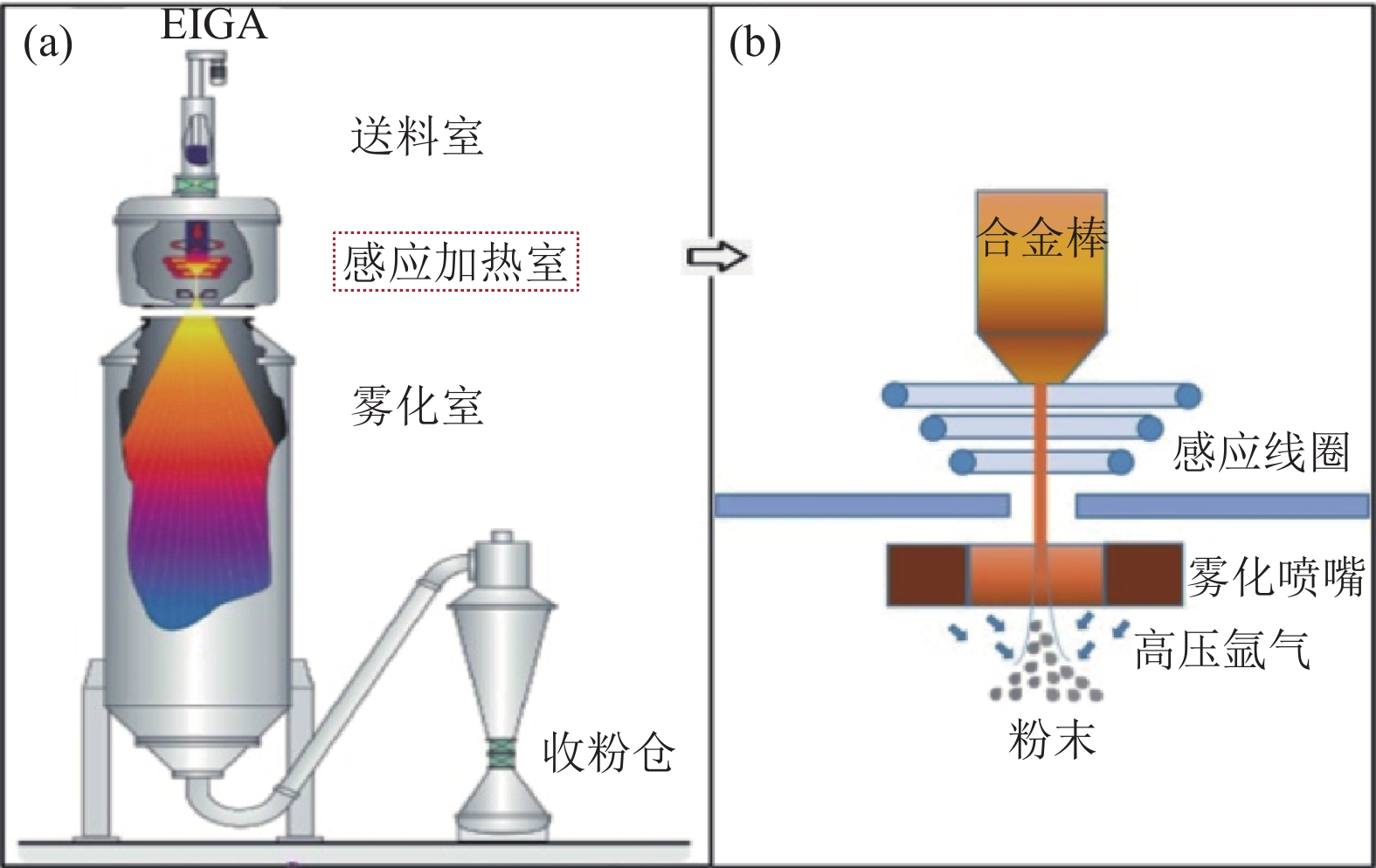
Preparation of new high hardness martensitic iron-based alloy powders by electrode induction gas atomization
-
摘要: 利用正交试验研究了电极感应气雾化(electrode induction gas atomization,EIGA)制粉工艺参数(雾化压力、雾化气体温度和熔炼功率)对新型高硬度马氏体铁基合金粉末粒径分布、粉末流动性和收得率的影响规律。结果表明,粉末粒径分布及其特征主要取决于雾化压力,粉末流动性及收得率主要受雾化压力及雾化气体温度的影响。当制粉工艺参数为雾化压力1.5 MPa、熔炼功率15 kW、雾化气体温度40 ℃时,所得粉末的收得率最高,粒径大小在53~180 μm之间的粉末质量占比高达68.24%,兼具较好的粉末流动性及粉末粒度分布标准偏差,粉末形貌最佳。Abstract: The effects of the electrode induction gas atomization parameters (atomization pressure, gas temperature, and melting power) on the particle size distribution, powder fluidity, and yield of the new high hardness martensitic iron-based alloy powders were studied by orthogonal test. The results show that, the particle size distribution is mainly affected by the atomization pressure, while the fluidity and yield of the powders are affected by the atomization pressure and the gas temperature. When the atomization pressure is 1.5 MPa, the melting power is 15 kW, and the atomization gas temperature is 40 ℃, the powders have the largest powder yield, the mass proportion of powders with the particle size of 53~180 μm accounts for 68.24%, and the powders show the well powder fluidity, the standard deviation of powder size distribution, and the best powder morphology.
-
图 2 正交试验各参数下的粉末粒径分布特征:(a)工艺1#;(b)工艺2#;(c)工艺3#;(d)工艺4#;(e)工艺5#;(f)工艺6#;(g)工艺7#;(h)工艺8#;(i)工艺9#
Figure 2. Particle size distribution characteristics under the different orthogonal test parameters: (a) process 1#; (b) process 2#; (c) process 3#; (d) process 4#; (e) process 5#; (f) process 6#; (g) process 7#; (h) process 8#; (i) process 9#
表 1 高硬度马氏体铁基合金棒化学成份(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of the high hardness martensitic iron-based alloy
% C Ni Cr Si B V P S Fe 0.12~0.20 1.5~2.8 16~17 0.5~1.0 0.4~1.0 0.1~0.3 ≤0.03 ≤0.03 余量 表 2 气雾化工艺正交实验表L9(3×3)
Table 2. Orthogonal test of the gas atomization parameters L9 (3×3)
工艺 F / MPa P / kW T / ℃ 1# 1.0 15 20 2# 1.0 20 40 3# 1.0 25 60 4# 1.5 15 40 5# 1.5 20 60 6# 1.5 25 20 7# 2.0 15 60 8# 2.0 20 20 9# 2.0 25 40 表 3 粉末粒径分布特征值、流速及粉末收得率
Table 3. Characteristic values of the particle size distribution, flow rate, and yield of powders
工艺 D50 / μm D84.13 / μm δ S / [s·(50 g)−1] w / % 1# 99.80±0.31 166.00±0.32 1.67 12.75±0.21 58.41±0.38 2# 101.00±0.40 165.00±0.35 1.63 12.94±0.13 65.32±0.32 3# 99.30±0.37 164.00±0.31 1.65 12.82±0.21 52.58±0.35 4# 91.90±0.45 161.00±0.24 1.75 13.40±0.24 68.24±0.40 5# 93.00±0.30 159.00±0.29 1.71 13.20±0.19 56.94±0.22 6# 91.70±0.28 159.00±0.21 1.73 12.75±0.18 65.41±0.27 7# 87.70±0.21 142.00±0.22 1.62 13.66±0.22 55.13±0.29 8# 88.10±0.24 142.00±0.19 1.61 13.00±0.23 50.38±0.23 9# 87.00±0.37 149.00±0.25 1.71 14.10±0.12 50.12±0.29 表 4 各影响因素显著性分析结果
Table 4. Significance analysis based on the various factors
粉末性能 F / MPa P / kW T / ℃ D50 12.43 1.36 0.13 δ 0.10 0.05 0.04 S 0.75 0.22 0.65 w 12.65 4.55 6.35 表 5 制备的高硬度铁基合金粉末化学成份(质量分数)
Table 5. Chemical composition of the high hardness iron-based alloys
% C Ni Cr Si B V P S Fe 0.12 2.46 16.87 0.77 0.64 0.22 0.019 0.0032 余量 -
[1] Zhu S, Zhou C J. Additive remanufacturing for “Made in China 2025”. Therm Spray Technol, 2016, 8(3): 1朱胜, 周超极. 面向“中国制造2025”的增材再制造技术. 热喷涂技术, 2016, 8(3): 1 [2] Strondl A, Lyckfeldt O, Brodin H, et al. Characterization and control of powder properties for additive manufacturing. JOM, 2015, 67(3): 549 doi: 10.1007/s11837-015-1304-0 [3] Fang Z Z, Paramore J D, Sun P, et al. Powder metallurgy of titanium-past, present, and future. Int Mater Rev, 2017, 63(7): 407 [4] Wang Q, Li S G, Lü H, et al. Research on high quality titanium alloy powder production by atomization technology. Titanium Ind Prog, 2010, 27(5): 17王琪, 李圣刚, 吕宏, 等. 雾化法制备高品质钛合金粉末技术研究. 钛工业进展, 2010, 27(5): 17 [5] Ouyang H W, Chen X, Yu W T, et al. Progress and prospect on the gas atomization. Powder Metall Technol, 2007, 25(1): 53 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2007.01.013欧阳鸿武, 陈欣, 余文焘, 等. 气雾化制粉技术发展历程及展望. 粉末冶金技术, 2007, 25(1): 53 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2007.01.013 [6] Xu L H, Zhou X L, Li J H. The study progress of metal powder gas atomization technology. Therm Spray Technol, 2008, 10(2): 1徐良辉, 周香林, 李景昊. 金属粉末气雾化技术研究新进展. 热喷涂技术, 2008, 10(2): 1 [7] Hu Y F, Li J H, Zhou X L. Research progress on solidification behavior of alloy droplets during the process of atomization. Therm Spray Technol, 2008, 10(1): 1胡云飞, 李景昊, 周香林. 气雾化过程中合金熔滴的凝固行为研究进展. 热喷涂技术, 2008, 10(1): 1 [8] Chen S Q, Huang B Y. The status and development of gas atomization for production of metal powders. Powder Metall Technol, 2004, 22(5): 297 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2004.05.009陈仕奇, 黄伯云. 金属粉末气体雾化制备技术的研究现状与进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2004, 22(5): 297 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2004.05.009 [9] Wu W H, Wu K Q, Xiao Y F, et al. Effect of atomization pressure on the properties of 316L stainless steel powder used in 3D printing. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(2): 83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.001吴文恒, 吴凯琦, 肖逸凡, 等. 雾化压力对3D打印用316L不锈钢粉末性能的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(2): 83 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.001 [10] Dowson A G. Atomization dominates powder production. Met Powder Rep, 1999, 54(1): 15 doi: 10.1016/S0026-0657(99)80162-3 [11] Zhang S G, Yang B C, Yang B, et al. A novel ultrasonic atomization process for producing spherical metal powder. Acta Metall Sin, 2002, 38(8): 888 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2002.08.022张曙光, 杨必成, 杨博, 等. 新型超声雾化技术制备球形金属粉末. 金属学报, 2002, 38(8): 888 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2002.08.022 [12] Yuan G. Preparation, Characterization and Application of Spherical Metal Powder for Additive Manufacturing [Dissertation]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2015原光. 面向增材制造的球形金属粉的制备、表征与应用[学位论文]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2015 [13] Guo K K, Liu C S, Chen S Y, et al. Effect of EIGA power parameter on the characteristics of TC4 alloy powder for 3D printing. Mater Sci Technol, 2017, 25(1): 16 doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20160377郭快快, 刘常升, 陈岁元, 等. 功率对EIGA制备3D打印用TC4合金粉末特性的影响. 材料科学与工艺, 2017, 25(1): 16 doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20160377 [14] Yang M. Research on Microstructure Evolution and Formation of Fe−C Based Powders by Gas Atomization [Dissertation]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2010杨敏. 气雾化铁−碳系合金粉体组织演化及其形成研究[学位论文]. 上海: 上海大学, 2010 [15] German R M. Powder Metallurgy Science. Princeton NJ: Metal Powder Industries Federation, 1994 [16] Lubanska H. Correlation of spray ring data for gas atomization of liquid metals. JOM, 1970, 22(2): 45 doi: 10.1007/BF03355938 [17] Tan M H, Huang Y Y. Surface Physical Chemistry. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 1985谈慕华, 黄蕴元. 表面物理化学. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 1985 [18] Long Q L, Wu W H, Lu L, et al. Effect of power on properties of Ti−6Al−4V alloy powder prepared by EIGA process. China Powder Sci Technol, 2018, 24(4): 49龙倩蕾, 吴文恒, 卢林, 等. 熔炼功率对 EIGA 制备 Ti−6Al−4V 合金粉末特性的影响. 中国粉体技术, 2018, 24(4): 49 -




 下载:
下载: