-
摘要: 以Zr (NO3)4·5H2O为锆源, 利用水热法分别制备ZrO2和kaolin/ZrO2复合纳米粉体, 采用扫描电子显微镜、X射线衍射仪、红外光谱仪分析了样品的微观形貌及特性, 使用紫外-可见分光光度计研究了样品的吸光特性, 利用Brunauer-Emmet-Teller (BET)气体吸附法(氮气吸附)测定并计算了样品的比表面积。结果表明, 经过400℃煅烧后, kaolin/ZrO2表面微球颗粒较纯ZrO2更加均匀、单一, 不存在成块团聚体; 两种样品均存在介孔结构, ZrO2主要以无定形形式存在, 但样品中都存在少量的四方相ZrO2; 在波长190~800nm范围内, kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体吸光率均高于纯ZrO2, 并且其BET比表面积也比纯ZrO2高19.05m2·g-1, kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体在防紫外光特种材料制备及光催化处理工业废水等方面具有更大的优势与潜力。
-
关键词:
- kaolin/ZrO2 /
- 纳米粉体 /
- 制备 /
- 吸附性能
Abstract: The ZrO2 and kaolin/ZrO2 nanopowders were prepared by hydrothermal method, using Zr(NO3)4·5H2O as the zirconium source. The properties and microstructures of the obtained powders were characterized by scanning electron microscope (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis), and Brunauer-Emmet-Teller (BET) nitrogen adsorption method. In the results, both ZrO2 and kaolin/ZrO2 samples show the nanoscale microspheres with the mesoporous structure, and the surface microspheres of kaolin/ZrO2 after calcination at 400℃ are more uniform without agglomeration; the ZrO2 mainly exists in amorphous form, but a small number of tetragonal ZrO2 phases are present in these two samples. The absorbance of kaolin/ZrO2 nanopowders is stronger than that of pure ZrO2 in the wavelength ranging from 190 to 800 nm, and the BET specific surface area is 19.05 m2·g-1 higher than that of pure ZrO2. The results indicate that the kaolin/ZrO2 nanopowders have the greater advantages and potential in the preparation of ultraviolet specific materials and photo-catalytic treatment industrial wastewater.-
Keywords:
- kaolin/ZrO2 /
- nanopowders /
- preparation /
- adsorption properties
-
ZrO2是一种P型多功能过渡金属氧化物,因性能优异被用来制备高性能陶瓷、传感器及固体燃料电池等。纳米ZrO2因具备酸碱性、优良的离子交换性、易产生氧空位、相组成可控性及较高的分散性等物化特性,成为一种重要的催化剂,近几年备受关注[1-13]。高岭土(kaolin)作为一种性能优异的天然黏土矿物,具有可塑性好、粘结性高、抗酸溶性好等特性,同时因其片层带电性,易于吸附带电离子和微粒,被认为是一种成本低廉的吸附剂和催化剂载体。
本文作者[14-16]一直研究纳米ZrO2粉体在光催化领域的应用,在结合前期研究成果的基础上,利用水热合成法制备ZrO2和kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体,以期制备出催化性能更加优异的ZrO2基纳米粉体,为进一步深入研究纳米ZrO2粉体及其催化应用提供参考。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 样品制备
ZrO2纳米粉体的制备:将0.1 mol∙L-1 NaBH4溶液(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司)滴加到0.1 mol∙L-1 Zr(NO3)4∙5H2O溶液中(分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司),滴加过程中会出现白色溶胶,均匀搅拌至沉淀产生,经过滤、洗涤至洗液呈中性为止;在干燥后的沉淀生成物中加入0.5 mol∙L-1Na HCO3溶液(分析纯,天津市博迪化工有限公司),经超声分散后转入自制四氟乙烯(teflon)衬胆不锈钢高压釜中,在烘箱中180 ℃保温12 h,随后自然冷却至室温;将所得样品在400 ℃煅烧4 h,冷却至室温,研磨后即得ZrO2纳米粉体。
Kaolin/ZrO2复合纳米粉体的制备:将分离提纯后的高岭土浆料在110 ℃下烘干,经粉碎、研磨后配制成固含量(质量分数)为5%左右的浆料,分散均匀后置于三颈烧瓶(250 mL)中;在60 ℃恒温水浴加热并搅拌的条件下,向浆料中滴加0.1 mol∙L-1Zr(NO3)4∙5H2O溶液,然后滴加Na BH4溶液,将沉淀生成物用去离子水洗涤数次,至洗液呈中性为止;在过滤、干燥后的沉淀生成物中加入0.5 mol∙L-1NaHCO3溶液,经超声分散为乳状悬浮液后转入自制聚四氟乙烯(teflon)衬胆不锈钢高压釜中,在180 ℃反应12 h,随后自然冷却至室温;经过滤、洗涤、干燥后,将所得样品在400 ℃煅烧4 h,冷却至室温,研磨后即为kaolin/ZrO2复合纳米粉体。
1.2 性能表征
采用德国Bruker公司D8 Advance型X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction, XRD)分析样品的相结构及组成,测试条件为Cu靶、6°/min扫速;使用美国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司Nicolet 6700 Flex傅立叶变换红外光谱仪(Fourier transform infrared spectrometer, FT-IR)分析样品的物质组成(KBr压片);通过荷兰FEI公司Sirion-200型场发射扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM)表征样品的微观形貌;利用日本JASCO公司UV-550紫外–可见分光光度计(ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry, UV-Vis)表征固体样品的吸光特性;采用美国Quantachrome公司Ausosorb1.2测定样品的比表面积。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 微观形貌表征
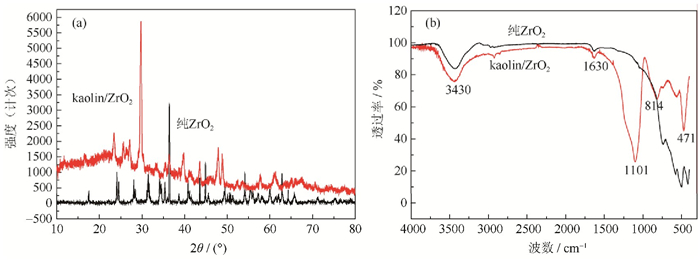
图 1为kaolin/ZrO2与纯ZrO2纳米粉体X射线衍射图与红外光谱图。由图 1(a)可见,kaolin/ZrO2的X射线衍射图谱中未见明显的ZrO2特征峰,样品中ZrO2主要为无定形态,2θ=29.74°处是煅烧高岭土的特征峰。由图 1(b)可见,在波数为3430 cm-1和1630 cm-1处分别出现了H2O中O–H特征峰,这可能是由于KBr压片测试中样品吸水所致;在波数为1101 cm-1和814 cm-1处分别出现了煅烧高岭土的特征峰;对于纯ZrO2纳米粉体,在波数为580~420 cm-1处出现几个细密的吸收峰,为四方相ZrO2的特征峰,对于kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体,仅在波数为471 cm-1左右出现了一个相对较弱的吸收峰,为四方相Zr–O振动吸收峰,这说明kaolin/ZrO2同样存在少量晶化的四方相ZrO2。
图 2是kaolin/ZrO2与纯ZrO2纳米粉体的扫描电子显微形貌。由图 2可见,kaolin/ZrO2表面微球颗粒整体较纯ZrO2更加均匀、单一,不存在成块的团聚体。颗粒外形及尺寸比纯ZrO2更加明晰,大颗粒尺寸更加一致,小颗粒明显增多,颗粒间空隙也明显增大。这是由于加入的煅烧高岭土微晶颗粒将ZrO2微球分开,阻碍其进一步团聚为大尺寸微球,从而形成尺寸较为均匀的ZrO2纳米微球颗粒。
2.2 吸光特性
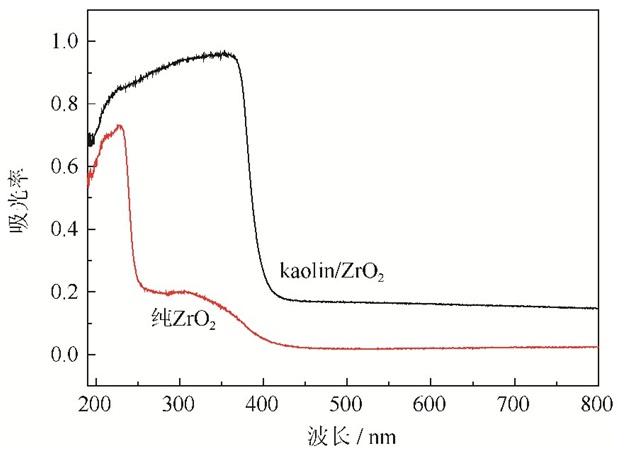
图 3是kaolin/ZrO2与纯ZrO2纳米粉体的紫外–可见吸收光谱。由图 3可见,kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体在190~800 nm范围内的吸光率均高于纯ZrO2,且kaolin/ZrO2在200~380 nm范围的吸光率均达到0.7以上。纯ZrO2的最大吸收出现在227 nm,吸光率为0.731, kaolin/ZrO2的最大吸收出现在353.5 nm,吸光率为0.966。因此,kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体比纯ZrO2在紫外光区具有更强吸光特性,有望在防紫外光特种材料制备领域发挥巨大作用。
2.3 表面特性
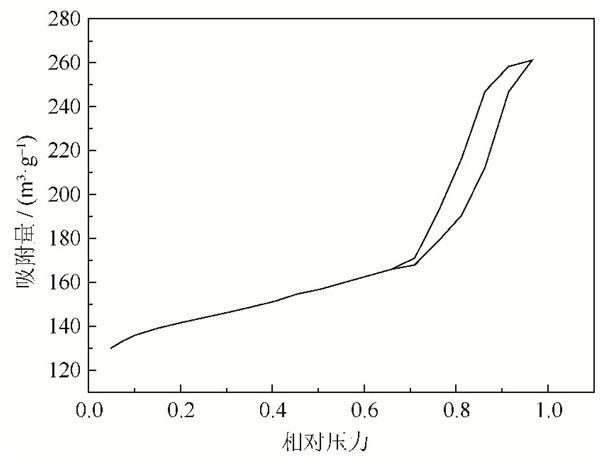
图 4是kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体的Brunauer-EmmetTeller(BET) 氮气(N2) 吸脱附等温线。由图可见,kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体的等温线吸附分支与脱附分支不一致,存在迟滞回线,属于典型的Ⅳ型等温线,这说明样品中存在介孔结构。根据BET方程线性拟合可计算负载kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体的比表面积为29.35 m2·g-1,要比纯ZrO2的比表面积高19.05 m2·g-1,详细数据如表 1所示,其中,A表示线性拟合方程的截距,B表示斜率,R2表示线性相关系数。因此,kaolin/ZrO2纳米粉体比纯ZrO2在催化剂、吸附剂及光催化处理工业废水等方面具有更大的应用潜力。
表 1 Kaolin/ZrO2与纯ZrO2纳米粉体的BET线性拟合数据Table 1. BET linear fitting of the kaolin/ZrO2 and the pure ZrO2 nanopowders样品 A B R2 比表面积/(m2·g-1) Kaolin/ZrO2 -0.1940 8.076 0.9999 29.35 纯ZrO2 330.6 7.645 0.9998 10.30 3. 结论
(1) 以Zr(NO3)4∙5H2O为锆源,经180 ℃水热反应12 h和400 ℃煅烧4 h,获得颗粒均匀的纯ZrO2和kaolin/ZrO2复合纳米微球粉体,两种样品均存在介孔结构的纳米微球,ZrO2以无定形为主,同时存在少量四方晶型ZrO2。
(2) Kaolin/ZrO2复合纳米粉体在波长为190~800 nm范围内的吸光率均高于纯ZrO2,尤其是在200~380 nm范围,kaolin/ZrO2复合纳米粉体的吸收性比纯ZrO2更具优势,有望在防紫外光特种材料领域发挥巨大作用。
(3) 根据BET方程线性拟合可得,kaolin/ZrO2复合纳米粉体的比表面积为29.35 m2∙g-1,而纯ZrO2的比表面积10.30 m2∙g-1。因此,kaolin/ZrO2复合纳米粉体比纯ZrO2在催化剂、吸附剂及光催化处理工业废水等方面具有更大的应用潜力。
-
表 1 Kaolin/ZrO2与纯ZrO2纳米粉体的BET线性拟合数据
Table 1 BET linear fitting of the kaolin/ZrO2 and the pure ZrO2 nanopowders
样品 A B R2 比表面积/(m2·g-1) Kaolin/ZrO2 -0.1940 8.076 0.9999 29.35 纯ZrO2 330.6 7.645 0.9998 10.30 -
[1] 李梦萱, 郭英奎, 范国峰, 等. 水热法制备纳米ZrO2粉体的条件. 哈尔滨理工大学学报, 2015, 20(5): 69 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLGX201505015.htm Li M X, Guo Y K, Fan G F, et al. Study on nano ZrO2 powder prepared by hydrothermal method. J Harbin Univ Sci Technol, 2015, 20(5): 69 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLGX201505015.htm
[2] 李文芳, 宋继梅, 陈波, 等. 纳米四方相二氧化锆的水热合成. 安徽大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 42(6): 88 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2162.2018.06.016 Li W F, Song J M, Chen B, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of tetragonal phase zirconia nanocrystalline. J Anhui Univ Nat Sci, 2018, 42(6): 88 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2162.2018.06.016
[3] 刘璐, 刘文燕, 徐坦, 等. ZrO2纳米粉体的形貌可控合成及其吸附性能研究. 人工晶体学报, 2016, 45(6): 1520 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2016.06.016 Liu L, Liu W Y, Xu T, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and adsorption properties of morphology-controlled ZrO2 nano powders. J Synth Cryst, 2016, 45(6): 1520 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2016.06.016
[4] 张小芳, 于景坤, 向东, 等. 沉淀剂对ZrO2(MgO)纳米粉体制备的影响. 材料与冶金学报, 2016, 15(1): 49 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUJI201601009.htm Zhang X F, Yu J K, Xiang D, et al. Effects of precipitation agent on preparation of nanosized ZrO2(MgO) powders. J Mater Metall, 2016, 15(1): 49 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HUJI201601009.htm
[5] 肖露, 许林峰, 花开慧, 等. 共沉淀法制备Al2O3-ZrO2复合纳米粉体. 人工晶体学报, 2015, 44(10): 2751 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2015.10.021 Xiao L, Xu L F, Hua K H, et al. Preparation of Al2O3-ZrO2 composite nanopowders by co-precipitation method. J Synth Cryst, 2015, 44(10): 2751 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2015.10.021
[6] 石连水, 张林, 陈萍华, 等. 机械化学法制备ZrO2纳米粉体的工艺研究. 硅酸盐通报, 2014, 33(6): 1443 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201406041.htm Shi L S, Zhang L, Chen P H, et al. Research process of ZrO2 nanopowders prepared by mechanochemical method. Bull Chin Ceram Soc, 2014, 33(6): 1443 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201406041.htm
[7] 刘凤馨, 冯国英, 杨超, 等. 电爆炸丝法制备纳米ZrO2粉末的实验研究. 强激光与粒子束, 2018, 30(7): 074103 DOI: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.180055 Liu F X, Feng G Y, Yang C, et al. Experimental analysis of ZrO2 nanopowders by electrical explosion of zirconium wire. High Power Laser Part Beams, 2018, 30(7): 074103 DOI: 10.11884/HPLPB201830.180055
[8] 郝一男, 王喜明. 纳米二氧化锆吸附Pb2+的研究. 环境工程, 2017, 35(8): 51 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201708011.htm Hao Y N, Wang X M. Study on the adsorption of Pb2+ by nano-zirconium dioxide. Environ Eng, 2017, 35(8): 51 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJGC201708011.htm
[9] 冯群, 鲍建国, 谢雄, 等. 纳米二氧化锆改性膜生物反应器处理生活污水的试验研究. 环境污染与防治, 2016, 38(10): 67 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR201610013.htm Feng Q, Bao J G, Xie X, et al. Research of membrane bioreactor modified by nanometer ZrO2 for treating domestic sewage. Environ Pollut Control, 2016, 38(10): 67 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HJWR201610013.htm
[10] 杜青. 锆基纳米复合材料深度净化水体中的微量重金属[学位论文]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2015 Du Q. Enhanced Removal of Heavy Metals in Waters by Ploymer-Supported Zirconium Oxide Nanocomposite[Dissertation]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2015
[11] 石国亮. 二氧化锆基纳米晶体的设计合成及其结构性能研究[学位论文]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2016 Shi G L. Synthesis and Structure of ZrO2-Based Nanocrystals[Dissertation]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2016
[12] 赵亮, 薛群虎. 添加Al2O3-ZrO2复合粉改性氧化锆质定径水口及其损毁机理. 工程科学学报, 2017, 39(2): 202 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201702006.htm Zhao L, Xue Q H. Damage mechanism of zirconia metering nozzles modified by Al2O3-ZrO2 composite powder. Chin J Eng, 2017, 39(2): 202 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201702006.htm
[13] 胡继林, 罗祎格, 罗金秋, 等. 醇-水法制备Al2O3-ZrO2复合粉体及其表征. 硅酸盐通报, 2016, 35(11): 3669 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201611030.htm Hu J L, Luo Y G, Luo J Q, et al. Preparation and characterization of alumina-zirconia composite powders by alcohol-water method. Bull Chin Ceram Soc, 2016, 35(11): 3669 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GSYT201611030.htm
[14] 郭春芳. 高岭土负载ZrO2/ZnO纳米复合粉体制备及光催化应用. 材料研究与应用, 2015, 9(3): 162 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2015.03.005 Guo C F. Preparation and applications of kaolin ZrO2/ZnO loaded photo-catalytic functional materials. Mater Res Appl, 2015, 9(3): 162 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2015.03.005
[15] 郭春芳. 纳米ZrO2/ZnO制备及光催化降解亚甲基蓝的研究. 印染助剂, 2016, 33(11): 37 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0439.2016.11.009 Guo C F. Preparation and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue by nano-sized ZrO2/ZnO. Text Auxil, 2016, 33(11): 37 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0439.2016.11.009
[16] 郭春芳. ZrO2棒形纳米粉末的制备及吸光特性研究. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2014, 42(3): 28 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJY201403008.htm Guo C F. Study on synthesis of the clavate ZrO2 nano-powders and their light absorptivity. Rare Met Cem Carb, 2014, 42(3): 28 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJY201403008.htm
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 郭春芳. 纳米NiO/ZrO_2复合光催化剂的制备及性能. 印染助剂. 2022(03): 31-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: