的法向载荷(70 N)下,磨痕上出现了显著且密集的长犁沟。随法向载荷的提高,奥氏体基体在磨损后期的加工硬化趋势显著提高,由图 4(c)和图 4(d)可以看到,磨痕上的切削犁沟并未显著增长。由于奥氏体、SIM及NbC的热膨胀系数及塑性应变常数有明显差异,相界面处易产生应力集中[20-22, 25],因此,SIM的形成也导致了堆焊合金局部的剥落趋势。尽管加工硬化有利于加剧材料局部微小区域的剥落,但奥氏体基体对于石英砂磨粒的耐磨性是逐渐增强的,由图 3(b)可以观察到,磨痕最大深度随磨粒切削速度增长的变化幅度逐渐减小,这意味着在磨痕最深处材料的流失得到了一定的抑制,因此,如图 3(a)所示,堆焊合金的整体磨损损失增长幅度随法向载荷提高而变慢。
3. 结论
(1)Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金物相主要为一次奥氏体枝晶基体、分布于基体上不规则形状的NbC硬质相和奥氏体枝晶间网状的共晶组织(γ-Fe +M7C3碳化物)。
(2)Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金的磨损机制主要为磨粒对奥氏体基体的切削及NbC、共晶M7C3的局部脆性剥落。法向载荷的增大倾向于提高磨粒的法向应力,从而加剧堆焊合金局部微小区域的剥落趋势。
(3)Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金的磨损损失及磨痕深度随法向载荷的增大而增大,磨粒强法向应力作用及磨损初期材料大幅移除带来的应变导致磨痕亚表面发生显著加工硬化,出现典型的针状应变诱发马氏体。
(4)随法向载荷增大,Fe-Cr-C-Nb堆焊合金磨痕亚表面硬化层增厚,加工硬化程度提高,这增强了奥氏体基体的耐磨性,导致磨损损失及磨痕深度随法向载荷提高的增长幅度逐渐减小。
-
表 1 堆焊合金化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of hard facing alloy
% C Cr Nb Mn Si Ni P、S Fe 1.0~2.5 ≤5.0 ≤15.0 ≤2.5 ≤2.0 0.3~0.5 ≤0.035 余量 表 2 磨损实验相关参数
Table 2 Related parameters of abrasive wear test
磨粒介质 磨粒粒径/μm 橡胶轮表面材料 橡胶轮表面材料硬度 磨粒流速/(g·min-1) 磨损时间/min 橡胶轮线速度/(m·s-1) 法向载荷(变量)/N 铸造石英砂 460~540 氯丁橡胶 A 60 276~288 12.5 3.15 70、100、130、160、190 -
[1] 杨博翔. 磨煤辊耐磨堆焊明弧自保护药芯焊丝的研究[学位论文]. 湘潭: 湘潭大学, 2015 Yang B X. Study on Open-Arc Self-Shield Hardfacing Flux-Cored Wire of Coal Grinding Roller [Dissertation]. Xiangtan: Xiangtan University, 2015
[2] 卢静, 李勇, 欧阳航, 等. 我国堆焊复合技术的应用与发展. 世界有色金属, 2018(10): 195 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2018.10.111 Lu J, Li Y, Ouyang H, et al. Application and development of surfacing compound technology in China. World Nonferrous Met, 2018(10): 195 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-5065.2018.10.111
[3] 田亮, 刘振英, 罗宇, 等. 面向再制造的硬面堆焊技术研究现状和展望. 电焊机, 2015, 45(2): 11 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DHJI201502003.htm Tian L, Liu Z Y, Luo Y, et al. Status and development prospects of hardfacing technology for remanufacturing. Electr Weld Mach, 2015, 45(2): 11 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DHJI201502003.htm
[4] Wang W J, Lewis R, Yang B, et al. Wear and damage transitions of wheel and rail materials under various contact conditions. Wear, 2016, 362-363: 146 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2016.05.021
[5] Yang J, Tian J J, Hao F F, et al. Microstructure and wear resistance of the hypereutectic Fe-Cr-C alloy hardfacing metals with different La2O3 additives. Appl Surf Sci, 2014, 289: 437 DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.10.186
[6] Wang J B, Yang J, Wang C X, et al. First-principles calculation on LaAlO3 as the heterogeneous nucleus of TiC. Comput Mater Sci, 2015, 101: 108 DOI: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2015.01.024
[7] Yun X, Zhou Y F, Zhao B, et al. Influence of nano-Y2O3 on wear resistance of hypereutectic Fe-Cr-C hardfacing coating. Tribol Lett, 2015, 58: 23 DOI: 10.1007/s11249-015-0475-8
[8] 龚建勋, 许继青, 路德斌, 等. TiC颗粒对铁-碳-铬-硅合金堆焊层显微组织及耐磨性的影响. 机械工程材料, 2015, 39(4): 43 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC201504010.htm Gong J X, Xu J Q, Lu D B, et al. Effects of TiC particles on microstructure and abrasion resistance of Fe-Cr-C-Si alloy hardfacing layers. Mater Mech Eng, 2015, 39(4): 43 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC201504010.htm
[9] 吴慧剑, 龚建勋, 刘江晴, 等. WC含量对明弧堆焊奥氏体合金显微组织及耐磨性的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2016, 21(4): 562 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.04.008 Wu H J, Gong J X, Liu J Q, et al. Effects of WC content on the microstructure and abrasion wear of open arc hardfacing austenitic alloy. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2016, 21(4): 562 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.04.008
[10] Gur A K, Ozay C, Orhan A, et al. Wear properties of Fe-Cr-C and B4C powder coating on AISI 316 stainless steel analyzed by the Taguchi method. Mater Test, 2014, 56(5): 393 DOI: 10.3139/120.110578
[11] Tozetti K D, Albertin E, Scandian C. Abrasive size and load effects on the wear of a 19.9% chromium and 2.9% carbon cast iron. Wear, 2017, 376-377: 46 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2017.02.008
[12] Petrica M, Katsich C, Badisch E, et al. Study of abrasive wear phenomena in dry and slurry 3-body conditions. Tribol Int, 2013, 64(3): 196 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0301679X13001758
[13] 王大峰, 张波萍, 贾成厂, 等. 超音速火焰喷涂技术制备的双峰WC-CoCr涂层磨粒磨损特性. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(2): 118 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.008 Wang D F, Zhang B P, Jiang C C, et al. Abrasive wear behaviour of bimodal WC-CoCr coatings sprayed by high velocity oxy-fuel. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(2): 118 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.008
[14] 崔忠圻, 覃耀春. 金属学与热处理. 2版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2011 Cui Z Q, Qin Y C. Metallography and Heat Treatment. 2nd Ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2011
[15] 宋杰光, 杜大明, 王芳, 等. 干压成型工艺对石英基多孔材料的性能影响研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2015, 33(1): 39 http://pmt.ustb.edu.cn/article/id/fmyjjs201501008 Song J G, Du D M, Wang F, et al. Effect of forming conditions on the properties of quartz sands porours materials. Powder Metall Technol, 2015, 33(1): 39 http://pmt.ustb.edu.cn/article/id/fmyjjs201501008
[16] Sadeghi F, Najafi H, Abbasi A. The effect of Ta substitution for Nb on the microstructure and wear resistance of an Fe-Cr-C hardfacing alloy. Surf Coat Technol, 2017, 324: 85 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2017.05.067
[17] Maroli B, Dizdar S. WC颗粒类型和数量对激光熔敷镍基涂层磨粒磨损性能的影响. 祝弘滨, 译. 热喷涂技术, 2017, 9(1): 50 Maroli B, Dizdar S. Effects of type and amount of tungsten carbides on the abrasive wear of laser cladded nickel based coatings. Translated by Zhu H B. Therm Spray Technol, 2017, 9(1): 50
[18] Correa E O, Alcântara N G, Valeriano L C, et al. The effect of microstructure on abrasive wear of a Fe-Cr-C-Nb hardfacing alloy deposited by the open arc welding process. Surf Coat Technol, 2015, 276: 479 DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2015.06.026
[19] Yang J, Huang J H, Fan D Y, et al. Microstructure and wear properties of Fe-6wt. %Cr-0.55wt. %C-Xwt. %Nb laser cladding coating and the mechanism analysis. Mater Des, 2015, 88: 1031 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.09.108
[20] Sabet H, Khierandish S, Mirdamadi S, et al. The microstructure and abrasive wear resistance of Fe-Cr-C hardfacing alloys with the composition of hypoeutectic, eutectic, and hypereutectic at Cr/C=6. Tribol Lett, 2011, 44(2): 237 DOI: 10.1007/s11249-011-9842-2
[21] Chotĕborský R, Hrabě P, Müller M, et al. Abrasive wear of high chromium Fe-Cr-C hardfacing alloys. Res Agric Eng, 2008, 54(4): 192 DOI: 10.17221/1/2008-RAE
[22] Buchanan V E, Mccartney D G, Shipway P H. A comparison of the abrasive wear behaviour of iron-chromium based hardfaced coatings deposited by SMAW and electric arc spraying. Wear, 2008, 264(7-8): 542 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2007.04.008
[23] Park M C, Shin G S, Yun J Y, et al. Damage mechanism of cavitation erosion in austenite-martensite phase transformable Fe-Cr-C-Mn/Ni alloys. Wear, 2014, 310(1-2): 27 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2013.12.015
[24] Yun J Y, Shin G S, Park M C, et al. Effect of strain-induced ε and α′-martensitic transformation on cavitation erosion resistance in austenitic Fe-Cr-C-MnFe-Cr-C-Mnti alloys. Wear, 2015, 338-339(2): 379
[25] Correa E O, Alcântara N G, Tecco D G, et al. The relationship between the microstructure and abrasive resistance of a hardfacing alloy in the Fe-Cr-C-Nb-V system. Metall Mater Trans A, 2007, 38(8): 1671 DOI: 10.1007/s11661-007-9220-8
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 段嘉旭,魏炜,陶文嘉,杨威,张海燕,高站起. TiC钢结硬质合金在滚动磨粒环境下的磨损行为研究. 新世纪水泥导报. 2022(04): 18-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 段嘉旭,黄智泉,魏炜,高站起,李恒. Fe-C-Mo-V堆焊合金的滚动三体磨粒磨损行为研究. 电焊机. 2021(03): 22-26+112 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 黄智泉. 堆焊制造与再制造技术发展综述. 金属加工(热加工). 2021(06): 23-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王月,韩志. 柱塞表面不锈钢堆焊工艺优化研究. 焊接技术. 2021(12): 114-117 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄智泉,段嘉旭,杨威,张海燕. 冲击能量对Fe-C-Mo-V堆焊合金抗磨粒磨损性能的影响. 焊接学报. 2020(12): 80-85+101-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: