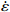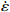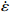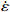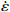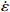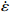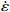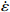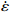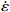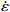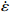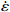-
摘要:
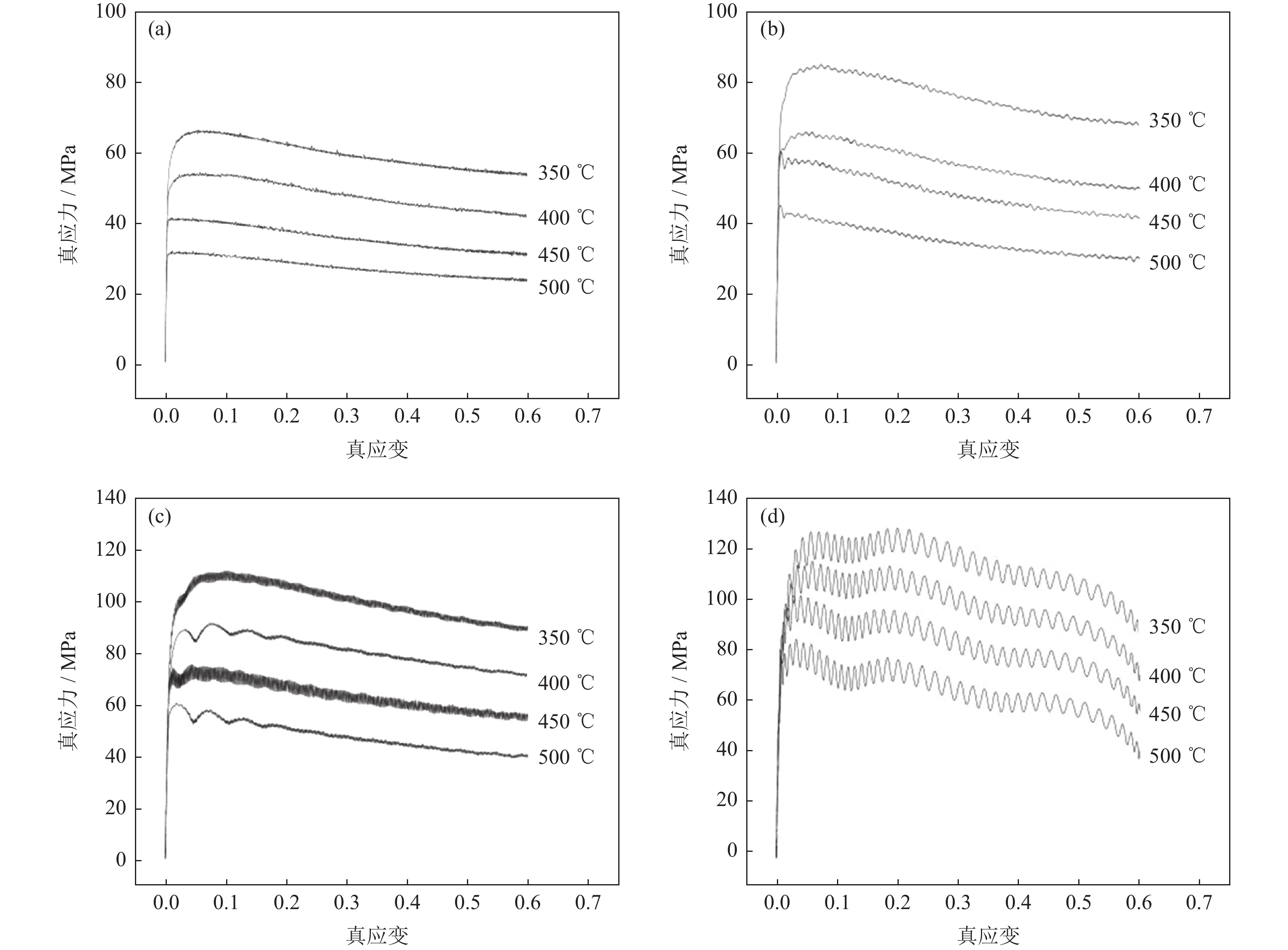
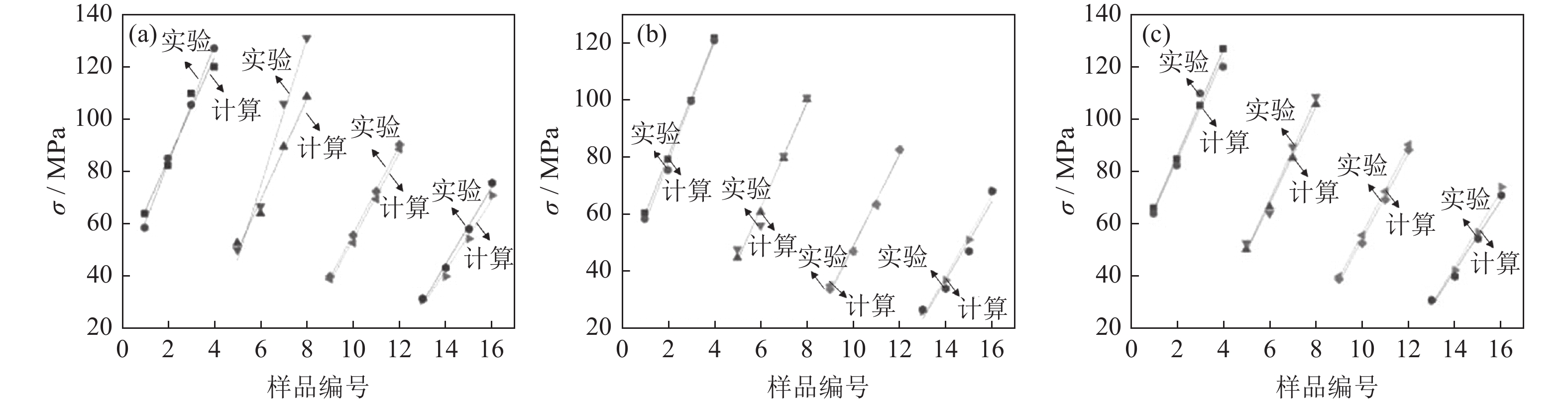
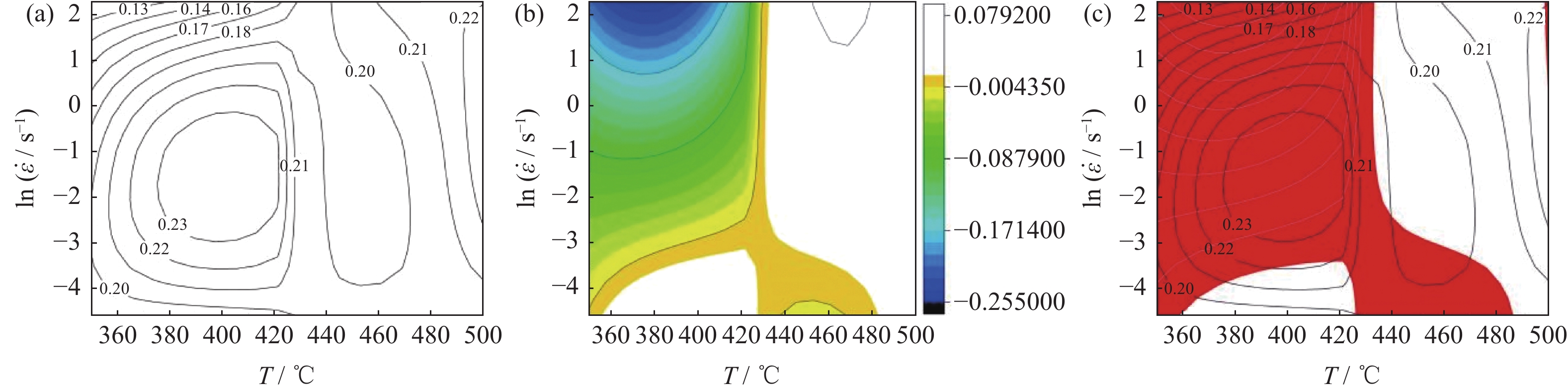
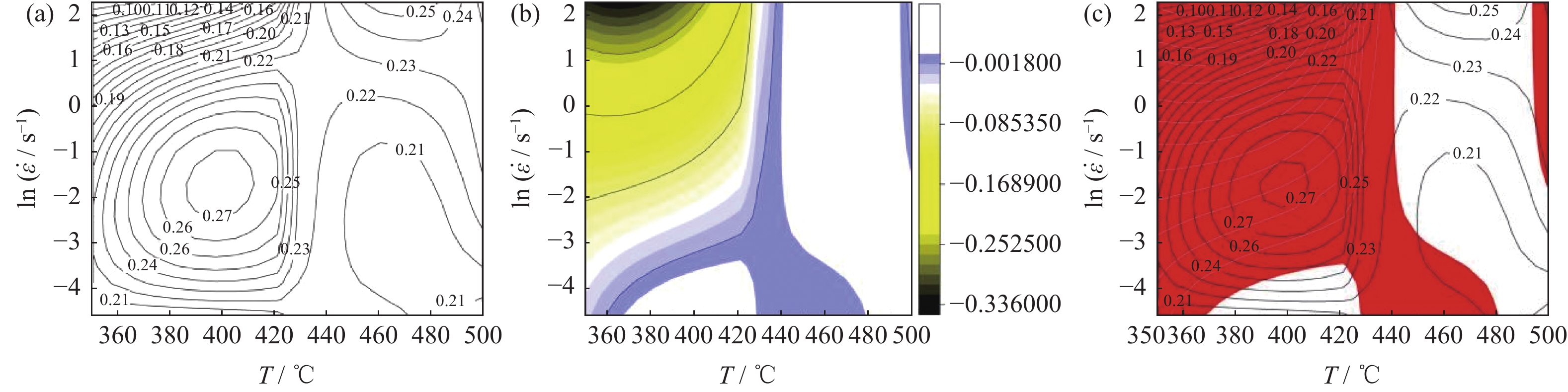
采用Glebble-1500D热模拟试验机,在350~500 ℃变形温度、0.01~10.00 s−1应变速率条件下进行等温压缩变形,研究40%SiCp/Al复合材料(体积分数)的热加工性能。通过热变形真应力-真应变曲线分析复合材料的热变形规律,建立材料本构方程,利用动态材料模型计算出应变速率敏感指数和功率耗散效率系数,绘制出功率耗散图、失稳图及二维加工图。结果表明,应变速率和变形温度显著影响流变应力,应变速率一定时,变形温度升高,流变应力减小;在相同的变形温度下,随应变速率的增加,流变应力也随之升高。根据加工图可知,在高温高应变速率条件下,材料的功率耗散效率系数大,说明该变形区域发生了组织转变;应变对失稳区域和加工区域影响不大,功率耗散效率系数随应变的增加而增大。40%SiCp/Al复合材料建议热加工条件为变形温度436~491 ℃,应变速率0.04~9.97 s−1。
-
关键词:
- SiCp/Al复合材料 /
- 热变形行为 /
- 本构方程 /
- 热加工图
Abstract:The hot workability of the 40%SiCp/Al composites (volume fraction) was studied by isothermal compression deformation on Glebble-1500D thermal simulated test machine at the deformation temperature of 350~500 ℃ under the strain rate of 0.01~10.00 s−1. The thermal deformation of the composites was analyzed according to the true stress-strain curves, and the constitutive equation was established. The strain rate sensitivity index and power dissipation efficiency factor were calculated by dynamic material model, and the power dissipation diagram, instability diagram, and two-dimensional processing map were obtained. The results show that, the strain rate and deformation temperature significantly affect the flow stress. Under the same strain rate, the flow stress decreases with the increase of deformation temperature; at the same deformation temperature, the flow stress increases with the increase of strain rate. According to the processing map, the power dissipation efficiency factor is large under the condition of high temperature and high strain rate, illustrating the microstructure transformation in the deformation region. The strain has little effect on the instability region and processing region, and the power dissipation efficiency factor increases with the increase of strain. The recommended hot working conditions for the composite is as the deformation temperature of 436~491 ℃ and the strain rate of 0.04~9.97 s−1.
-
-
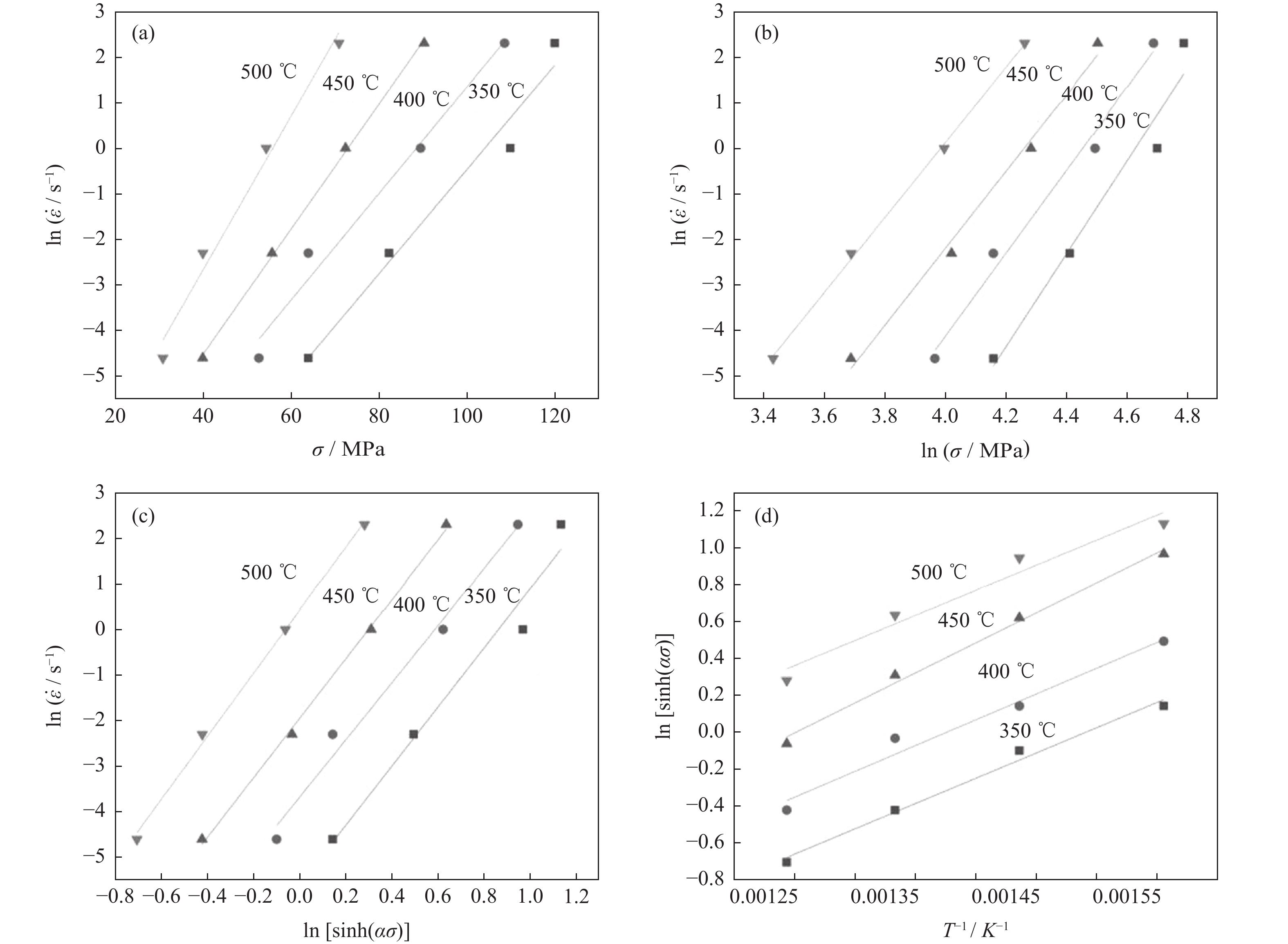
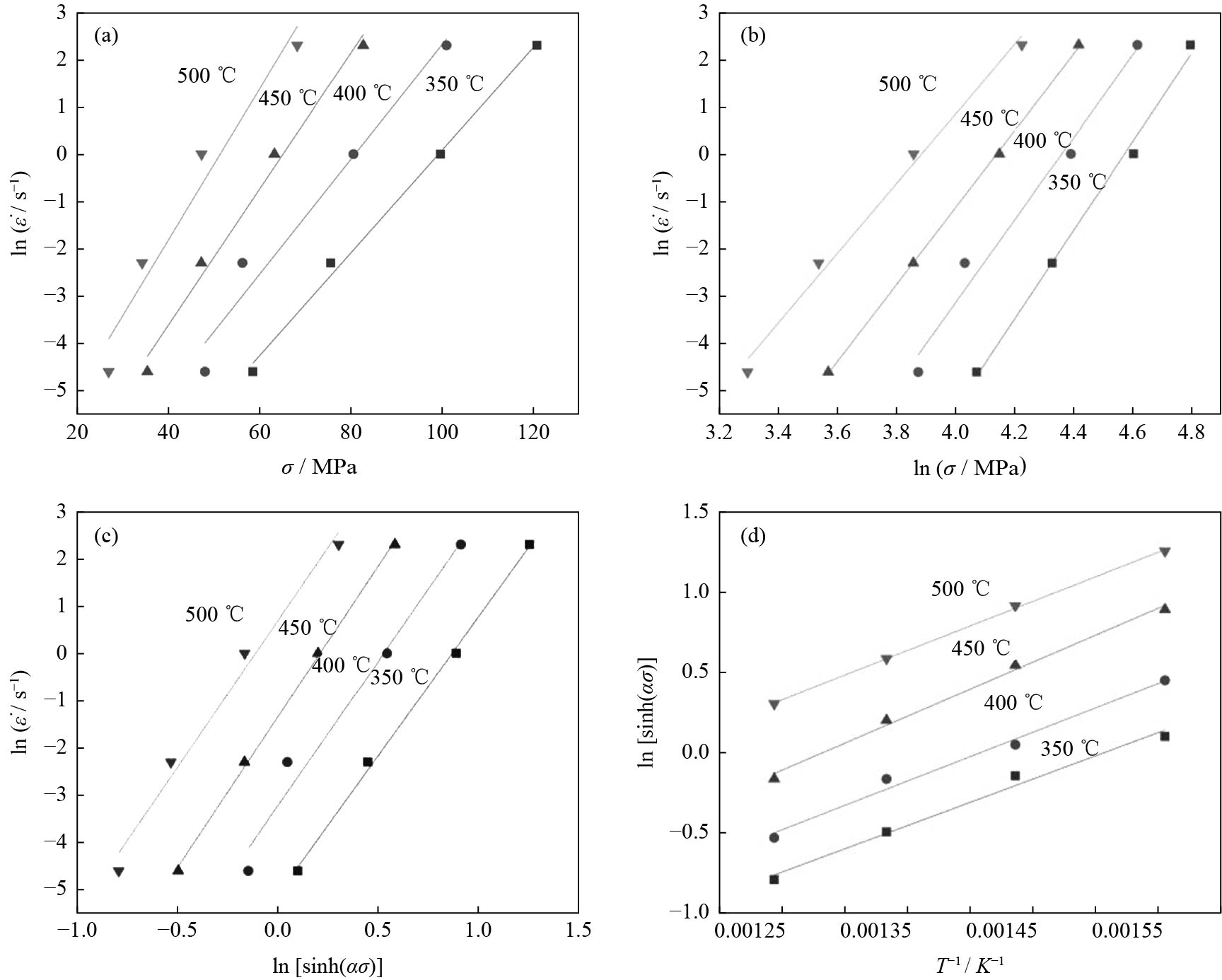
图 3 真应变为0.1时应力、应变速率和温度关系:(a)ln
$ \dot \varepsilon $ -σ;(b)ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -lnσ;(c)ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -ln[sinh(ασ)];(d)ln[sinh(ασ)]-1/TFigure 3. Relationship between stress, stress rate, and temperature at true strain of 0.1: (a) ln
$ \dot \varepsilon $ -σ; (b) ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -lnσ; (c) ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -ln[sinh(ασ)]; (d) ln[sinh(ασ)]-1/T图 4 真应变为0.3时应力、应变速率和温度关系:(a)ln
$ \dot \varepsilon $ -σ;(b)ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -lnσ;(c)ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -ln[sinh(ασ)];(d)ln[sinh(ασ)]-1/TFigure 4. Relationship between stress, stress rate, and temperature at true strain of 0.3: (a) ln
$ \dot \varepsilon $ -σ; (b) ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -lnσ; (c) ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -ln[sinh(ασ)]; (d) ln[sinh(ασ)]-1/T图 5 真应变为0.5时应力、应变速率和温度关系:(a)ln
$ \dot \varepsilon $ -σ;(b)ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -lnσ;(c)ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -ln[sinh(ασ)];(d)ln[sinh(ασ)]-1/TFigure 5. Relationship between stress, stress rate, and temperature at true strain of 0.5: (a) ln
$ \dot \varepsilon $ -σ; (b) ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -lnσ; (c) ln$ \dot \varepsilon $ -ln[sinh(ασ)]; (d) ln[sinh(ασ)]-1/T表 1 不同应变量时材料常数计算结果
Table 1 Calculation results of the material constants at the different strains
ε β n1 n M α / MPa−1 lnA Q / (kJ·mol−1) 0.1 0.134408 8.973713 6.656257 2882.649 0.015438 24.52115 157.288 0.3 0.133552 8.387507 6.149667 3088.224 0.016263 24.97749 157.903 0.5 0.134407 8.973715 6.601892 2865.210 0.015245 24.62439 157.273 -
[1] 郑晶, 贾志华, 马光. 碳化硅颗粒增强铝基复合材料的研究进展. 钛工业进展, 2006, 23(6): 13 Zheng J, Jia Z H, Ma G. Progress in research of SiC particle reinforced Al-based composites. Titanium Ind Prog, 2006, 23(6): 13
[2] 王莹, 刘向东. 碳化硅颗粒增强铝基复合材料的现状及发展趋势. 铸造设备研究, 2003(3): 20 Wang Y, Liu X D. Present status and development trend of SiCp/Al composites. Foundry Equip Technol, 2003(3): 20
[3] 刘洋, 李雷, 历长云, 等. 高强高导铝−石墨烯复合材料研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2021, 39(4): 358 Liu Y, Li L, Li C Y, et al. Research progress on high-strength and high-conductivity Al-graphene composites. Powder Metall Technol, 2021, 39(4): 358
[4] 周艳华. 碳化硅颗粒增强铝基复合材料主要制备技术. 工具技术, 2017, 51(4): 7 Zhou Y H. Main preparation processes and research status of SiC particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Tool Eng, 2017, 51(4): 7
[5] 王明, 郭丹, 丁成富, 等. 碳化硅颗粒增强铝基复合材料加工研究进展. 机电产品开发与创新, 2016, 29(6): 76 Wang M, Guo D, Ding C F, et al. Research progress of machining of SiC particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Dev Innov Mach Electr Prod, 2016, 29(6): 76
[6] 魏少华, 聂俊辉, 刘彦强, 等. 等温锻造对碳化硅颗粒增强铝基复合材料断裂韧性的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(11): 3464 Wei S H, Nie J H, Liu Y Q, et al. Effect of isothermal forging on fracture toughness of SiC particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2017, 46(11): 3464
[7] Gui M C, Wang D B, Wu J J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of cast (Al-Si)/SiCp composites produced by liquid and semisolid double stirring process. Mater Sci Technol, 2013, 16(5): 556
[8] Cui Y, Geng L, Yao Z K, et al. A new advance in the development of high-performance SiCp/Al composite. J Mater Sci Technol, 1997(3): 227
[9] 武高辉, 匡泽洋. 装备升级换代背景下金属基复合材料的发展机遇和挑战. 中国工程科学, 2020, 22(2): 79 DOI: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2020.02.012 Wu G H, Kuang Z Y. Opportunities and challenges for metal matrix composites in the context of equipment upgrading. Strategic Study CAE, 2020, 22(2): 79 DOI: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2020.02.012
[10] Rawal S P. Metal-matrix composites for space applications. JOM, 2001, 53(4): 14 DOI: 10.1007/s11837-001-0139-z
[11] Miracle D B. Metal matrix composites from science to technological significance. Compos Sci Technol, 2005, 65(15-16): 2526 DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2005.05.027
[12] Shao J C, Xiao B L, Wang Q Z, et al. Constitutive flow behavior and hot workability of powder metallurgy processed 20vol.% SiCp/2024Al composite. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527(29): 7865
[13] Rajamuthamil selvan M, Ramanathan S. Effect of silicon carbide volume fraction on the hot workability of 7075 aluminium-based metal-matrix composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol, 2013, 67(5-8): 1711 DOI: 10.1007/s00170-012-4604-3
[14] Ghazani M S, Eghbali B. Strain hardening behavior, strain rate sensitivity and hot deformation maps of AISI 321 austenitic stainless steel. Int J Miner Metall Mater, 2021, 28(11): 1799 DOI: 10.1007/s12613-020-2163-4
[15] Sivakesavam O, Prasad Y V R K. Hot deformation behaviour of as-cast Mg-2Zn-1Mn alloy in compression: a study with processing map. Mater Sci Eng A, 2003, 362(1-2): 118 DOI: 10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00296-X
[16] Xiao B L, Huang Z Z, Ma K, et al. Research on hot deformation behaviors of discontinuously reinforced aluminum composites. Acta Metall Sin, 2019, 55(1): 59
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: