Study on microstructures and properties of S136 die steel formed by selective laser melting after heat treatment
-
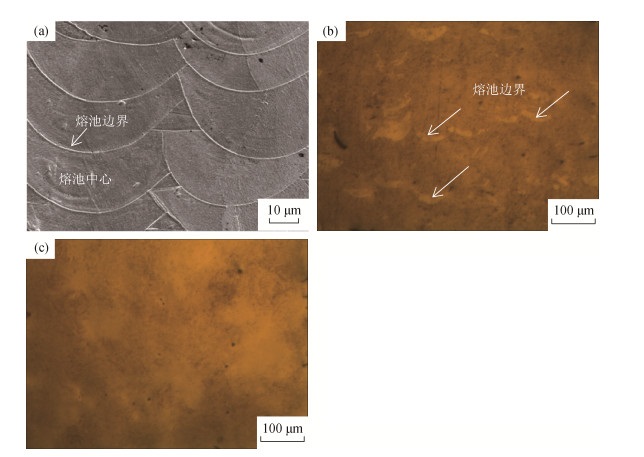
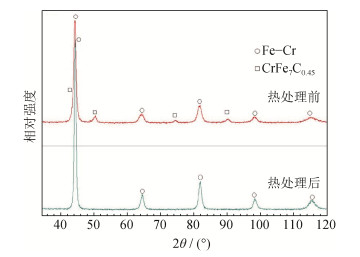
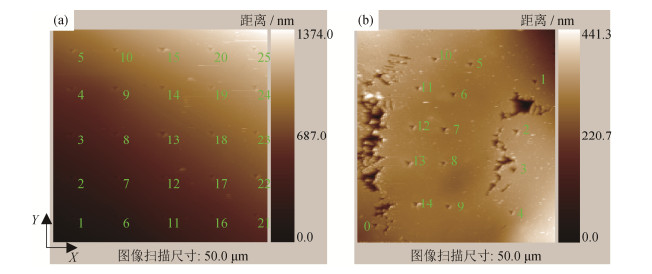
摘要: 激光选区熔化是非平衡凝固过程,成形过程会产生热应力及组织应力,造成金属零件开裂、变形等缺陷,后期热处理是改善激光选区熔化金属零件微观组织和提升性能的有效手段。本文研究了后期热处理参数(热处理温度、保温时间及冷却方式)对激光选区熔化成形的S136模具钢零件微观组织和性能的影响。结果表明:最优热处理参数为1050℃,保温30 min,水冷。在最优热处理工艺下S136模具钢试样洛氏硬度达到HRC 53.7,比热处理之前提高了8.6%,洛氏硬度标准差比热处理之前降低了37.14%,硬度均匀性得到显著改善;试样的耐磨性、最大显微硬度和最大弹性模量比热处理前分别提升33.5%、3.3%和8.6%;试样的熔池形态鳞状形貌结构消失,碳化物相CrFe7C0.45溶解,组织均匀,基本呈现各向同性特征。Abstract: Selective laser melting (SLM) is a non-equilibrium solidification process and can cause the thermal and structural stress, resulting in the cracking and deformation of metal parts. Post-heat treatment is an important way to improve the microstructures and properties of SLM metal parts. The effects of post-heat treatment parameters on microstructures and properties of S136 die steel formed by SLM were investigated in this paper, including heat treatment temperature, holding time, and cooling mode. In the results, the optimal heat treatment parameters are found as 1050℃, 30 min, and water cooling. Rockwell hardness is found up to HRC 53.7, increasing by 8.6% than that of as-formed sample. The uniformity of hardness is greatly improved as the standard deviation of Rockwell hardness decreased by 37.14%. The wear resistance, maximum micro-hardness, and maximum elastic modulus of heat treated sample are increased by 33.5%, 3.3% and 8.6%, respectively. The scaly structure morphology of molten pool is disappeared, CrFe7C0.45 carbide is dissolved, and the uniform and isotropic microstructures are present.
-
Keywords:
- selective laser melting /
- heat treatment /
- hardness /
- wear resistance /
- microstructures
-
航空发动机正向高功率、大推力的方向发展,涡轮发动机进口温度的提高导致现有高温合金难以满足要求,热障涂层(thermal barrier coatings,TBCs)的应用是提高涡轮发动机工作温度最有效的途径[1–3]。热障涂层多采用双层结构,表层为以ZrO2为主的陶瓷层,陶瓷层与基体之间为MCrAlY粘结层(M为过渡族金属Co、Ni或CoNi)。因性能优异,MCrAlY合金在20世纪中叶就得到广泛的关注。20世纪七八十年代,英、美、德、俄等国的MCrAlY制粉和涂层技术已趋成熟,目前仍被广泛应用和持续改进[4]。国内对MCrAlY的研发起步较晚,与欧美等国存在明显差距。近年来,我国航空业蓬勃发展,对高性能航空发动机的市场需求巨大,MCrAlY合金粉的制备和涂层性能亟待改善。国内外有关MCrAlY涂层性能研究的报道很多,但关于MCrAlY合金粉末制备方面的报道较少,而制备高性能粉末是获得理想涂层的首要条件。北京矿冶研究总院、中科院金属所在气雾化制备MCrAlY合金粉末和合金体系改进方面进行了一些试验探索[1,5]。本文采用紧耦合气雾化技术制备了NiCrAlY合金粉末,研究了粉末形貌、粘结形式、显微组织及元素偏析,分析了凝固组织、颗粒尺寸及冷却速率之间的关系,并讨论了凝固组织、缩孔空洞、元素偏析的产生和变化原因,以期为生产高质量热喷涂用MCrAlY粉末提供实验数据。
1. 实验材料及方法
NiCrAlY合金成分(质量分数)为25.0% Cr、8.0% Al、0.5% Y、0.2% Si,余量为Ni。实验采用真空感应熔炼气雾化(vacuum inert gas atomization,VIGA)工艺,合金粉制备工艺路线为合金原料准备(电解Ni板、Cr块、Al块、Si块和Y锭)→真空感应熔炼→紧耦合气雾化→粉末冷凝→粉末收集→分级→粉末后处理。原料称量后,在真空感应炉镁砂坩埚内布料。冶炼炉通电前,首先使用机械泵和罗茨泵对熔炼室和雾化筒进行抽真空处理,炉料在中频感应炉内熔炼成金属液,控制金属液温度等参数适宜后雾化。采用自行设计的紧耦合气雾化喷盘,导液管材质为氧化锆,内径8 mm。雾化介质为纯氩气、气压3.5 MPa,气体流量>30 m3·min−1。金属液雾化温度1630~1670 ℃,金属液流经中间包底部导液管雾化成熔滴,在雾化筒内冷凝成粉,原粉分级制成各粒度区间样品。
在熔炼工序采用真空感应熔炼装置大大减轻活泼元素Al、Y熔炼的控制难度,减少钢液吸氧和夹杂形成,中频感应炉的电磁搅拌有利于钢液在熔炼期和雾化过程的元素均质化。紧耦合超音速气雾化喷嘴结构如图1所示[6],其中α为喷嘴气流夹角,(°);β为金属导液管的锥顶角,(°);h为金属导液管的突出高度,mm。雾化时,导液管流出的钢液流与高速雾化气流紧密耦合,雾化气流动能转化为钢液滴表面能,在导液管下方形成“V”形气体回流区,有利于熔体成膜和初破碎,促进粉末产品细化。紧耦合气雾化技术与真空感应熔炼工艺组合应用,促使雾化粉末产品具有粒度小、球形度好、成分精准、元素分布均匀、低氧低夹杂等特点。
采用斯科特漏斗测定粉末松装密度与流动性,通过筛分析法测试粒度分布,利用化学滴定法测试化学成分。使用JSM-6400扫描电镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)检测粉末形貌和分析元素成分。采用德国Bruker公司D8 Discover型3 kW旋转电极X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction,XRD)对粉末进行物相分析,X射线源采用Cu靶Kα射线,λ=1.5406 nm,激发电压40 kV,电流40 mA。将样品粉经过机械研磨、抛光和王水腐蚀后制成金相试样,在GX51光学金相显微镜观察微观组织。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 粉末物理性能
NiCrAlY合金粉的流动性、松装密度和微量元素O、N含量(质量分数)如表1所示。不同粒径粉末的松装密度与流动性明显不同,随粉末粒径减小,松装密度减少,粗中粒径粉末流动性相近且优良,而细粒径粉末流动性急剧恶化。松装密度不仅与合金材质有关,还与粉末形貌和聚集状态紧密相关。对粒径大的粉末,虽然颗粒间隙增大,但颗粒间粘附搭桥现象减少,单位体积内粉末累积间隙体积减小,致使松装密度增大;同理,当粒径小时,虽然颗粒间隙少,但颗粒间容易形成粘附搭桥,致使松装密度减小。当粉末具有较高的松装密度时,喷涂沉积速率高。粉末流动性受粉末形貌、颗粒表面状态、粒度组成等参数影响。同样,当颗粒间有粘附搭桥现象时,既阻碍粉末移动,颗粒表面也易吸附水分和气体,使流动性变差。流动性是影响喷涂过程送粉流畅性的关键参数,较好的流动性有利于喷涂时获得高质量涂层[1,6]。粉末含氧量是原料氧含量、冶炼雾化过程系统真空度以及后处理各工序参数控制状态等因素共同作用的结果。粗颗粒粉由于冷凝时间长,从环境吸氧较多,细颗粒粉由于颗粒总表面积大,总含氧量偏大。表1中不同粒径粉的含氧量也呈现这一规律,细粒径粉末含氧量数值最大,粗粒径次之,中粒径最低。从表1还可以看到,无论粉末粗细,氮含量几乎相同,较为稳定,这可能与氮是熔于固溶体内而非富集在颗粒表面相关。粉末中的O、N等杂质元素,通常会以MxOy或AluNv形式存在,热喷涂时会严重损害涂层结合强度、寿命等,因此粘结层合金粉要严格控制O、N含量。本文未采用氮气而选用高纯氩气为雾化介质,从粉末杂质含量来看,达到预期目的。
表 1 不同粒径NiCrAlY合金粉的物理性能Table 1. Physics properties of the NiCrAlY powders with the different particle sizes粒径 / μm 松装密度 / (g·cm−3) 流动性 / [s·(50g)−1] 质量分数 / % O N 106~297 4.089 18.50 0.0078 0.0043 45~106 4.063 17.37 0.0057 0.0045 25~38 3.850 — 0.0231 0.0047 2.2 粉末粒度分布
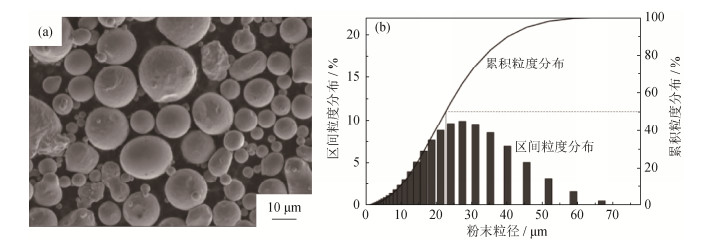
合金粉粒度分布受雾化过程影响。紧耦合气雾化过程可分为初次破碎、二次破碎和冷却凝固三阶段[7]。柱状钢液流在气体回流区完成初次破碎后,遵循韦伯数准则We=ρ·v2·d·σ−1,其中ρ为雾化气体密度,v为气体与熔滴之间的相对速度,d为熔滴直径,σ为熔滴的表面张力。当熔滴的韦伯数达到临界值,才可能发生二次破碎,且随韦伯数由小到大,熔滴二次破碎表现为“哑铃式破碎”、“袋式破碎”、“延展式破碎”、“爆炸式破碎”等多种模式,最终得到的粉末粒度差异较大。
图2为NiCrAlY合金粉的区间粒度分布和累积粒度分布曲线。可以看出,85%的粉末粒径小于150 μm。50 μm以下粒度粉末占41%。以累积体积分数50%所对应粉末粒径表示粉末的平均粒度D50,其值大约为58 μm;同理,D84为124 μm。粉末粒度分布宽度δ=D84/D50,可计算得到δ=2.138,表明合金粉粒度区间较宽,分布不均匀。热障涂层粘结底层材料需要根据喷涂工艺、陶瓷粉参数、应用领域以及粉末综合参数选用某一粒度区间的粉末,其粒度分布与雾化气压、导液管内径、钢液过热度等工艺参数紧密相关,可通过调整雾化参数改变收得粉末的粒度分布。
2.3 粉末形貌
图3为不同粒度NiCrAlY合金粉的形貌。从图3可以看出,不论粒径大小,粉末主要由球形或近球形颗粒组成,均含有少量的异形颗粒。合金粉末粒度越细小,颗粒球形度越好,表面也越光滑。随粒径增大,粉末球形度变差,形貌更近泪滴状,颗粒表面褶皱突起和卫星颗粒增多,光滑度变差。
从图3(a)和图3(b)可以看出,细小粉末(微米级)多为单颗粒状态,随粒径略增大,部分粉末发生粘连。这是因为微米级颗粒冷却快,碰撞前已完全凝固,在飞行冷却中不易相互粘结。粘连颗粒多呈“包覆式”粘连和“葫芦式”粘连,“包覆式”粘连是由包覆在内的颗粒先凝固成形,随后另一熔滴撞击在此颗粒上,熔滴发生延展和冷凝;“葫芦式”粘连是两个凝固颗粒中至少有一个未完全凝固,两者碰撞时局部粘连形成。这两种粘连在颗粒直径相差不大时,发生几率较多[8‒9]。紧耦合气雾化的“V”型气体回流区较小,但回流区内发生钢液柱→液膜→熔滴的初次、二次破碎,流场结构十分复杂[7],大大加剧不同尺寸熔滴冷凝中相互粘连的几率。从图3(c)和图3(d)可以看出,随粒度变大,带卫星颗粒的粉末明显增多,许多大粉末甚至有多个卫星颗粒,此时粘连方式主要是“凸起式”粘连。一般认为,“凸起式”粘连是快速凝固的小颗粒与表面仍未完全凝固的大颗粒发生碰撞而粘接在一起。
通常认为,粘连粉末与气雾化参数紧密相关。雾化喷盘结构、气压、气温、气体流量,雾化筒内气体回流场尺寸、排气速率等均是影响因素。结合表1中数据可看出,细颗粒粉末虽有较好的球形度,颗粒表面光滑,可是粉末流动性差,松装密度低。粗颗粒粉虽球形度差,颗粒表面有严重的褶皱起伏和卫星颗粒,然而粉末有较好的流动性,松装密度高。这也再次表明,松装粒度和流动性不仅与粉末形貌和表面有关,还受粉末的粒度分布和聚集状态等参数影响。
2.4 粉末显微结构
图4为不同粒度NiCrAlY合金粉末颗粒断面显微组织。粉末内部组织既反映了合金的凝固状态,也体现了凝固过程中合金的结晶和长大状况。从图4可以看出,粉末颗粒具有胞状晶和树枝晶两 种典型组织,不同尺寸颗粒均为胞状晶+树枝晶的混合体。
由图4(d)可见,粒径小于30 μm的粉末内部主要是胞状晶组织,但已经出现少量树枝晶组织,颗粒截面内可观察到少量凝固缩孔。随粉末粒径增大,如图4(b)和图4(c),凝固组织由胞状晶+树枝晶组成,胞状晶呈放射状生长,与图4(d)相比,树枝晶比例明显增多,且树枝晶生长趋于完整,晶粒更加粗大,颗粒内明显可见分散着一些凝固缩孔。随粉末颗粒尺寸继续增大,从图4(a)可见,粉末显微组织以树枝晶为主,部分树枝晶还出现二次晶组织,胞状晶仅在局部区域内存在。对比图4(b)发现,颗粒内出现的凝固孔洞数目更多,尺寸明显增加。
从图4还可看出,无论粉末粒径大小,截面边缘主要为胞状晶组织,树枝晶主要出现在靠近颗粒截面中间的位置,同时,粉末内部的胞状晶和树枝晶的晶粒尺寸都极不均匀。熔滴冷却速度是影响粉末内部组织的关键参数。金属熔滴的凝固是一个高温高速过程,涉及从液态熔体到固态的转变,直接测量熔滴冷凝速度是相当困难的,通常采用间接法推导。二次树枝晶臂距与冷却速率之间的关系为λ=b·T−n,其中λ为二次枝晶臂距,μm;T为冷却速率,K·s−1;b为修正常数,μm∙(K∙s‒1)n;n取值为1/3~1/2[10]。采取“截线法”[11],在图4中随机量取6~8个胞晶或枝晶间距,取测量值的平均值作为晶间距,取b=50 μm∙(K∙s‒1)n,n=0.33,推导颗粒冷速。不同尺寸颗粒的晶间距和冷速数据见表2所示。
表 2 不同粒度NiCrAlY粉末的晶间距和冷速Table 2. Grain spacing and cooling rate of the NiCrAlY powders with different particle sizes粉末粒度 / μm 晶间距 / μm 颗粒冷速 / (K·s−1) 251.5 3.144 4020 145.9 2.456 8400 72.9 1.500 37000 40.6 1.350 51000 25.5 1.229 67000 NiCrAlY合金主元素Ni、Cr、Al的熔点、原子半径、密度差距明显,熔滴冷凝过程中趋向发生选择性凝固,形成树枝晶组织,所以小粒径粉末内也出现明显的枝晶组织。随熔滴增大,冷速降低,大粒径粉末趋向形成树枝晶组织。但是大熔滴内不同部位与环境之间热交换较为复杂,情况各异。因此,图4的大粒径粉末内才会出现细化胞状晶和枝状晶的混合组织,甚至出现二次枝晶。
不同粒径粉末的表面光洁度也受凝固冷速影响。如图3所示,粒径小的粉末冷凝速率高,使得熔滴内结晶过程受到抑制,冷凝后熔滴表面只有轻微收缩,所以粉末表面光洁;大颗粒粉末冷速低,冷凝时间长,冷凝中容易形成凝固收缩差异,使大粒径粉末表面光洁度较差[12]。
图5是NiCrAlY粉末(45~106 μm)断面的扫描电镜背散射(scanning electron microscope-back scattered electron,SEM-BSE)形貌。从图5(a)可知,组织整体均匀致密,具有缩孔或空心缺陷的粉末数量占比约为8%~10%。观察单个放大颗粒发现[12],截面直径<50 μm粉末内部结构致密,未观察到明显的冶金缺陷,如图5(b)所示。部分截面直径>50 μm的粉末内出现不规则的凝固缩孔,大粒径颗粒内甚至出现多处缩孔,如图5(c)所示。这是因为冷凝过程中小尺寸熔滴冷速快、过冷度大,促进内部大量形核,晶粒之间相互接触而抑制晶粒长大。大尺寸熔滴冷速慢、凝固时间长,易形成树枝晶组织。凝固缩孔是由于熔滴冷凝收缩形成的,当大粒径颗粒内形成多个树枝晶,冷凝收缩程度更大,易形成多处缩孔[13]。
![]() 图 5 粒径为45~106 μm的NiCrAlY粉末断面扫描电镜背散射电子形貌:(a)粉末显微组织;(b)无缺陷颗粒;(c)凝固缩孔颗粒;(d)空心颗粒Figure 5. SEM-BSE images of the NiCrAlY powders in the cross-section with the particle size of 45~106 μm: (a) overall microstructure of the powders; (b) featureless structure powder; (c) solidification shrinkage; (d) hollow defects
图 5 粒径为45~106 μm的NiCrAlY粉末断面扫描电镜背散射电子形貌:(a)粉末显微组织;(b)无缺陷颗粒;(c)凝固缩孔颗粒;(d)空心颗粒Figure 5. SEM-BSE images of the NiCrAlY powders in the cross-section with the particle size of 45~106 μm: (a) overall microstructure of the powders; (b) featureless structure powder; (c) solidification shrinkage; (d) hollow defects在截面直径>50 μm的颗粒内还观察到空心缺陷,空心主要出现在颗粒中心部位,如图5(d)所示。紧耦合雾化时,受韦伯系数(We)影响,液柱破碎可能发生初次破碎或二次破碎。研究表明,当满足12<We<50,二次破碎易发生“袋式(Bag)破碎”模式。随液膜快冷,钢液的表面张力迅速上升,阻碍液膜继续破碎,并可能将雾化气包裹,熔滴冷凝后就会形成空心缺陷。当粉末粒径大时,首先是容易满足发生“袋式破碎”的韦伯系数条件,其次是颗粒由铺展面积更大的液膜冷凝生成,更增加包裹气泡形成空心粉的发生几率[14]。
合金粉内出现凝固缩孔和空心缺陷是由合金成分、制备工艺和凝固机理共同作用造成的,难于彻底消除。制备热障涂层时,若粘结底层粉末中缩孔或空心不能消除,包裹的气体不能逸散,对涂层结合强度、孔隙度等指标是有影响的。冷却速率是影响粉末显微组织的关键因素,晶体组织状态的形成,凝固缩孔和空心缺陷的形成都受其作用,而冷速又受雾化器结构和雾化工艺参数的影响。
2.5 粉末内部元素的偏析
由于粉末将成分偏析锁定在单个颗粒内,解决了传统冶金产品的宏观偏析,但粉末颗粒内部元素的富集和贫化、晶胞内外的偏析也会影响粉末性能的稳定。
图6是NiCrAlY合金粉末断面的能谱(energy disperse spectroscope,EDS)面扫描分析。从图6可以看出,主要元素Ni、Cr、Al均匀分布,没有明显的富集和贫化现象,而微合金化元素Y、Si则分布不均匀。主要元素均匀分布是由于熔融液滴雾化过程中处于103~104 K·s−1冷速下,粉末内部元素来不及聚集,就已快速凝固所致。
为进一步探明粉末内部晶胞元素分布,利用扫描电镜及能谱对NiCrAlY合金粉进行元素测定,测量位置如图7(a)所示,对区域A进行面扫描,探测晶内B点、晶界C点、晶间D点元素分布。图7(b)和图7(c)为晶内B点和晶界C点的能谱分析,各元素含量数据见表3。由表3可知,与区域A面扫描均值相比,晶界C点Si、Y含量偏高,Al含量偏低,晶内B点表现相反。各测试点Cr、Ni含量基本一致,表明晶界和晶内存在轻微的元素偏析现象[15‒16]。研究表明[2],Si、Y在NiCrAlY合金固溶度较低,当金属液元素含量高及熔滴低速冷凝时,就可能发生元素偏析。Si可降低热障涂层的氧化速率,提高氧化膜黏附强度和高温抗氧化性能。Y可细化晶粒,提高热障涂层氧化膜和基体的结合力。Si、Y在晶界处发生富集偏析可起到阻碍晶界移动、提高热障涂层结合强度的作用。
表 3 图7(a)中各点能谱分析Table 3. EDS analysis of each spots in Fig.7(a)位置 质量分数 / % Al Si Y Cr Mn Ni 能谱面扫A 6.42 0.57 0.48 28.06 — 64.47 晶内B 9.05 0.21 0.29 27.15 — 63.30 晶界C 5.63 1.02 1.65 27.02 0.75 63.93 晶间D 6.65 0.67 0.58 27.74 0.39 63.96 名义含量 7.82 0.32 0.57 25.70 — 65.59 图6、图7和表3的数据表明,NiCrAlY合金粉主元素分布均匀,微合金化元素Si、Y分布不均匀,存在偏析。要抑制此种偏析较为困难。小粒径颗粒还可依靠高凝固冷速抑制合金元素扩散,弱化偏析。对于冷速较低的大尺寸粉末,措施就少得多。
2.6 粉末的相结构
图8是不同粒度NiCrAlY粉末的X射线衍射图谱。如图所示,不同粒度粉末的物相组成基本相同,主要由γ'-Ni3Al、γ-Ni、α-Al2O3、Cr2O3相组成,形成γ'+γ相结构。由于冷速不同,不同粒度粉末的相组成和晶体结构可能存在差异[17]。随粉末粒度减小,衍射曲线中γ-Ni(2θ=45°)衍射峰强度和面积逐渐增强,表明其含量明显增加[18]。如图8(b)所示,随粉末粒度减小,γ'-Ni3Al(2θ=52°附近)的峰位向小角度方向发生了偏移倾斜,这是由快速凝固形成过饱和固溶体效应造成的。粒径<20 μm的NiCrAlY粉末冷速最大,发生的偏移程度也最大,晶格畸变也最严重,反映出凝固速率越高,γ'-Ni3Al固溶体里的溶质原子饱和度越高[19‒20]。
3. 结论
(1)采用紧耦合气雾化技术制备NiCrAlY合金粉末,大部分粉末(约85%)粒径小于150 μm,以球形和近球形颗粒为主。随粒度增大,球形度变差,粘连和卫星颗粒现象严重。
(2)粉末显微组织主要由树枝晶和胞状晶组成,直径25~250 μm熔滴的凝固冷速为4000~67000 K·s−1。
(3)小粒径粉末(粒径<50 μm)内部结构致密,少量大粒径(粒径>50 μm)粉末内部出现凝固缩孔和空心,粉末颗粒晶界和晶内存在元素Si、Y偏析。
(4)粉末相组成主要为γ'-Ni3Al和γ-Ni,且晶格畸变程度随粒度变小而加重。
-
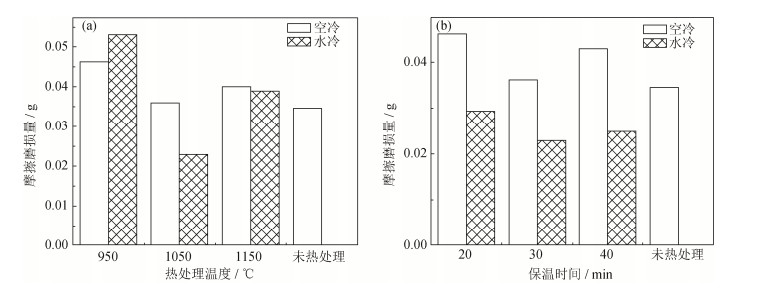
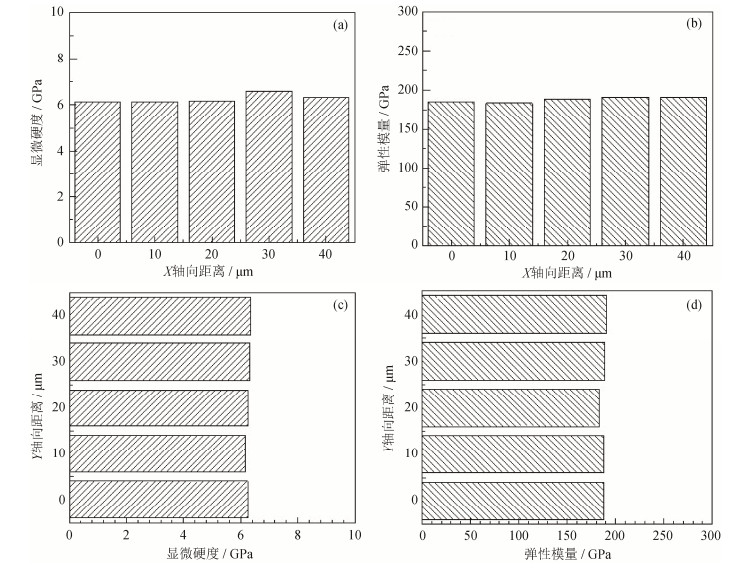
图 10 S136模具钢SLM成形件热处理后显微硬度和弹性模量:(a)X轴方向显微硬度;(b)X轴方向弹性模量;(c)Y轴方向显微硬度;(d)Y轴方向弹性模量
Figure 10. Micro-hardness and elastic modulus of S136 die steel by SLM after heat treatment: (a) micro-hardness in X-axis direction; (b) elastic modulus in X-axis direction; (c) micro-hardness in Y-axis direction; (d) elastic modulus in Y-axis direction
表 1 S136模具钢粉化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of S136 die steel powders
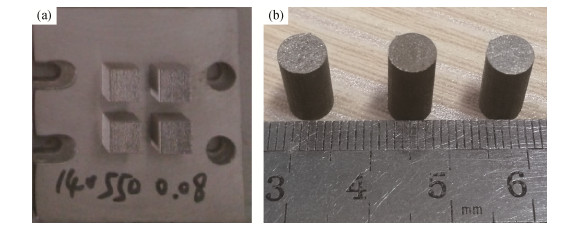
% C Cr Mn Si V Fe 0.34 14.64 < 0.81 < 0.55 0.35 余量 表 2 3D打印成形实验参数
Table 2 Experimental parameters of 3D printing forming
扫描功率,P/W 扫描速度,V/(mm·s-1) 扫描间距,S/mm 铺粉厚度,H/mm 140 550 0.08 0.02 表 3 SLM成形S136模具钢试样后续热处理制度
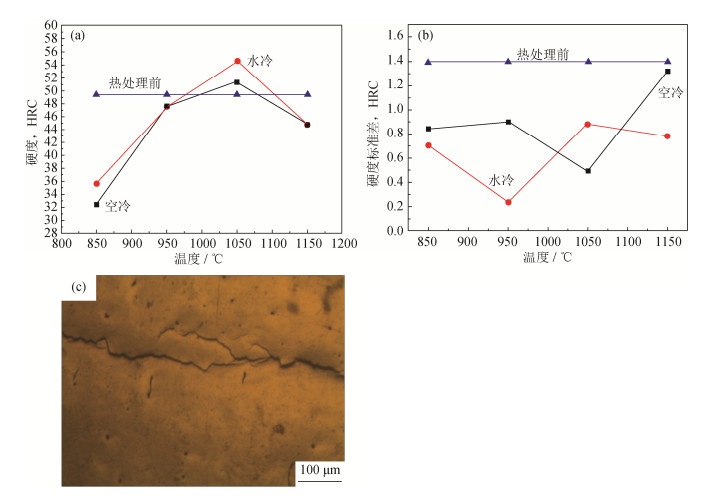
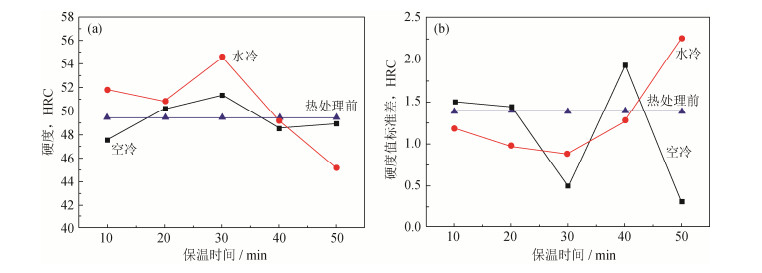
Table 3 Heat treatment process of S136 die steel samples formed by SLM
试样编号 加热温度/℃ 保温时间/min 冷却方式 1# 850 30 水冷,空冷 2# 950 30 水冷,空冷 3# 1050 30 水冷,空冷 4# 1150 30 水冷,空冷 5# 1050 10 水冷,空冷 6# 1050 20 水冷,空冷 7# 1050 40 水冷,空冷 8# 1050 50 水冷,空冷 表 4 显微硬度和弹性模量热处理前后变化幅度
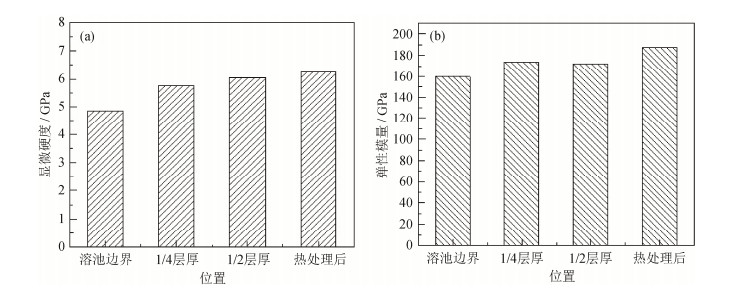
Table 4 Changes on the micro-hardness and elastic modulus of S136 die steel by SLM before and after heat treatment
测试时间 位置 弹性模量变化幅度/% 显微硬度变化幅度/% 热处理前 熔池法向 7.15 19.87 热处理后 X轴方向(5列) 4.02 7.19 热处理后 Y轴方向(5行) 3.96 2.89 注:变化幅度=[(最大值‒最小值)/最大值]×100% -
[1] 王会杰, 崔照雯, 孙峰, 等. 激光选区熔化成形技术制备高温合金GH4169复杂构件. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(5): 368 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.05.009 Wang H J, Cui Z W, Sun F, et al. Superalloy GH4169 complicated components prepared by selective laser melting forming technique. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(5): 368 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.05.009
[2] 董鹏, 陈济轮. 国外选区激光熔化成形技术在航空航天领域应用现状. 航天制造技术, 2014(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTGY201401001.htm Dong P, Chen J L. Current status of selective laser melting for aerospace applications abroad. Aerosp Manuf Technol, 2014(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HTGY201401001.htm
[3] 陈帅, 陶凤和, 贾长治, 等. H13模具钢选区激光熔化成型工艺及其性能研究. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(10): 162 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201710043.htm Chen S, Tao F H, Jia C Z, et al. Research on selective laser melting forming process and property of H13 die steel. Hot Working Technol, 2017, 46(10): 162 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201710043.htm
[4] 任武, 张刚刚, 徐云喜. 3D打印选区激光熔化成形4Cr13模具钢及性能研究. 石油机械, 2016, 44(11): 107 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYJI201611022.htm Ren W, Zhang G G, Xu Y X. Performance of 4Cr13 die steel by selective laser melting. China Pet Mach, 2016, 44(11): 107 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SYJI201611022.htm
[5] Zhang S, Wei Q S, Cheng L Y, et al. Effects of scan line spacing on pore characteristics and mechanical properties of porous Ti6Al4V implants fabricated by selective laser melting. Mater Des, 2014, 63: 185 DOI: 10.1016/j.matdes.2014.05.021
[6] Wen S F, Li S, Wei Q S, et al. Effect of molten pool boundaries on the mechanical properties of selective laser melting parts. J Mater Process Technol, 2014, 214(11): 2660 DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2014.06.002
[7] 文世峰, 吴雪良, 周燕, 等. 激光选区熔化成形S136模具钢的成形性能研究. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(2): 51 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201802010.htm Wen S F, Wu X L, Zhou Y, et al. Microstructure and property of S136 mould steel fabricated by selective laser melting. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technol Nat Sci, 2018, 46(2): 51 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZLG201802010.htm
[8] Zhao X, Wei Q S, Song B, et al. Fabrication and characterization of AISI 420 stainless steel using selective laser melting. Mater Manuf Process, 2015, 30(11): 1283 DOI: 10.1080/10426914.2015.1026351
[9] 刘斌, 谭景焕, 吴成龙. 基于3D打印的随形冷却水道注塑模具设计. 工程塑料应用, 2015, 43(10): 71 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2015.10.014 Liu B, Tan J H, Wu C L. Design of injection mould with conformal cooling channel based on 3D printing. Eng Plast Appl, 2015, 43(10): 71 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2015.10.014
[10] Wang Y, Yu K M, Wang C C L, et al. Automatic design of conformal cooling circuits for rapid tooling. Comput-Aided Des, 2011, 43(8): 1001 DOI: 10.1016/j.cad.2011.04.011
[11] Dang X P, Park H S. Design of U-shape milled groove conformal cooling channels for plastic injection mold. Int J Precis Eng Manuf, 2011, 12(1): 73 DOI: 10.1007/s12541-011-0009-8
[12] 单忠德, 杨立宁, 戎文娟, 等. 熔融堆积3D打印成形金属件层间结合研究. 机械设计与制造, 2016(8): 135 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2016.08.037 Shan Z D, Yang L N, Rong W J, et al. The study on parts' interlayer binding during three-dimensional printing based on metal fused and deposition. Mach Des Manuf, 2016(8): 135 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2016.08.037
[13] 何寅. 随形冷却水道注塑硬模快速制造方法研究[学位论文]. 武汉: 湖北工业大学, 2012 He Y. Study on Rapid Manufacturing of Hard Injection Mold with Conformal Cooling Channels [Dissertation]. Wuhan: Hubei University of Technology, 2012
[14] 张骁丽, 齐欢, 魏青松. 铝合金粉末选择性激光熔化成形工艺优化试验研究. 应用激光, 2013, 33(4): 391 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYJG201304008.htm Zhang X L, Qi H, Wei Q S. Experimental study of selective laser melted AlSi12. Appl Laser, 2013, 33(4): 391 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YYJG201304008.htm
[15] Song B, Zhao X, Li S, et al. Differences in microstructure and properties between selective laser melting and traditional manufacturing for fabrication of metal parts: A review. Front Mech Eng, 2015, 10(2): 111 DOI: 10.1007/s11465-015-0341-2
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 班伟,陈嘉琪,刘璐璐,葛涛,张帅. 紧耦合气雾化喷嘴流场特性研究. 粉末冶金技术. 2024(03): 312-319 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 朱本章,朱协彬,汪国成,卢燕,姚廷鑫. 真空气雾化法制备纯铜粉末工艺及性能研究. 安徽工程大学学报. 2024(04): 52-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: