Effects of quenching temperature on the microstructure and properties of M4 powder metallurgy high speed steel
-
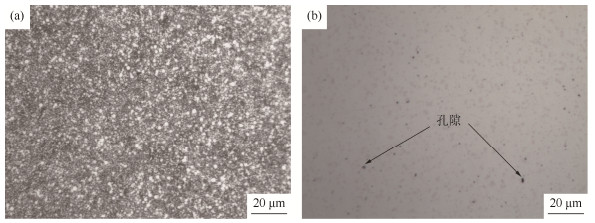
摘要: 为了研究淬火温度对M4粉末高速钢组织和性能的影响, 利用光学显微镜观察高速钢试样的金相组织, 对淬火组织的晶粒度进行评级, 并对回火组织中碳化物的组成和分布进行统计; 采用洛氏硬度计和材料万能试验机测试试样的硬度和抗弯强度。结果表明: 随淬火温度的升高, M4粉末高速钢淬火后硬度先上升后下降, 在1200 ℃时出现最大值HRC62.9;淬火态试样的晶粒度随淬火温度的升高而降低。经三次回火后M4粉末高速钢硬度值较淬火态均有提高, 且随淬火温度的升高, 先增高后下降, 在淬火温度为1190 ℃时达到最大值HRC66.4。随淬火温度的升高, 回火态试样的抗弯强度逐渐下降, 碳化物聚集长大倾向明显, 尺寸均匀性下降。M4粉末高速钢的最优淬火温度区间为1180~1190 ℃。Abstract: To investigated the effects of quenching temperature on the microstructures and properties of M4 powder metallurgy high speed steel (PM HSS), the metallographic structures of the PM HSS samples were observed by optical microscope, the grain sizes of the quenched microstructure were graded, and the composition and distribution of carbide in the tempered microstructure were analyzed. The hardness and bending strengthen of the PM HSS samples were tested by the Rockwell hardness tester and the universal testing machine, respectively. The results show that the hardness of the quenched samples first increases and then decreases with the increase of quenching temperature, reaching a maximum as HRC 62.9 at 1200 ℃. The grain size of the quenched samples declines with the increase of quenching temperature. After the triple tempering, the hardness of the tempered samples is higher than that of the quenched samples, showing the same trend with the increase of quenching temperature. The maximum hardness of the tempered samples reaches HRC 66.4 at the quenching temperature of 1190 ℃. With the increase of quenching temperature, the bending strength of the tempered samples gradually decreases, the carbides coarsen markedly, and the uniformity of carbide dimension deteriorates. According to the results, the optimal quenching temperature of M4 powder metallurgy high speed steel is 1180~1190 ℃.
-
表 1 M4粉末高速钢化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of M4 PM HSS
% C W V Mo Cr Si Mn S 1.40 5.53 4.05 5.28 3.95 0.45 0.30 0.06 -
[1] Badisch E, Mitterer C. Abrasive wear of high speed steels: Influence of abrasive particles and primary carbides on wear resistance. Tribol Int, 2003, 36(10): 765 doi: 10.1016/S0301-679X(03)00058-6 [2] García C, Romero A, Herranz G, et al. Effect of vanadium carbide on dry sliding wear behavior of powder metallurgy AISI M2 high speed steel processed by concentrated solar energy. Mater Charact, 2016, 121: 175 doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2016.10.001 [3] Zhou X F, Yin X F, Fang F, et al. Influence of rare earths on eutectic carbides in AISI M2 high speed steel. J Rare Earths, 2012, 30(10): 1075 doi: 10.1016/S1002-0721(12)60181-1 [4] Zhou X F, Liu D, Zhu W L, et al. Morphology, microstructure and decomposition behavior of M2C carbides in high speed steel. J Iron Steel Res Int, 2017, 24(1): 43 doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(17)30007-9 [5] Ma K, Yang F L, Huang K, et al. Effects of quenching methods on microstructure and properties of M42 high speed steel. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2014, 19(2): 241 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2014.02.013马凯, 杨伏良, 黄珂, 等. 淬火方式对M42高速钢组织和性能的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2014, 19(2): 241 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2014.02.013 [6] Peng H L, Hu L, Ngai T W, et al. Effects of austenitizing temperature on microstructure and mechanical property of a 4-GPa-grade PM high-speed steel. Mater Sci Eng A, 2018, 719: 21 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.02.010 [7] Pi Z Q, Lu X, Jia C C, et al. Research progress on the spray formed high speed steel. Powder Metall Technol, 2013, 31(5): 379 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2013.05.012皮自强, 路新, 贾成厂, 等. 喷射成形高速钢的研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2013, 31(5): 379 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2013.05.012 [8] Wang H B, Zhang J X, Lu L, et al. High-temperature thermal deformation and microstructure evolution of spray formed M4 high speed steel. Chin J Mater Res, 2013, 27(2): 167 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJB201302011.htm王和斌, 张金祥, 卢林, 等. 喷射成形M4高速钢的高温热变形及组织演变. 材料研究学报, 2013, 27(2): 167 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CYJB201302011.htm [9] Wu Y C. Evolution of technology of powder metallurgy high speed steel. Powder Metall Ind, 2007, 17(2): 30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2007.02.007吴元昌. 粉末冶金高速钢生产工艺的发展. 粉末冶金工业, 2007, 17(2): 30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2007.02.007 [10] Yan L C, Lu G F, Meng L B, et al. Research on microstructure and properties of powder metallurgy high speed steel. Powder Metall Ind, 2011, 21(3): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2011.03.001闫来成, 卢广锋, 孟令兵, 等. 粉末冶金高速钢的组织和性能研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2011, 21(3): 1 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2011.03.001 [11] Sun S Q. Heat treatment and thermo-magnetic analysis of powder metallurgy high speed steel. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2013, 18(2): 250 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMGC201302017.htm孙世清. 粉末冶金高速钢的热处理与热磁分析. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2013, 18(2): 250 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMGC201302017.htm [12] Zhao Y, Wang C L, Yang K N. Microstructural changes of high speed steel powders during heating in vacuum. Powder Metall Technol, 2003, 21(3): 145 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2003.03.004赵越, 王崇琳, 杨克努. 高速钢粉末真空高温处理时组织结构之变化. 粉末冶金技术, 2003, 21(3): 145 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2003.03.004 [13] Deng Y K, Chen J R, Wang S Z. High Speed Tool Steel. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2002邓玉昆, 陈景榕, 王世章. 高速工具钢. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2002 [14] Li X M, Ye J, Zhu Z C. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and properties of S390 powder metallurgy high speed steel. Mater Mech Eng, 2013, 37(12): 42 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC201312010.htm李响妹, 叶俭, 朱祖昌. 热处理工艺对S390粉末高速钢组织和性能的影响. 机械工程材料, 2013, 37(12): 42 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXGC201312010.htm [15] Liu B W, Lu X, Pi Z Q, et al. Effect of quenching temperature on transformation mechanism of carbides of M42. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2017, 46(3): 829 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201703044.htm刘博文, 路新, 皮自强, 等. M42热处理中淬火温度对碳化物转变机制的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2017, 46(3): 829 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-COSE201703044.htm [16] Trabadelo V, Giménez S, Iturriza I. Microstructural characterisation of vacuum sintered T42 powder metallurgy high-speed steel after heat treatments. Mater Sci Eng A, 2009, 499(1-2): 360 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2008.08.043 [17] Xia L F. Heat Treatment Technology of Metals. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2012夏立芳. 金属热处理工艺学. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2012 [18] Wu Y C. The effect of surface condition of hardened PM HSS on its bending strength. Powder Metall Ind, 1999, 9(4): 36 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYG904.007.htm吴元昌. 试样表面状态对淬硬粉末冶金高速钢抗弯强度的影响. 粉末冶金工业, 1999, 9(4): 36 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYG904.007.htm [19] Zhao B Q. Motallographic examination for quenched high-speed steel tool. Heat Treat Met, 2010, 35(6): 122 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSRC201006042.htm赵步青. 高速钢刀具淬火后的金相检验. 金属热处理, 2010, 35(6): 122 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSRC201006042.htm [20] Mesquita R A, Barbosa C A, Gonçalves C S, et al. Effect of hardening conditions on mechanical properties of high speed steels. Int Heat Treat Surf Eng, 2011, 5(1): 36 doi: 10.1179/174951411X12956208225221 [21] Liu S F, He Y H, Zhang Q K, et al. Effect of quenching temperature on microstructures and mechanical properties of ASP30 added B4C powder metallurgy high speed steel. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2016, 21(6): 855 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.06.006刘少峰, 贺跃辉, 张乾坤, 等. 淬火温度对添加B4C的ASP30粉末冶金高速钢组织及力学性能的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2016, 21(6): 855 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.06.006 -




 下载:
下载: