Fabrication and properties of large size aluminum-based boron carbide composites by hot isostatic pressing
-
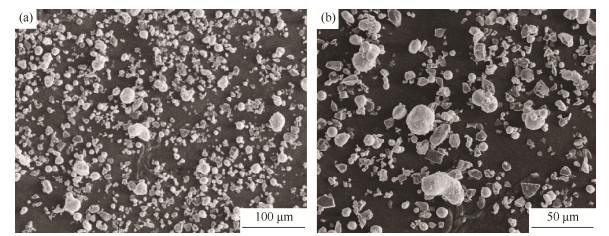
摘要: 采用热等静压法制备铝基碳化硼复合材料(Al-B4C)板材, 测试板材的密度和抗拉强度, 并观察复合材料的微观组织和拉伸断口形貌。结果表明, Al-31% B4C (质量分数)板材的尺寸为3 mm×200 mm×5000 mm; Al-31% B4C复合材料的相对密度大于99.69%, 抗拉强度大于300 MPa, 断后延伸率大于3%, B4C颗粒均匀分布在基体中, 并与基体紧密结合; Al-B4C复合材料板材的力学性能符合工程用中子吸收材料的要求。比较含不同质量分数B4C颗粒(10%、15%、20%、25%、30%、31%、35%、40%)的Al-B4C复合材料性能, 当B4C质量分数为10%~40%时, 随基体中B4C颗粒含量的增加, Al-B4C复合材料的密度和相对密度均逐渐降低; 当B4C质量分数为10%~35%时, 随基体中B4C颗粒含量的增加, Al-B4C复合材料的抗拉强度逐渐增大, 断后延伸率逐渐降低。Abstract: The aluminum-based boron carbide composites (Al-B4C) were fabricated by hot isostatic pressing. The density, tensile strength, microstructures, and fracture morphology of the Al-B4C composites were investigated. The results show that, the plate size of Al-31% B4C composites by mass is 3 mm×200 mm×5000 mm; the relative density of Al-31% B4C composites is greater than 99.69%, the tensile strength is greater than 300 MPa, and the elongation is greater than 3%; the B4C particles are evenly embedded in the Al matrix, and the B4C particles are tightly bound to the Al matrix; the physical properties of aluminum-based boron carbide composite plates meet the requirement of the neutron-absorbing materials used in engineering. The physical properties of Al-B4C composites with different B4C contents by mass (10%, 15%, 20%, 25%, 30%, 31%, 35%, and 40%)are compared. When the content of B4C is 10%~40% by mass, with the increase of B4C content in the matrix, the density and relative density of Al-B4C composites gradually decrease; when the B4C content by mass ranges from 10% to 35%, with the increase of B4C content in the matrix, the tensile strength of Al-B4C composites gradually increases, and the elongation gradually decreases.
-
Key words:
- hot isostatic pressing /
- aluminum-based composites /
- boron carbide /
- physical properties /
- plates
-
表 1 实验用6061Al粉的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of 6061Al alloy powders used in experiment %
实验材料 Si Fe Cu Mn Mg Cr Zn Ti Al EN AW-6061Al粉标准值 0.40~0.80 ≤0.70 0.15~0.40 ≤0.15 0.8~1.2 0.04~0.35 ≤0.250 ≤0.15 余量 实验用6061Al粉测量值 0.62 0.13 0.23 <0.01 0.8 0.04 0.027 <0.01 余量 表 2 实验用碳化硼粉的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 2. Chemical composition of boron carbide powders used in experiment %
实验材料 Ca Fe B+C F Cl ASTM C750 Type 1碳化硼粉标准值 ≤0.300 ≤1.00 ≥98.00 ≤0.0025 ≤0.0075 实验用碳化硼粉测量值 0.027 0.03 99.73 ≤0.0015 ≤0.0015 表 3 Al‒B4C复合材料的抗拉强度和断后延伸率
Table 3. Tensile strength and elongation of Al‒B4C composites
B4C质量分数/ % 抗拉强度/ MPa 断后延伸率/ % 10 177 16.00 15 201 13.70 20 254 9.10 25 291 6.80 31 307 3.50 35 356 2.46 40 — — -
[1] China Nuclear Energy Association. Review of global nuclear power in 2014. China Nucl Ind, 2015(3): 60 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHGY201503031.htm中国核能行业协会. 2014年全球核电综述. 中国核工业, 2015(3): 60 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHGY201503031.htm [2] Bi G W, Si S Y, Zhang H J. Spent fuel characteristics analyses for thorium-uraniun breeding recycle in PWRs. Atom Energy Sci Technol, 2012, 46(8): 961 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZJS201208013.htm毕光文, 司胜义, 张海俊. 压水堆内钍-铀增殖循环研究——乏燃料特性分析. 原子能科学技术, 2012, 46(8): 961 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YZJS201208013.htm [3] Alizadeh M. Comparison of nanostructured A1/B4C composite produced by ARB and Al/B4C composite produced by RRB process. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 528(2): 578 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.08.093 [4] Tuncer N, Tasdelen B, Arslan G. Effect of passivation and precipitation hardening on processing and mechanical properties of B4C-A1 composites. Ceram Int, 201l, 37(7): 2861 doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.05.007 [5] Carden R A. Fabrication Methods for Metal Matrix Composites: United States Patent, 5722033. 1996-7-1 [6] Topcu I, Gulsoy H O, Kadioglu N, et al. Processing and mechanical properties of B4C reinforced Al matrix composites. J Alloys Compd, 2009, 482(1-2): 516 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2009.04.065 [7] Arslan G, Kara F, Turan S. Quantitative X-ray diffraction analysis of reactive infiltrated boron carbide-aluminum composites. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2003, 23(8): 1243 doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(02)00304-7 [8] Khakbiz M, Akhlaghi F. Synthesis and structural characterization of Al-B4C nano-composite powders by mechanical alloying. J Alloys Compd, 2009, 479(1-2): 334 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.12.076 [9] Kim K, Chung S, Hong J. Performance evaluation of METAMIC neutron absorber in spent fuel storage rack. Nucl Eng Technol, 2018, 50(5): 788 doi: 10.1016/j.net.2018.01.017 [10] Kang P C, Cao Z W, Wu G H, et al. Phase identification of Al-B4C ceramic composites synthesized by reaction hot-press sintering. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2010, 28(2): 297 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2009.11.004 [11] Zhang Z, Fortin K, Charette A, et al. Effect of titanium on microstructure and fluidity of Al-B4C composites. J Mater Sci, 2011, 46: 3176 doi: 10.1007/s10853-010-5201-1 [12] Li Y L, Zhang P, Gao Z P, et al. Effect of B4C particle size on strength of B4C/6061Al compositions. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2012, 17(5): 611 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2012.05.011李宇力, 张鹏, 高占平, 等. B4C增强相颗粒粒度对Al基体复合板材强度的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2012, 17(5): 611 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2012.05.011 [13] Zhang P, Zhang Z W, Li Y L, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high content B4C-aluminium composites fabricated by hot-pressing sintering. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2014, 19(1): 95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2014.01.016张鹏, 张哲维, 李宇力, 等. 热压法制备高含量B4C/铝基复合材料的显微结构和力学性能. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2014, 19(1): 95 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2014.01.016 [14] Shen C L, Shi J M, Zhang L, et al. Effect of ball milling technics on B4C-Al composite performance. J Funct Mater, 2011, 42(Suppl 2): 365 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GNCL2011S2044.htm沈春雷, 石建敏, 张玲, 等. 球磨工艺对B4C-Al复合粉末性能的影响. 功能材料, 2011, 42(增刊2): 365 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GNCL2011S2044.htm [15] Energy Resources International, Inc. Industry Spent Fuel Storage Hand Book. Palo Alto: Electric Power Research Institute, 2010 -




 下载:
下载: