-
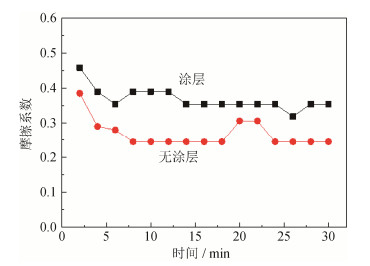
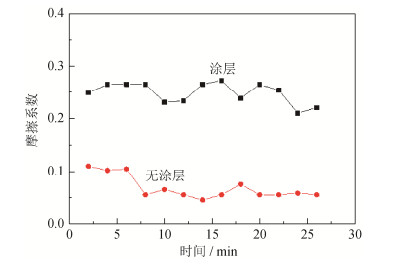
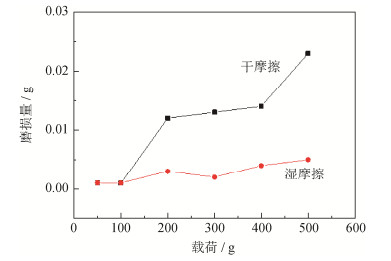
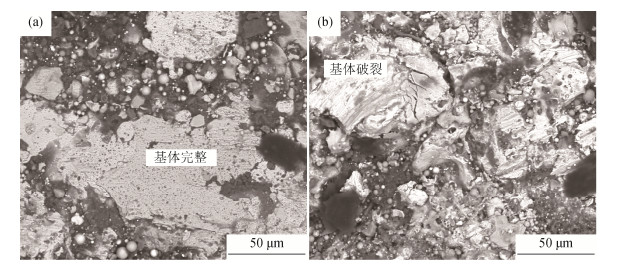
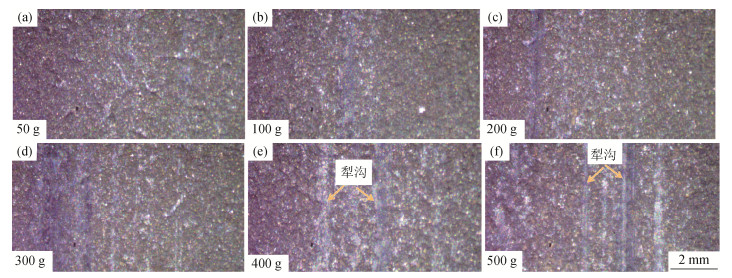
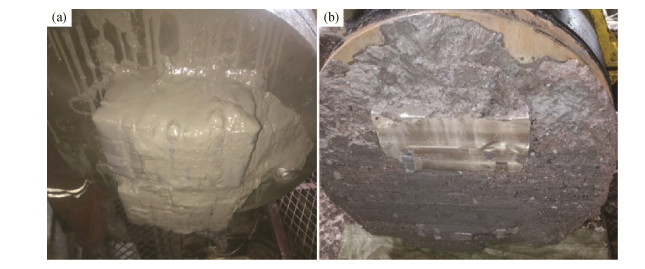
摘要: 为了解决盾构施工的泥饼问题,利用火焰喷涂在Q345钢板表面制备了石墨-镍涂层,通过摩擦磨损试验分析了涂层和无涂层试样与泥岩渣土的摩擦行为,研究了石墨-镍涂层对摩擦系数、表面磨损量和表面磨痕的影响。结果表明,干摩擦条件下,泥岩渣土与无涂层表面和涂层表面的摩擦系数分别为0.4和0.3;湿摩擦条件下,泥岩渣土与无涂层表面和涂层表面的摩擦系数分别为0.25和0.05。随着载荷从50 g增加到500 g,湿摩擦条件下涂层表面磨损量增加缓慢,干摩擦条件下涂层表面磨损量呈台阶式增加;在干摩擦条件下,随载荷增加,磨痕宽度和深度增加,局部出现犁沟形态。现场试验结果证实,滚刀刀桶端面火焰喷涂石墨-镍涂层能够有效抑制盾构在泥岩地质层施工过程中的刀盘结泥现象。Abstract: The graphite-nickel coatings on the surface of Q345 steel plates were prepared by flame spraying to solve the mud-caking problems of shield tunneling. The friction behaviors of Q345 steel samples with and without graphite-nickel coatings against mudstone compacts were analyzed by friction-wear tests, and the influences of graphite-nickel coatings on the friction coefficient, wear loss, wear scars were systemically studied. The results show that, the dry-friction coefficients of Q345 steel samples with and without graphite-nickel coatings against mudstone compacts are 0.4 and 0.3, respectively, and the wet-friction coefficients are 0.25 and 0.05, respectively. As the load increasing from 50 to 500 g, the wear loss of samples with coating increases slowly under the wet friction condition; while it takes a step-change upward under the dry friction condition. Under the dry friction condition, both width and depth of wear scar increase as increasing the load, and the furrows occur locally. The in-situ testing proves that the flame sprayed graphite-nickel coatings on the end surfaces of disc cutter barrels can effectively inhibit the mud-caking phenomena during shield tunneling in mudstone layers.
-
Keywords:
- coatings /
- mudstone /
- friction /
- wear /
- shield tunneling
-
钛合金是一种比强度高、耐蚀性能优异的合金材料, 对航空航天、汽车制造等领域发挥了重要的作用。但在实际应用过程中, 钛合金存在抗高温氧化与耐磨性不足的问题, 严重限制了该合金材料在高温载荷领域的进一步推广应用[1-3]。为了进一步提升钛合金的各项性能, 大多数研究人员主要通过喷焊、气相沉积、激光熔覆等工艺对钛合金进行表面处理[4-6]。其中, 激光熔覆技术可以在不改变钛合金性能的前提下使涂层间形成良好冶金结合状态, 对于钛合金材料摩擦性能的提升起到了明显的促进作用[7-8]。现阶段, 许多学者在Ti4合金耐磨性方面主要是通过增加该材料的表面硬度来实现。不过, 加入钛合金中的TiN、WC、VC等硬质相颗粒在860℃温度下却存在容易被空气氧化的问题[9-10]。例如, Feng等[11]利用激光熔覆处理工艺对Ti5合金表面进行处理, 生成包含增强相TiNi/Ti2Ni基涂层, 并对该涂层进行了表征, 得到涂层中形成了具有均匀分布状态的陶瓷相颗粒, 从而增加了合金材料的耐磨性。Guo等[12]则利用激光熔覆技术对Ni Cr BSi/WC–Ni合金涂层进行了处理, 制得了具有良好耐磨性能的合金涂层。齐鸣等[13]采用激光熔覆工艺使高温合金表面生成MoSi2/Al涂层, 之后在1050℃下对该涂层实施了耐高温氧化性测试, 当涂层中含有的Al比例上升后, 生成的氧化膜中的Al2O3会显著提高熔覆层的耐高温氧化性。余鹏程等[14]对Ti4合金表面进行激光熔覆处理后得到了含有增强相Al3Ti/Ni Ti基涂层, 研究得到当涂层内含有的Al3Ni2脆性颗粒数量增加后, 涂层耐磨性发生了降低的现象。
到目前为止, 大部分学者都是将研究重点集中于通过激光熔覆处理方法来提升钛合金的耐磨性方面, 但很少有文献报道关于钛合金耐高温抗氧化性能的改善内容[15]。本文主要通过激光熔覆处理工艺使Ti4合金表面生成Ni Al Si涂层, 并深入探讨了在860℃温度下该涂层对抗氧化性提升的效果及其作用机理。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 实验原料
实验用原料为Ti4合金, 试样尺寸40 mm×40 mm×8 mm, 用砂纸打磨试样熔覆面, 充分去除表面氧化膜。选择80Ni–40Al–20Si复合粉末作为熔覆材料, 采用QM-3SP04型行星球磨机对该粉末进行12 h的球磨处理。
1.2 涂层制备
先在Ti4合金试样涂覆一层甲基纤维素黏结剂, 再铺设一层厚度为1.5 mm的混合粉末, 再将其放入120℃的干燥箱内进行2 h的保温。本实验在DLS-980.10-3000C半导体激光器上完成激光熔覆过程, 工艺参数为: 输出功率2 kW, 扫描速度3.5 mm·s-1, 光斑大小5 mm×2.5 mm。
1.3 涂层性能测试
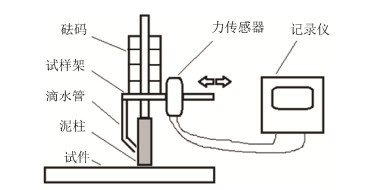
通过线切割方式得到熔覆层的截面金相试样, 并对该试样进行了X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction, XRD) 表征。利用S-4700型场发射扫描电镜(scanning electron microscopy, SEM) 对涂层微观组织进行了观察, 同时在该电镜附带的能谱仪(energy disperse spectroscope, EDS) 上表征了涂层的各元素组成情况。利用HMF1400-50高温电阻炉测试其抗高温氧化性能, 并计算单位面积对应的质量变化情况。对经过氧化处理的合金与涂层进行金相观察。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 合金涂层显微组织
从图 1 (a) 中可以看到涂层横截面的扫描电子显微形貌。根据图 1 (a) 可知, 在涂层内也没有观察到裂纹结构, 只有少数气孔存在。从图 1 (b) 中可以看到在Ti4和涂层的结合部位形成了熔合线, 可以推断涂层和钛合金之间形成了良好的冶金结合状态。同时还可以观察到在涂层的底部区域形成了众多的柱状晶, 这主要是因为受到凝固冷却的影响, 钛合金垂直的方向上具有最快的冷却速率, 从而导致涂层的下部晶粒优先从垂直钛合金表面的方向上开始生长。图 1 (c) 是对应于图 1 (b) 的放大图, 可以明显看到该图包含了块状区域A与网状区域B两种, 对这些区域进行能谱测试可知, 区域A中的元素类型包括Ti与Si, 两者的原子数分数比接近5:3, 可见该区域的成分主要是Ti5Si3金属间化合物; 对区域B进行元素分析得到该区域包含Ni与Al两种元素, 其原子数分数比接近3:2, 进一步结合X射线衍射图谱可知, 区域B的成分主要是Al3Ni2金属间化合物, 因此可以推断涂层中包含了Ti5Si3与Al3Ni2两种主要成分。
表 1 图 1 (c) 中区域A和区域B能谱分析Table 1. EDS analysis of area A and area B in Fig. 1 (c)区域 原子数分数/% Ti Ni Al Si A 44.28 22.18 5.48 28.06 B 23.54 42.18 30.02 4.26 2.2 高温抗氧化性能及机理
从表 2中可以看到对钛合金与合金涂层进行高温氧化测试得到的试样单位面积质量变化值, 其中钛合金的单位面积质量增加值显著高于合金涂层, 可见合金涂层的耐高温氧化性能优于钛合金。经过40 h的恒温氧化处理后, 试样单位面积质量增加了24.4 mg·cm-2, 可见在860℃温度下, Ti4合金的表面发生了明显的氧化过程, 此时形成的氧化膜也不能有效抑制氧原子的扩散过程。其中, 在初期高温氧化阶段, 合金涂层具有很快的氧化速率, 当氧化时间不断增加后, 合金涂层的氧化速率降低, 因此可以推断合金涂层表面氧化膜具有降低氧化速率的作用; 经过40 h的高温氧化处理后, 粉末合金涂层的质量增加值是2.19 mg·cm-2, 比Ti4合金的耐高温氧化性能提高了12倍左右。
表 2 Ti4合金和合金涂层高温氧化(860℃) 测试结果Table 2. High temperature oxidation test results of Ti4 alloy and alloy coating at 860℃样品 单位面积质量变化/(mg·cm2) 5 h 10 h 20 h 30 h 40 h Ti4 合金 2.40 4.40 9.20 16.70 24.40 合金涂层 1.82 1.90 2.02 2.11 2.19 Ti4合金与粉末合金涂层在860℃温度下进行40 h的氧化处理后, 对其表面氧化层进行X射线衍射测试得到如图 2所示的谱图。从图 2的测试谱图中可以发现, Ti4合金的氧化层基本包含Al2O3与TiO2两种物相成分, 并且TiO2的衍射峰强度显著高于Al2O3, 说明氧化膜主要是由TiO2构成。由于在860℃下V2O5的挥发性较高, 因此在X射线衍射谱图中未观察到该氧化物的衍射峰, 同时氧化膜也因为V2O5的挥发而形成多孔结构, 使氧原子更易向膜内扩散, 导致合金耐高温氧化性降低。
图 3 (a) 为在860℃下进行40 h氧化处理后得到的Ti4合金横截面扫描电子显微形貌, 可以发现此时Ti4合金表面出现了较严重腐蚀的情况, 生成的氧化膜表现出了明显的热脆性特征, 较易从表面发生脱落的现象。对Ti4合金的氧化膜微观形貌进行分析可知, 氧化膜主要由许多球形颗粒与柱状物构成, 根据能谱分析(表 3) 可知, 柱状物成分主要是TiO2。在TiO2的形核与生长期间, 还会形成少量的Al2O3, 使氧化膜中形成众多微孔, 这种不连续的氧化膜结构不能发挥有效阻止氧原子扩散的作用, 不利于提高合金的耐高温氧化性。
图 3 (b) 为在860℃下进行40 h氧化处理后得到的合金涂层氧化膜扫描电子显微形貌。从图中可知, 合金涂层与氧化膜之间保持紧密结合状态, 未看到有脱落情况出现。对该涂层进行能谱分析(表 3) 可知, 其表面氧化膜中的元素主要为O、Al, 同时还有部分Si、Ni、Ti, 因此可以推断该氧化膜的主要成分时Al2O3, 此外还含有部分NiO、SiO2、TiO等。因为Al2O3能够形成致密的连续结构, 起到明显抑制O元素扩散的效果, 使合金涂层耐高温抗氧化性能获得显著提高。
3. 结论
(1) Ti4合金和合金涂层的结合部位形成了熔合线, 可以推断合金涂层和钛合金之间形成了良好的冶金结合状态。同时还可以观察到在涂层的底部区域形成了众多的柱状晶, 涂层中包含了Ti5Si3与Al3Ni2两种主要成分。
(2) 钛合金的单位面积质量增加值显著高于合金涂层, 可见合金涂层的耐高温氧化性能优于钛合金。经过40 h的高温氧化处理后, 粉末涂层的质量增加值是2.19 mg·cm-2, 比Ti4合金的耐高温氧化性能提高了12倍左右。
(3) 在860℃下进行40 h氧化处理得到的合金涂层与氧化膜之间保持紧密结合状态, 未看到有脱落情况出现, 氧化膜的主要成分是Al2O3。
-
表 1 摩擦磨损试验工艺参数
Table 1 Process parameters of friction-wear test
试件类型 载荷/ g 摩擦环境 涂层、无涂层 50、100、200、300、400、500 干摩擦、湿摩擦 表 2 试验用泥岩渣土的物质组成(质量分数)
Table 2 Compositions of mudstone used in friction-wear test
% 石英 方解石 钠长石 伊利石 绿泥石 50.63 2.51 15.71 15.37 15.78 -
[1] 王梦恕. 中国盾构和掘进机隧道技术现状、存在的问题及发展思路. 隧道建设, 2014, 34(3): 179 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD201403001.htm Wang M S. Tunneling by TBM/shield in China: state-of-art, problems and proposals. Tunnel Constr, 2014, 34(3): 179 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD201403001.htm
[2] 彭琦. 隧道掘进机技术的发展和研究现状. 隧道建设, 2013, 33(6): 443 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD201306007.htm Peng Q. Application, research and future of tunnel boring machine technology. Tunnel Constr, 2013, 33(6): 443 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD201306007.htm
[3] Fountaine E R. Investigations into the mechanism of soil adhesion. Eur J Soil Sci, 1954, 5(2): 251 DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2389.1954.tb02191.x
[4] 王国义, 张波. 土压平衡盾构泥饼防治技术浅析. 施工技术, 2016, 45(增刊2): 222 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGJS2016S2053.htm Wang G Y, Zhang B. Analysis of mud-cake prevention technology for earth pressure balance shield tunnel boring machine. Constr Technol, 2016, 45(Suppl 2): 222 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SGJS2016S2053.htm
[5] 李志军, 翟志国, 赵康林. 泥水盾构刀盘结泥饼形成原因及防治技术. 地下空间与工程学报, 2014, 10(增刊2): 1866 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE2014S2022.htm Li Z J, Zai Z G, Zhao K L. Causes of mud cake formation on cutter head of slurry shield and its control technology. Chin J Underground Space Eng, 2014, 10(Suppl 2): 1866 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BASE2014S2022.htm
[6] 杨志勇, 程学武, 江玉生. 泥水平衡盾构刀盘扭矩计算及其影响因素分析. 铁道工程学报, 2016(5): 59 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.05.011 Yang Z Y, Cheng X W, Jiang Y S. Analysis of cutterhead torque calculation and its influence factors for slurry balance shield. J Railway Eng Soc, 2016(5): 59 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2106.2016.05.011
[7] 左翠凤, 唐德高, 戎晓力, 等. 基于刀盘摩擦扭矩参数的刀具磨损状态识别. 隧道建设, 2016, 36(3): 344 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD201603021.htm Zuo C F, Tang D G, Rong X L, et al. State recognition of cutter wear based on frictional torque parameters of cutterhead. Tunnel Constr, 2016, 36(3): 344 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSSD201603021.htm
[8] Zhou S H, Li X, Ji C, et al. Back-fill grout experimental test for discharged soils reuse of the large-diameter size slurry shield tunnel. KSCE J Civ Eng, 2017, 21(3): 725 DOI: 10.1007/s12205-016-0856-z
[9] Bryan P J, Gutshall P L, Taylor L H. A study of mechanisms of graphite friction and wear. Wear, 1964, 7(1): 118 DOI: 10.1016/0043-1648(64)90083-3
[10] Li J L, Xiong D S. Tribological behavior of graphite-containing nickel-based composite as function of temperature, load and counterface. Wear, 2009, 266(1-2): 360 DOI: 10.1016/j.wear.2008.06.020
[11] Yang J F, Jiang Y, Hardell J, et al. Influence of service temperature on tribological characteristics of self-lubricant coatings: A review. Front Mater Sci, 2013, 7(1): 28 DOI: 10.1007/s11706-013-0190-z
[12] Rawal S P. Metal-matrix composites for space applications. JOM, 2001, 53(4): 14 DOI: 10.1007/s11837-001-0139-z
[13] Sass I, Burbaum U. A method for assessing adhesion of clays to tunnelling machines. Bull Eng Geol Environ, 2010, 69(4): 671 DOI: 10.1007/s10064-010-0304-0
[14] 丁华东, 傅苏黎, 朱有利, 等. 自润滑材料滑动摩擦失效分析. 粉末冶金技术, 2001, 19(5): 270 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2001.05.004 Ding H D, Fu S L, Zhu Y L, et al. Failure analyzing of self-lubrication material. Powder Metall Technol, 2001, 19(5): 270 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2001.05.004
[15] 吴俊, 袁大军, 李兴高, 等. 盾构刀具磨损机理及预测分析. 中国公路学报, 2017, 30(8): 109 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.08.012 Wu J, Yuan D J, Li X G, et al. Analysis on wear mechanism and prediction of shield cutter. China J Highway Ttransport, 2017, 30(8): 109 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2017.08.012
[16] 温诗铸, 黄平. 摩擦学原理. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2002 Wen S Z, Huang P. Principles of Tribology. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2002
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: