-
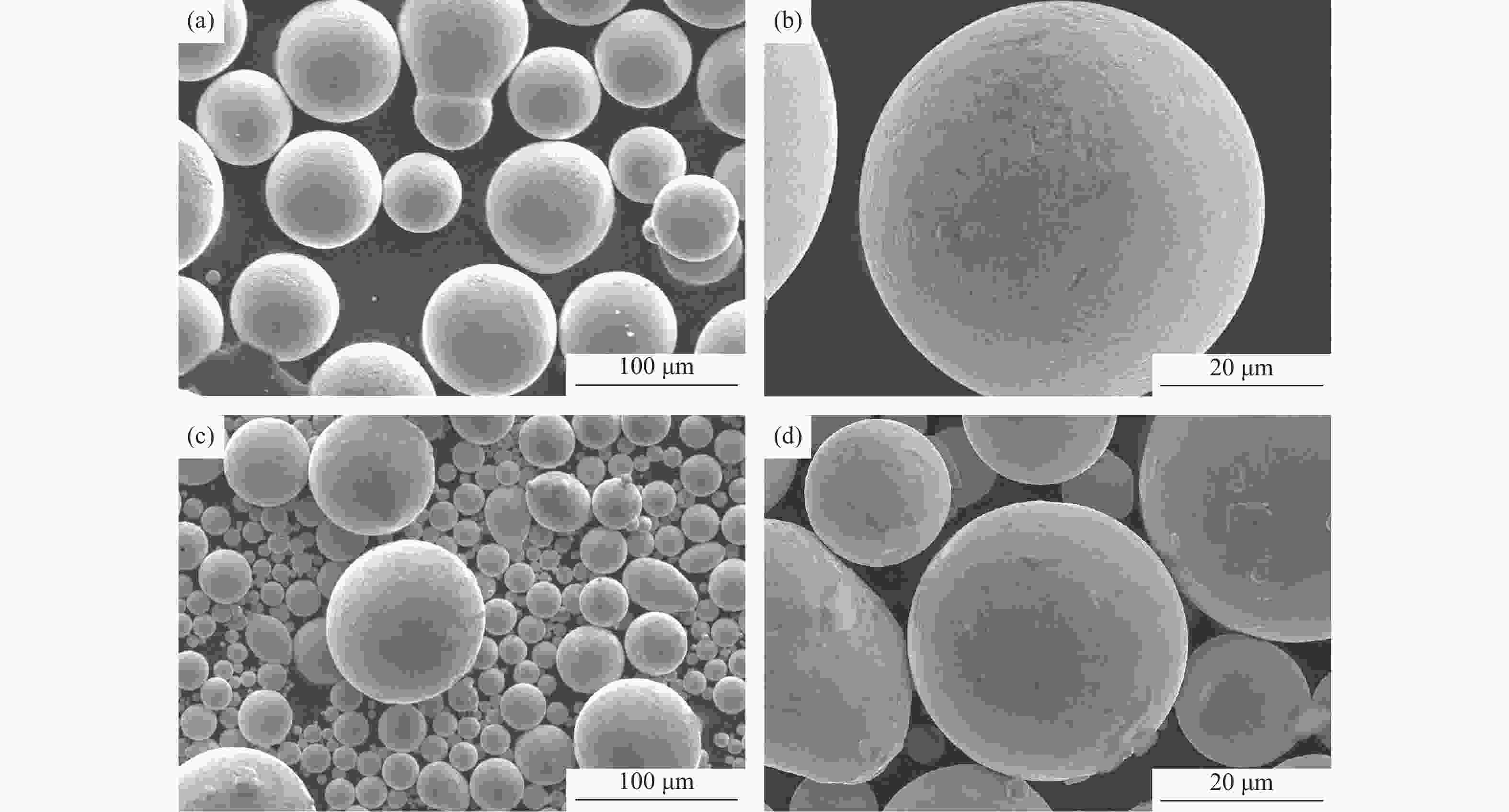
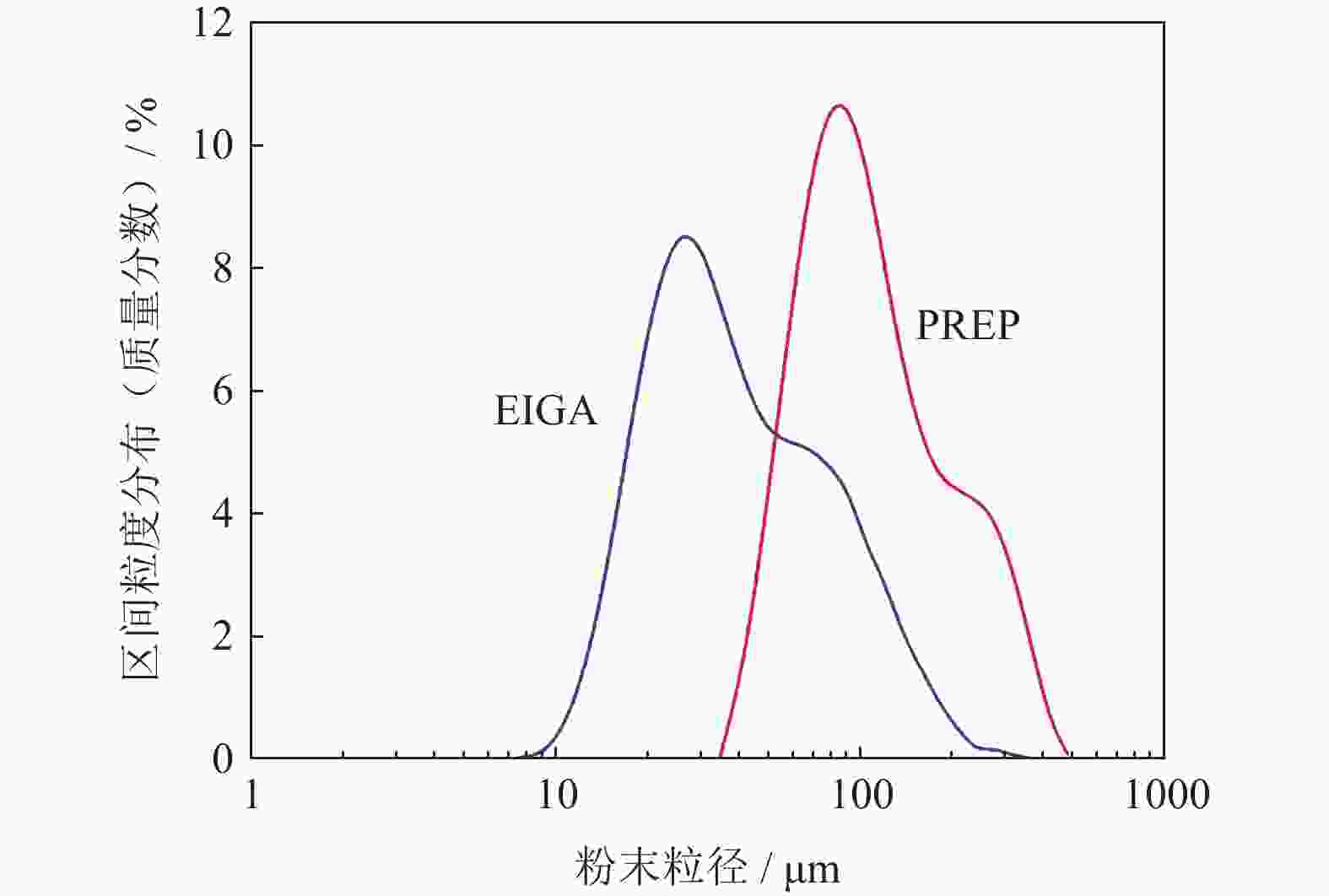
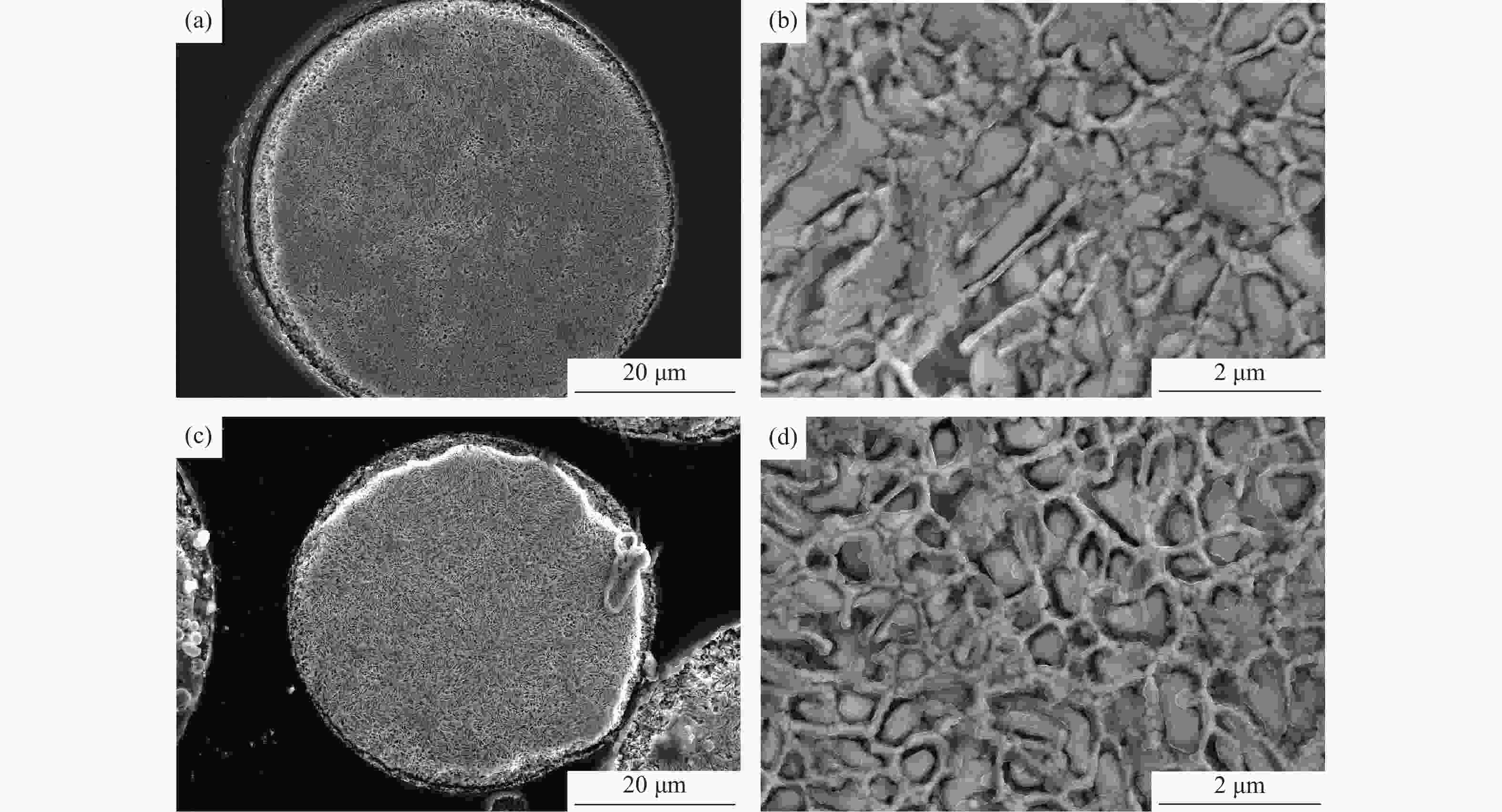
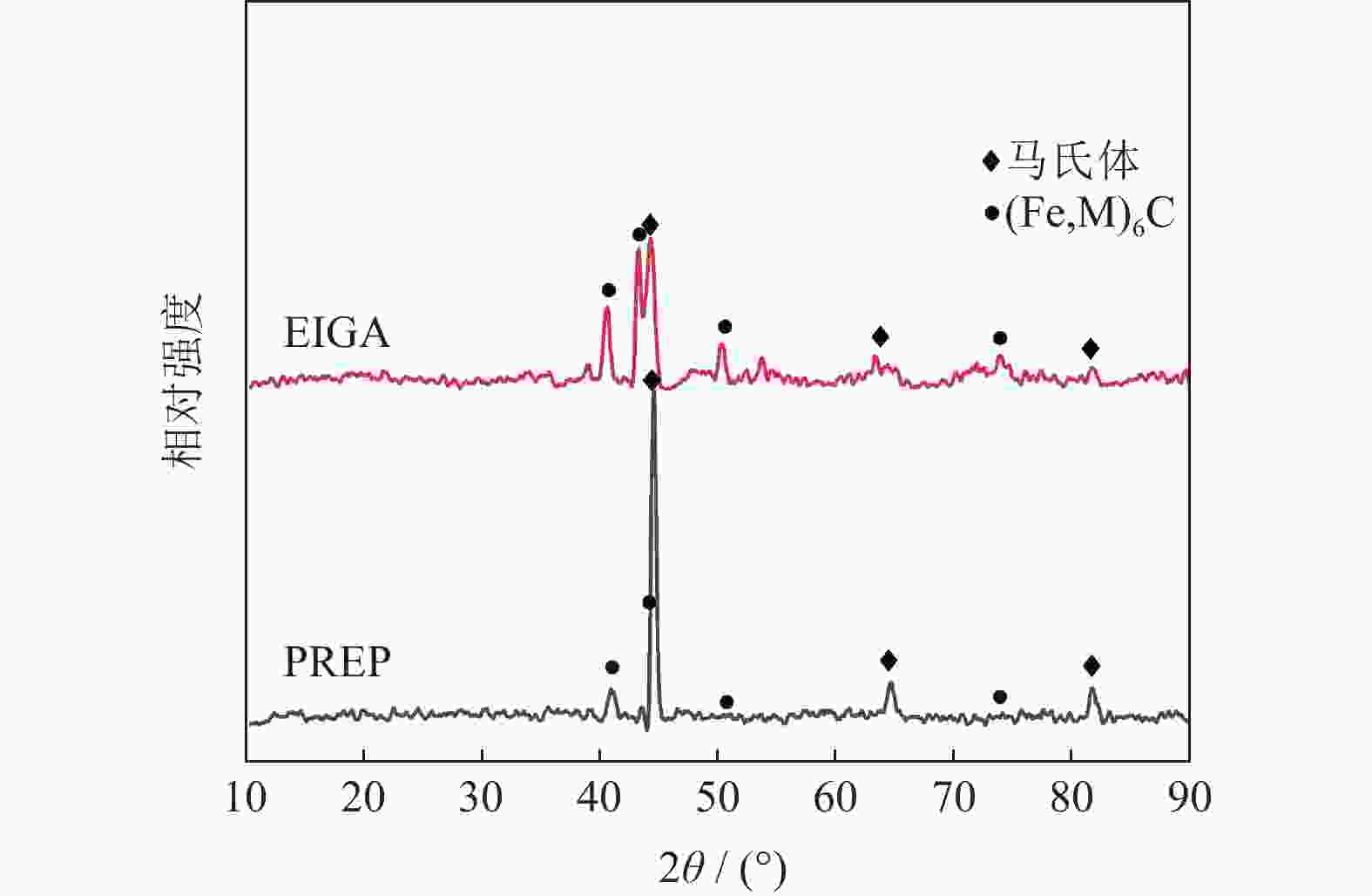
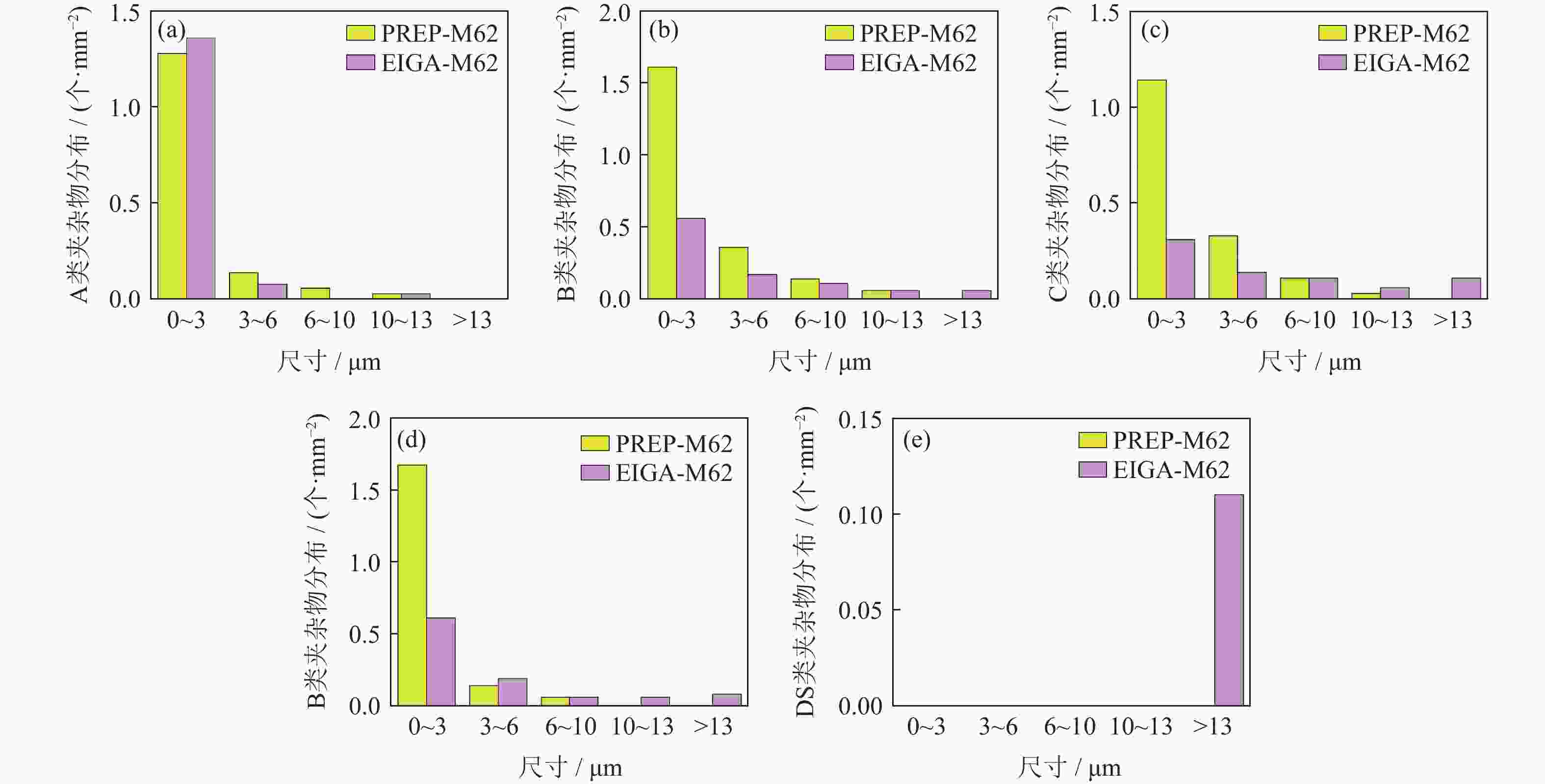
摘要: 采用电极感应熔炼气雾化法(electrode induction melting gas atomization,EIGA)和等离子旋转电极雾化法(plasma rotating electrode process,PREP)分别制备出了高纯度M62轴承钢粉末,利用激光粒度分析仪、氧氮分析仪、扫描电子显微镜对M62轴承钢粉末的粒径分布、氮氧含量、微观形貌进行了对比分析。结果表明:两种粉末都以球形粉为主,其中PREP制备的粉末(M62-PREP)球形度更高,而EIGA制备的粉末(M62-EIGA)中卫星粉和不规则粉末的比例较多;M62-PREP粉末的中值粒度(D50)为108.11 μm,明显高于M62-EIGA粉末的中值粒度(D50=38.68 μm)。两种粉末成分分布均匀,无明显元素偏析,其中M62-EIGA粉末颗粒内部的晶粒更细,两种粉末都具有良好的流动性。预合金电极棒、M62-PREP粉末、M62-EIGA粉末的N含量(质量分数)分别为0.0070%、0.0072%、0.0068%,N元素的含量变化不大;M62-PREP粉末的O含量(质量分数)由预合金电极棒的0.0008%增加到了0.0035%,而M62-EIGA粉末的O含量增加到了0.0089%,粉末中O含量明显增多。对热等静压后的烧结试样进行了夹杂物分析,M62-EIGA粉末轴承钢中大尺寸含氧夹杂物数量更多,选用M62-PREP粉末轴承钢应有更好的性能。Abstract: High-purity bearing steel powders were prepared by electrode induction melting gas atomization (EIGA) and plasma rotating electrode atomization (PREP), respectively. The particle size distribution, nitrogen and oxygen content, and microstructure of the two high-purity bearing steel powders were analyzed and compared by laser particle size analyzer, oxygen nitrogen analyzer, and scanning electron microscope. The results show that both of the powders are mainly spherical with the PREP powders (M62-PREP) having the higher sphericity, while the EIGA powders (M62-EIGA) has the higher proportion of satellite powders and irregular powders. The median particle size (D50) of the M62-PREP powders is 108.11 μm, significantly higher than that of M62-EIGA powders (D50=38.68 μm). The composition of the two powders is evenly distributed, there is no obvious element segregation, and the M62-EIGA powders are finer. Both of the powders have the good flowability. The N content (mass fraction) of the pre-alloy electrode rods, M62-PREP powders, and M62-EIGA powders are 0.0070%, 0.0072%, and 0.0068%, respectively. The content of N element does not change much. The O content (mass fraction) of M62-PREP powders increases from 0.0008% of the pre-alloy electrode rods to 0.0035%, while the O content of M62-EIGA powders increases to 0.0089%, indicating the significant increase in the O content. The M62-EIGA powder bearing steels after hot isostatic pressing and sintering have the more oxygen containing inclusions, and the M62-PREP powder bearing steels should have the better performance.
-
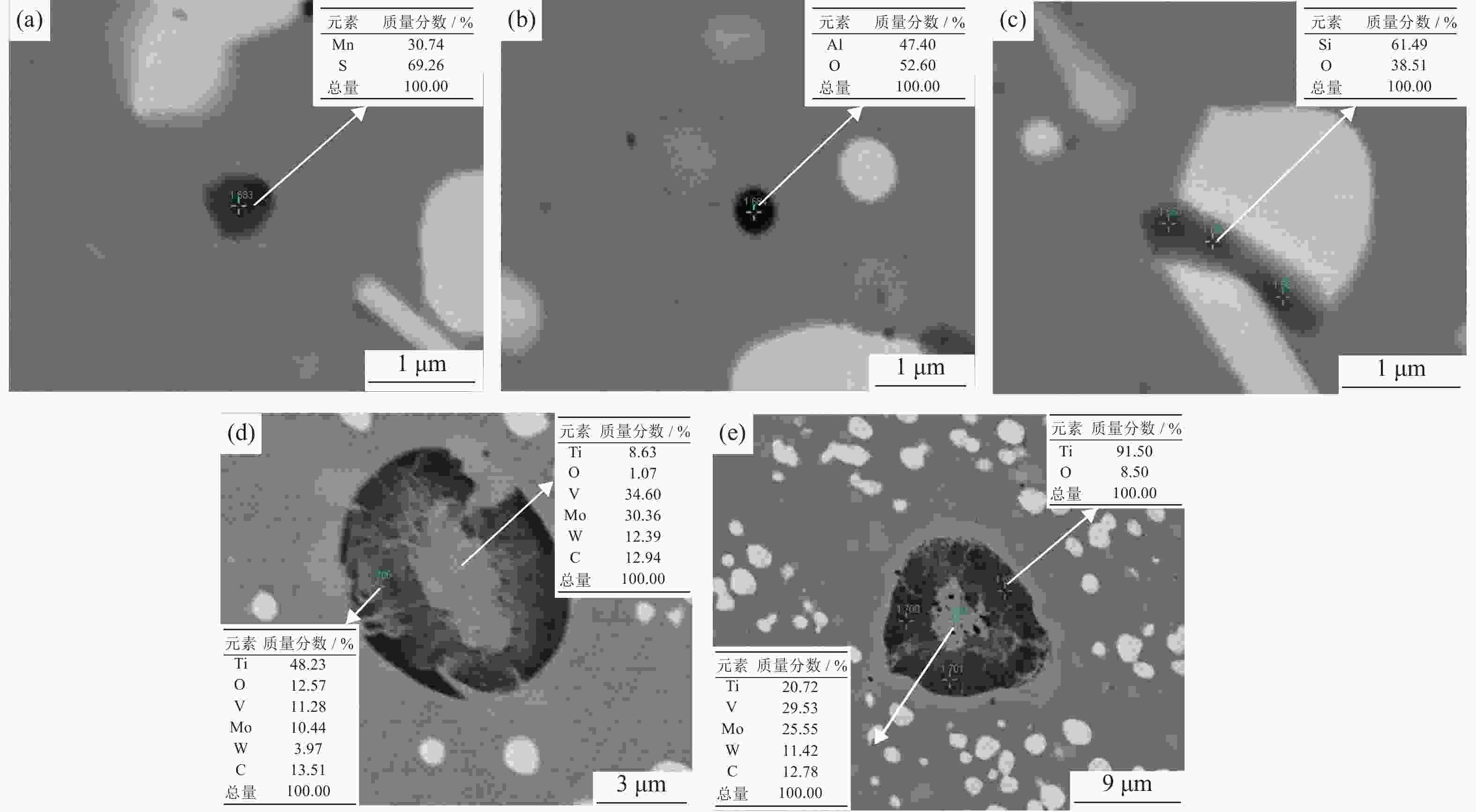
图 6 PREP和EIGA制备的M62粉末截面形貌和C、Cr、Fe、V、Mo、W、Co元素能谱分析:(a)、(c)、(e)、(g)、(i)、(k)、(m)、(o)M62-PREP粉末;(b)、(d)、(f)、(h)、(j)、(l)、(n)、(p)M62-EIGA粉末
Figure 6. Cross-sectional morphology and EDS analysis (C, Cr, Fe, V, Mo, W, and Co elements) of M62 powders prepared by PREP and EIGA: (a), (c), (e), (g), (i), (k), (m), (o) M62-PREP powders; (b), (d), (f), (h), (j), (l), (n), (p) M62-EIGA powders
表 1 轴承钢预合金电极棒化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of the bearing steel pre alloy electrode rods
% C Cr Mo W V Co Fe 1.24 3.45 11.3 6.02 2.00 0.42 余量 表 2 M62-PREP和M62-EIGA轴承钢粉末的工艺性能
Table 2. Performance of the M62-PREP and M62-EIGA bearing steel powders
粉末 流动性指数 松装密度 / (g·cm−3) 振实密度 / (g·cm−3) M62-EIGA 101(最优) 4.988 5.631 M62-PREP 98(最优) 5.052 5.361 表 3 预合金电极棒和轴承钢粉末中N、O质量分数
Table 3. N and O mass fraction of the pre-alloy electrode rods and bearing steel powders
% 材料 N O 预合金电极棒 0.0070 0.0008 M62-PREP粉末 0.0072 0.0035 M62-EIGA粉末 0.0068 0.0089 -
[1] Beswick J M, Zhou X B. Rolling Bearing Comprising a Powder Metallurgical Component: US Patent, 7018107. 2006-3-28 [2] Li X M, Lu J, Wang Q, et al. Production and research status of powder metallurgy high speed steels in the world. Heat Treat Technol Equip, 2011, 32(5): 34李响妹, 卢军, 王琦, 等. 世界粉末冶金高速钢的研究和生产现状. 热处理技术与装备, 2011, 32(5): 34 [3] Liu D H, Zhao Y J. Analysis and study on crack defect of bearing steel. Steel Roll, 2015, 32(3): 36柳东徽, 赵亚娟. 轴承钢裂纹缺陷分析与研究. 轧钢, 2015, 32(3): 36 [4] Wang K, Hu F, Zhou W, et al. Research status and development trend of bearing steel. China Metall, 2020, 30(9): 119王坤, 胡锋, 周雯, 等. 轴承钢研究现状及发展趋势. 中国冶金, 2020, 30(9): 119 [5] Persson F, Hulme C N, Jönsson P G. Particle morphology of water atomised iron-carbon powders. Powder Technol, 2022, 397: 116993 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.11.037 [6] Cui Y J, Zhao Y F, Numata H, et al. Effects of plasma rotating electrode process parameters on the particle size distribution and microstructure of Ti−6Al−4V alloy powder. Powder Technol, 2020, 376: 363 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2020.08.027 [7] Walker P F F. Improving the reliability of highly loaded rolling bearings: the effect of upstream processing on inclusions. Mater Sci Technol, 2014, 30(4): 385 doi: 10.1179/1743284713Y.0000000491 [8] Zhao Q C, Luo H, Pan Z M, et al. Study on mechanical properties of rare earth elements modified high carbon chromium bearing steel. Mater Today Commun, 2023, 34: 105329 doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2023.105329 [9] Zeng Q, Hui W J, Zhang Y J, et al. Very high-cycle fatigue performance of high carbon-chromium bearing steels with different metallurgical qualities. Int J Fatigue, 2023, 172: 107632 doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2023.107632 [10] Li Z, Liu P, Yang C Y, et al. Effect of rare earth elements on microstructure and mechanical properties of bainite/martensite bearing steel. J Mater Res Technol, 2023, 22: 1546 doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2022.12.033 [11] Antony L V M, Reddy R G. Processes for production of high-purity metal powders. JOM, 2003, 55: 14 [12] Chen G, Zhao S Y, Tan P, et al. A comparative study of Ti−6Al−4V powders for additive manufacturing by gas atomization, plasma rotating electrode process and plasma atomization. Powder Technol, 2018, 333: 38 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.04.013 [13] Tang J J, Nie Y, Qian L, et al. Characteristics and atomization behavior of Ti−6Al−4V powder produced by plasma rotating electrode process. Adv Powder Technol, 2019, 30(10): 2330 doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2019.07.015 [14] Yamamoto T D, Takeya H, Saito A T, et al. Magnetocaloric particles of the Laves phase compound HoAl2 prepared by electrode induction melting gas atomization. J Magn Magn Mater, 2022, 547: 168906 doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2021.168906 [15] Liu W S, Duan Y T, Ma Y Z, et al. Surface characterization of plasma rotating electrode atomized 30CrMnSiNi2A steel powder. Appl Surf Sci, 2020, 528: 147004 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.147004 [16] Yu H S, Zhang N N, Zhou G, et al. Physical models for vacuum-induced multistage atomization of high-entropy FeCoCrNiMo alloy powder for 3D printing. J Mater Res Technol, 2023, 24: 5947 doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.04.167 [17] Cui B, Zhu Q L, Chen J, et al. Preparation and characterization of Cu6AlNiSnInCe imitation-gold powder by vacuum nitrogen gas atomization for 3D printing. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2019, 24(1): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2019.01.001崔波, 朱权利, 陈进, 等. 真空氮气雾化法制备3D打印Cu6AlNiSnInCe仿金粉末及表征. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2019, 24(1): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2019.01.001 [18] Wei M W, Chen S Y, Liang J, et al. Effect of atomization pressure on the breakup of TA15 titanium alloy powder prepared by EIGA method for laser 3D printing. Vacuum, 2017, 143: 185 doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2017.06.014 [19] Qaddah B, Chapelle P, Bellot J P, et al. Swirling supersonic gas flow in an EIGA atomizer for metal powder production: Numerical investigation and experimental validation. J Mater Process Technol, 2023, 311: 117814 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2022.117814 [20] Zai X F, Chen S Q, Wu H, et al. Preparation of spherical high-purity Zr powders by gas atomization without crucible. Chin J Rare Met, 2018, 42(8): 864宰雄飞, 陈仕奇, 吴宏, 等. 无坩埚熔炼气雾化技术制备高纯球形锆粉. 稀有金属, 2018, 42(8): 864 [21] Tang H P. Progress of plasma rotating electrode processing technology. Powder Metall Technol, 2023, 41(1): 2汤慧萍. 等离子旋转电极制粉技术研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2023, 41(1): 2 [22] Sun N G, Chen B K, Xiang C S, et al. The current situation and innovation of plasma rotating electrode processing technology. Powder Metall Ind, 2020, 30(5): 84孙念光, 陈斌科, 向长淑, 等. 等离子旋转电极雾化制粉技术现状和创新. 粉末冶金工业, 2020, 30(5): 84 -



 下载:
下载: