Effect of manganese source powders on microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe-Mn-C sintered steel
-
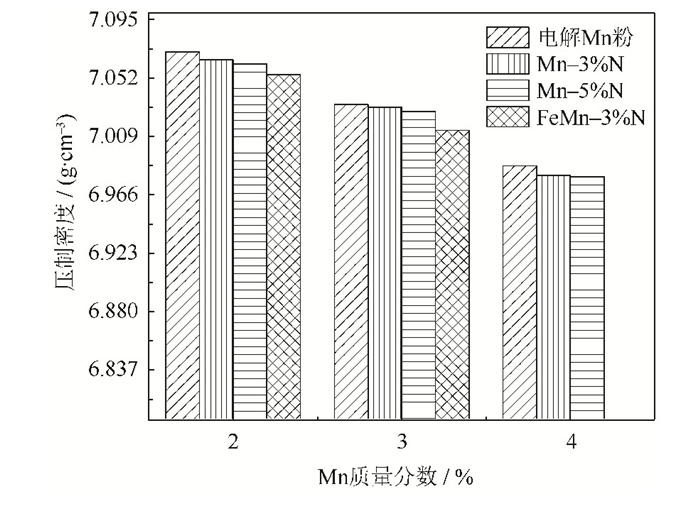
摘要: 以电解锰粉和Fe-76% Mn粉末(质量分数)为原料,在600℃和70% N2+30% H2混合气体(体积分数)管式炉中氮化得到三种抗氧化含氮锰源粉末(Mn-3% N、Mn-5% N和FeMn-3% N,质量分数),研究锰含量以及锰源粉末种类对压制烧结Fe-Mn-C烧结钢组织和力学性能的影响。研究表明:使用氮化锰源粉末制备的Fe-Mn-C烧结钢的力学性能明显优于采用电解锰粉为原料制备的同类材料,随着锰源粉末中N含量的升高,烧结钢烧结膨胀率减小,对合金的强化作用增加。以Mn-5% N作为锰源制备的Fe-2Mn-0.5C烧结钢,其拉伸强度为576 MPa,断后延伸率为3.8%,与电解锰粉为锰源相比,烧结钢的拉伸强度和断后延伸率分别提升了29%和123%。使用氮化锰粉作为锰源的烧结钢内孔隙数量减小,珠光体增多,片层间距降低。Abstract: Using the electrolytic manganese powders and Fe-76%Mn powders (mass fraction) as the raw materials, the antioxidative nitrogen-manganese source powders (Mn-3%N, Mn-5%N, and FeMn-3%N, mass fraction) were prepared in the tube furnace with 70%N2 + 30%H2 gas (volume fraction) at 600 ℃, the effects of the manganese mass fraction and the type of manganese source powders on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the Fe-Mn-C sintered steels were investigated. In the results, the mechanical properties of the Fe-Mn-C sintered steels prepared by the nitrogen-manganese source powders are obviously better than those prepared by the electrolytic manganese powders. With the increase of the nitrogen mass fraction in the manganese source powders, the sintering expansion rate of the sintered steels decreases, and the strengthening of the Fe-Mn-C alloy is increased. The tensile strength of the Fe-2Mn-0.5C sintered steels prepared by Mn-5%N powders is 576 MPa, and the fracture elongation is 3.8%, which is improved by 29% and 123%, respectively, compared with those prepared by the electrolytic manganese powders. The number of pores in the sintered steels prepared by the nitrogen-manganese source powders decreases, the pearlite increases, and the lamellar spacing decreases.
-
Key words:
- sintered steels /
- manganese powders /
- nitrogenization /
- mechanical properties /
- microstructure
-
表 1 水雾化铁粉化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of the water atomized ironpowders
% C Si S P Mn Fe ≤0.01 ≤0.04 ≤0.012 ≤0.012 ≤0.12 余量 -
[1] Šalak A, Selecká M, Bureš R. Manganese in ferrous powder metallurgy. Powder Metall Prog, 2001, 1(1): 41 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/267294771_Manganese_in_ferrous_powder_metallurgy/download [2] Dudrová E, Kabátová M, Bidulský R, et al. Industrial processing, microstructures and mechanical properties of Fe-(2-4)Mn(-0.85Mo)-(0.3-0.7)C sintered steels. Powder Metall, 2004, 47(2): 180 doi: 10.1179/003258904225015518 [3] Suciu C, Arghir G, Brandusan L, et al. Microstructure of the Fe-FeMn transition zone. Powder Metall Prog, 2011, 11(1-2): 153 http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=768981387bc3474e745935de00f77262 [4] Šalak A, Selecká M. Effect of manganese content and manganese carrier on properties of sintered and sintered hardened hybrid Fe-3Cr-0.5Mo-xMn-0.24C steel. Powder Metall, 2008, 51(4): 327 doi: 10.1179/174329008X284976 [5] Chen H Z. Preparation and Mechanical Properties of Fe-Mn-(Mo)-C Powder Metallurgy Low Alloy Steel[Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2015陈荟竹. Fe-Mn-(Mo)-C粉末冶金低合金钢制备及力学性能研究[学位论文]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2015 [6] Chen H Z, Luo P, Yang Y J, et al. Effect of Mn addition and its nitridation on microstructure and properties of sintered Fe-1Mn-0.5C low-alloy steel. J Mater Eng Perform, 2017, 26(9): 4481 doi: 10.1007/s11665-017-2677-8 [7] Karlsson H, Nyborg L, Berg S. Surface chemical analysis of prealloyed water atomized steel powder. Powder Metall, 2005, 48(1): 51 doi: 10.1179/0032589005X37675 [8] Hryha E, Gierl C, Nyborg L, et al. Surface composition of the steel powders pre-alloyed with manganese. Appl Surf Sci, 2010, 256(12): 3946 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.01.055 [9] Morioka Y. Recent advances in production of steel powders for high strength PM parts. Met Powder Rep, 1990, 45(3): 181 doi: 10.1016/S0026-0657(10)80085-2 [10] Zhou G L, Hong H Q, He F M, et al. Effect of silicon-manganese master alloy on properties and microstructure of sintered steel. Powder Metall Technol, 1996, 14(4): 282 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYJ604.007.htm周国理, 洪恒泉, 何凤鸣, 等. 硅锰母合金对烧结钢性能和组织的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 1996, 14(4): 282 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYJ604.007.htm [11] Šalak A, Selecká M. Manganese in Powder Metallurgy Steels. Cambridge: Cambridge International Science Publishing, 2012 [12] Šalak A, Selecká M, Danninger H. Machinability of Powder Metallurgy Steels. Cambridge: Cambridge International Science Publishing, 2005 [13] Liu D, Xiang H L, Hu Y R. Effect of N content on microstructure and properties of CE8MN cast duplex stainless steel. Foundry Technol, 2015(6): 1342 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZJS201506004.htm刘东, 向红亮, 胡育瑞. N含量对铸造CE8MN双相不锈钢组织和性能影响. 铸造技术, 2015(6): 1342 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZZJS201506004.htm [14] Sun G X, Zhang Y, Sun S C, et al. Plastic flow behavior and its relationship to tensile mechanical properties of high nitrogen nickel-free austenitic stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng A, 2016, 662(5): 432 http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=8a4e3925e0987e572b055d2129a5c2e5 [15] James W B, Lindsiey B, Narasimhan K S. PM manganese steels for powder metallurgy parts. Powder Metall Prog, 2012, 12(1): 3 doi: 10.1007/978-1-907343-75-9 -




 下载:
下载: