-
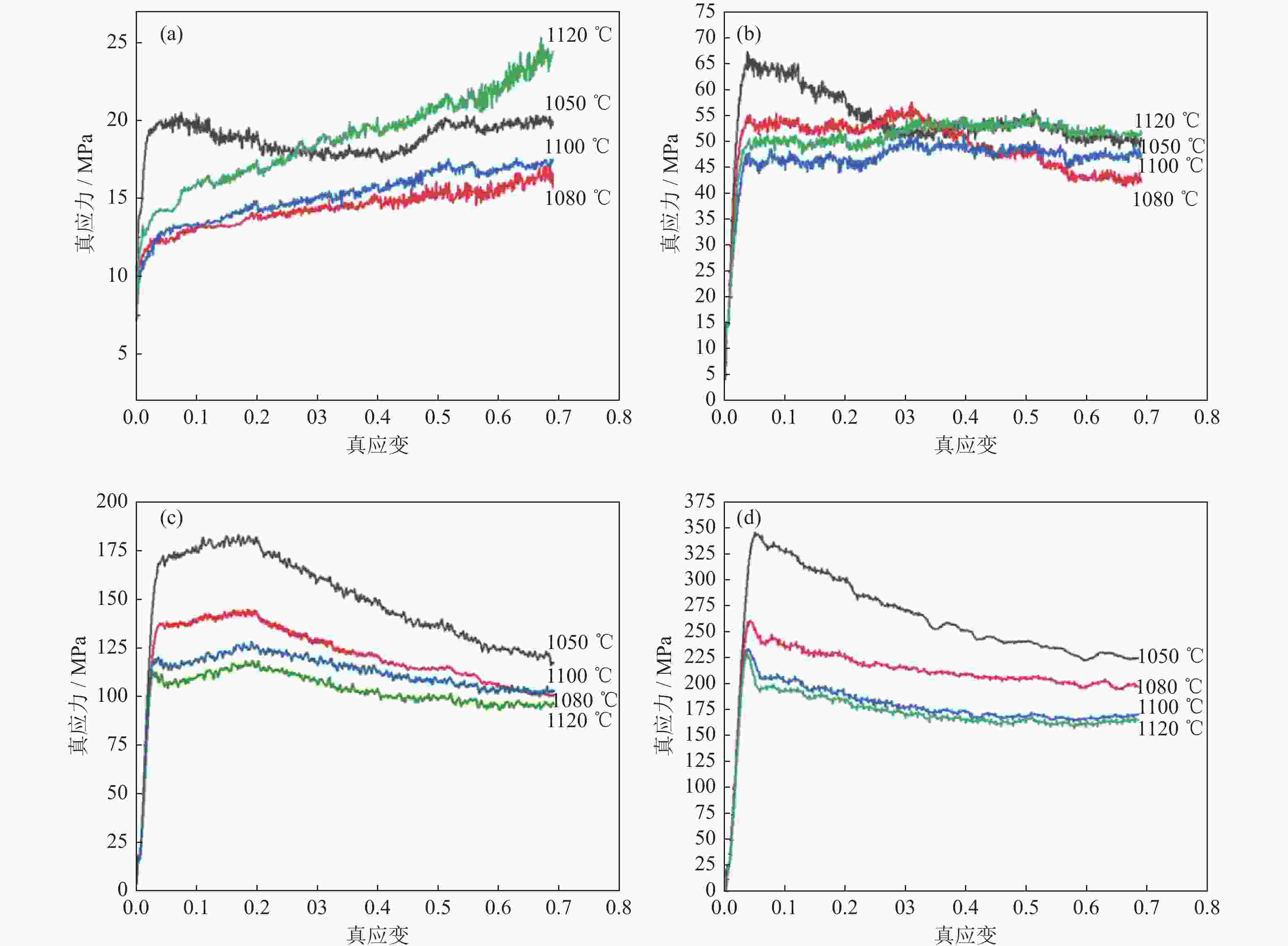
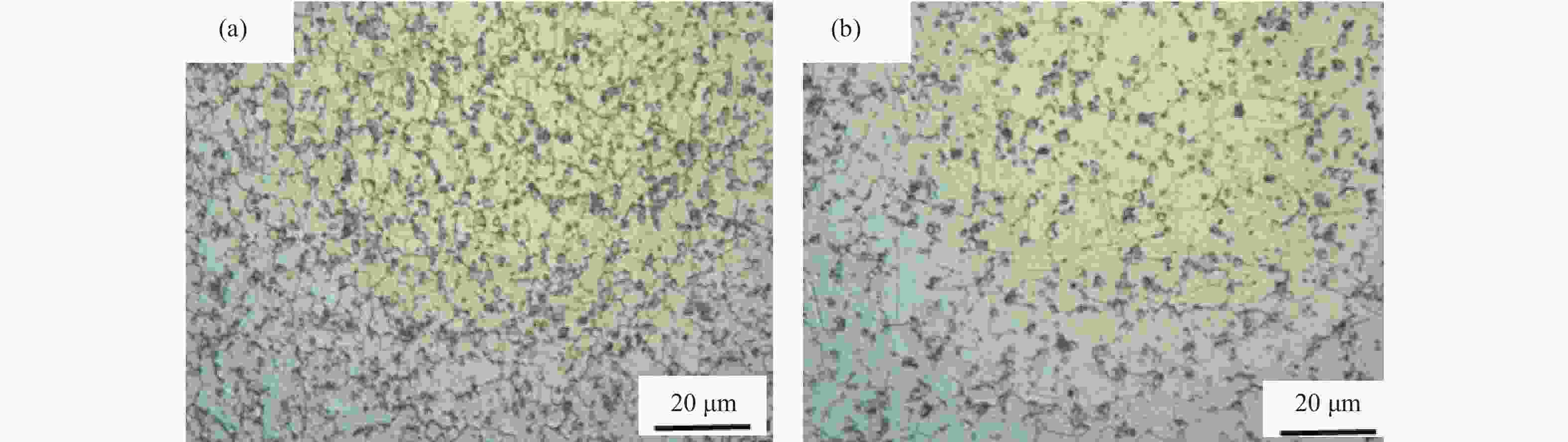
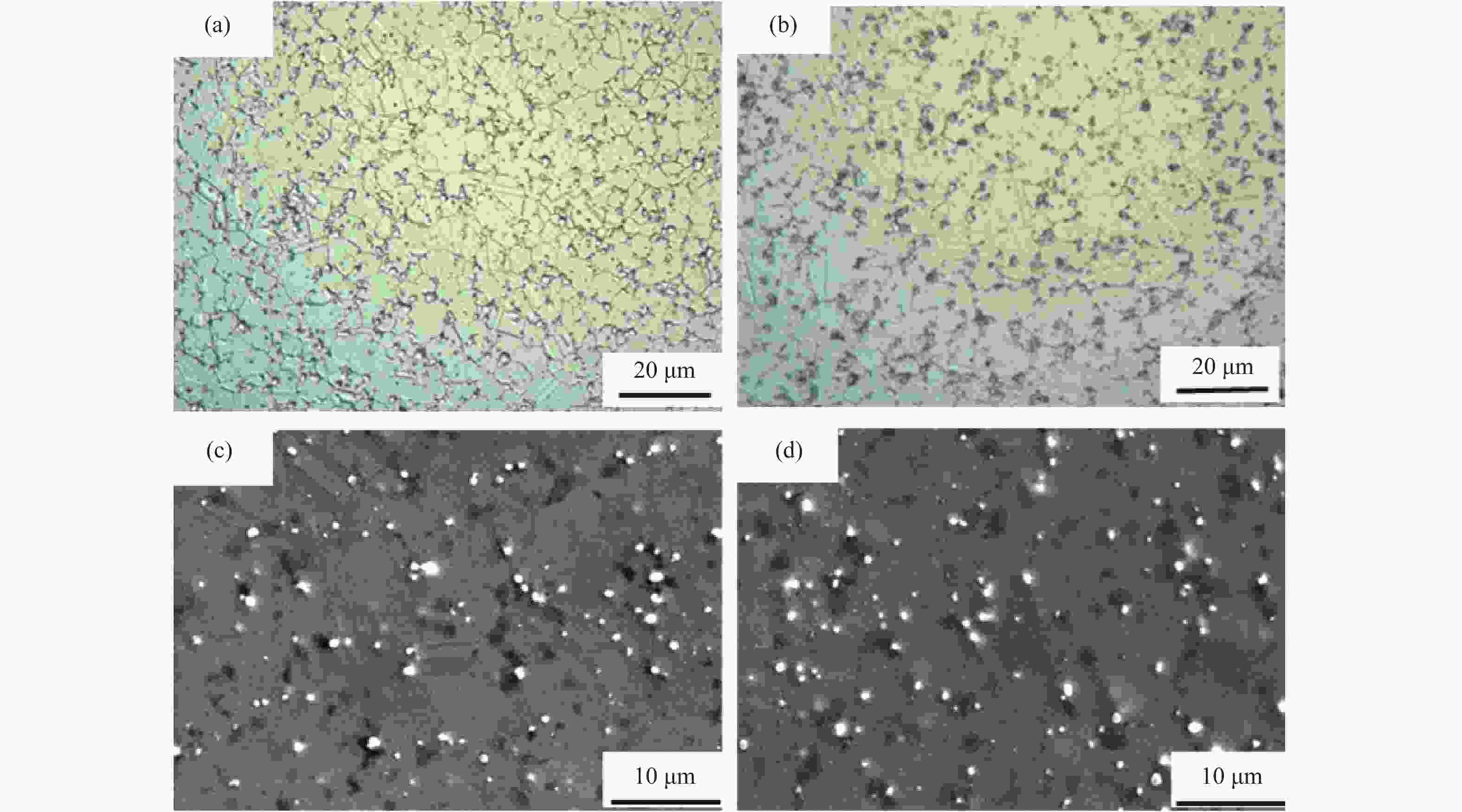
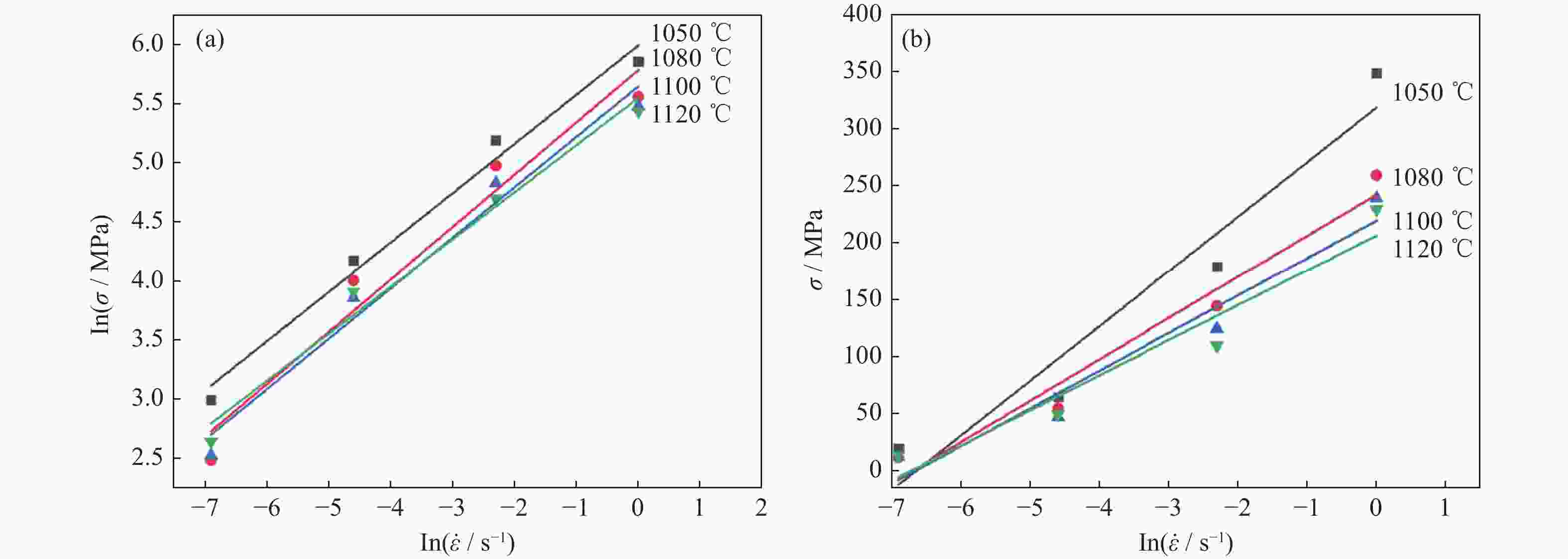
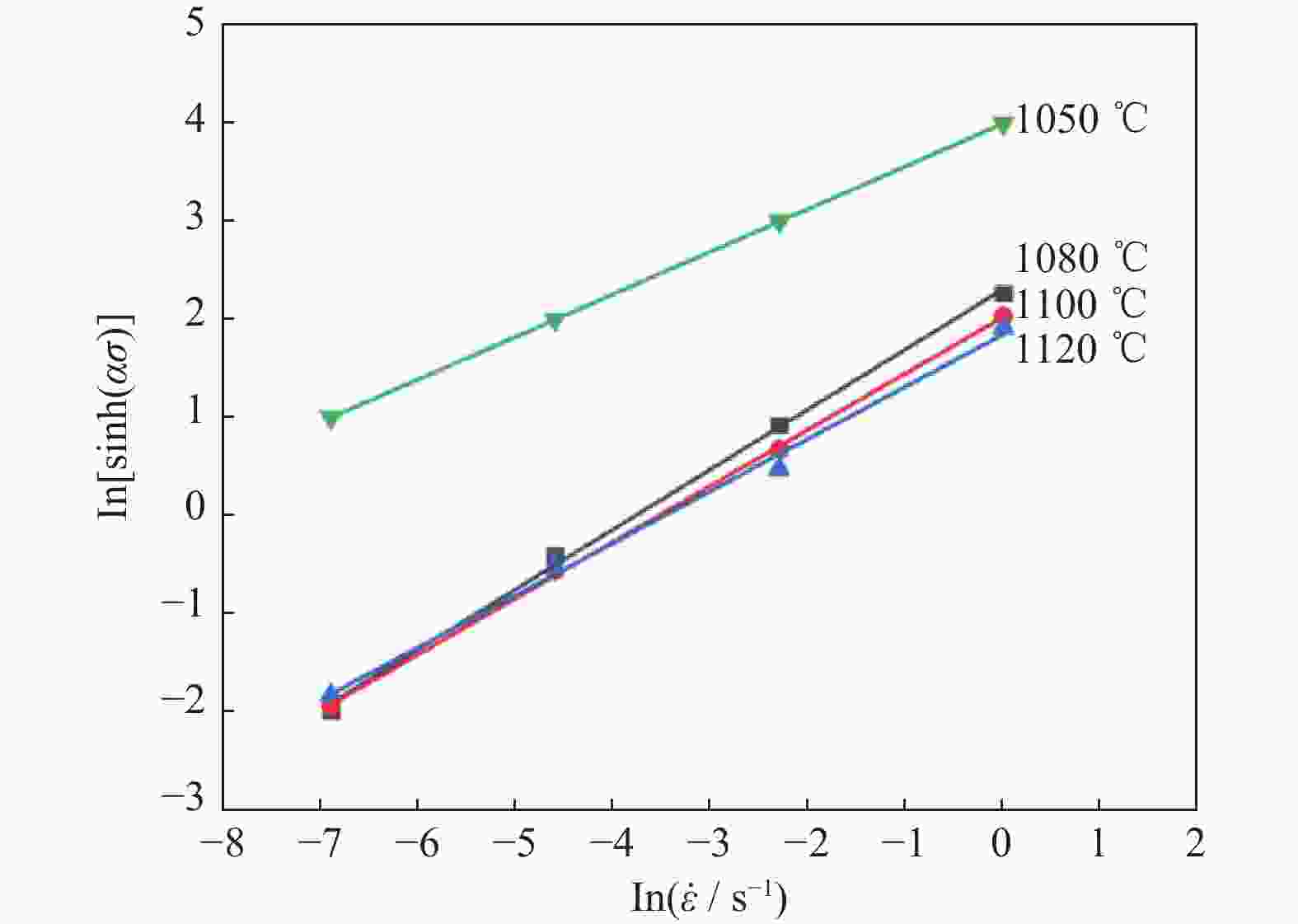
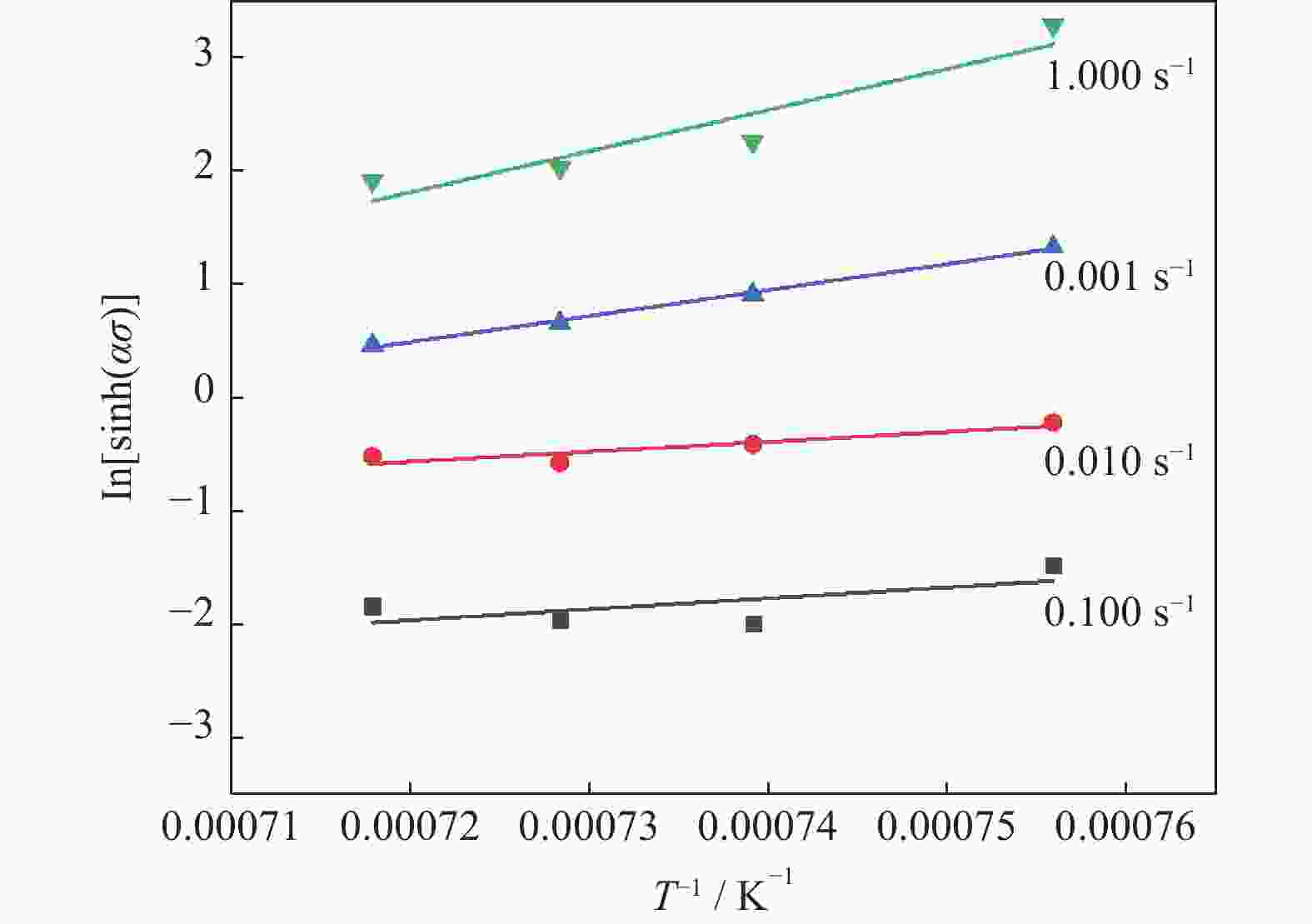
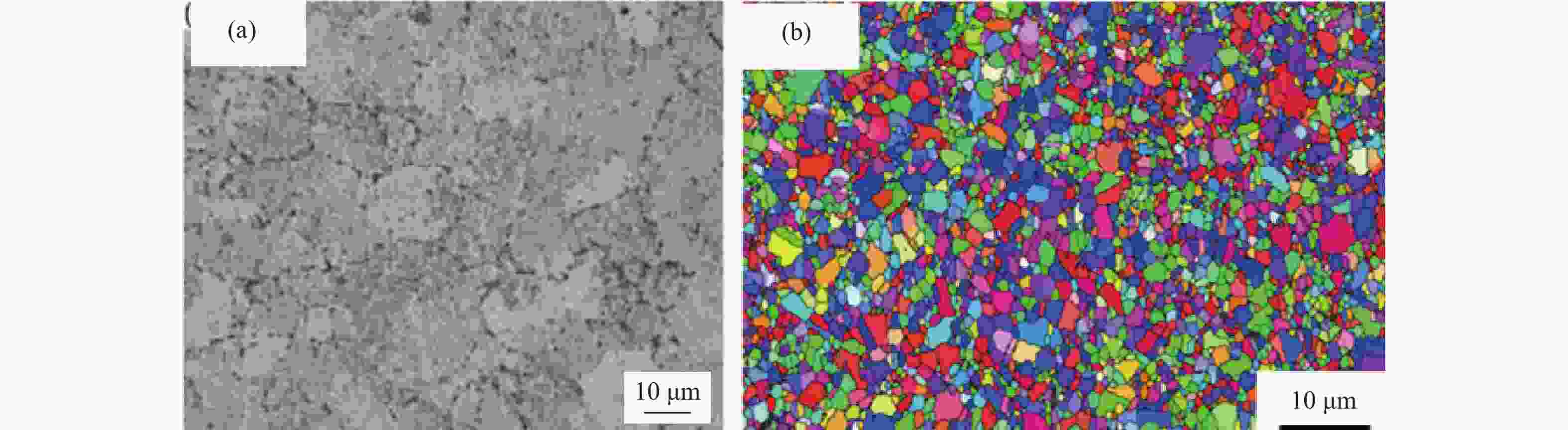
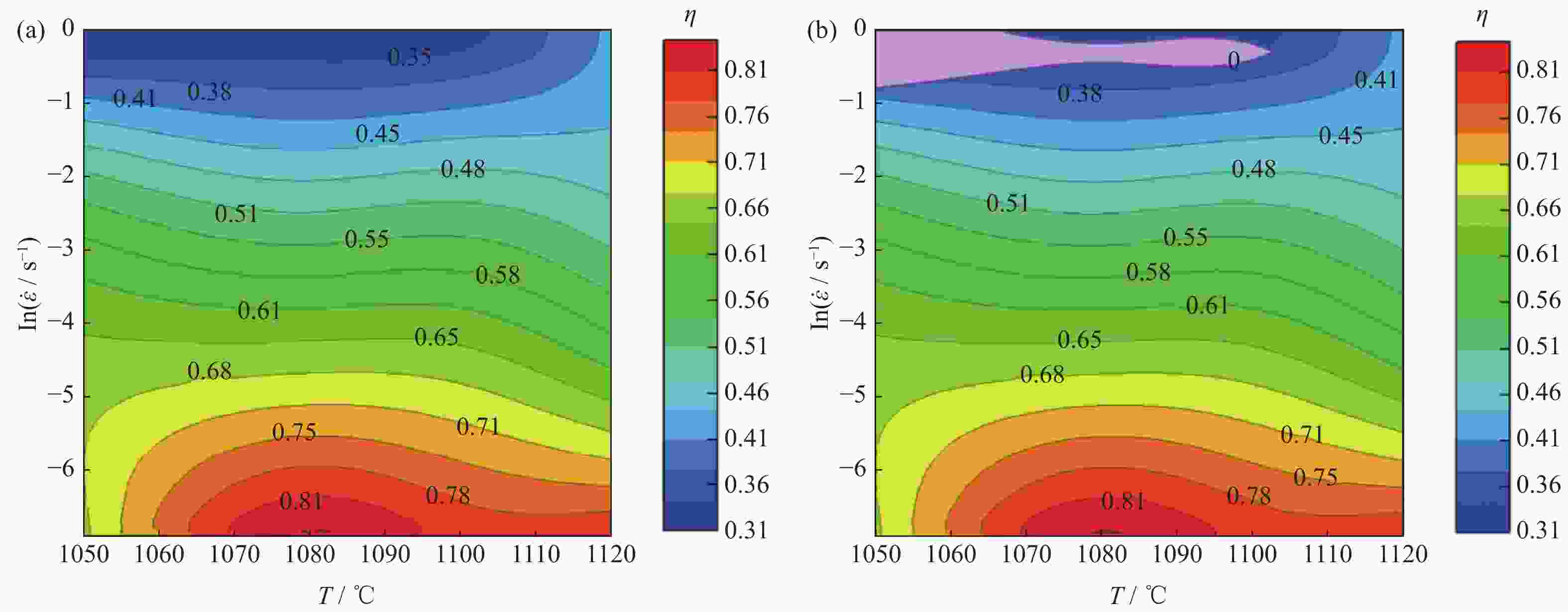
摘要: 采用Gleeble 3800D热模拟压缩试验机系统地研究了挤压态FGH95合金在变形温度1050~1120 ℃、应变速率0.001~1.000 s−1条件下的热压缩变形行为,获得了挤压态FGH95合金的应力应变曲线,建立了挤压态FGH95合金的本构方程,并基于动态材料模型,绘制了合金的热加工图。结果表明,挤压态FGH95合金的热变形本构方程高温材料常数分别为热变形激活能Q=300.925 kJ·mol−1,常数α=0.01139 MPa−1,参数n=1.86。相较于热等静压态,挤压态合金激活能下降50%以上。根据热加工图能量耗散效率并结合微观组织分析,找到了挤压态FGH95合金的加工安全区和失稳区,提出了热加工工艺参数范围:应变速率为0.010~0.100 s−1,变形温度为1050~1120 ℃。Abstract: The thermal compression deformation behaviors of the hot extruded (HEX) FGH95 alloys were investigated systematically using the Gleeble 3800D thermal-mechanical simulator in the strain rate of 0.001~1.000 s−1 at the deformation temperature range of 1050~1120 ℃. The constitutive equations of the hot extruded FGH95 alloys were derived from the stress-strain curves obtained in the isothermal compression tests. Furthermore, the hot processing maps were established based on the dynamic models. In the results, the corresponding material constants of the constitutive equation are determined as Q=300.925 kJ·mol−1, α=0.01139 MPa−1, and n=1.86. Compared with the hot isostatic pressing (HIP) alloys, the activation energy of the hot extruded FGH95 alloys is declined by more than 50%. According to the energy dissipation efficiency and the microstructure analysis of the hot extruded FGH95 alloys, the processing safety zone and instability zone are identified during the hot extrusion process. Ultimately, the optimal processing conditions of the FGH95 alloys are proposed as the strain rate of 0.010~0.100 s−1 and the deformation temperature of 1050~1120 ℃.
-
C Zr Cr Co W Mo Al Ti Nb B Ni 0.060 0.045 13.100 8.100 3.600 3.600 3.500 2.600 3.400 0.010 余量 表 2 热挤压态FGH95高温合金本构方程模型参数
Table 2. Calculated constants in the constitutive equation for the hot extruded FGH95 superalloys
Q / (kJ·mol−1) α / MPa−1 n A / s−1 300.925 0.01139 1.86 1.12×1010 -
[1] Wang W Y, He F, Zou J W. The application and development of P/M superalloys. Aviat Maint Eng, 2002(6): 26汪武洋, 何峰, 邹金文. 粉末高温合金的应用与发展. 航空工程与维修, 2002(6): 26 [2] Zou X M, Feng Y F, Zeng W H, et al. Effect of aging treatment on the behavior of room temperature tensile of P/M superalloys used for inertia friction welding joints. Power Metall Technol, 2021, 39(1): 8周晓明, 冯业飞, 曾维虎, 等. 时效处理对粉末高温合金惯性摩擦焊接头室温拉伸行为的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2021, 39(1): 8 [3] Yang J, Liu G X, Zhang J, et al. Microstructure and failure mechanism of FGH96 solid-state diffusion bonding interface. Power Metall Technol, 2021, 39(4): 9杨杰, 刘光旭, 张晶, 等. FGH96合金固相扩散连接界面组织与失效机制. 粉末冶金技术, 2021, 39(4): 9 [4] Wang X Q, Zhang M C, Luo J P, et al. Thermal simulation test of AA-FGH95 superalloy. J Aeron Mater, 2016, 36(6): 9王旭青, 张敏聪, 罗俊鹏, 等. 氩气雾化FGH95合金的热模拟实验. 航空材料学报, 2016, 36(6): 9 [5] Wang X Q, Luo X J. Study on microstructure and properties of complicate shape disk of FGH95 PM superalloy. J Mater Eng, 2009(Suppl 1): 61王旭青, 罗学军. 复杂形状FGH95粉末盘形件固溶处理组织及性能研究. 材料工程, 2009(增刊1): 61 [6] Guo W M, Zhao M H, Dong J X, et al. Research and development in FGH95 P/M nickel based superalloy. J Mech Eng, 2013, 49(18): 38国为民, 赵明汉, 董建新, 等. FGH95镍基粉末高温合金的研究和展望 机械工程学报, 2013, 49(18): 38 [7] Tian S G, Xie J, Zhou X M, et al. Microstructure and creep behavior of FGH95 nickel-base superalloy. Mater Sci Eng A, 2011, 528: 2076 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.11.038 [8] Liu M X, W H, Wang Y, et al. Hot deformation behavior and hot processing map of annealed FGH96 superalloy. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2019, 29(11): 2561刘敏学, 吴宏, 王岩, 等. 退火态FGH96合金的热变形行为及热加工图. 中国有色金属学报, 2019, 29(11): 2561 [9] Chen L, Si J Y, Liu S H, et al. Hot deformation behavior and hot processing map of extruded FGH4096 superalloy. Mater Rev, 2019, 33(12): 2047陈龙, 司家勇, 刘松浩, 等. 挤压态FGH4096合金的热变形行为及热加工图, 材料导报, 2019, 33(12): 2047 [10] Li H Z, Yang L, Wang Y, et al. Hot working behavior of hot-extruded Ni–Co–Cr-based powder metallurgy superalloy. J Mater Eng, 2020, 48(9): 115李慧中, 杨雷, 王岩, 等. 热挤压态Ni–Co–Cr基粉末高温合金热加工行为. 材料工程, 2020, 48(9): 115 [11] Wu H, Liu M X, Wang Y, et al. Experimental study and numerical simulation of dynamic recrystallization for a FGH96 superalloy during isothermal compression. J Mater Res Technol, 2020, 9(3): 5090 doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.03.026 [12] Gajalappa Y, Krishnaiah A, Basanth Kumar K, et al. Flow behaviour kinetics of Inconel 600 superalloy under hot deformation using gleeble 3800. Mater Today Proceed, 2021, 45(6): 5320 [13] Li Y J, Zhang Y, Chen Z Y, et al. Hot deformation behavior and dynamic recrystallization of GH690 nickel-based superalloy. J Alloys Compd, 2020, 847: 156507 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156507 [14] Tan G, Li H Z, Wang Y, et al. Effect of Zener-Hollomon parameter on microstructure evolution of a HEXed PM nickel-based superalloy. J Alloys Compd, 2021, 874: 159889 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159889 [15] Tan G, Li H Z, Wang Y, et al. Hot working characteristics of HEXed PM nickel-based superalloy during hot compression. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2020, 30(10): 2709 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(20)65414-0 [16] Wang C Y, Dong Y P, Wang S Y, et al. Study on hot deformation behavior and microstructure characteristics of extruded Ni-base powder metallurgy superalloy. Forg Stamp Technol, 2014, 39(4): 126王超渊, 东赟鹏, 王淑云, 等. 挤压态镍基粉末高温合金热变形行为与组织研究. 锻压技术, 2014, 39(4): 126 [17] Li H Z, Lei Y, Tan G, et al. Thermal deformation and dynamic recrystallization of a novel HEXed PM nickel-based superalloy. Mater Charact, 2020, 163: 110285 doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2020.110285 [18] He G, Liu F, Huang L, et al. Microstructure evolutions and nucleation mechanisms of dynamic recrystallization of a powder metallurgy Ni-based superalloy during hot compression. Mater Sci Eng A, 2016, 677: 496 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2016.09.083 [19] Huang G C, Liu G Q, Feng M N, et al. Effect of solution heat treatment on microstructure and properties of FGH95 alloy. Trans Mater Heat Treat, 2017, 38(7): 71黄国超, 刘国权, 冯敏楠, 等. 固溶热处理工艺对FGH95合金组织和性能的影响. 材料热处理学报, 2017, 38(7): 71 [20] McQueen H J, Ryan N D. Constitutive analysis in hot working. Mater Sci Eng A, 2002, 322: 43 doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01117-0 [21] Na Y S, Yeom J T, Park N K, et al. Simulation of microstructure for alloy 718 blade forging using 3D FEM simulation. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 693(4): 1076 -



 下载:
下载: