Application of ultrafine metal powder injection moulding on tungsten components in fusion devices
-
摘要: 从超细粉末制备、喂料准备、注射工艺、烧结工艺和热等静压处理等方面研究了超细纯钨粉以及超细稀土氧化物弥散增强钨粉的金属注射成形技术,利用该技术制备了聚变装置中的钨零部件,并对这种超细金属粉末注射成形钨零件的微观组织和热力学性能进行了分析。结果表明:超细纯钨粉零件相对密度可达98%以上,平均晶粒尺寸10~15 μm,500℃以上的热导率与锻造钨零件相当;超细稀土氧化物弥散增强钨粉零件相对密度可达99%以上,平均晶粒尺寸3~5 μm,抗热冲击性能优良。Abstract: Metal injection moulding (MIM) technology used for ultrafine pure W powders and rare earth oxides dispersion strengthened-W (ODS-W) powders was investigated, including ultrafine powders preparation, feedstock preparation, injection molding technology, sintering technology, and hot isostatic pressing treatment. This technology was applied to manufacture the tungsten components in fusion devices. Microstructures and thermodynamic performances of the tungsten components prepared by this ultrafine metal powder injection moulding technology were analyzed. The results show that, the MIM tungsten components used with ultrafine pure W powders (MIM-W) can achieve the relative density more than 98%, the average grain size is about 10~15 μm, and the thermal conductivity (above 500℃) of MIM-W is close to that of the wrought tungsten components. The MIM tungsten components used with rare earth oxides dispersion strengthened-W powders (MIM-ODS-W) can achieve the relative density more than 99%, the average grain size is 3~5 μm, and the thermal shock resistance of MIM-ODS-W shows excellent.
-
图 6 室温下未经热等静压处理的MIM–W和W–1.2Y2O3样品初步热冲击测试结果:(a)MIM–W,160 MW·m-2;(b)MIM–W,220 MW·m-2;(c)MIM–W,330 MW·m-2;(d)MIM–W–1.2Y2O3,220 MW·m-2;(e)MIM–W–1.2Y2O3,330 MW·m-2
Figure 6. Preliminary thermal shock test results at room temperature of MIM–W and W–1.2Y2O3 samples without HIP treatment: (a) MIM–W, 160 MW·m-2; (b) MIM–W, 220 MW·m-2; (c) MIM–W, 330 MW·m-2; (d) MIM–W–1.2Y2O3, 220 MW·m-2; (e) MIM–W–1.2Y2O3, 330 MW·m-2
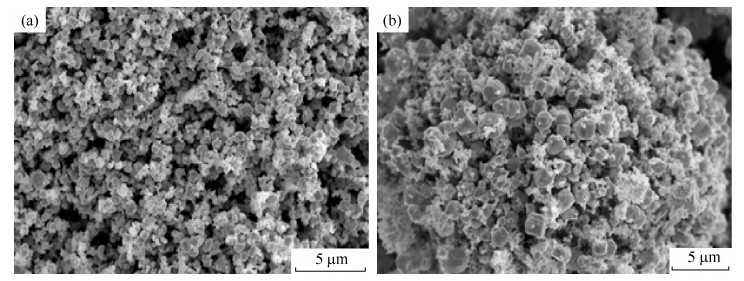
表 1 超细W粉和W–1.2Y2O3粉中气体元素成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Composition of gaseous elements in ultrafine W and W–1.2Y2O3 powders
% 粉末 N O C W 0.0151 0.1500 0.0048 W–1.2Y2O3 0.0150 0.0820(排除Y2O3中的O元素) 0.0035 表 2 超细W粉和W–1.2Y2O3粉末物理性能
Table 2. Physical properties of ultrafine W and W–1.2Y2O3 powders
粉末 粒度分布/ μm 平均粒度/ μm 松装密度/ (g·cm-3) 振实密度/ (g·cm-3) 理论密度/ (g·cm-3) D10 D50 D90 W 1.422 3.145 5.738 0.70 2.47 4.81 19.23 W–1.2Y2O3 2.264 4.846 9.711 0.82 2.04 4.08 18.61 表 3 超细纯W粉生坯注射工艺
Table 3. Injection molding parameters of green prepared by ultrafine W powders
温度/ ℃ 注射参数 保压参数 喷嘴 料筒温区2 料筒温区3 料筒温区4 料筒温区5 模温 速度/ (cm3·s-1) 压力/ MPa 进料量/ cm3 料垫/ cm3 背压/ MPa 冷却时间/ s 速度/ (cm3·s-1) 压力/ MPa 时间/ s 153 157 157 157 153 40 14 160 9.2 2.1 2.5 10 15 50 0.5 表 4 超细W–1.2Y2O3粉生坯注射工艺
Table 4. Injection molding parameters of green prepared by ultrafine W–1.2Y2O3 powders
温度/ ℃ 注射参数 保压参数 喷嘴 料筒温区2 料筒温区3 料筒温区4 料筒温区5 模温 速度/ (cm3·s-1) 压力/ MPa 进料量/ cm3 料垫/ cm3 背压/ MPa 冷却时间/ s 速度/ (cm3·s-1) 压力/ MPa 时间/ s 155 158 158 158 155 25 12 100 5.3 2.1 2.5 10 12 50 0.3 表 5 超细金属粉末注射成形钨材化学成分(质量分数)
Table 5. Chemical composition of MIM–W materials
×10-6 C O N Ta Th Al S Ca Hg U Cr Fe Ti Re Ni Zn Co F 其他 W < 5 < 10 < 5 < 1 < 0.0001 0.03 0.02 0.03 < 0.1 < 0.0001 0.08 0.01 0.02 < 0.05 0.02 0.02 0.008 < 0.01 < 0.38 基体 表 6 MIM–W粉和MIM–W–1.2Y2O3粉烧结后物理性能
Table 6. Physical properties of W powders and W–1.2Y2O3 powders after sintering
加工参数和物理性能 W粉 W–1.2Y2O3粉 烧结 烧结+ 热等静压 烧结 烧结+ 热等静压 烧结参数 1950 ℃,4 h 1700 ℃,2 h 1950 ℃,4 h 1700 ℃,2 h 热等静压参数 — 1700 ℃,180 MPa,1 h — 1700 ℃,180 MPa,1 h 密度/ (g·cm-3) 18.95 18.97 18.35 18.47 相对密度/ % 98.2 98.5 98.6 99.2 硬度,HV30 388 403 450 447 晶粒尺寸/ μm 20~30 10~15 3~5 3~5 -
[1] Maier H, Luthin J, Balden M, et al. Properties of tungsten coatings deposited onto fine grain graphite by different methods. Surf Coat Technol, 2001, 142-144: 733 doi: 10.1016/S0257-8972(01)01177-X [2] Lassner E, Schubert W D. Tungsten: Properties, Chemistry, Technology of the Element, Alloys, and Chemical Compounds. New York: Springer US, 1999 [3] Neu R, ASDEX Upgrade Team, EU PWI Taskforce, et al. Preparing the scientific basis for an all metal ITER. Plasma Phys Controlled Fusion, 2011, 53(12): 124040 doi: 10.1088/0741-3335/53/12/124040 [4] Rieth M, Dudarev S L, Gonzalez de Vicente S M, et al. Recent progress in research on tungsten materials for nuclear fusion applications in Europe. J Nucl Mater, 2013, 432(1-3): 482 doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2012.08.018 [5] Ritz G, Hirai T, Linke J, et al. Post-examination of helium-cooled tungsten components exposed to DEMO specific cyclic thermal loads. Fusion Eng Des, 2009, 84(7-11): 1623 doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2009.01.048 [6] Holstein N, Krauss W, Konys J. Structuring of tungsten by pulsed ECM processes for He-cooled divertor application. Fusion Eng Des, 2008, 83(10-12): 1512 doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2008.05.020 [7] Raffray A R, Nygren R, Whyte D G, et al. High heat flux components—Readiness to proceed from near term fusion systems to power plants. Fusion Eng Des, 2010, 85(1): 93 doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2009.08.002 [8] Norajitra P, Gervash A, Giniyatulin R, et al. Helium-cooled divertor for DEMO: Manufacture and high heat flux tests of tungsten-based mock-ups. J Nucl Mater, 2009, 386-388: 813 doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2008.12.233 [9] German R M, Song J P. Powder Injection Molding — Materials, Properties, Designs and Applications. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2011格尔曼R M, 宋久鹏. 粉末注射成形—材料、性能、设计与应用. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2011 [10] Antusch S, Norajitra P, Piotter V, et al. Powder injection molding—An innovative manufacturing method for He-cooled DEMO divertor components. Fusion Eng Des, 2011, 86(9-11): 1575 doi: 10.1016/j.fusengdes.2011.01.009 [11] Liu S Y. Study on Preparation Technology of Large Lods Ternary Composite Rare Earth Tungsten Electrode[Dissertation]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2009刘山宇. 大坯条三元复合稀土钨电极的制备工艺研究[学位论文]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2009 [12] Luo T G, Qu X G, Qin M L, et al. Study on injection forming of refractory metal powder. Chin J Rare Met, 2008, 32(4): 437 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2008.04.009罗铁刚, 曲选辉, 秦明礼, 等. 难熔金属注射成形的研究. 稀有金属, 2008, 32(4): 437 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2008.04.009 [13] Wang W, Ouyang M L, Song J P, et al. Application of metal injection molding in turbocharger parts manufacturing. Veh Eng, 2014, 212(3): 90 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYFD201403020.htm王威, 欧阳明亮, 宋久鹏, 等. 金属注射成形技术在涡轮增压器零部件制造中的应用. 车用发动机, 2014, 212(3): 90 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYFD201403020.htm [14] Zhao M Y. The Design, Fabrication and Property Evaluation of Yttrium-doped Tungsten Alloys for Fusion Reactor Applications [Dissertation]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2017赵明月. 聚变堆用钇掺杂钨合金的设计、制备及性能评价[学位论文]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2017 [15] Antusch S, Armstrong D E J, Britton T B, et al. Mechanical and microstructural investigations of tungsten and doped tungsten materials produced via powder injection molding. Nucl Mater Energy, 2015, 3-4: 22 doi: 10.1016/j.nme.2015.04.002 -




 下载:
下载: