Analysis on thermal debinding kinetics of iron-based powders by warm flow compaction
-
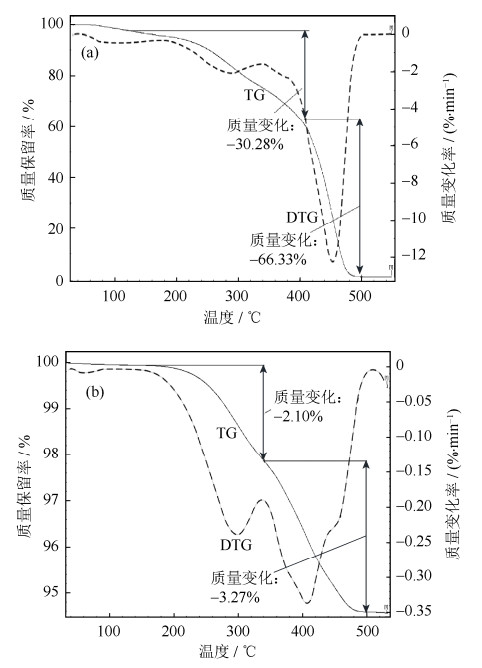
摘要: 采用流动温压工艺,以铁基粉末为原料、石蜡基聚合物为黏结剂成功制备出十字坯试样;在不同热脱脂速率下脱除聚合物黏结剂,利用热重分析(thermogravimetric analysis,TGA)法研究黏结剂在N2气氛下的热脱脂行为,采用微分法计算脱脂过程动力学相关参数,改进脱脂工艺;借助优化后的脱脂工艺对压坯进行脱脂,并在1300℃烧结获得烧结坯,对烧结坯的烧结收缩率、密度分布、微观组织进行研究。结果表明:聚合物黏结剂的脱除共有2个阶段,激活能为31.3~72.7 kJ·mol-1,指前因子为0.96×106~1.14×1010 min-1;脱脂第1阶段的激活能整体上均低于第2阶段的激活能,说明脱脂第1阶段中的低分子组元更易脱除,保证脱脂质量的关键因素是控制第1阶段的升温速率。Abstract: Cross-shaped parts were prepared by flow warm compaction using iron-based powders as raw material and paraffin wax-based polymer as binder, the polymer binder was removed at different debinding rates. The thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to study the thermal debinding behavior of binder under N2 atmosphere, and the kinetic parameters were investigated by derivative thermogravimetric method. The parts prepared by the optimized debinding parameters were sintered at 1300℃, and the shrinkage, density distribution, and microstructures of the sintered parts were studied. Results show that, the thermal debinding processes can be divided into two stages, the activation energy and pre-exponential factor are ranging from 31.3 to 72.7 kJ·mol-1 and 0.96×106 to 1.14×1010 min-1, respectively. The activation energy of stage 1 is lower than that of stage 2, which means that it is easier to remove low molecular polymer binder in stage 1. The key factor of debinding quality is to control the heating rate of stage 1.
-
Key words:
- warm flow compaction /
- iron-based powders /
- thermal debinding /
- debinding rate /
- kinetic
-
表 1 实验用金属粉末的成分与粒度
Table 1. Composition and particle sizes of the raw powders
粉末 粒度/μm 质量分数/% 水雾化铁粉 ≤147 78.5 羟基铁粉 5 20.0 还原钼粉 ≤75 0.5 石墨粉 ≤75 1.0 表 2 黏结剂组元热解温度和成分
Table 2. Thermal characteristic and composition of binder components
组元 熔点/ ℃ 热分解温度/ ℃ 质量分数/ % 聚酰胺(PA) 170.6 316.6~500.5 65.0 聚乙烯蜡(PE) 113.1 192.3~480.9 17.5 普通石蜡(PW) 64.7 180.1~307.0 17.5 表 3 生坯脱脂过程动力学参数
Table 3. Kinetic parameters of green compact with diffeent heating rates
热解阶段 升温速率,β/(℃·min-1) 激活能,Ea/(kJ·mol-1) 指前因子,A / min-1 拟合系数,r2 第1阶段(低温阶段) 2 44.3 5.82×106 0.9954 5 31.3 0.96×106 0.9970 8 34.8 3.23×106 0.9916 11 31.6 1.94×106 0.9954 第2阶段(高温阶段) 5 56.3 1.45×108 0.9914 8 70.2 4.65×109 0.9937 11 72.7 1.14×1010 0.9938 表 4 生坯密度、烧结坯密度和烧结收缩率
Table 4. Green density, sintered part density, and sintered part shrinkages
生坯密度/ (g·cm-3) 烧结密度/ (g·cm-3) 烧结收缩率/% 轴向方向 轴向直径 横向方向 横向直径 5.971 6.720 -5.83 -0.27 -6.10 -0.31 -
[1] Sokolowski P, Milbrath A, Vitti D, et al. Industrial performance of a new lubricant for manufacturing PM gears. Met Powder Rep, 2016, 71(3): 180 doi: 10.1016/j.mprp.2015.12.002 [2] Xiao Z Y, Ke M Y, Li Y Y, et al. New development of warm compaction—Warm flow compaction. Powder Metall Ind, 2002, 12(5): 28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2002.05.005肖志瑜, 柯美元, 李元元等. 温压工艺最新进展—流动温压技术. 粉末冶金工业, 2002, 12(5): 28 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2002.05.005 [3] St-Laurent S, Thomas Y, Azzi L. High performance lubricants for demanding pm applications. Powder Metall Technol, 2014, 32(3): 226 http://pmt.ustb.edu.cn/article/id/fmyjjs201403013St-Laurent S, Thomas Y, Azzi L. 粉末冶金零件需要的高性能润滑剂. 粉末冶金技术, 2014, 32(3): 226 http://pmt.ustb.edu.cn/article/id/fmyjjs201403013 [4] St-Laurent S, Chagnon F. Key parameters for warm compaction of high density materials. Powder Metall Ind, 2012, 22(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYG201201002.htmSt-Laurent S, Chagnon F. 用温压制造高密度材料的关键参数. 粉末冶金工业, 2012, 22(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYG201201002.htm [5] Xiao Z Y, Zhang J H, Shao M, et al. Characteristics of warm flow compaction forming of metallic powder and its technological problem analysis. China Mech Eng, 2005, 16(3): 257 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2005.03.020肖志瑜, 张菊红, 邵明, 等. 金属粉末流动温压成形的特点及其技术问题分析. 中国机械工程, 2005, 16(3): 257 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2005.03.020 [6] Liu C Y, Ji G S, Meng J H. Debinding process of superfine 316L stainless steel powder preform fabricated by injection molding. J Mater Sci Eng, 2013, 31(3): 451 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLKX201303028.htm刘长洋, 季根顺, 孟军虎. 超细316不锈钢粉末注射成形的脱脂工艺. 材料科学与工程学报, 2013, 31(3): 451 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLKX201303028.htm [7] Zhao L G, Li Y M. Thermal debinding behavior of the initial stage in MIM. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2002, 7(3): 175 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2002.03.003赵利刚, 李益民. MIM热脱脂初始阶段行为研究. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2002, 7(3): 175 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2002.03.003 [8] Zhou S Y, Cai Y X, Luo T G, et al. Research on preparation and properties of catalytic debinding feedstock for titanium metal injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2015, 33(2): 95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.02.003周时宇, 蔡一湘, 罗铁钢, 等. 钛注射成形用催化脱脂型喂料的制备与性能研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2015, 33(2): 95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.02.003 [9] Li Y, Wang X Q, Han Y L. Technique of debinding wax-based binder for powder injection molding. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2011, 16(1): 150 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.01.025李永, 王兴庆, 韩义林. 粉末注射成形石蜡基成形剂的脱除工艺. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2011, 16(1): 150 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.01.025 [10] Chen H, Ji X L, Liu B, et al. Catalytic debinding for 304L powder injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(6): 440 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.06.008陈慧, 敬小龙, 刘兵, 等. 304不锈钢粉末注射成形研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(6): 440 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.06.008 [11] Zheng J J, Ni D H, Hu C X, et al. A Study on fabrication and sintering process of cross-shaped part formed by warm flow compaction. Powder Metall Ind, 2010, 20(1): 32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2010.01.006郑军君, 倪东惠, 胡昌旭, 等. 流动温压成形"十"字形零件及其烧结工艺的研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2010, 20(1): 32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2010.01.006 [12] Rath J, Staudinger G. Cracking reactions of tar from pyrolysis of spruce wood. Fuel, 2001, 80(10): 1379 doi: 10.1016/S0016-2361(01)00016-3 [13] Enneti R K, Shivashankar T S, Park S J, et al. Master debinding curves for solvent extraction of binders in powder injection molding. Powder Technol, 2012, 228: 14 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.04.027 [14] Jee C S Y, Guo Z X, Stoliarov S I, et al. Experimental and molecular dynamics studies of the thermal decomposition of a polyisobutylene binder. Acta Mater, 2006, 54: 4803 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2006.06.014 [15] Alshehri S M, Al-Fawaz A, Ahamad T. Thermal kinetic parameters and evolved gas analysis (TG-FTIR-MS) for thiourea-formaldehyde based polymer metal complexes. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2013, 101: 215 doi: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.01.004 [16] Yuan H Y, Jia C C, Zhang X X, et al. Thermal degradation mechanism and kinetics of aluminum-copper green bodies prepared by gelcasting. Chin J Eng, 2016, 38(1): 102 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201601014.htm袁海英, 贾成厂, 张新新, 等. 凝胶注模制备的铝铜胚体脱脂过程及动力学. 工程科学学报, 2016, 38(1): 102 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201601014.htm -




 下载:
下载: