-
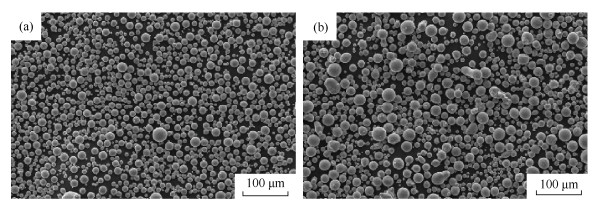
摘要: 钛及钛合金具有高比强度、低弹性模量、优良的耐蚀性和绝佳的生物相容性,但较差的加工性能大大限制了其应用范围。钛及钛合金金属粉末注射成形工艺克服了机加工、模压等传统加工工艺的缺点,结合传统粉末冶金和注塑成型的优势,实现了结构复杂的钛及钛合金产品低成本、大批量近净成形,提高了材料利用率。本文利用水溶性黏结剂和粉末粒度为16 μm和22 μm的商用球形Ti6Al4V合金粉制备了注射料和相应的试样,通过实验确定了气氛热脱黏结合真空烧结的最佳工艺,基于该工艺制备得到了两种注射料的烧结试样。结果表明:粉末粒度为16 μm注射料烧结件杂质含量未能满足外科植入用金属注射成形Ti6Al4V组件标准;粉末粒度为22 μm注射料烧结件物理化学性能如下,极限拉伸强度880 MPa,屈服强度830 MPa,延伸率13.2%,相对密度96.8%,氧质量分数为0.195%,氮质量分数为0.020%,碳质量分数为0.022%,该试样整体性能满足外科植入用金属注射成形Ti6Al4V组件标准。Abstract: Titanium and titanium alloys show the fantastic performances because of the high specific strength, low elastic modulus, good corrosion resistance, and excellent bio-compatibility. However, the application of titanium and titanium alloys is restricted due to the poor machinability. By integrating the advantages of traditional powder metallurgy and plastic injection molding technology, the metal injection molding (MIM) of titanium and titanium alloys overcomes the disadvantages of traditional machining and molding process. The parts of titanium and titanium alloys in complex structures are near net-shape manufactured by MIM in low-cost mass production, which increases the material utilization ratio. In this paper, the water soluble binder and spherical Ti6Al4V powders with particle size of 16 μm and 22 μm were employed to prepare the feedstock and specimens. An optimum process of atmosphere thermal debinding combined with vacuum sintering was determined by a series of experiments. In the results, the specimens with particle size of 16 μm fail to meet the surgical implant requirements for titanium and titanium alloys. In contrasts, the specimens with particle size of 22 μm demonstrate the properties as the relative density of 96.8%, ultimate tensile strength of 880 MPa, yield strength of 830 MPa, plastic elongation of 13.2%, oxygen mass fraction of 0.195%, nitrogen mass fraction of 0.020%, carbon mass fraction of 0.022%, meeting the surgical implant requirements for titanium and titanium alloys.
-
表 1 试样S1~S4工艺条件、杂质元素质量分数及相对密度测试结果
Table 1. Process conditions, chemical composition of impurity by mass, and relative density of samples S1~S4
试样编号 工艺条件 杂质元素质量分数/ % 相对密度/ % 热脱黏 烧结 O N C S1 真空 真空 0.226 0.035 0.042 96.2 S2 氩气氛 氩气氛 0.210 0.030 0.025 95.8 S3 氩气氛 真空 0.195 0.020 0.022 97.2 S4 真空 氩气氛 0.230 0.040 0.050 95.7 表 2 烧结件化学成分与力学性能
Table 2. Chemical composition and mechanical properties of sintered samples
试样 化学成分(质量分数)/ % 极限拉伸强度/ MPa 屈服强度/ MPa 延伸率/ % 相对密度/ % O N Fe C H M1料烧结件 0.210 0.032 0.215 0.030 0.0008 900 867 12.0 97.6 M2料烧结件 0.195 0.020 0.200 0.022 0.0010 880 830 13.2 96.8 ASTM F2885–11 0.200 0.050 0.300 0.080 0.0150 780 680 10.0 96.0 -
[1] Cao Y J. Titanium alloys by metal injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2001, 19(1): 45 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2001.01.009曹勇家. 金属注射成形钛合金. 粉末冶金技术, 2001, 19(1): 45 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2001.01.009 [2] He S W, Ouyang H W, Liu Y, et al. New powder metallurgy technologies of producing titanium alloys. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2004, 9(1): 29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2004.01.005何世文, 欧阳鸿武, 刘咏, 等. 制备钛合金件的粉末冶金新技术. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2004, 9(1): 29 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2004.01.005 [3] Froes F H S. Advances in titanium metal injection molding. Powder Metall Met Ceram, 2007, 46(5-6): 303 doi: 10.1007/s11106-007-0048-y [4] Lu X, Liu C C, Qu X H, Research progress of powder injection molding for titanium alloys. Powder Metall Technol, 2013, 31(2): 139 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2013.02.011路新, 刘程程, 曲选辉. 钛及钛合金粉末注射成形技术研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2013, 31(2): 139 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2013.02.011 [5] Zhu K P, Zhu J W, Qu H L. Development and application of biomedical Ti alloys abroad. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2012, 41(11): 2058 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-185X.2012.11.039朱康平, 祝建雯, 曲恒磊. 国外生物医用钛合金的发展现状. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(11): 2058 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-185X.2012.11.039 [6] Guo S B, Duan B H, He X B, et al. Powder injection molding of pure titanium. Rare Met, 2009, 28(3): 261 doi: 10.1007/s12598-009-0052-0 [7] Guo S B, Qu X H, He X B, et al. Powder injection molding of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. J Mater Process Technol, 2006, 173(3): 310 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.12.001 [8] Weil K S, Nyberg E, Simmons K. A new binder for powder injection molding titanium and other reactive metals. J Mater Process Technol, 2006, 176(1-3): 205 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.03.154 [9] Zhou S Y, Cai Y X, Luo T G, et al. Research on preparation and properties of catalytic debinding feedstock for titanium metal injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2015, 33(2): 95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.02.003周时宇, 蔡一湘, 罗铁钢, 等. 钛注射成形用催化脱脂型喂料的制备与性能研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2015, 33(2): 95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.02.003 [10] Sidambe A T, Figueroa I A, Hamilton H, et al. Improved processing of titanium alloys by metal injection moulding. J Phys Conf Ser, 2011, 26(1): 012005 [11] Mohamad Nor N H, Muhamad N, Mohd Ihsan A K A, et al. Sintering parameter optimization of Ti–6Al–4V metal injection molding for highest strength using palm stearin binder. Procedia Eng, 2013, 68: 359 doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2013.12.192 [12] Ebel T, Blawert C, Willumeit R, et al. Ti–6Al–4V–0.5B — a modified alloy for implants produced by metal injection molding. Adv Eng Mater, 2011, 13(12): B440 doi: 10.1002/adem.201180017 [13] Thian E S, Loh N H, Khor K A, et al. Ti–6A1–4V/HA composite feedstock for injection molding. Mater Lett, 2002, 56(4): 522 doi: 10.1016/S0167-577X(02)00544-X [14] Li Y, Guo Z M, Hao J J. Research on gelcasting of medical porous titanium implants. Powder Metall Ind, 2008, 18(1): 10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2008.01.003李艳, 郭志猛, 郝俊杰. 医用多孔钛植入材料凝胶注模成形工艺研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2008, 18(1): 10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2008.01.003 [15] Zhang X H, Xiao P A, Liu S H, et al. Study of sintering processes for powder injection molding of TiH2. Powder Metall Technol, 2012, 30(4): 293 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2012.04.009张小虎, 肖平安, 刘素红, 等. TiH2粉末注射成形坯烧结工艺研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2012, 30(4): 293 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2012.04.009 [16] Ebel T. Metal injection molding (MIM) of titanium and titanium alloys, Handbook of Metal Injection Molding. UK: Woodhead Publishing, 2012 -




 下载:
下载: