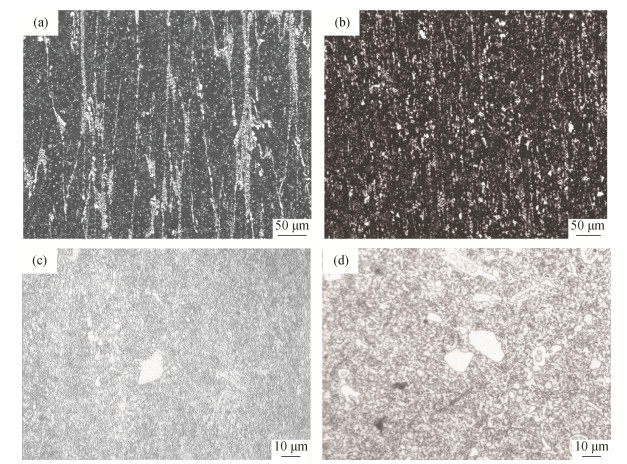
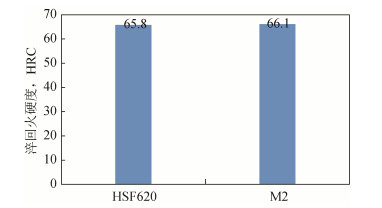
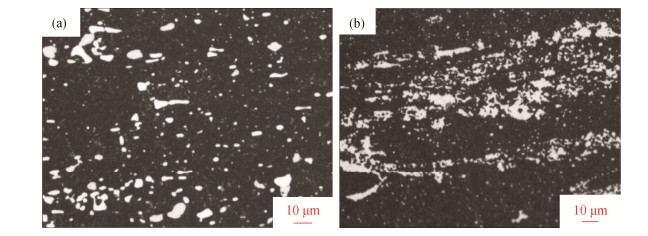
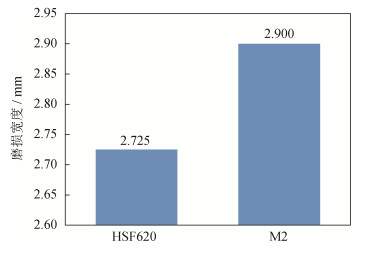
Research on the microstructures and mechanical properties of high speed steel M2 produced by spray forming and traditional melting
-
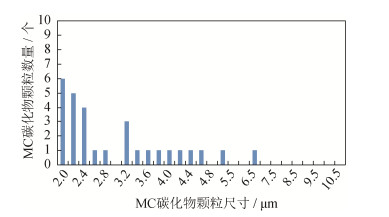
摘要: 通过喷射成形和传统熔炼(中频冶炼+电渣重熔)两种工艺生产了高速钢M2(W6Mo5Cr4V2)试样,利用金相显微镜和M-200磨损试验机对同规格同位置的两种试样的退火组织、非金属夹杂物、淬回火硬度、显微组织和力学性能进行了研究。结果表明,喷射成形M2试样的碳化物分布均匀、尺寸细小,传统熔炼M2试样碳化物呈条带状分布;在相同热处理制度和位置下,喷射成形M2试样的回火硬度与传统熔炼M2试样相当;喷射成形M2试样的耐磨性要比传统M2试样提高约41%;喷射成形M2试样中尺寸大于2μm的MC类碳化物数量明显多于传统M2试样,使得在同等硬度下喷射成形M2试样的耐磨性能要优于传统M2试样。由此可知,喷射成形M2试样的组织及力学性能均优于传统熔炼M2试样,喷射成形技术具有工艺先进性。Abstract: Two kinds of high speed steel specimens (M2, W6Mo5Cr4V2) were prepared by spray forming and traditional melting, respectively. The annealing structures, non-metal inclusions, hardness after quenching and tempering, microstructures, and mechanical properties of M2 specimens in the same size at the same location were studied by metallographic microscope and M-200 wear tester. In the results, the carbides in spray formed M2 specimens show more uniform distribution and smaller size, and the carbides in traditional melted M2 specimens are present as the zonal distribution. In the same heat treatment process, the tempering hardness of M2 specimens prepared by spray forming and traditional melting is similar at the same location. Compared with the traditional melted M2 specimens, the wear resistance of spray formed M2 specimens is increased by ~41%. The number of MC carbides in spray formed M2 specimens with the size more than 2μm is apparently higher than that in the traditional melted M2 specimens, resulting in the higher wear resistance of spray formed M2 specimens in the same hardness. It can be seen that the microstructures and mechanical properties of spray formed M2 specimens are better than those of the traditional melted M2 specimens, showing the advancement of spray forming technology.
-
Keywords:
- spray forming /
- traditional melting /
- high speed steel /
- microstructures /
- mechanical properties
-
钛合金是一种比强度高、耐蚀性能优异的合金材料, 对航空航天、汽车制造等领域发挥了重要的作用。但在实际应用过程中, 钛合金存在抗高温氧化与耐磨性不足的问题, 严重限制了该合金材料在高温载荷领域的进一步推广应用[1-3]。为了进一步提升钛合金的各项性能, 大多数研究人员主要通过喷焊、气相沉积、激光熔覆等工艺对钛合金进行表面处理[4-6]。其中, 激光熔覆技术可以在不改变钛合金性能的前提下使涂层间形成良好冶金结合状态, 对于钛合金材料摩擦性能的提升起到了明显的促进作用[7-8]。现阶段, 许多学者在Ti4合金耐磨性方面主要是通过增加该材料的表面硬度来实现。不过, 加入钛合金中的TiN、WC、VC等硬质相颗粒在860℃温度下却存在容易被空气氧化的问题[9-10]。例如, Feng等[11]利用激光熔覆处理工艺对Ti5合金表面进行处理, 生成包含增强相TiNi/Ti2Ni基涂层, 并对该涂层进行了表征, 得到涂层中形成了具有均匀分布状态的陶瓷相颗粒, 从而增加了合金材料的耐磨性。Guo等[12]则利用激光熔覆技术对Ni Cr BSi/WC–Ni合金涂层进行了处理, 制得了具有良好耐磨性能的合金涂层。齐鸣等[13]采用激光熔覆工艺使高温合金表面生成MoSi2/Al涂层, 之后在1050℃下对该涂层实施了耐高温氧化性测试, 当涂层中含有的Al比例上升后, 生成的氧化膜中的Al2O3会显著提高熔覆层的耐高温氧化性。余鹏程等[14]对Ti4合金表面进行激光熔覆处理后得到了含有增强相Al3Ti/Ni Ti基涂层, 研究得到当涂层内含有的Al3Ni2脆性颗粒数量增加后, 涂层耐磨性发生了降低的现象。
到目前为止, 大部分学者都是将研究重点集中于通过激光熔覆处理方法来提升钛合金的耐磨性方面, 但很少有文献报道关于钛合金耐高温抗氧化性能的改善内容[15]。本文主要通过激光熔覆处理工艺使Ti4合金表面生成Ni Al Si涂层, 并深入探讨了在860℃温度下该涂层对抗氧化性提升的效果及其作用机理。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 实验原料
实验用原料为Ti4合金, 试样尺寸40 mm×40 mm×8 mm, 用砂纸打磨试样熔覆面, 充分去除表面氧化膜。选择80Ni–40Al–20Si复合粉末作为熔覆材料, 采用QM-3SP04型行星球磨机对该粉末进行12 h的球磨处理。
1.2 涂层制备
先在Ti4合金试样涂覆一层甲基纤维素黏结剂, 再铺设一层厚度为1.5 mm的混合粉末, 再将其放入120℃的干燥箱内进行2 h的保温。本实验在DLS-980.10-3000C半导体激光器上完成激光熔覆过程, 工艺参数为: 输出功率2 kW, 扫描速度3.5 mm·s-1, 光斑大小5 mm×2.5 mm。
1.3 涂层性能测试
通过线切割方式得到熔覆层的截面金相试样, 并对该试样进行了X射线衍射(X-ray diffraction, XRD) 表征。利用S-4700型场发射扫描电镜(scanning electron microscopy, SEM) 对涂层微观组织进行了观察, 同时在该电镜附带的能谱仪(energy disperse spectroscope, EDS) 上表征了涂层的各元素组成情况。利用HMF1400-50高温电阻炉测试其抗高温氧化性能, 并计算单位面积对应的质量变化情况。对经过氧化处理的合金与涂层进行金相观察。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 合金涂层显微组织
从图 1 (a) 中可以看到涂层横截面的扫描电子显微形貌。根据图 1 (a) 可知, 在涂层内也没有观察到裂纹结构, 只有少数气孔存在。从图 1 (b) 中可以看到在Ti4和涂层的结合部位形成了熔合线, 可以推断涂层和钛合金之间形成了良好的冶金结合状态。同时还可以观察到在涂层的底部区域形成了众多的柱状晶, 这主要是因为受到凝固冷却的影响, 钛合金垂直的方向上具有最快的冷却速率, 从而导致涂层的下部晶粒优先从垂直钛合金表面的方向上开始生长。图 1 (c) 是对应于图 1 (b) 的放大图, 可以明显看到该图包含了块状区域A与网状区域B两种, 对这些区域进行能谱测试可知, 区域A中的元素类型包括Ti与Si, 两者的原子数分数比接近5:3, 可见该区域的成分主要是Ti5Si3金属间化合物; 对区域B进行元素分析得到该区域包含Ni与Al两种元素, 其原子数分数比接近3:2, 进一步结合X射线衍射图谱可知, 区域B的成分主要是Al3Ni2金属间化合物, 因此可以推断涂层中包含了Ti5Si3与Al3Ni2两种主要成分。
表 1 图 1 (c) 中区域A和区域B能谱分析Table 1. EDS analysis of area A and area B in Fig. 1 (c)区域 原子数分数/% Ti Ni Al Si A 44.28 22.18 5.48 28.06 B 23.54 42.18 30.02 4.26 2.2 高温抗氧化性能及机理
从表 2中可以看到对钛合金与合金涂层进行高温氧化测试得到的试样单位面积质量变化值, 其中钛合金的单位面积质量增加值显著高于合金涂层, 可见合金涂层的耐高温氧化性能优于钛合金。经过40 h的恒温氧化处理后, 试样单位面积质量增加了24.4 mg·cm-2, 可见在860℃温度下, Ti4合金的表面发生了明显的氧化过程, 此时形成的氧化膜也不能有效抑制氧原子的扩散过程。其中, 在初期高温氧化阶段, 合金涂层具有很快的氧化速率, 当氧化时间不断增加后, 合金涂层的氧化速率降低, 因此可以推断合金涂层表面氧化膜具有降低氧化速率的作用; 经过40 h的高温氧化处理后, 粉末合金涂层的质量增加值是2.19 mg·cm-2, 比Ti4合金的耐高温氧化性能提高了12倍左右。
表 2 Ti4合金和合金涂层高温氧化(860℃) 测试结果Table 2. High temperature oxidation test results of Ti4 alloy and alloy coating at 860℃样品 单位面积质量变化/(mg·cm2) 5 h 10 h 20 h 30 h 40 h Ti4 合金 2.40 4.40 9.20 16.70 24.40 合金涂层 1.82 1.90 2.02 2.11 2.19 Ti4合金与粉末合金涂层在860℃温度下进行40 h的氧化处理后, 对其表面氧化层进行X射线衍射测试得到如图 2所示的谱图。从图 2的测试谱图中可以发现, Ti4合金的氧化层基本包含Al2O3与TiO2两种物相成分, 并且TiO2的衍射峰强度显著高于Al2O3, 说明氧化膜主要是由TiO2构成。由于在860℃下V2O5的挥发性较高, 因此在X射线衍射谱图中未观察到该氧化物的衍射峰, 同时氧化膜也因为V2O5的挥发而形成多孔结构, 使氧原子更易向膜内扩散, 导致合金耐高温氧化性降低。
图 3 (a) 为在860℃下进行40 h氧化处理后得到的Ti4合金横截面扫描电子显微形貌, 可以发现此时Ti4合金表面出现了较严重腐蚀的情况, 生成的氧化膜表现出了明显的热脆性特征, 较易从表面发生脱落的现象。对Ti4合金的氧化膜微观形貌进行分析可知, 氧化膜主要由许多球形颗粒与柱状物构成, 根据能谱分析(表 3) 可知, 柱状物成分主要是TiO2。在TiO2的形核与生长期间, 还会形成少量的Al2O3, 使氧化膜中形成众多微孔, 这种不连续的氧化膜结构不能发挥有效阻止氧原子扩散的作用, 不利于提高合金的耐高温氧化性。
图 3 (b) 为在860℃下进行40 h氧化处理后得到的合金涂层氧化膜扫描电子显微形貌。从图中可知, 合金涂层与氧化膜之间保持紧密结合状态, 未看到有脱落情况出现。对该涂层进行能谱分析(表 3) 可知, 其表面氧化膜中的元素主要为O、Al, 同时还有部分Si、Ni、Ti, 因此可以推断该氧化膜的主要成分时Al2O3, 此外还含有部分NiO、SiO2、TiO等。因为Al2O3能够形成致密的连续结构, 起到明显抑制O元素扩散的效果, 使合金涂层耐高温抗氧化性能获得显著提高。
3. 结论
(1) Ti4合金和合金涂层的结合部位形成了熔合线, 可以推断合金涂层和钛合金之间形成了良好的冶金结合状态。同时还可以观察到在涂层的底部区域形成了众多的柱状晶, 涂层中包含了Ti5Si3与Al3Ni2两种主要成分。
(2) 钛合金的单位面积质量增加值显著高于合金涂层, 可见合金涂层的耐高温氧化性能优于钛合金。经过40 h的高温氧化处理后, 粉末涂层的质量增加值是2.19 mg·cm-2, 比Ti4合金的耐高温氧化性能提高了12倍左右。
(3) 在860℃下进行40 h氧化处理得到的合金涂层与氧化膜之间保持紧密结合状态, 未看到有脱落情况出现, 氧化膜的主要成分是Al2O3。
-
表 1 试验用钢材化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1 Chemical composition of testing steels
% 试样材料 C Cr Mo V W HSF620 0.91 4.36 5.27 2.12 5.7 传统M2 0.88 4.1 4.77 1.86 6.11 表 2 试样1/4直径处非金属夹杂物
Table 2 Non-metal inclusion at 1/4 diameter of specimens
钢材 非金属夹杂物级别 HSF620 B0.5D0.5DS1 传统M2 B0.5DS1 -
[1] 姜春梅, 高元植, 胡宜平, 等. 喷射沉积合金的半固态成形的研究现状与发展前景. 北京联合大学学报, 2001, 15(增刊1): 89 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJLH2001S1022.htm Jiang C M, Gao Y Z, Hu Y P, et al. The present status and future development of semisolid forming of spray deposition materials. J Beijing Union Univ, 2001, 15(Supple 1): 89 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJLH2001S1022.htm
[2] 周灿栋, 祝新发, 樊俊飞, 等. 喷射成形取代粉末冶金生产超高合金高速钢的可行性研究. 稀有金属, 2006, 30(专辑): 57 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXJS2006S1014.htm Zhou C D, Zhu X F, Fan J F, et al. Probability of production of super high alloyed high speed steel by spray forming instead of powder metallurgy. Chin J Rare Met, 2006, 30(Spec Issue): 57 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXJS2006S1014.htm
[3] 崔成松, 章靖国. 喷射成形快速凝固技术制备高性能钢铁材料的研究进展(一)—喷射成形技术的原理、特点及发展现状. 上海金属, 2012, 34(2): 42 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2012.02.010 Cui C S, Zhang J G. Research progress of spray forming technology for the manufacture of high performance iron and steel materials (Ⅰ)—Principle, characteristics and development status. Shanghai Met, 2012, 34(2): 42 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2012.02.010
[4] 李荣德, 刘敬福. 喷射成形技术国内外发展与应用概况. 铸造, 2009, 58(8): 797 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZZZ200908008.htm Li R D, Liu J F. Development and application of spray forming technology at home and abroad. Foundry, 2009, 58(8): 797 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZZZ200908008.htm
[5] 陈敬超, 孙加林. 喷射成形技术的研究现状与展望. 昆明理工大学学报, 1997, 22(1): 47 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KMLG701.008.htm Chen J C, Sun J L. Present-day research situation and prospect of spring forming. J Kunming Univ Sci Technol, 1997, 22(1): 47 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KMLG701.008.htm
[6] 滑有录, 王海龙. 喷射成形技术的发展与应用. 热加工工艺, 2010, 39(21): 192 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2010.21.063 Hua Y L, Wang H L. Development and application of spray forming technology. Hot Working Technol, 2010, 39(21): 192 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2010.21.063
[7] 张永安, 熊柏青, 石力开. 喷射成形技术产品的研究现状. 材料导报, 2002, 16(3): 11 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2002.03.004 Zhang Y A, Xiong B Q, Shi L K. Research on spray forming technology and products. Mater Rev, 2002, 16(3): 11 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2002.03.004
[8] 宋学森, 周灿栋, 轩福贞, 等. 喷射成形高速钢中碳化物的类型与形貌. 机械工程材料, 2009, 33(3): 57 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC200903018.htm Song X S, Zhou C D, Xuan F Z, et al. Type and morphology of carbide in spray formed high speed steel. Mater Mech Eng, 2009, 33(3): 57 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC200903018.htm
[9] 张勇, 张国庆, 李周, 等. 喷射成形高速钢沉积坯性能分析. 航空材料学报, 2008, 28(6): 32 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2008.06.007 Zhang Y, Zhang G Q, Li Z, et al. Research on properties of high speed steel prepared by spray forming. J Aeronaut Mater, 2008, 28(6): 32 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2008.06.007
[10] 王军, 徐政, 史海生, 等. 喷射成形超高碳钢的微观组织与工艺研究. 材料科学与工程学报, 2003, 21(5): 660 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2812.2003.05.009 Wang J, Xu Z, Shi H S, et al. Microstructure and process of as-sprayed UHCS. J Mater Sci Eng, 2003, 21(5): 660 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2812.2003.05.009
[11] 魏宽, 徐轶, 刘宪, 等. 喷射成形—热等静压9V高钒钢的组织与性能研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2012, 22(3): 21 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2012.03.004 Wei K, Xu Y, Liu X, et al. Microstructure and properties of high vanadium steel with 9% vanadium fabricated by spray forming-hot isostatic pressing. Powder Metall Ind, 2012, 22(3): 21 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2012.03.004
[12] 卢林, 黄进峰, 侯陇刚, 等. 铌对喷射成形M3: 2型高速钢组织和性能的影响. 北京科技大学学报, 2014, 36(10): 1292 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201410003.htm Lu L, Huang J F, Hou L G, et al. Effect of niobium on the microstructure and properties of spray-formed M3: 2 high speed steel. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2014, 36(10): 1292 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201410003.htm
[13] 于一鹏, 黄进峰, 崔华, 等. 喷射成形M3型高速钢碳化物组织特征与加热过程演化. 北京科技大学学报, 2012, 34(7): 793 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201207011.htm Yu Y P, Huang J F, Cui H, et al. Microstructural characterization of carbides in spray-formed M3 high speed steel and its evolution during heating process. J Univ Sci Technol Beijing, 2012, 34(7): 793 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201207011.htm
[14] 徐轶, 葛昌纯, 魏宽, 等. 喷射成形高钒高速钢环坯制备技术研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2012, 30(1): 22 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2012.01.005 Xu Y, Ge C C, Wei K, et al. Research on preparation technology of high-vanadium HSS by spray forming. Powder Metall Technol, 2012, 30(1): 22 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2012.01.005
[15] 刘冬冬, 张国赏, 魏世忠, 等. 高钒高速钢磨损性能的研究现状. 铸造技术, 2013, 34(2): 135 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZJS201302004.htm Liu D D, Zhang G S, Wei S Z, et al. Investigation of wear performance of high vanadium high speed steel. Foundry Technol, 2013, 34(2): 135 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZJS201302004.htm
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)




 下载:
下载: