Optimum structure design of free-fall nozzle in preparation process of superalloy powders by electrode induction gas atomization technology
-
摘要: 采用电极感应熔化气雾化制粉法(electrode induction gas atomization,EIGA)制备粉末过程中,非限制式喷嘴的结构设计直接决定气雾化粉末的质量;非限制式喷嘴结构中不合理的喷射角度常常会引起反喷、片状粉、细粉收率低等问题,严重影响粉末的生产效率和质量。采用商业计算流体动力学(computational fluid dynamics,CFD)软件Fluent,以自主设计的第三代EIGA制备高温合金粉末装置中非限制式喷嘴为研究对象进行数值模拟建模,对带有气体回流区的非限制式喷嘴在熔体初次雾化过程中,喷射角度对反喷现象的影响以及反喷产生的机理进行了研究。结果表明,非限制式喷嘴射流角度过大时,熔体液滴会出现明显反喷现象;当非限制式喷嘴射流角度过小时,熔体液流雾化前过热度不足,生产的粉末球形度较差。因此,在优化设计非限制式喷嘴时,要应尽量控制气体回流区位置低于非限制式喷嘴熔体入口位置,保证合金熔体的过热度,同时防止反喷等现象。
-
关键词:
- 电极感应熔化气雾化技术 /
- 高温合金粉末 /
- 非限制式喷嘴结构 /
- 喷射角度 /
- 计算流体动力学
Abstract: The structure design of free-fall nozzle directly determines the quality of gas-atomized powders in electrode induction melting gas atomization (EIGA) process, the unreasonable jet angle in free-fall nozzle structure often causes the regurgitation phenomenon, the flake powders, and the low yield of fine powders, which seriously affect the production efficiency and quality of powders. The numerical modeling of free-fall nozzle structure in the self-designed third generation of EIGA superalloy powder preparation device was established using Fluent commercial software for computational fluid dynamics (CFD). The effect of jet angle on the regurgitation phenomenon and the regurgitation mechanism of free-fall nozzle with gas flow recirculation were investigated in the initial atomization of melt. In the results, when the jet angle of free-fall nozzle is too large, there is an obvious regurgitation phenomenon; when the jet angle is too small, the superheat of the melt stream before atomization is insufficient, resulting in the poor sphericity of produced powders. Therefore, to ensure the superheat of melt flow and prevent the regurgitation phenomenon, it is necessary to control the recirculation zone position of gas flow to be lower than the melt inlet position of free-fall nozzle. -
粉末高温合金是航空发动机关键核心热端部件的必选材料[1-2],其研发水平代表一个国家的综合实力。粉末高温合金中最常见的缺陷有热诱导孔洞[3]、非金属夹杂物[4]和原始颗粒边界沉积物[5],在这些缺陷中,热诱导孔洞和原始颗粒边界可以通过改进制备工艺得到改善,但非金属夹杂物至今仍是粉末高温合金工作者需要解决的问题[4]。超洁净少/无夹杂物高温合金粉末是制备高性能高温合金部件的基础原材料,目前主流的高温合金粉末制备工艺包括氩气雾化法(argon atomization,AA)[6]与等离子体旋转电极法(plasma rotating electrode process,PREP)[7-8]。以美国为代表的西方国家多采用氩气雾化法制粉[9],国内北京航空材料研究院对氩气雾化制备高温合金粉末进行了大量系统的研究工作[10],该法制得的高温合金粉末较细,但制粉设备(如熔炼坩埚、导流管等)中的耐火材料在制粉过程中会带入一定数量的非金属夹杂物。俄罗斯主要采用等离子体旋转电极法制备高温合金粉末[11],国内钢铁研究总院等科研单位对这种制粉方法也进行了大量的研究。
电极感应融化气雾化法(electrode induction gas atomization,EIGA)是近十来年发展起来的超洁净气雾化制粉技术之一,其原理是通过超高频感应线圈加热合金棒材,在整个熔化过程中,高温合金不接触耐火材料,形成直径大小连续可控的合金液流,在高速气体和非限制式喷嘴(无陶瓷导流管)的作用下,将合金液流破碎雾化,从而制得超洁净的合金粉末。德国ALD公司开发了EIGA制粉装备,主要用于制备TiAl合金、Ti合金、Zr合金、Nb合金粉末等[12]。EIGA制粉在国内逐步兴起,北京科技大学葛昌纯研究团队自2008年便开始了对EIGA制备高温合金粉末的研究。EIGA制粉工艺的核心技术主要包括合金的可控连续感应熔化和连续金属液流的气雾化(非限制式喷嘴的设计优化)。气雾化喷嘴主要有限制式喷嘴与非限制式喷嘴两类[13-15],限制式喷嘴是由坩埚与含有导流管的喷嘴系统组成,非限制式喷嘴是不含耐火材料坩埚与陶瓷导流管的开放式喷嘴。由于限制式喷嘴具有生产效率高、制备的粉末颗粒细小等优点,对气雾化制粉技术的研究大都集中在限制式喷嘴上,企业生产目前也主要使用限制式喷嘴[16-18]。EIGA工艺采用的是非限制式喷嘴,在使用过程中,极易出现反喷堵塞喷嘴以及片状粉等问题,严重影响粉末的生产效率、产量以及质量。在非限制式喷嘴设计中(包括气体喷射角度[19]、气体出口之间的距离、喷盘的整体厚度、以及增加初始气流和限流环等[20]),可以通过保留回流区(合理的回流区位置和强度)或完全消除回流区[20]来改善反喷及片状粉的问题。回流区对于雾化效果有弊也有利,例如在消除反喷的情况下,回流区的存在可以使高温金属液流“撑伞破碎”[21],金属液流在回流区的作用下首先破碎为金属薄层液流或大液体颗粒,这些预先破碎的金属薄层或大颗粒在高速气体作用下进一步破碎,有利于得到细粉收得率更高的粉体。在非限制式喷嘴的结构设计中,气体喷射角度是极其重要的参数,它直接影响回流区的强度以及位置。气体射流的喷射角度太大容易造成气体回流区位置过于靠近合金熔体入口,此时在回流区作用下形成的金属溶体伞状结构边缘液滴剥离雾化后,容易撞击非限制式喷嘴的空腔壁面,从而容易产生片状粉或者反喷堵塞喷嘴的现象。气体喷射角度太小,气体回流区的位置过于远离合金熔体入口的位置,合金熔体发生雾化前,合金熔体的流动行程太远,合金熔体在流动过程中冷却凝固,雾化时合金熔体过热度不足,造成雾化的合金熔体黏度高,雾化后液滴粗大并且液滴没有足够的时间收缩成球形粉末,最终产生粗大的片状粉末或者球形度低的粉末。
气雾化过程非常复杂,在密闭空间中的高速气体在极短时间内对高温流体进行冲击破碎,采取常规实验手段难以表征气体射流喷射角度对雾化合金熔体造成的影响,也很难再现不同喷射角度的气体射流破碎合金熔体的过程。数值模拟可以实现对气液两相流的合金熔体破碎过程的可视化重现。本文以自主设计的第三代EIGA制备高温合金粉末装置中非限制式喷嘴为研究对象,运用商业计算流体力学(computational fluid dynamics,CFD)软件Fluent,采用流体体积法(volume of fluid,VOF)与欧拉-拉格朗日法,对高温合金粉末的初次雾化过程进行仿真模拟[22-23],研究气体喷射角度对高温合金熔体初次雾化(反喷、片状粉等)的影响,讨论喷射角度、回流区、反喷之间的关系,并分析回流区对反喷的作用机理。
1. 非限制式喷嘴结构模拟方法及过程
1.1 不同喷射角度喷嘴物理模型描述
为适应计算机硬件条件,提高计算效率,将具有旋转对称性的非限制式喷嘴几何模型简化为二维轴对称模型。运用CAXA软件建立简化后的非限制式喷嘴几何模型,导入网格划分软件Gambit中,对非限制式喷嘴的二维几何模型进行网格划分。网格划分采用四边形非结构网格,通过尺寸函数(size function,SF)控制面网格梯度,以实现需要关注的部位网格画密(尺寸为0.1),其他部位网格相对画粗(尺寸为1.0),最终网格数目为54990,大大减小了网格数目,加快了计算速度。使用商业CFD软件Fluent将符合实际气体雾化物理过程的物理模型加载到划分好网格的几何模型上,利用瞬态求解计算模拟非限制式喷嘴不同喷射角度下的几何模型合金熔体初次雾化过程。
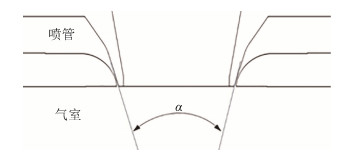
实验用非限制式喷嘴结构如1图所示(α为喷射角度),喷嘴主要由气室与喷管组成。根据实际生产经验,为避免喷射角度过大或者太小对气雾化粉末产生影响,将喷射范围划分为五个区间:[0 30°)、[30° 35°)、[35° 40°)、[40° 45°)、[45° 90°],分别选取区间的四个中间端点(典型喷射角度:30°、35°、40°、45°)对非限制式喷嘴几何模型进行建模。采用VOF多相流模型对不同喷射角度下的合金熔体主雾化过程进行模拟。
几何模型建立与边界条件选择的正确性直接决定了计算模拟结果的正确性与可信度。本文不同喷射角度下的非限制式喷嘴几何模型与边界条件如图 2所示,模型中喷射角度α分别选取30°、35°、40°和45°。该模型主要由气体喷嘴和雾化室两部分组成,由金属壁面包围的气体喷嘴连接着进气口和雾化室,将气体喷嘴的金属壁面视为壁面(wall)。实际真正的雾化室是一个巨大的炉体,高温合金熔体雾化需要考虑的只是非限制式喷嘴下方一个合金熔体雾化很小的区域。几何模型上边界与左边界是与雾化室联通的空间位置,视为压力出口边界(pressure outlet),实际雾化时炉体内压力101325 Pa。为简化模型,减少计算量,将模型简化为二维轴对称模型。Fluent软件要求以X轴作为轴对称模型的旋转轴,故选择几何模型X轴位置边界为旋转轴边界(axis)。非限制式喷嘴合金熔体入口位置边缘是雾化室内空间位置,同样视为压力出口边界(pressure outlet),其边界压力与雾化炉体内压力相等(101325 Pa)。合金母材在超高频感应线圈中熔化,并以一定速度落入非限制式环缝喷嘴系统,高温合金熔体入口视为速度入口边界(velocity intlet)。
实验中雾化气体为氩气,进口压力为4 MPa,因此将氩气进口视为压力进口边界(pressure intlet),其余为固体壁面边界条件。实验材料采用某牌号镍基高温合金,其对应的熔体参数如下表 1所示。模拟过程中雾化气体氩气物理参数与喷嘴雾化工艺参数如表 2和表 3所示。
表 1 某牌号镍基高温合金熔体参数表[10]Table 1. Physical properties of a certain Ni-based superalloy热容/[J·(kg·K)-1] 热导率/[W·(m·K)-1] 黏度/(mPa·s) 表面张力/(mN·m-1) 密度/(kg·m-3) 720 29.6 0.05 1.84 7705 表 2 氩气物理参数Table 2. Physical properties of Ar gas密度/(kg·m-3) 黏度/(mPa·s) 热导率/[W·(m·K)-1] 热容/[J·(kg·K)-1] ideal-gas sutherland 0.0158 520.64 表 3 雾化模拟和实验工艺参数Table 3. Simulated and experimental parameters in EIGA process合金类型 合金液流直径/mm 进气口压力/MPa 喷嘴类型 镍基高温合金 4 4 非限制式环缝喷嘴 1.2 不同喷射角度的喷嘴初次雾化过程模拟
采用分离式求解器,利用速度-压力耦合算法(pressure-velocity coupling coupled)求解数值模拟。密度、能量等参数采用二阶迎风格式(second order upwind)以保证雾化过程计算精度,在减少网格数目的基础上进一步减小计算量,同时加快计算过程的收敛。首先选取RANS(reynolds averaged navier-stokes simulation)标准k-ε湍流模型(standard k-epsilon model),对超音速气体雾化高温合金熔体过程进行初始计算。当高温合金熔体计算到开始雾化破碎位置同时计算得到收敛时,初始计算结束;随后将湍流模型转换为大涡模拟模型(large eddy simulation)。VOF多相流模型对雾化过程液滴的捕捉是基于网格粗细进行的,不同喷射角度的非限制式喷嘴几何模型雾化位置网格(0.1)远远达不到捕捉初次雾化所有液滴的精度要求,因此在初始计算结束时,在原先几何模型网格划分的基础上,运用Fluent软件自带的梯度自适应功能(gradient adaption),以初次破碎高温合金熔体体积分数为考量参数,将非限制式喷嘴网格进行加密,加密后的网格数目达到890388,最细网格数目为0.006,即最小可捕捉8 m液滴,达到需要捕捉初次雾化液滴的网格要求。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同喷射角度非限制式喷嘴的速度场
由于合金熔体与高速气体两相流动的复杂性,大多数数值模拟仅限于单相气体流动模拟,但是对不同喷射角度的非限制式喷嘴几何模型仅仅只进行单相气体研究,很难直观准确的反应高速气流喷射角度对合金熔体雾化造成的影响。本文采用多相流VOF模型,对不同高速气体喷射角度下的合金熔体雾化过程进行模拟,分析喷射角度对合金熔体雾化造成的影响。
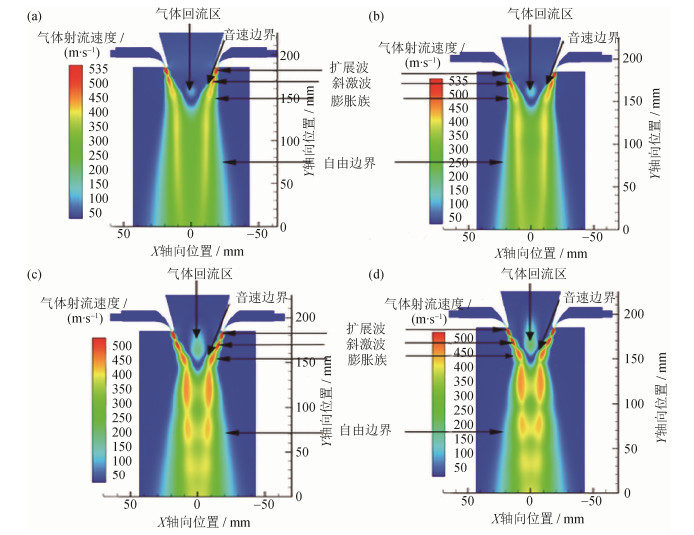
非限制式喷嘴不同喷射角度对初次雾化过程的影响来源于不同角度高速气体射流形成的气流场结构对合金熔体初次雾化的影响。数值模拟开始于气流流量的计算,不同喷射角度下的非限制式喷嘴超音速气体射流速度结构云图如图 3所示。非限制式喷嘴气体在出口处形成一系列Prandtl-Meyer膨胀波和再压缩冲击膨胀,以匹配雾化室内的大气压力,这与多文献中论述的压缩流和高速射流理论一致[14-15, 22, 24],其对应的流场结构与位置如图 3所示。
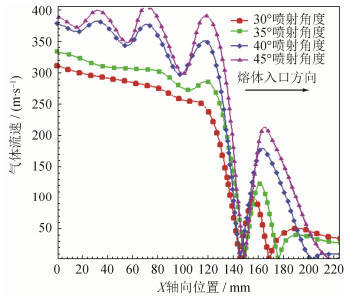
如图所示,不同喷射角度对应的喷嘴出口气流斜激波衰减程度存在明显差异。喷射角度为30°与35°时,喷嘴出口超音速气体的气体斜激波在第三个激波位置就几乎衰减消失,气体速度强度也从出口的535 m·s-1衰减至激波心部的低于450 m·s-1,速度衰减大于85 m·s-1。与之相对应的是,当喷射角度增加到40°与45°时,喷嘴出口的超音速气体在第三个斜激波位置,激波依然很明显,并且速度强度从超音速气体出口的536 m·s-1衰减至心部的500 m·s-1,速度衰减仅为36 m·s-1。此外,喷射角度为40°与45°时,超音速气体在喷嘴出口第三个斜激波位置以后的气体速度强度也保持相对较大的状态,速度衰减较慢。从速度场模拟结果可以看出,随着喷射角度的增加,喷嘴出口超音速气流的速度衰减减慢。另外,从图 3中还可以看出,随着喷射角度的变化,回流区的位置、形状、速度大小等都有明显的变化,关于回流区差异的分析,将在下一节进行详细的介绍。
2.2 不同喷射角度非限制式喷嘴的回流区
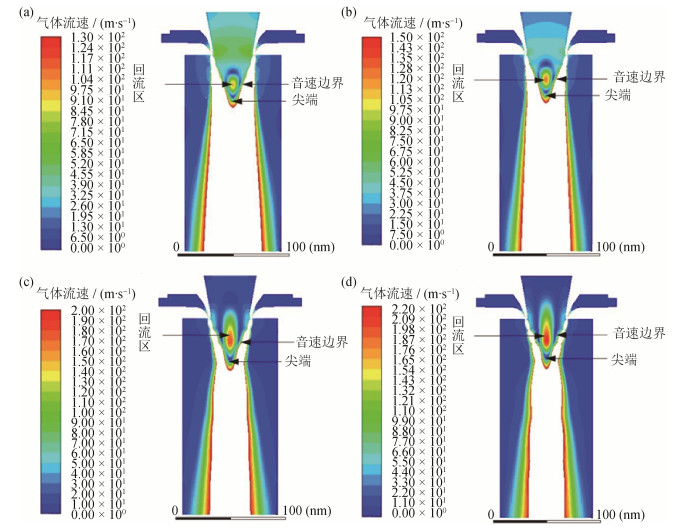
高速气体流入雾化室炉体内,属于湍流流动,由于气体黏性剪切力的作用,在高速气体自由边界附近会形成一系列湍动涡流,这些涡流的存在使得气体具有旋转动量,从而改变部分气体的流动的方向。非限制式喷嘴气体射流交叉后,在高速气体汇聚位置的湍动涡流作用加强,较多的气体改变了传播方向,聚集形成回流区[10, 25]。图 4为不同喷射角度下的非限制式喷嘴气体回流区速度云图,显然在气体交汇点位置上方的回流区是一个局部高速涡流团,其特点是回流区中心到边缘速度是衰减的,回流区中心速度最大。图 5所示为不同喷射角度下的非限制式喷嘴回流区气体流动轨迹,回流区气体在轴中间附近流动向上,达一定高度位置后向径向方向延伸;在气体扰动作用下,径向方向延伸的回流区气体改变流动方向,同非限制式喷嘴出口气体音速边界一起向下流动,重新回到气体交汇位置的回流区起点,完成一个回流过程。
如图 6不同喷射角度下非限制式喷嘴轴线速度分布图所示,在气体回流区末端存在一个速度下降至0的滞点。喷射角度不同,气体回流区的速度强度、位置以及影响范围存在明显差异,随着喷射角度的增大,喷嘴出口的高速气体交点位置略微向合金熔体入口方向移动,回流区顶部向合金熔体入口位置延伸。
表 4对非限制式喷嘴不同气体喷射角度下喷射气体的交点位置以及回流区位置、范围进行了详细统计,对比图 4、图 5以及表 4可知,喷射角度为30°时,喷嘴的喷射气体交点位置轴向坐标为X=142 mm,两股交汇气体的音速边界形成类似三角形的尖端;回流区位置明显远离非限制式喷嘴的高温合金熔体入口位置,回流区顶部轴向坐标为X=169 mm,距离高温合金熔体入口位置56 mm;回流区速度强度相对较弱,最大速度强度为99 m·s-1;回流区覆盖范围小,宽度只有18 mm,回流区底部轴向坐标为X=146 mm。喷射角度为35°时,喷嘴的喷射气体交点位置轴向坐标为X=146 mm,交点位置略微向上移动4 mm,两股气流的音速边界形成的三角形尖端同样略微向上移动4 mm,其尖端位置附近有径向Y方向变窄的趋势;相比30°喷射角度,35°喷射喷嘴气体回流区X轴向坐标范围向合金熔体入口位置延伸6.5 mm,顶端轴向位置X=175.5 mm,底端轴向位置X=168 mm,回流区顶端正好在非限制式喷嘴与雾化塔交界位置正下端10 mm位置处;回流区最大速度强度相比30°喷射角度,从99 m·s-1增加到140 m·s-1;回流区宽度范围从原来的18 mm增加至22 mm。喷射角度为40°时,喷嘴的喷射气体交汇位置轴向坐标为X=143 mm,交点位置略微向下移动3 mm,两股高速气流音速边界形成的三角形尖端明显变窄;气体回流区轴向X轴向坐标范围在35°喷射角度回流区基础上,向合金熔体入口位置移动27.5 mm,顶端X坐标为203 mm,已经深入非限制式喷嘴空腔17 mm,回流区底端轴向位置坐标在X=146 mm;回流区最大速度强度相比35°喷射角度的140 m·s-1增加到180 m·s-1;回流区宽度从原来22 mm,增加到30 mm。喷射角度增加至45°时,喷嘴的喷射气体交点位置轴向坐标为X=146 mm,交点位置相比40°喷射角度时,略微向上移动3 mm;两股气流的音速边界形成的三角形尖端进一步变窄;气体回流区范围在40°喷射角度范围的基础上,向合金熔体入口位置移动15 mm,顶端X坐标为218 mm,深入非限制式喷嘴空腔32 mm,明显已接近高温合金熔体入口位置顶端,回流区最底端轴向X位置为X=146 mm;回流区最大速度强度从40°喷射角度的180 m·s-1增加到215 m·s-1;回流区宽度从原来30 mm增加到33 mm。
表 4 非限制式喷嘴不同气体喷射角度下回流区参数Table 4. Parameters in the recirculation area of gas flow for the free-fall nozzle in different spray angles喷射角度/(°) 气体交点位置X轴向坐标/mm 轴向X轴范围/mm 径向Y轴范围/mm 回流区宽/mm 回流区最大速度/(m·s-1) 30 142 146~169 -9~9 18 99 35 146 148.0~175.5 -11~11 22 140 40 143 146~203 -15~15 30 180 45 146 148~180 -16.5~16.5 33 215 从回流区模拟结果可以看出,随着非限制式喷嘴喷射角度的增加,回流区滞点位置、回流区范围以及峰值延轴线方向向合金熔体入口位置延伸,速度峰值增大,且速度峰值位置向合金熔体入口位置移动。因此,非限制式喷嘴的喷射角度直接影响回流区在轴线方向的位置、范围与大小。
2.3 不同喷射角度的非限制式喷嘴初次破碎模拟
为了更直观的反应回流区对反喷现象的影响,通过Fluent软件的VOF多相流模型,计算模拟非限制式喷嘴初次破碎时气液相互作用的过程,研究不同射流角度生成的气体回流区对高温合金熔体破碎过程的影响,分析回流区破碎及反喷作用的机理。
当圆柱状合金熔体从喷嘴上部垂直自由下落进入非限制式喷嘴雾化系统后,逐渐开始与气体回流区接触并与之作用。回流区气体在喷嘴中间位置向上流动,正好与合金熔体的向下重力作用相反,造成合金熔体流动受阻。由非限制式喷嘴流场结构分析可知,越靠近回流区中心部位,气体作用在喷嘴顶部的作用力越大。合金熔体在自身重力作用下流动,接触气体回流区后,受回流区中心气体向喷嘴顶部方向作用力的影响,做减速运动。熔体在逐渐接近回流区气体中心部位过程中,受到气体的阻力逐渐增大;在回流区某一位置,当合金熔体向下流动速度降低为0时,合金熔体开始沿不受气体阻力的径向方向流动,合金熔体被挤压成薄圆片;随着合金熔体向径向方向延伸,离高速气体的音速边界也越发靠近,气体脉动作用与湍流强度开始加强,薄圆片状合金熔体边缘最终在强烈湍流与脉动作用下发生破裂,出现合金熔体初次破碎。
非限制式喷嘴的气体回流区范围随喷射角度的改变而发生变化,喷射角度增大,气体回流区向合金熔体入口方向延伸,回流区的范围增大,气体速度强度增强。由此可知,非限制式喷嘴的气体喷射角度直接影响回流区的位置和回流区内气体速度的大小;同时,非限制式喷嘴的回流区又直接影响合金熔体的初次破碎;因此,对非限制式喷嘴喷射角度研究意义重大。
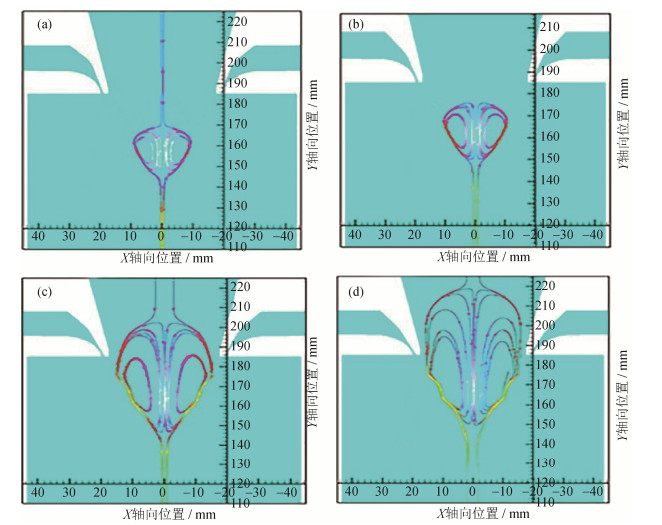
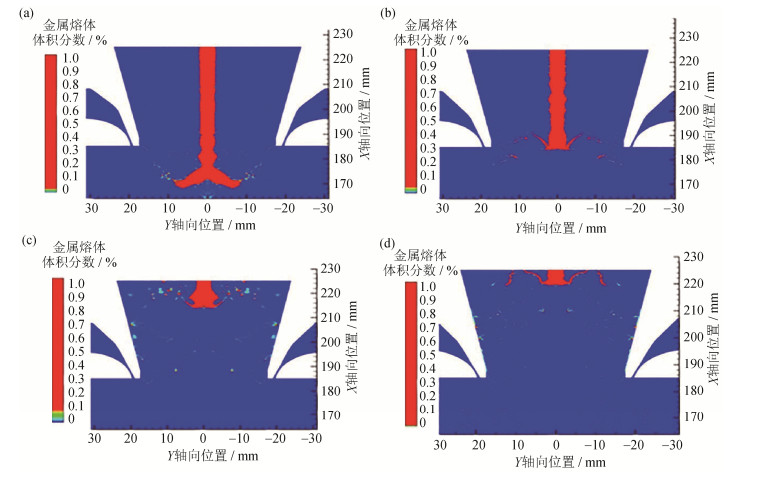
图 7为不同喷射角度下高温合金熔体初次破碎体积分数的分布情况。如图 7(a)所示,在30°喷射时,合金熔体破碎位置在雾化塔内部进行,距离熔体入口位置55 mm,并且雾化的液片很粗。图 7(b)在35°喷射时,合金熔体初次破碎发生在雾化塔与非限制式喷嘴交界处,破碎位置上移,距离熔体入口40 mm,同时雾化的液片比较细。如图 7(c)和7(d)所示,在40°和45°喷射时,合金熔体破碎位置已经非常靠近熔体入口,并且明显出现破碎液滴反喷现象,未反喷的液滴也在气流的影响下附着或者撞击在喷嘴的金属壁面上。
2.4 喷射角度和回流区对反喷、片状粉、细粉收得率的影响
通过对图 4、图 5与图 7的对比分析可知,当非限制式喷嘴喷射角度增大至40°和45°时,气体回流区顶部过于靠近合金熔体入口位置,雾化位置不合理,熔体液滴出现明显反喷现象。如图 7(c)和图 7(d)所示,在喷射角度为40°和45°的初次雾化中没有出现反喷的高温液滴,这是因为在下落过程中,气体回流区的高温液滴直接撞击非限制式喷嘴空腔体壁面。当喷射角度减小至30°和35°时,回流区范围明显缩小,回流区位置远离喷嘴熔体入口,甚至在喷射角度30°时,气体回流区完全深入雾化塔内部。如图 7(a)和7(b)所示,回流区范围向雾化塔方向缩小,合金熔体的主雾化位置同时也向下移动,随着喷射角度减小,合金熔体的初次雾化位置逐渐向雾化室位置移动,同时合金熔体初次雾化后的高温液滴撞击喷嘴内腔壁面的现象也开始减弱甚至消失。如图 7(a)所示,喷射角度30°的非限制式喷嘴初次雾化位置已经完全深入雾化室内部,基本避免了由于回流区位置太靠近合金熔体入口而造成的问题。与图 7(b)~图 7(d)对化,图 7(a)合金熔体在发生初次雾化之前熔体的流动距离明显增加,流动时间过长导致大量热量散失,引起合金熔体初次雾化过热度不足甚至已接近凝固状态,熔体黏度增加,产生大量球形度差、粒度粗的粉末。在图 7(b)中,喷射角度35°的非限制式喷嘴的初次雾化位置正好在喷嘴与雾化室的交界处,避免了由于回流区位置太靠近熔体入口造成的雾化合金液滴的反喷现象,同时初次雾化的液滴碰撞喷嘴壁面的现象也显著减弱,但是还是存在少许液滴碰撞喷嘴与雾化室交界壁面的情况。
通过对不同喷射角度下非限制式喷嘴流场结构、回流区结构以及高温合金熔体初次破碎模拟结果的分析可知,非限制式喷嘴的射流角度影响回流区范围,进而影响高温合金熔体雾化。随着气体喷射角度的增加,喷射气体交点位置出现略微浮动,可认为几乎不发生变化,但气体交汇形成的音速边界尖端在径向方向一直变窄,挤压在其上方的气体回流区,导致回流区的范围向高温合金熔体入口位置延伸扩大。一旦回流区位置开始深入非限制式喷嘴的空腔体内(喷射角度40°),就会导致破碎的初次雾化熔体液滴直接撞击喷嘴壁面,造成高温液滴的污染。高温液滴与常温喷嘴壁面接触,破碎的高温液滴失去过热度,由于初次雾化大液滴的过热度不足,二次雾化作用被减弱,过热度不足还会导致液滴没有足够的时间收缩成球形,产生片状粉末。有时,破碎液滴甚至会直接凝固粘附在喷嘴壁面上,堵塞喷嘴入口。如果非限制式喷嘴的喷射角度继续增大(喷射角度45°),回流区的位置将继续向高温合金熔体入口位置移动,同时回流区的速度强度将进一步增加,造成高温熔体雾化液滴的反喷现象。减小喷射角度(喷射角度30°),气体回流区范围将向雾化塔内缩小,随着回流区与熔体入口位置距离的增加,熔体碰撞喷嘴壁面、破碎反喷等现象将得到解决,但是高温熔体流入非限制式喷嘴到主雾化位置的距离增加,熔体流动过程中将失去大量热量,气体速度降低明显,容易出现熔体过热度不足,产生片状粉、粗粉以及球形度差粉末。
3. 结论
以自主设计的第三代EIGA高温合金粉末制备装置中的非限制式喷嘴为研究对象,采用商业CFD软件Fluent,对带有气体回流区的非限制式喷嘴的熔体初次雾化过程进行数值模拟,研究了不同喷射角度下非限制式喷嘴流场结构、回流区结构以及高温合金熔体初次破碎。结果表明,非限制式喷嘴的射流角度通过影响回流区范围进而影响高温合金熔体雾化。
(1)非限制式喷嘴射流角度过大,会导致回流区顶部太靠近合金熔体入口位置,高温合金熔体雾化位置控制不合理,熔体液滴出现明显反喷现象。
(2)非限制式喷嘴射流角度过小,会导致高温熔体流入喷嘴到主雾化位置的距离增加,熔体流动过程中将失去大量热量,气体速度降低,熔体过热度不足,产生片状粉、粗粉以及球形度差粉末。
(3)非限制式喷嘴气体回流区位置的移动是由气体交汇位置形成的音速边界尖端发生变化造成的。气体喷射角度增大,气体交汇位置形成的音速边界尖端在径向方向变窄,气体回流区受到挤压,向高温合金熔体入口位置延伸扩大,导致雾化过程中反喷现象的出现。
(4)雾化过程中,通过控制非限制式喷嘴的射流角度,调整气体回流区的位置及大小,可保证合金熔体具有足够过热度的同时,避免熔体液滴出现撞击、粘附喷嘴壁面现象和反喷问题。因此在优化设计非限制式喷嘴时,应尽量控制气体回流区位置低于非限制式喷嘴熔体入口位置。
-
表 1 某牌号镍基高温合金熔体参数表[10]
Table 1 Physical properties of a certain Ni-based superalloy
热容/[J·(kg·K)-1] 热导率/[W·(m·K)-1] 黏度/(mPa·s) 表面张力/(mN·m-1) 密度/(kg·m-3) 720 29.6 0.05 1.84 7705 表 2 氩气物理参数
Table 2 Physical properties of Ar gas
密度/(kg·m-3) 黏度/(mPa·s) 热导率/[W·(m·K)-1] 热容/[J·(kg·K)-1] ideal-gas sutherland 0.0158 520.64 表 3 雾化模拟和实验工艺参数
Table 3 Simulated and experimental parameters in EIGA process
合金类型 合金液流直径/mm 进气口压力/MPa 喷嘴类型 镍基高温合金 4 4 非限制式环缝喷嘴 表 4 非限制式喷嘴不同气体喷射角度下回流区参数
Table 4 Parameters in the recirculation area of gas flow for the free-fall nozzle in different spray angles
喷射角度/(°) 气体交点位置X轴向坐标/mm 轴向X轴范围/mm 径向Y轴范围/mm 回流区宽/mm 回流区最大速度/(m·s-1) 30 142 146~169 -9~9 18 99 35 146 148.0~175.5 -11~11 22 140 40 143 146~203 -15~15 30 180 45 146 148~180 -16.5~16.5 33 215 -
[1] 国为民, 赵明汉, 董建新, 等. FGH95镍基粉末高温合金的研究和展望. 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(18): 38 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201318006.htm Guo W M, Zhao M H, Dong J X, et al. Research and development in FGH95 P/M nickel based superalloy. J Mech Eng, 2013, 49(18): 38 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JXXB201318006.htm
[2] 邹金文, 汪武祥. 粉末高温合金研究进展与应用. 航空材料学报, 2006, 26(3): 244 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.03.051 Zou J W, Wang W X. Development and application of P/M superalloy. J Aeronaut Mater, 2006, 26(3): 244 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.03.051
[3] 张国星, 韩寿波, 孙志坤. 热诱导孔洞对粉末冶金高温合金性能的影响. 粉末冶金工业, 2015, 25(1): 42 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYG201501015.htm Zhang G X, Han S B, Sun Z K. Effects of thermal induced porosity on mechanical properties of PM superalloy. Powder Metall Ind, 2015, 25(1): 42 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYG201501015.htm
[4] 张丽娜, 张麦仓, 李晓, 等. 粉末高温合金中非金属夹杂物问题的研究进展. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2001, 24(3): 64 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2001.03.018 Zhang L N, Zhang M C, Li X, et al. Progress in study of nonmetallic inclusion in powder metallurgy (P/M) superalloys. Ordn Mater Sci Eng, 2001, 24(3): 64 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-244X.2001.03.018
[5] 张义文, 杨士仲, 李力, 等. 我国粉末高温合金的研究现状. 材料导报, 2002, 16(5): 1 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2002.05.001 Zhang Y W, Yang S Z, Li L, et al. Current status of research on PM superalloy in China. Mater Rev, 2002, 16(5): 1 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2002.05.001
[6] 何国爱, 丁晗晖, 刘琛仄, 等. 粉末特性对镍基粉末冶金高温合金组织及热变形行为的影响. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(1): 37 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201601006.htm He G A, Ding H H, Liu C Z, et al. Effects of powder characteristics on microstructure and deformation activation energy of nickel based superalloy. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2016, 26(1): 37 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201601006.htm
[7] Ahsan M N, Pinkerton A J, Moat R J, et al. A comparative study of laser direct metal deposition characteristics using gas and plasma-atomized Ti–6Al–4V powders. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528(25-26): 7648 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.06.074
[8] 陆亮亮, 刘雪峰, 张少明, 等. 高频感应熔化金属丝气雾化制备球形钛粉. 材料导报, 2018, 32(8): 1267 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB201808012.htm Lu L L, Liu X F, Zhang S M, et al. A combinatorial technique incorporating high frequency inductive heating and gas atomization for preparing spherical titanium powders from titanium wires. Mater Rep, 2018, 32(8): 1267 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB201808012.htm
[9] 袁华, 李周, 许文勇, 等. 氩气雾化制备高温合金粉末的研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2010, 20(4): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2010.04.001 Yuan H, Li Z, Xu W Y, et al. The study of argon atomized superalloy powders. Powder Metall Ind, 2010, 20(4): 1 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2010.04.001
[10] 刘杨, 李周, 张国庆, 等. 双层雾化器流场的模拟研究. 航空材料学报, 2015, 35(5): 63 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKCB201505012.htm Liu Y, Li Z, Zhang G Q, et al. Flow field of double layer atomizer. J Aeronaut Mater, 2015, 35(5): 63 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKCB201505012.htm
[11] 韩志宇, 曾光, 梁书锦, 等. 镍基高温合金粉末制备技术的发展现状. 中国材料进展, 2014, 32(12): 748 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJKB201412006.htm Han Z Y, Ceng G, Liang S J, et al. Development in powder production technology of Ni-based superalloy. Mater China, 2014, 32(12): 748 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJKB201412006.htm
[12] Jia C L, Ge C C, Yan Q Z. Innovative technologies for powder metallurgy-based disk superalloys: Progress and proposal. Chin Phys B, 2016, 25(2): 320 DOI: 10.1088/1674-1056/25/2/026103
[13] Ting J, Peretti M W, Eisen W B. The effect of wake-closure phenomenon on gas atomization performance. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 326(1): 110 DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01437-X
[14] Motaman S, Mullis A M, Cochrane R F, et al. Numerical and experimental investigations of the effect of melt delivery nozzle design on the open- to closed-wake transition in closed-coupled gas atomization. Metall Mater Trans B, 2015, 46(4): 1990 DOI: 10.1007/s11663-015-0346-6
[15] Ting J, Anderson I E. A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) investigation of the wake closure phenomenon. Mater Sci Eng A, 2004, 379(1): 264 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921509304002254
[16] Zeoli N, Gu S. Numerical modelling of droplet break-up for gas atomisation. Comput Mater Sci, 2006, 38(2): 282 DOI: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2006.02.012
[17] Zeoli N, Gu S. Computational simulation of metal droplet break-up, cooling and solidification during gas atomisation. Comput Mater Sci, 2008, 43(2): 268 DOI: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2007.10.005
[18] Motaman S, Mullis A M, Cochrane R F, et al. Numerical and experimental modelling of back stream flow during close-coupled gas atomization. Comput Fluids, 2013, 88: 1 DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2013.08.006
[19] Zhao W J, Cao F Y, Ning Z L, et al. A computational fluid dynamics (CFD) investigation of the flow field and the primary atomization of the close coupled atomizer. Comput Chem Eng, 2012, 40: 58 DOI: 10.1016/j.compchemeng.2012.02.014
[20] Fritsching U, Uhlenwinkel V. Hybrid gas atomization for powder production. [in] Powder Metallurgy. Eds by Kondoh K. Rijeka: In Tech, 2012
[21] 陈欣. 紧耦合气雾化流场结构和雾化机理研究[学位论文]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2007 Chen X. Study on Structure and Atomization Mechanism of Closely Coupling Gas Atomization[Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2007
[22] Fritsching U. Spray Simulation: Modeling and Numerical Simulation of Sprayforming Metals. New York: American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2006
[23] Ashgriz N. Handbook of Atomization and Sprays. Boston: Springer, 2011
[24] Firmansyah D A, Kaiser R, Zahaf R, et al. Numerical simulations of supersonic gas atomization of liquid metal droplets. Jpn J Appl Phys, 2014, 53: 5S3 http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2014JaJAP..53eHA09A
[25] Aydin O, Unal R. Experimental and numerical modeling of the gas atomization nozzle for gas flow behavior. Comput Fluids, 2011, 42(1): 37 DOI: 10.1016/j.compfluid.2010.10.013
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 尹超,李雪嵩,高健宝,刘鹏. 片状银粉制备方法的研究进展. 黄金. 2024(03): 1-4 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邱择栋,季鑫,魏玉杭,杨向民,张震,方斌. 大尺寸银纳米片的可控、高效制备及在导电胶中的应用. 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(02): 57-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨文涛,薛冰,代永富,蒲传金,肖定军. 球磨时间对钨粉粒度分布及形貌影响. 粉末冶金技术. 2021(05): 423-428 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 黎应芬,童子文,陈雷,朱义祥. 电极银浆用微纳米银粉的制备与性能研究. 粉末冶金技术. 2020(04): 275-282 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: