Effect of quenching temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of S590 powder metallurgy high speed steels
-
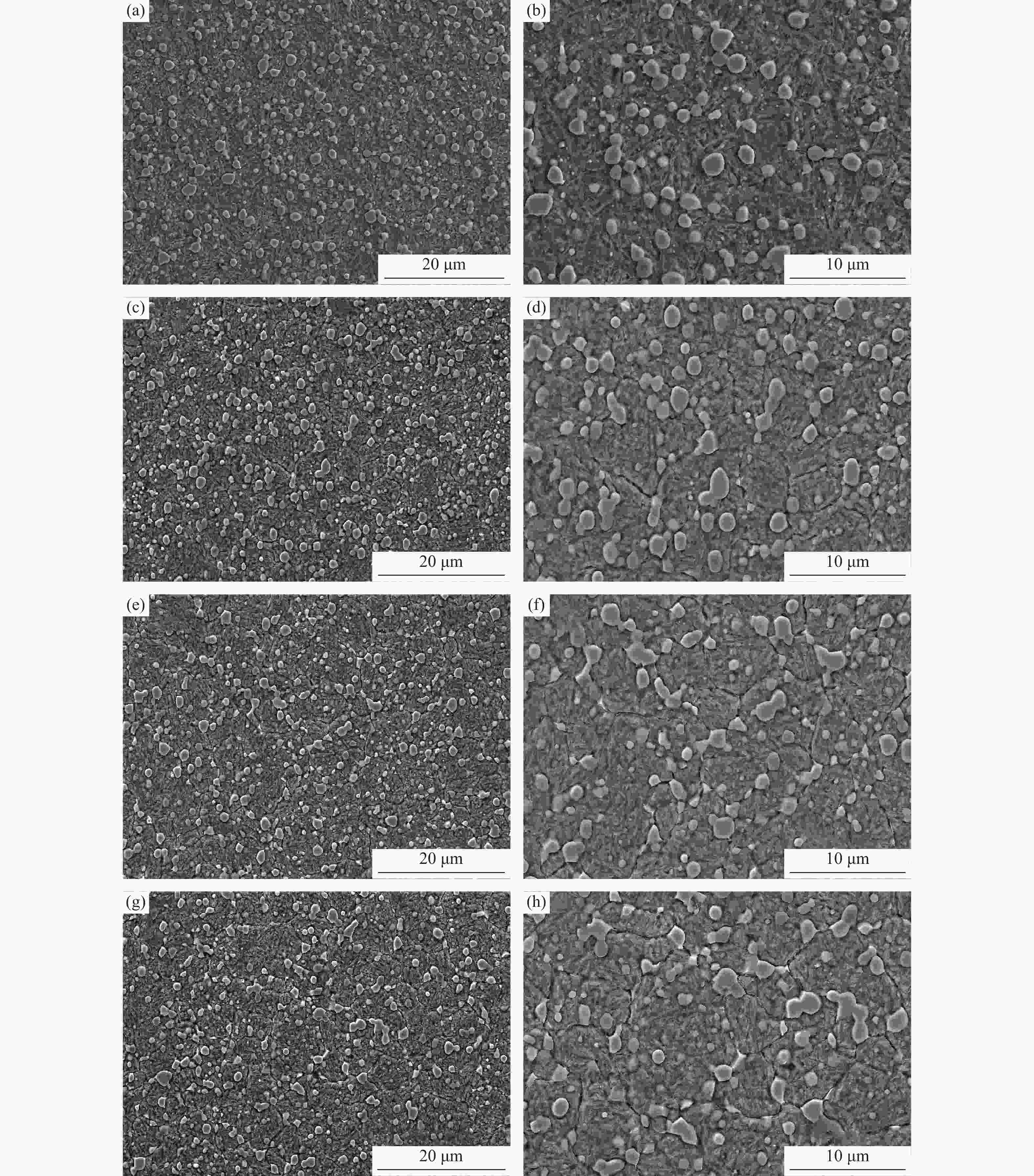
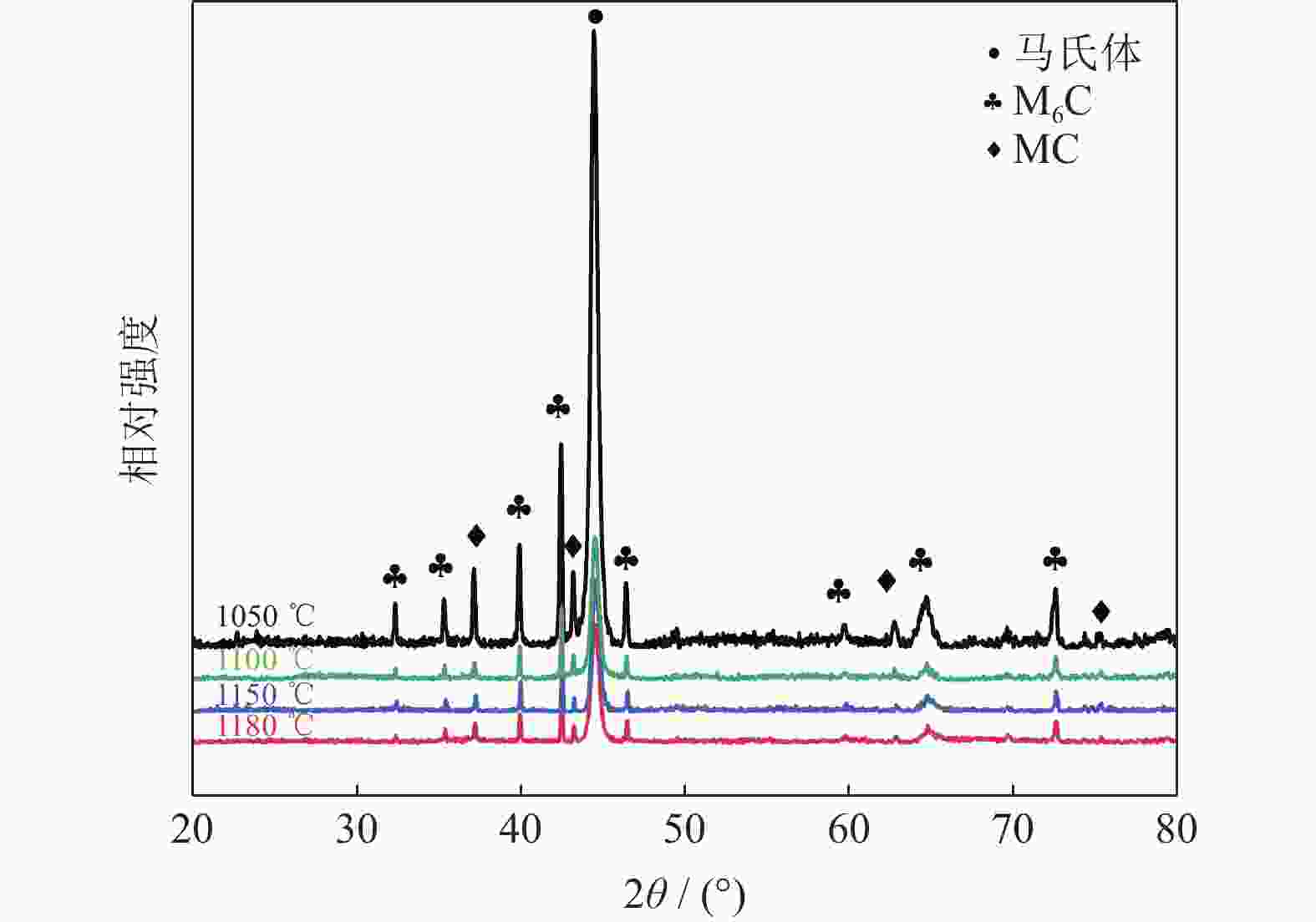
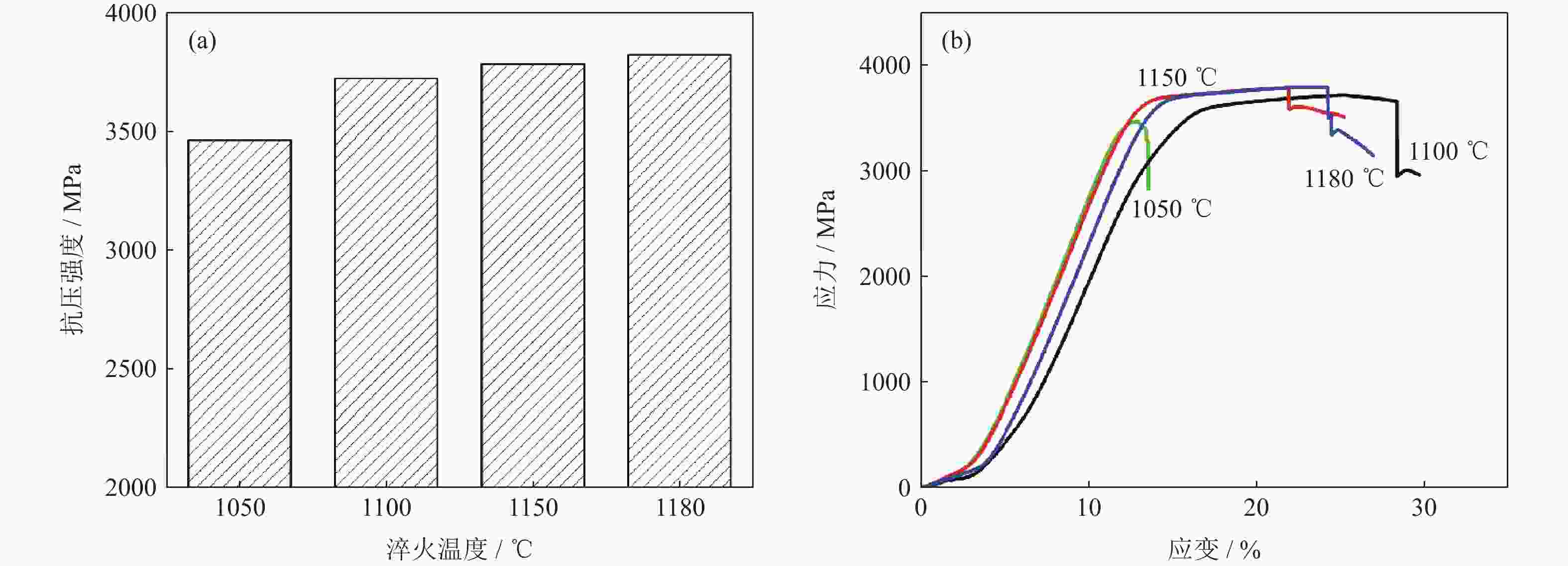
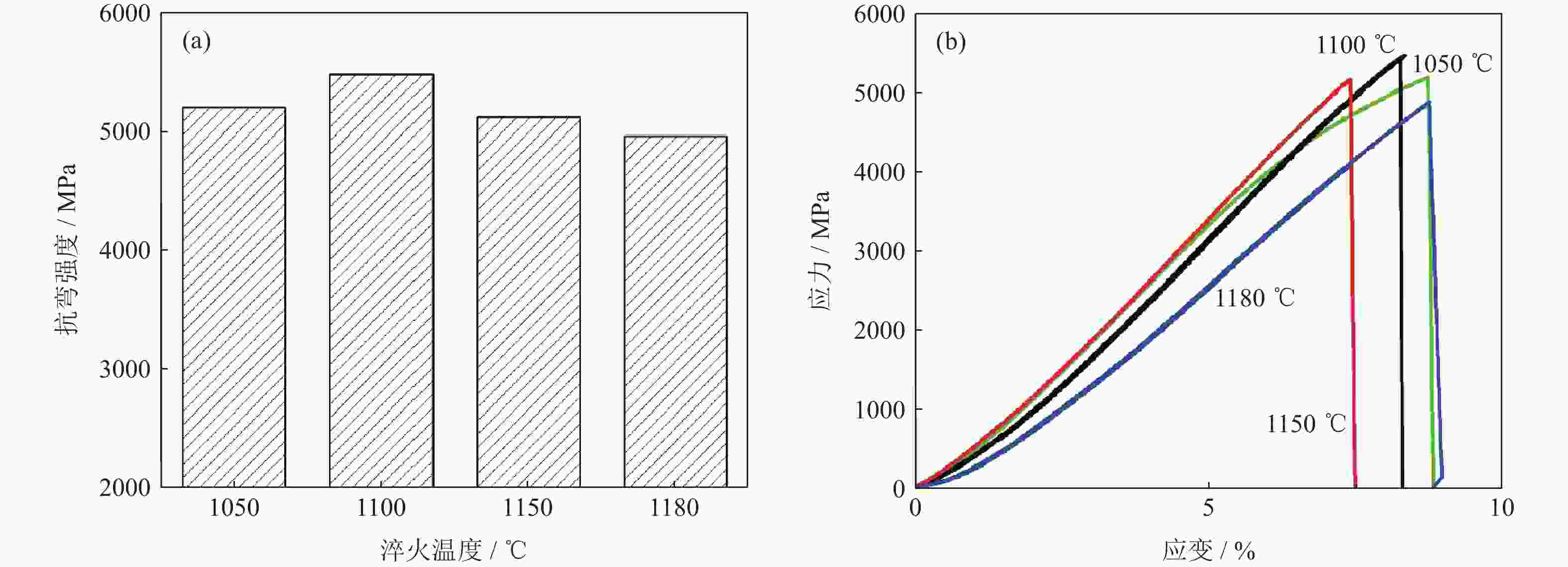
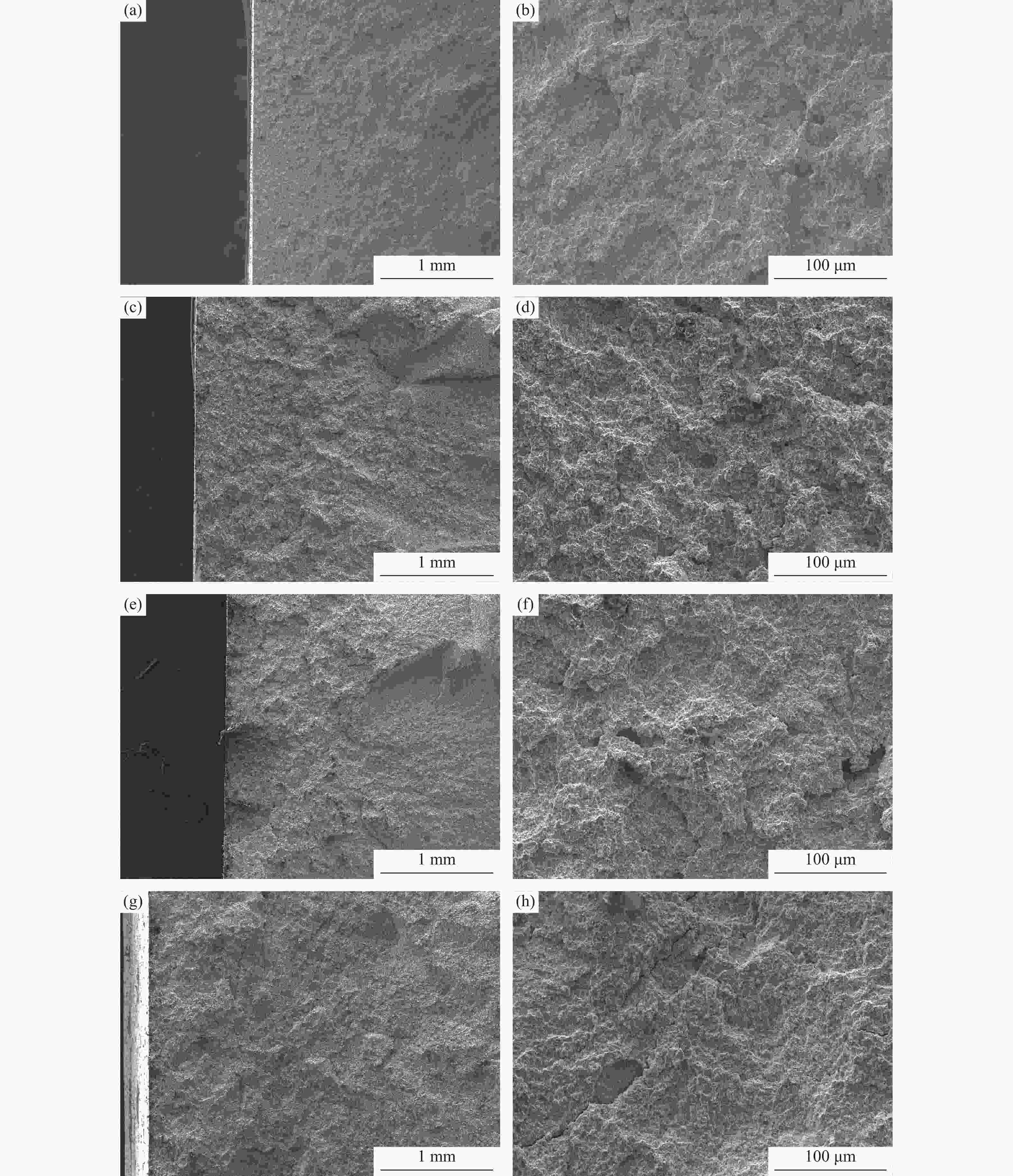
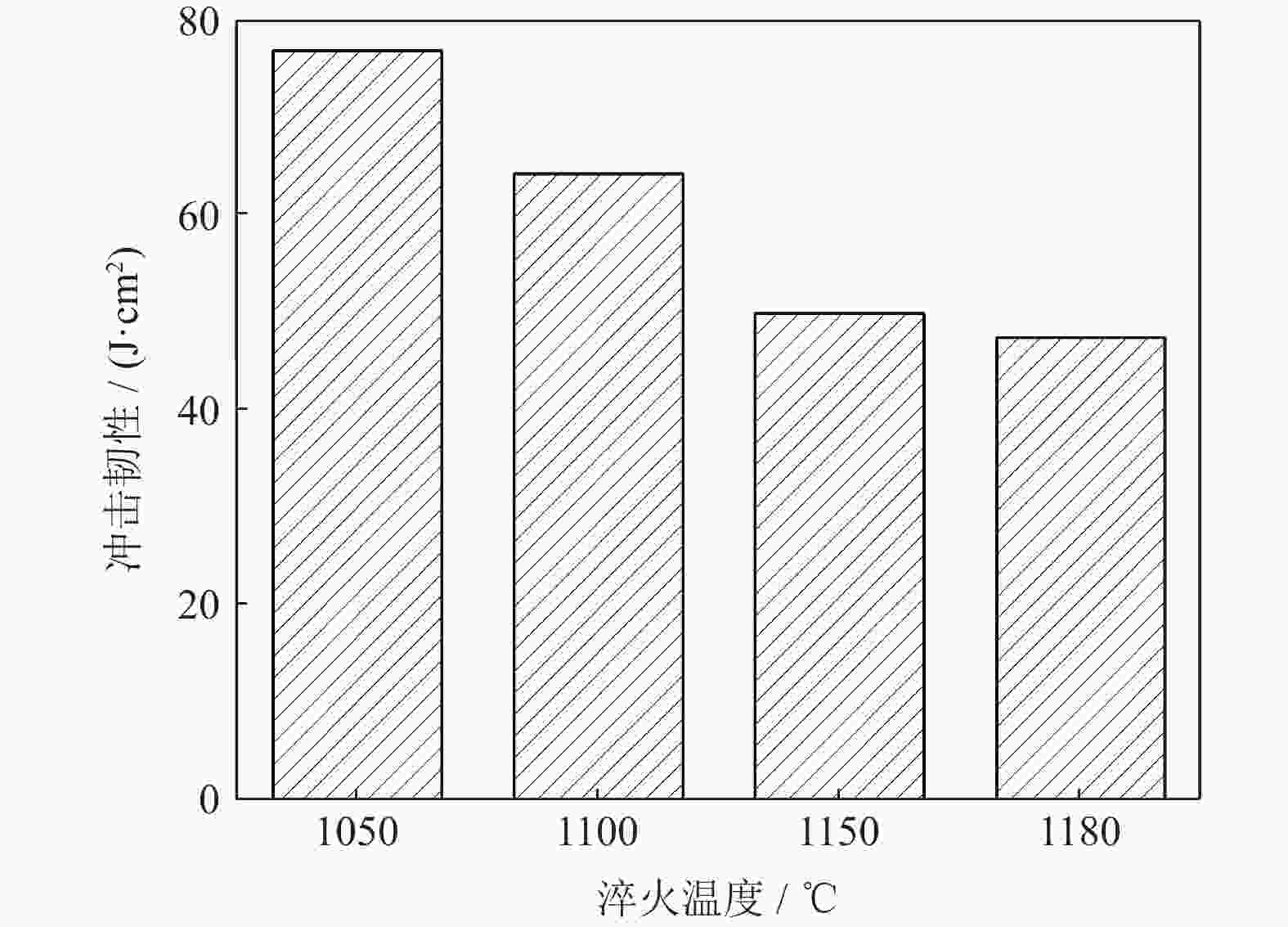
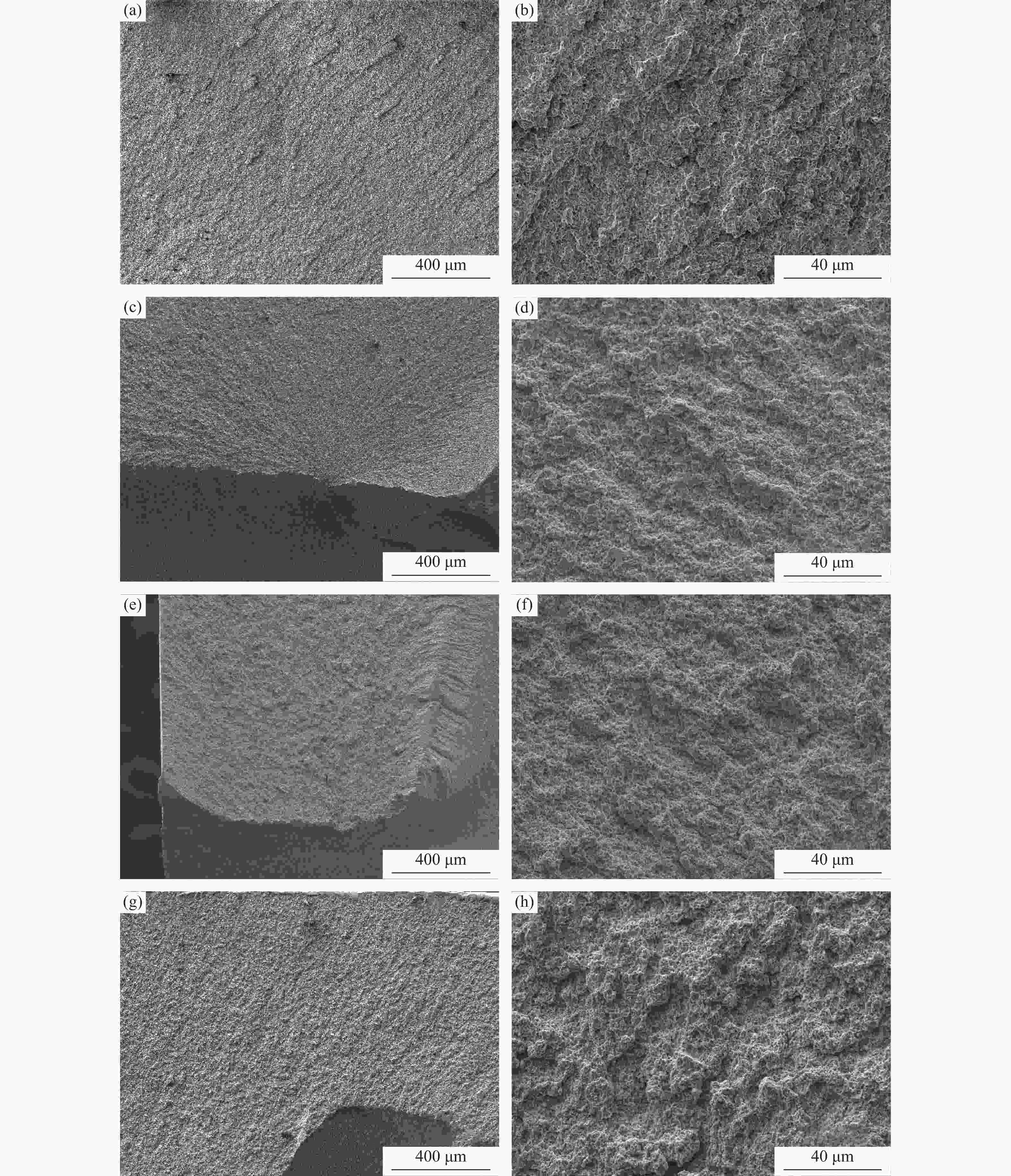
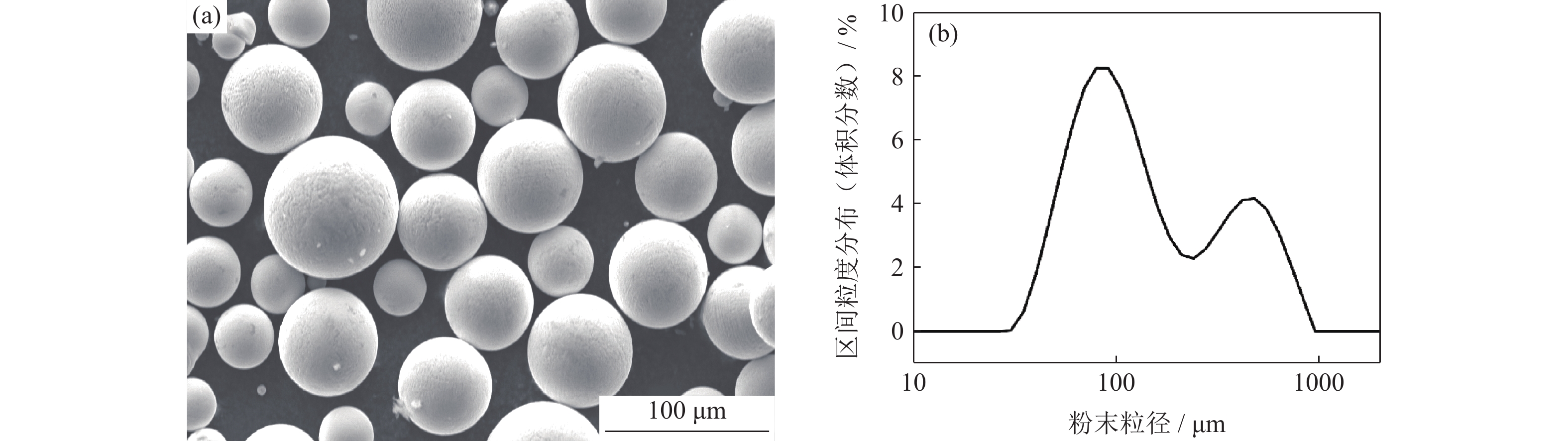
摘要: 采用等离子旋转电极雾化和热等静压法制备S590粉末冶金高速钢,分别在1050、1100、1150和1180 ℃进行淬火热处理,并经过一次550 ℃回火(1 h),一次−196 ℃深冷处理(4 h)和两次550 ℃回火(1 h),研究不同淬火温度对S590粉末冶金高速钢微观组织和力学性能的影响。结果表明:热处理后S590高速钢微观组织主要包括马氏体、M6C型碳化物和MC型碳化物。随淬火温度升高,碳化物逐渐溶入基体中,数量减少,基体晶粒尺寸变大。高速钢硬度和抗压强度随淬火温度升高呈上升趋势,1180 ℃淬火试样经后续热处理后,硬度可达HRC 67.8,抗压强度为3827 MPa;抗弯强度随淬火温度的升高先上升后下降,冲击韧性随淬火温度升高而下降,1100 ℃淬火试样抗弯强度达到最高,为5473 MPa;1050 ℃淬火试样冲击韧性最高,为76.9 J·cm−2。综合考虑显微组织和力学性能,S590粉末冶金高速钢的最优淬火温度为1100 ℃。Abstract: S590 powder metallurgy high speed steels (S590 HSS) were prepared by plasma rotating electrode atomization and hot isostatic pressing. The S590 HSS samples were quenched at 1050, 1100, 1150, and 1180 ℃, respectively, followed by the tempering at 550 ℃ for 1 h (once), −196 ℃ cryogenic treatment for 4 h (once), and tempering at 550 ℃ for 1 h (twice). The effect of quenching temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of S590 HSS was studied. The results show that, the microstructure of S590 HSS after the heat treatments mainly consists of martensite, M6C carbides, and MC carbides. With the increase of quenching temperature, the carbides gradually dissolve into the matrix, the carbide content decreases, and the matrix grain size increases. The hardness and compressive strength of S590 HSS increase with the increase of quenching temperature. After quenching at 1180 ℃ and the subsequent heat treatments, the hardness of S590 HSS is up to HRC 67.8, and the compressive strength is 3827 MPa. With the increase of quenching temperature, the bending strength first increases and then decreases, and the impact toughness decreases. The bending strength of the samples quenched at 1100 ℃ reaches the highest as 5473 MPa. The impact toughness of the samples quenched at 1050 ℃ reaches the highest as 76.9 J·cm−2. Considering the microstructure and mechanical properties, the optimum quenching temperature of S590 HSS is 1100 ℃.
-
表 1 S590粉末冶金高速钢化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of S590 HSS
% C Si Mn Cr Mo W V Co Fe 1.28 0.60 0.29 4.10 4.88 6.18 2.99 8.17 余量 表 2 不同热处理工艺下S590粉末高速钢的硬度
Table 2. Hardness of S590 HSS with the different heat treatment processes
温度 / ℃ 状态 硬度,HRC 1050 一次回火 64.2 1100 67.5 1150 67.4 1180 67.8 1050 深冷 64.1 1100 67.1 1150 67.5 1180 68.0 1050 二次回火 63.5 1100 67.1 1150 67.9 1180 68.0 1050 三次回火 63.2 1100 66.9 1150 66.8 1180 67.8 -
[1] Wu L Z. Developments and challenges of China high-speed steel industry over last decade // Advanced Steels: The Recent Scenario in Steel Science and Technology. Berlin and Beijing: Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg and Metallurgical Industry Press, 2011: 453 [2] Godec M, Večko Pirtovšek T, Šetina Batič B, et al. Surface and bulk carbide transformations in high-speed steel. Sci Rep, 2015, 5(1): 16202 doi: 10.1038/srep16202 [3] Peng H L, Hu L, Ngai T W, et al. Effects of austenitizing temperature on microstructure and mechanical property of a 4-GPa-grade PM high-speed steel. Mater Sci Eng A, 2018, 719: 21 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.02.010 [4] Wu W D, Xiong X, Liu R T, et al. Effects of carbon content on microstructure and properties of M2 high speed steel prepared by elemental powder method. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2019, 24(3): 273 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2019.03.011伍文灯, 熊翔, 刘如铁, 等. 碳含量对元素粉末法制备M2高速钢组织与性能的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2019, 24(3): 273 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2019.03.011 [5] Xin L X, Liu L X. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high speed steel cutting tools. Foundry Technol, 2018, 39(3): 665辛李霞, 刘丽霞. 高速钢刀具组织和力学性能研究. 铸造技术, 2018, 39(3): 665 [6] Chen Z M, Zhang Q K, Xiao Y F, et al. Effect of hot rotary swaging deformation on microstructure and properties of ASP30 grade powder metallurgical high speed steels strengthened by TiCN. Powder Metall Technol, 2022, 40(4): 376陈泽民, 张乾坤, 肖逸锋, 等. 热旋锻变形对TiCN强化ASP30粉末冶金高速钢的组织及性能研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2022, 40(4): 376 [7] Li X M, Ye J, Zhu Z C. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of S390 powder metallurgy high speed steel. Mater Mech Eng, 2013, 37(12): 42李响妹, 叶俭, 朱祖昌. 热处理工艺对S390粉末高速钢组织和性能的影响. 机械工程材料, 2013, 37(12): 42 [8] Veerababu R, Prasad K S, Karamched P S, et al. Austenite stability and M2C carbide decomposition in experimental secondary hardening ultra-high strength steels during high temperature austenitizing treatments. Mater Charact, 2018, 144: 191 doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2018.07.013 [9] Luo Y W, Guo H J, Sun X L. Precipitation behaviors of carbides in M42 high speed steel during ESR and forging. Iron Steel, 2017, 52(7): 68罗乙娲, 郭汉杰, 孙晓林. M42高速钢电渣重熔及锻造退火后碳化物的析出. 钢铁, 2017, 52(7): 68 [10] Damon J, Schüßler P, Mühl F, et al. Short-time induction heat treatment of high speed steel AISI M2: laboratory proof of concept and application-related component tests. Mater Des, 2023, 230: 111991 doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2023.111991 [11] Hou H, Qi L, Zhao Y H. Effect of austenitizing temperature on the mechanical properties of high-strength maraging steel. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, 587: 209 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.08.070 [12] Sato K. Improving the Toughness of Ultrahigh Strength Steel [Dissertation]. Berkeley: University of California, 2002 [13] Wang Y J, Chu S J, Mao B, et al. Microstructure, residual stress, and mechanical property evolution of a spray-formed vanadium-modified high-speed steel processed by post-heat treatment. J Mater Res Technol, 2022, 18: 1521 doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.03.053 [14] Jovičević-Klug P, Puš G, Jovičević-Klug M, et al. Influence of heat treatment parameters on effectiveness of deep cryogenic treatment on properties of high-speed steels. Mater Sci Eng A, 2022, 829: 142157 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2021.142157 [15] Fantineli D G, Parcianello C T, Rosendo T S, et al. Effect of heat and cryogenic treatment on wear and toughness of HSS AISI M2. J Mater Res Technol, 2020, 9(6): 12354 doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.090 [16] Liu B W, Lu X, Pi Z Q, et al. Effect of quenching temperature on transformation mechanism of carbides of M42. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2017, 46(3): 829刘博文, 路新, 皮自强, 等. M42热处理中淬火温度对碳化物转变机制的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(3): 829 [17] Hao Y F, Cheng G G, Xie Y. Precipitation behavior of carbides in W4Mo3Cr4VSi high-speed steel. Iron Steel, 2018, 53(8): 73郝勇飞, 成国光, 谢有. 高速钢W4Mo3Cr4VSi中碳化物的析出行为. 钢铁, 2018, 53(8): 73 [18] Li Q, Guo B, Wu H, et al. Effects of quenching temperature on the microstructure and properties of M4 powder metallurgy high speed steel. Powder Metall Technol, 2020, 38(3): 183李强, 郭彪, 吴辉, 等. 淬火温度对M4粉末高速钢组织和性能的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2020, 38(3): 183 [19] Shen Y, Cao R, Yan Y J, et al. Effect of carbides on fracture mechanism of powder metallurgy tool steels. Powder Metall Technol, 2023, 41(4): 296沈漪, 曹睿, 闫英杰, 等. 碳化物对粉末冶金刀具钢断裂机理的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2023, 41(4): 296 -



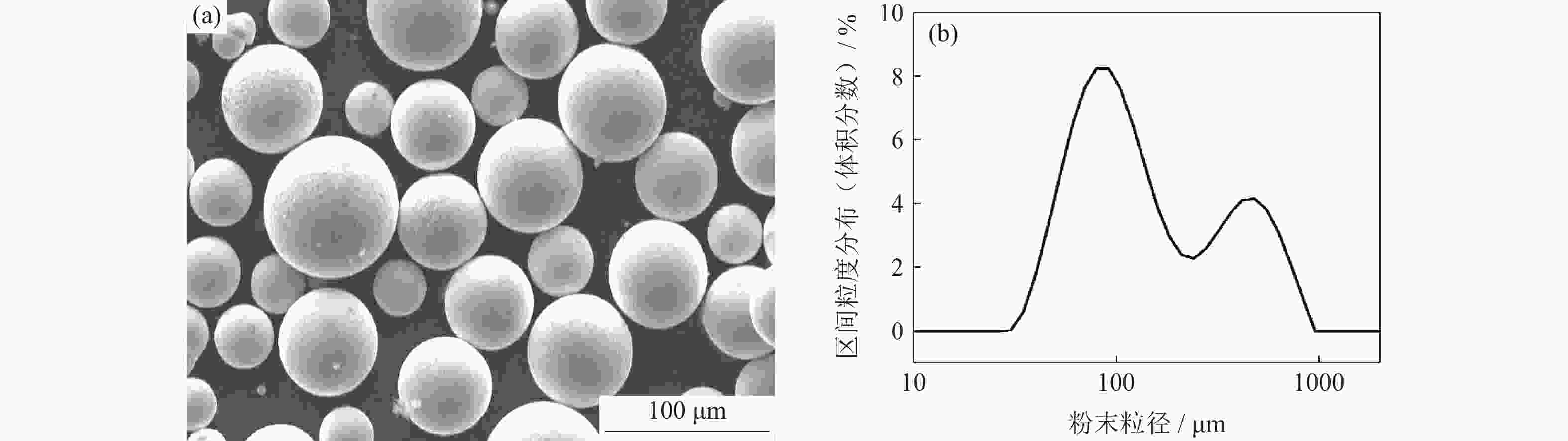
 下载:
下载: