Microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe–Co–Ni based superalloy prepared by hot isostatic pressing
-
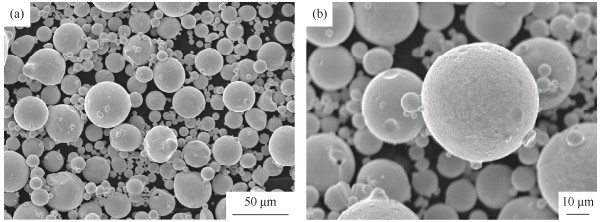
摘要: 以气雾化(gas atomization,GA)粉末为原料,采用热等静压(hot isostatic pressing,HIP)致密化烧结工艺制备Fe18Ni23Co25Cr21Mo8WNbC2铁钴镍基高温合金,研究热等静压温度对致密化Fe18Ni23Co25Cr21Mo8WNbC2粉末高温合金金相组织、力学性能和断口形貌的影响。结果表明:热等静压技术制备的高温合金致密化程度很高,烧结体由(Fe,Ni)固溶体相和弥散分布的M6C碳化物强化相组成;热等静压温度为950~1050 ℃时,烧结体的密度、力学性能随着热等静压烧结温度的提高而提高;当热等静压温度达到1100 ℃时,致密化烧结体晶粒组织明显长大,其力学拉伸性能降低;致密化烧结体的室温拉伸断口以穿晶断裂为主,局部区域晶粒被拉伸开裂,650 ℃高温断口为穿晶断裂和沿晶断裂的混合形貌,基体相存在沿应力方向被拉长的韧窝。Abstract: The Fe-Co-Ni based superalloys (Fe18Ni23Co25Cr21Mo8WNbC2) were prepared by the hot isostatic pressing (HIP), using the gas atomization powders as the raw material, and the effects of HIP temperatures on the microstructure, mechanical properties, and fracture morphology of the densified Fe18Ni23Co25Cr21Mo8WNbC2 superalloys were studied. The results show that, the HIPed superalloys have the high densification degree, and the sintered superalloys are composed of the (Fe, Ni) solidsolution phase and the dispersed M6C carbide strengthening phase. With the increase of sintering temperature from 950 ℃ to 1050 ℃, the density and mechanical properties of the HIPed sintered superalloys increase. When the HIP temperature reaches 1100 ℃, the grains of the densified sintered superalloys grow significantly and the mechanical tensile properties decrease. The tensile fracture of the densified sintered superalloys at room-temperature is mainly transgranular, and the grains in the local area are stretched and cracked. The tensile fracture of the densified sintered superalloys at 650 ℃ is a mixture of the transgranular and intergranular fracture, and the dimples in matrix are elongated along the direction of stress.
-
图 8 经过不同热等静压烧结温度制备的试样在室温和650 ℃高温拉伸断口形貌:(a)烧结温度1050 ℃,室温;(b)烧结温度1050 ℃,高温;(c)烧结温度1100 ℃,室温;(d)烧结温度1100 ℃,高温
Figure 8. Tension fracture morphology at room temperature and 650 ℃ of the samples prepared by HIP at different sintering temperatures: (a) 1050 ℃, room temperature; (b) 1050 ℃, high temperature; (c) 1100 ℃, room temperature; (d) 1100 ℃, high temperature
表 1 铁镍基合金粉末化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of the Fe–Co–Ni based alloy powders
% Fe Ni Co Cr Mo W Nb C 其余 14.18 20.36 23.41 17.80 11.82 4.32 3.25 0.45 4.41 -
[1] Wang Q, Li S G, Lü H J, et al. Research on high quality titanium alloy powder production by atomization technology. Titanium Ind Prog, 2010, 27(5): 16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2010.05.004王琪, 李圣刚, 吕宏军, 等. 雾化法制备高品质钛合金粉末技术研究. 钛工业进展, 2010, 27(5): 16 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2010.05.004 [2] Yuan W X, Mei J, Samarov V, et al. Computer modeling and tooling design for near net shaped components using hot isostatic pressing. J Mater Process Technol, 2006, 182(1-3): 39 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0924013606006571 [3] Hu W B, Jia C C, Hu B F, et al. Solidification microstructure of FGH96 superalloy powder prepared by argon gas atomization. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2011, 16(5): 671 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.05.006胡文波, 贾成厂, 胡本芙, 等. 氩气雾化法制备FGH96高温合金粉末颗粒的凝固组织. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2011, 16(5): 671 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.05.006 [4] Xu Y L. Chemical Composition Optimization, Microstructure and High Temperature Strengthening Mechanism of Nimonic 80A for Ultra-Supercritical Steam Turbine Blade [Dissertation]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2013徐裕来. 超超临界汽轮机叶片用高温合金Nimonic 80A成分优化、微结构及其高温强化机理研究[学位论文]. 上海: 上海大学, 2013 [5] He S X, Wang J, Sun B D. Effect of HIP treatment on the microstructures and properties of K4169 superalloy. Foundry Technol, 2013, 34(12): 1646 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZJS201312018.htm何树先, 王俊, 孙宝德. 热等静压处理对K4169高温合金显微形貌及性能的影响. 铸造技术, 2013, 34(12): 1646 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZJS201312018.htm [6] Wu X Q, Jing H M, Zheng Y G, et al. The eutectic carbides and creep rupture strength of 25Cr20Ni heat-resistant steel tubes centrifugally cast with different solidification conditions. Mater Sci Eng A, 2000, 293(1-3): 252 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0921509300009849 [7] Xiao X, Zhou L Z, Guo J T. Microstructural stability and creep behavior of nickel base superalloy U720Li. Acta Metall Sinica, 2001, 37(11): 1159 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2001.11.006肖璇, 周兰章, 郭建亭. 镍基高温合金U720Li的组织稳定性及蠕变行为. 金属学报, 2001, 37(11): 1159 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2001.11.006 [8] Guo J T, Zhou L Z, Yuan C, et al. Microstructure and properties of several originally invented and unique superalloys in China. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2011, 21(2): 237 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201102002.htm郭建亭, 周兰章, 袁超, 等. 我国独创和独具特色的几种高温合金的组织和性能. 中国有色金属学报, 2011, 21(2): 237 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201102002.htm [9] Sun C F, Dang X F, Li S W, et al. Sintering properties and microstructure of Fe–Ni–Co-based superalloy atomized powder. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2016, 45(12): 3115 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201612016.htm孙崇锋, 党晓凤, 李生文, 等. 铁镍钴基高温合金雾化粉末烧结特性及显微组织. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(12): 3115 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201612016.htm [10] Xie F Z, Yang S W, Gao L, et al. Study on high temperature oxidation properties of aluminized coating on superalloy. Hot Working Technol, 2004(3): 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2004.03.005谢辅洲, 杨世伟, 高丽, 等. 高温合金渗铝涂层抗高温氧化性能的研究. 热加工工艺, 2004(3): 11 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2004.03.005 [11] Furrer D U, Shankar R, White C. Optimizing the heat treatment of Ni-based superalloy turbine discs. JOM, 2003, 55: 32 doi: 10.1007/s11837-003-0157-0 [12] Cui L J, Lin X Y, Zhu Q, et al. Research progress on heat treatment process of superalloys. Mater Rev, 2016, 30(13): 106 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB201613017.htm崔令江, 林熙原, 朱强, 等. 高温合金热处理工艺研究进展. 材料导报, 2016, 30(13): 106 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLDB201613017.htm [13] Huang Q Y, Li H K. High Temperature Alloy. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000黄乾尧, 李汉康. 高温合金. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000 [14] Shao W D, Tong C S, Zhuang W. Composition design of a new cobalt base superalloy and its microstructure and properties. Mater Mechan Eng, 2005, 29(9): 41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2005.09.013邵卫东, 童潮山, 庄伟. 新型钴基高温合金成分设计及其组织与性能. 机械工程材料, 2005, 29(9): 41 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3738.2005.09.013 [15] Lei Y Y, Yao Z K, Ning Y Q, et al. Improvement of forging heat treatment on inhomogeneous deformation of P/M superalloy. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2012, 41(9): 1689 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-185X.2012.09.039雷应毅, 姚泽坤, 宁永权, 等. 热处理对粉末高温合金不均匀变形的改善作用. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(9): 1689 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-185X.2012.09.039 [16] Zou J W, Wang W X. Development and application of P/M superalloy. J Aeron Mater, 2006, 26(3): 244 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.03.051邹金文, 汪武祥. 粉末高温合金研究进展与应用. 航空材料学报, 2006, 26(3): 244 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.03.051 -




 下载:
下载: