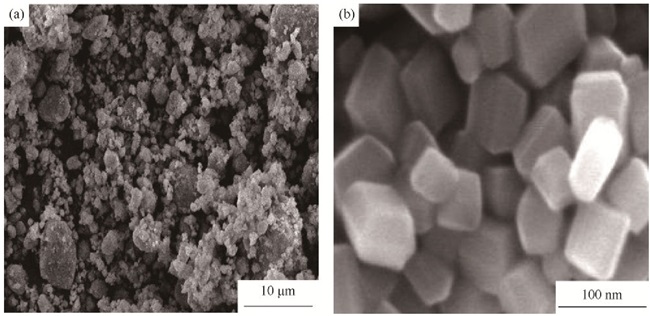
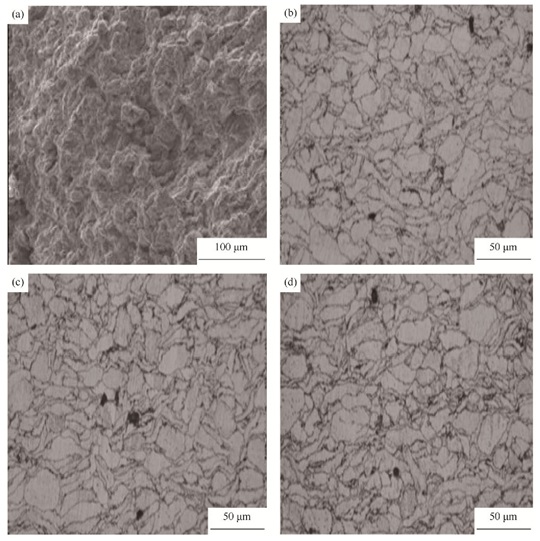
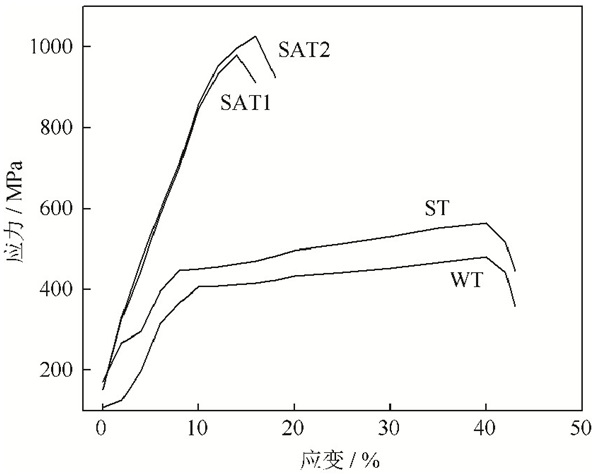
Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-21.5Nb alloy prepared by powder sintering used for internal combustion engine
-
摘要: 采用放电等离子烧结技术制备内燃机用Ti-21.5Nb-2Zr-1.2Mo-0.1Y钛合金材料(Ti-21.5Nb), 并对其进行固溶和时效处理, 通过扫描电子显微镜、金相显微镜、X射线衍射仪、万能拉伸测试仪等设备分析试样的微观形貌、组织结构、物相组成以及力学性能。结果表明: 采用等离子旋转电极法制备的预合金球形粉末相对密度较高, 并且未形成孔洞; 烧结试样和固溶试样都是由β相与α相组成, 放电等离子烧结Ti-21.5Nb合金和常规铸锭合金具有相同的相结构变化规律; 合金烧结组织由β等轴晶和一些小尺寸α相构成, 其中β等轴晶的粒径介于30~80μm; 在800 ℃下对烧结试样进行固溶时效处理, 得到的固溶组织主要是由β相构成, 同时在β相中还生成了椭球形α弥散组织; 在500 ℃下对Ti-21.5Nb固溶试样进行时效处理, 在合金基体中析出ω相, 而原先的α相全部消失; 在380 ℃时效处理时, 组织中只存在α相, ω相完全消失; 在800 ℃对Ti-21.5Nb合金进行固溶时效处理可以获得力学性能更优的钛合金材料。Abstract: The spark plasma sintering (SPS) technology was selected to prepare the Ti-21.5Nb-2Zr-1.2Mo-0.1Y titanium alloy materials (Ti-21.5Nb) used in internal combustion engine, and then the solid solution and aging treatments were operated. The microstructure, phase composition, and mechanical properties of the samples were investigated by scanning electron microscope, metallographic microscope, X-ray diffractometer, and universal tensile tester. The results show that the pre-alloyed spherical powders with high relative density are obtained by plasma rotating electrode method, and no holes are formed. The microstructures of both the sintered and the solid solution samples are composed of β phase and α phase. The Ti-21.5Nb alloys prepared by SPS and the conventional ingot alloys have the same change rule of phase structure. The sintered samples are composed of β isometric grain and α phase in a smaller size, and the particle size of β isometric grain is between 30 μm and 80 μm. After the solid solution treatment on the sintered samples at 800 ℃, the samples mainly consist of β phase, and the dispersive α phase in ellipsoid is also present in the β phase. After the solid solution treatment on the Ti-21.5Nb at 500 ℃, and the ω phase is precipitated in the alloys, while all the original α phase disappear. The solid solution treatment at 380 ℃, only α phase exist in the alloys, ω phase completely disappear. The Ti-21.5Nb alloys with the better mechanical properties can be obtained by solid solution treatment at 800 ℃.
-
Keywords:
- titanium alloys /
- spark plasma sintering /
- microstructure /
- mechanical properties
-
碳纳米管(carbon nanotubes, CNTs) 自从被发现以来[1], 以其独特的力学、热学、磁学和电学性能广泛应用于电极材料、纳米电子材料、结构材料等诸多领域, 表现出良好的应用前景[2, 3]。镁作为实际应用中最轻的金属结构材料, 具有密度小, 比强度和比刚度高, 切削和加工性能好等优点, 在航天、汽车和通讯领域都有广泛的应用。但是镁的高温性能差, 尤其是高温下耐腐蚀、耐磨损性能差, 限制了它的应用; 通过加入颗粒或纤维制备镁基复合材料, 可大大提高复合材料的强度, 改善其耐磨性能。磨损不仅会损害工程部件的力学性能, 还会降低部件的公差精度, 破坏其表面精整度, 降低零部件的使用寿命, 在材料加工和装配过程中(例如滚压、挤压、锻造等), 摩擦磨损性能是重要的考虑因素[4]。因此, 研究镁基复合材料的摩擦磨损性能, 具有实际的工程意义。
碳纳米管是由石墨卷曲而成的中空管状物质, 这就决定了其具有类似石墨的润滑作用, 并已经广泛应用于汽车润滑轴承、减磨活塞构件等方面。碳纳米管添加进入镁基体后, 镁基体抗拉强度、维氏硬度均得到显著提高[5]。因此, 从理论上讲碳纳米管具备了高强和减磨强化相的特点, 有望在提高镁基体力学性能的同时, 又能降低基体的摩擦系数和磨损量[6]。
以多壁碳纳米管镁基复合材料为研究对象, 采用金属有机化学气相沉积工艺(metal organic chemical vapor deposition, MOCVD) 对多壁碳纳米管进行镀钨处理, 以增加碳纳米管与Mg基体之间界面润湿性。采用磁力搅拌(magnetic stirring, MS) 工艺对镀钨碳纳米管(W-CNTs) 与Mg粉进行混合, 使镀钨碳纳米管在镁基体中均匀分散, 并对混合粉体进行放电等离子体烧结(spark plasma sintering, SPS) 制备镀钨碳纳米管增强镁基复合材料((W-CNTs) /Mg)。对复合材料的摩擦系数和磨损量进行测试, 力求制备具有低摩擦系数、低磨损量的碳纳米管镁基复合材料。
1. 实验材料及方法
实验用碳纳米管为北京纳辰科技有限公司提供的多壁碳纳米管, 管壁外径20~30 nm, 长度为20~30μm, 纯度 > 95%。镁粉平均粒径-200目, 纯度 > 99.9%。使用浓H 2SO4/HNO3 (体积比3:1) 混酸对原始碳纳米管进行纯化处理30 min, 除去碳纳米管表面残留的金属Fe催化剂杂质, 酸洗后采用去离子水对碳纳米管冲洗2~3遍。以羰基钨(W (CO) 6) 为前驱体, 对酸洗纯化的碳纳米管进行金属有机化学气相沉积镀钨处理, 镀覆温度和时间分别为400℃和60 min。图 1为金属有机化学气相沉积工艺示意图, 镀钨原理如式(1) 所示。
$$ {\text{W}}{({\text{CO}})_6}\xrightarrow[{{\text{CNTs}}}]{\Delta }6{\text{CO + (W - CNTs)}} $$ (1) 将质量分数为0.25%、0.50%、0.75%、1.00%、1.25%和1.75%的W-CNTs与Mg粉进行磁力搅拌混合。采用无水乙醇为介质, 磁子转速为300 r/min, 时间为240 min。粉体混合后真空烘干进行放电等离子体烧结, 烧结压力和温度分别为30 MPa和580℃, 保温时间为10 min。
采用阿基米德排水法测量烧结块体的密度, 并根据测试密度与理论密度结果计算块体的相对密度; 利用ZEISS ULTRA 55场发射扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM) 观察试样磨损表面形貌; 使用高精密电子天平称量试样磨损前后的质量差, 并进行相减获得试样的质量磨损量。分别用400#、800#、1000#、1500#和2000#砂纸磨光试样, 采用WTM-2E型可控气氛摩擦磨损试验仪对材料的摩擦磨损性能进行测试。图 2为WTM-2E型可控气氛摩擦磨损试验仪实物图, 设定的摩擦磨损实验工艺参数如表 1所示。
表 1 摩擦磨损实验工艺参数Table 1. Process parameters of friction and wear test对磨材料 磨球直径/mm 摩擦回转半径/mm 主轴转速/(r·min-1) Si3N4 5 4 480 2. 结果与分析
2.1 W-CNTs的表征
图 3 (a)和图 3(b)为原始碳纳米管与W-CNTs的扫描电子显微形貌, 图 3(c)为W-CNTs的能谱图。由图可知, 金属有机化学气相沉积工艺使得碳纳米管表面获得了连续的钨金属涂层, 且碳纳米管被金属钨层完全包裹, 未出现碳纳米管裸露现象, 镀覆效果良好。能谱结果显示所得镀层含有W、C两种元素, 其中C元素可能来源于碳纳米管。此外, 相比于传统化学镀和电镀[7]工艺繁多的镀覆步骤以及较长的镀覆时间, 金属有机化学气相沉积工艺是一种经济简便的金属镀覆工艺。
2.2 W-CNTs质量分数对混粉效果的影响
图 4为Mg粉与不同质量分数的W-CNTs经磁力搅拌混合后的扫描电子显微形貌。由图 4(a) 和图 4(b) 可知, 当W-CNTs质量分数为0.25%和0.75%时, 由于W-CNTs添加量较少, W-CNTs在Mg基体中获得了良好的分散, 均匀地分布在Mg粉颗粒表面, 表明混粉效果良好; 图 4(c) 和图 4(d) 为添加质量分数1.25%和1.75%W-CNTs的混合粉体扫描电子显微形貌, 当W-CNTs质量分数为1.25%时, W-CNTs在基体中开始出现团聚现象, 当W-CNTs质量分数增加到1.75%时(图 4(d)), W-CNTs团聚现象更加明显。
一般而言, W-CNTs团聚体往往是孔隙的集中处, 可导致复合材料相对密度的下降[8]。图 5为添加不同质量分数W-CNTs的复合材料相对密度, 由图 5可知, 经过30 MPa和580℃放电等离子烧结后, 纯镁块体的相对密度高达99.8%, 接近全致密, 表明所选烧结工艺合适。加入W-CNTs后, 复合材料的相对密度下降, 但材料整体相对密度仍可大于93%。此外, 随W-CNTs质量分数增加, 复合材料相对密度下降, 这是因为随W-CNTs质量分数的增加, W-CNTs在基体中的分散性减弱, 更易形成团聚体(见图 4)。
2.3 W-CNTs质量分数对复合材料摩擦性能的影响
W-CNTs添加量的多少对于复合材料的各项性能指标都有很明显的影响。为探讨W-CNTs质量分数对复合材料摩擦磨损性能的影响, 选取了一组固定载荷(6 N)、添加不同质量分数W-CNTs的镁基复合材料作为研究对象, 从摩擦系数、磨损量以及对磨损形貌的影响三个方面来研究碳纳米管质量分数的变化对复合材料摩擦性能的影响。图 6为固定载荷(6 N) 作用下复合材料摩擦系数随碳纳米管质量分数的变化曲线。由图可以看出, 纯镁中添加碳纳米管后的各样品的摩擦系数均远小于纯镁的摩擦系数, 可见碳纳米管的加入可以很好的降低基体的摩擦系数, 起到了润滑减磨的作用。
当W-CNTs质量分数较低时, 复合材料的摩擦系数随W-CNTs质量分数的增大而逐渐降低; 当W-CNTs质量分数为0.75%时, 材料的摩擦系数最小, 较纯镁块体降低了43.7%。碳纳米管可以被看作是由石墨片卷曲而成的中空结构, 片层之间的弱范德华力使管壁之间容易发生相对滑动, 表现在复合材料中为碳纳米管的自润滑性能, 碳纳米管的这种性能能够有效的降低复合材料的摩擦系数。其次, 碳纳米管在摩擦过程中会形成一层较为光滑的保护膜, 减小了基体与对磨触头的接触, 所以使得材料的摩擦系数降低。另外, 添加W-CNTs后复合材料的维氏硬度得到了提高, 可有效的抵抗塑性变形, 从而使复合材料磨损减少。当W-CNTs的质量分数高于0.75%时, 随着W-CNTs质量分数的进一步增加, 复合材料的摩擦系数呈现上升的趋势。这是由于随着W-CNTs质量分数的增加, W-CNTs在基体中的分散效果较差, 团聚现象较为明显, 团聚体的出现破坏了复合材料的连续性, 使得在摩擦的过程中摩擦副容易将基体整体一块刮起, 而不易在摩擦副和基体中形成稳定的碳膜, 从而使得材料的摩擦系数增加。
2.4 W-CNTs质量分数对复合材料磨损量的影响
在材料摩擦过程中, 最明显的特征是材料表面会遭到摩擦对偶不同程度的磨损破坏, 并使材料的表面产生物料损失, 造成材料磨损的发生。因此, 磨损量也是表征材料耐磨性好坏的重要指标。由图 7可知, 添加W-CNTs降低了基体的磨损量, 且磨损量随W-CNTs质量分数的增加呈现先减小后增加的趋势, 当W-CNTs质量分数为0.75%时, 复合材料磨损量较纯镁降低了71.4%。
当W-CNTs质量分数少时, 碳纳米管的自润滑作用使复合材料摩擦系数降低, 当质量分数达到0.75%时, 减磨作用最明显, 从而减少了材料在摩擦过程中的剥落, 磨损量降低。当W-CNTs质量分数高于0.75%时, 由于W-CNTs团聚体的出现影响了复合材料的连续性, CNTs容易团聚在颗粒的边界处, 基体的连续使得复合材料在摩擦过程之中更加容易产生剥层磨损, 从而当碳纳米管质量分数进一步增加后材料的磨损量提高[9]。另外, 添加W-CNTs后, 复合材料的硬度得到不同程度的提高, 材料抵抗局部塑性变形能力增强, 材料磨损量减小, 且当质量分数0.75%时硬度最大, 复合材料耐磨性最好, 故其磨损量最小。
为分析复合材料的摩擦磨损行为, 对(W-CNTs) /Mg复合材料的表面磨损形貌进行了扫描电子显微形貌观察, 结果如图 8所示。从图中可以看出, 纯镁的表面磨损形貌非常明显, 可以很清楚地看到犁沟和磨削颗粒。当材料中加0.25%W-CNTs时, 试样表面也有明显的犁沟产生, 犁沟变细且不连续, 但是表面的破坏程度明显的比纯镁要低, 这说明当材料硬度较低的时候, 会比较容易产生塑性变形。当试样中W-CNTs添加量为0.75%时, 磨损表面较为光滑, 磨痕较浅, 无明显的犁沟出现, 且磨屑数量也很少, 磨损表面相对完整。因为此时W-CNTs的自润滑效果较为明显, 同时W-CNTs大大促进了基体硬度的提高, 材料抵抗塑性变形能力增加, 磨损较少, 表明0.75%W-CNTs对复合材料起到了良好的减磨作用。当W-CNTs质量分数达到1.25%~1.75%时, 复合材料表面磨损逐渐加剧, 但磨损表面主要由剥落的颗粒磨屑组成, 并无明显的犁沟, 磨痕发生了较严重的塑性变形。这是因为, 随着W-CNTs的增多, 碳纳米管分散效果变差, 容易发生团聚, 碳纳米管的自润滑作用减弱。高添加量W-CNTs会使材料的相对密度下降, 孔隙率增加, 高孔隙量会促进复合材料裂纹的萌生、扩展、合并, 直至使裂纹处的颗粒断裂和剥离基体[10], 并最终形成磨屑。因此, W-CNTs质量分数过高时, 会导致材料的磨损加剧。
![]() 图 8 (W-CNTs) /Mg复合材料磨损表面形貌与W-CNTs质量分数关系: (a) 纯镁; (b) 0.25%W-CNTs; (c) 0. 7 5%W-CNTs; (d) 1. 2 5%W-CNTs; (e) 1.75%W-CNTsFigure 8. Relationship between wear morphologies and W-CNTs contents by mass of (W-CNTs) /Mg composites: (a) pure Mg; (b) 0.25%W-CNTs; (c) 0. 7 5%W-CNTs; (d) 1. 2 5%W-CNTs; (e) 1.75%W-CNTs
图 8 (W-CNTs) /Mg复合材料磨损表面形貌与W-CNTs质量分数关系: (a) 纯镁; (b) 0.25%W-CNTs; (c) 0. 7 5%W-CNTs; (d) 1. 2 5%W-CNTs; (e) 1.75%W-CNTsFigure 8. Relationship between wear morphologies and W-CNTs contents by mass of (W-CNTs) /Mg composites: (a) pure Mg; (b) 0.25%W-CNTs; (c) 0. 7 5%W-CNTs; (d) 1. 2 5%W-CNTs; (e) 1.75%W-CNTs3. 结论
(1) 通过羰基钨的金属有机化学气相沉积工艺在碳纳米管表面镀覆了连续的钨金属层, 通过磁力搅拌实现了镀钨碳纳米管(W-CNTs) 与镁粉的均匀混合, 采用放电等离子烧结成功地制备了镀钨碳纳米管/镁基((W-CNTs) /Mg) 复合材料。
(2) W-CNTs的加入可对镁基体起到降低摩擦系数、减少磨损量的作用, 且W-CNTs质量分数为0.75%时, 复合材料的摩擦系数和磨损量均最小, 分别较纯镁降低了43.7%和71.4%, 增加或降低复合材料中W-CNTs质量分数, 材料的摩擦系数、磨损量均将增大。
-
-
[1] 段永刚, 丁英奇, 张龙, 等. 新型β钛合金Ti35Nb3Zr2Ta在人工关节假体应用中的生物相容性. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(34): 5536 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.34.024 Duan Y G, Ding Y Q, Zhang L, et al. Biocompatibility of Ti35Nb3Zr2Ta, a new beta-titanium alloy, as joint prosthesis material. Chin J Tissue Eng Res, 2015, 19(34): 5536 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.34.024
[2] Breme H, Biehl V, Reger N, et al. Chapter 1a Metallic Biomaterials: Introduction, Handbook of Biomaterial Properties. Eds. by Murphy W, Black J, Hastings G. New York: Springer, 2016
[3] Yu Z T, Zhang M H, Tian Y X, et al. Designation and development of biomedical Ti alloys with finer biomechanical compatibility in long-term surgical implants. Front Mater Sci, 2014, 8(3): 219 DOI: 10.1007/s11706-014-0254-8
[4] 麻西群, 于振涛, 牛金龙, 等. 热处理对Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-25Nb合金超弹性的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(6): 1588 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201606035.htm Ma X Q, Yu Z T, Niu J L, et al. Effect of heat treatment on superelasticity of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-25Nb Alloy. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2016, 45(6): 1588 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201606035.htm
[5] 刘万理, 张玉勤, 蒋业华, 等. 固溶温度对SPS烧结Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn合金组织和力学性能的影响. 金属热处理, 2017, 42(4): 99 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSRC201704022.htm Liu W L, Zhang Y Q, Jiang Y H, et al. Effect of solution temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn alloy prepared by spark plasma sintering. Heat Treat Met, 2017, 42(4): 99 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSRC201704022.htm
[6] He Z Y, Zhang L, Shan W R, et al. Mechanical and corrosion properties of Ti-35Nb-7Zr-xHA composites fabricated by spark plasma sintering. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2017, 27(4): 848 DOI: 10.1016/S1003-6326(17)60097-9
[7] Zhang Y S, Zhao Y H, Zhang W, et al. Core-shell structured titanium-nitrogen alloys with high strength, high thermal stability and good plasticity. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 40039 DOI: 10.1038/srep40039
[8] Zhang Y S, Wang X, Zhang W, et al. Elevated tensile properties of Ti-O alloy with a novel core-shell structure. Mater Sci Eng A, 2017, 696: 360 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.04.088
[9] 李智, 覃富城, 肖瑶, 等. 机械合金化对Ti-Zr-B粉末烧结制备TiB2-ZrB2复合材料的影响. 热加工工艺, 2019, 48(2): 105 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201902027.htm Li Z, Qin F C, Xiao Y, et al. Effect of mechanical alloying on Ti-Zr-B sintering prepared TiB2-ZrB2 Composite. Hot Working Technol, 2019, 48(2): 105 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SJGY201902027.htm
[10] Wang D J, Huang Y J, Wu L Z, et al. Mechanical behaviors of diamond reinforced Ti-based bulk metallic glassy composites prepared by spark plasma sintering. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, 560: 841 DOI: 10.1016/j.msea.2012.10.067
[11] Deng S S, Wang D J, Luo Q, et al. Spark plasma sintering of gas atomized AlNiYLaCo amorphous powders. Adv Powder Technol, 2015, 26(6): 1696 DOI: 10.1016/j.apt.2015.10.009
[12] 倪锋, 傅丽华, 邓攀, 等. SiO2-B2O3-Al2O3助焊剂对粉末烧结Cu-C-SnO2多孔材料组织与性能的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2018, 36(5): 335 DOI: 10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2018.05.003 Ni F, Fu L H, Deng P, et al. Effects of SiO2-B2O3-Al2O3 scaling powder on microstructures and properties of Cu-C-SnO2 porous materials sintered by powders. Powder Metall Technol, 2018, 36(5): 335 DOI: 10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2018.05.003
[13] 颜士伟, 黄尚宇, 胡建华, 等. 数值仿真技术在粉末冶金零件制造中的应用及研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(1): 57 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.01.010 Yan S W, Huang S W, Hu J H, et al. Development and application of numerical simulation in powder metallurgy manufacturing. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(1): 57 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.01.010
[14] 王伟, 周海雄, 王庆娟, 等. 湿法球磨元素粉放电等离子烧结制备Ti-22Al-25Nb合金. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2019, 42(4): 40 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCKG201904012.htm Wang W, Zhou H X, Wang Q J, et al. Preparation of Ti-22Al-25Nb alloy by wet ball milling element powder discharge plasma sintering. Ordn Mater Sci Eng, 2019, 42(4): 40 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BCKG201904012.htm
[15] 麻西群, 于振涛, 刘汉源, 等. SPS法制备Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-25Nb合金的组织与性能. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(1): 74 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201901009.htm Ma X Q, Yu Z T, Liu H Y, et al. Microstructure and properties of Ti-3Zr-2Sn-3Mo-25Nb alloy prepared by SPS method. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2019, 29(1): 74 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201901009.htm
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 贾征,喻兵,牛建平,宋婷婷,邵一川. 基于材料成型大赛与《液态成型原理》课程实验的深度融合. 铸造技术. 2021(08): 739-744 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 朱晓蒙,蔡晓兰,周蕾,吴少鹏,潘文豪. 离散元软件EDEM在矿冶工程中的应用与研究. 软件导刊. 2021(12): 93-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李亚杰,闫宏伟,袁飞,彭方现,杨雄,侯相荣. 倾斜式直线筛筛分机理分析. 煤矿机械. 2020(02): 78-81 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: