Influence of temperature on the oxidation behaviors of the nickel-based superalloy powders
-
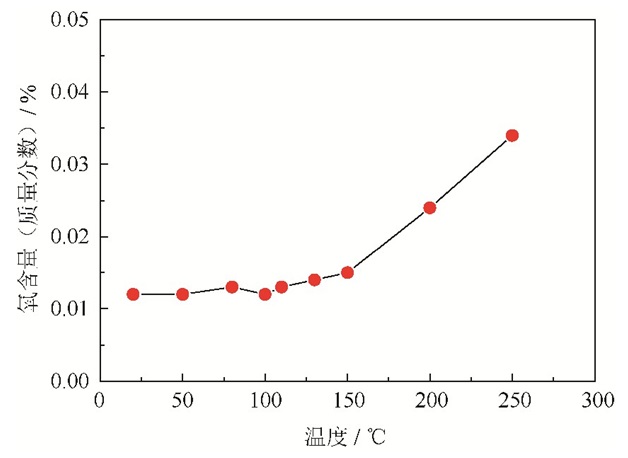
摘要: 通过化学分析、扫描电子显微镜观察、X射线衍射分析及X射线光电子能谱分析等方法, 研究了温度对镍基高温合金粉末氧化行为的影响。结果表明, 室温条件下, 粉末氧含量(质量分数)较低(0.012%), 粉末表面发生部分氧化, 表面存在Ni、Cr、Ti等元素的单质态和以Ni (OH)2、Cr2O3、TiO2为主的氧化物/氢氧化物; 当温度上升至150 ℃, 氧含量增加不明显; 随着温度进一步提高至250 ℃, 粉末氧含量明显增加, 达到0.034%, 粉末表面全部氧化, 表面主要由Ni (OH)2、Cr2O3、TiO2组成。温度对镍基高温合金粉末氧化行为影响显著, 合理控制温度可以获得低氧含量的粉末, 本研究所用镍基高温合金粉末大气条件下最高处理温度为150 ℃。Abstract: Influence of temperature on the oxidation behaviors of the nickel-based superalloy powders was investigated by chemical analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The results indicate that the oxygen content by mass fraction of the nickel-based superalloy powders is 0.012% at room temperature (RT). The oxidation layer partly covers the powder surface in the formation of metallic element (Ni, Cr, Ti) and oxidation state (Ni(OH)2, Cr2O3, TiO2). With the increase of temperature from RT to 150 ℃, the oxygen content seems stable. As the temperature rises to 250 ℃, the oxygen content by mass fraction is 0.034%, showing the obviously increase. The powder surface is completely covered by the oxidation layer at 250 ℃, which is mainly composed of Ni(OH)2, Cr2O3, and TiO2. The elevated temperature significantly affects the oxidation behaviors of the nickel-based superalloy powders, the reasonable control of temperature can obtain the powders with low oxygen content. In this study, the maximum post-process temperature of the nickel-based superalloy powders exposed to the air is 150 ℃.
-
Key words:
- nickel-based superalloy /
- powders /
- oxidation /
- temperature
-
表 1 不同热处理温度下镍基高温合金粉末能谱分析
Table 1. EDS analysis of the nickel-based superalloy powders at the different thermal treatment temperatures
温度/ ℃ 元素质量分数/% C O Al Ti Cr Mn Co Ni 25 5.08 0 2.51 3.10 15.07 0.40 11.79 62.05 150 6.79 0 2.70 2.77 14.79 0.48 11.70 60.77 250 7.62 1.27 2.18 2.25 15.22 0.47 11.45 59.54 -
[1] Reed R C. The Superalloys Fundamentals and Application. London: Cambridge University Press, 2006 [2] Huang Q Y, Li H K. Superalloy. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2000黄乾尧, 李汉康. 高温合金. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2000 [3] Reed R C, Mottura A, Crudden D J. Alloys-by-design: towards optimization of compositions of nickel-based superalloys//Proceedings of The 13th International Symposium of Superalloys. Pennsylvania, 2016: 15 [4] Gessinger G H. Powder Metallurgy of Superalloys. London: Cambridge University Press, 1984 [5] Zhang J, Lou L H. Basic research in development and application of cast superalloy. Acta Metall Sinica, 2018, 54(11): 1637 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00371张健, 楼琅洪. 铸造高温合金研发中的应用基础研究. 金属学报, 2018, 54(11): 1637 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2018.00371 [6] Gu Y F, Osada T, Yokokawa T, et al. Development of nickel-cobalt base P/M superalloys for disk applications//Proceedings of The 13th International Symposium of Superalloys. Pennsylvania, 2016: 209 [7] Raisson G. Evolution of PM nickel base superalloy processes and products. Powder Metall, 2008, 51(1): 10 doi: 10.1179/174329008X286631 [8] Zhang Y W, Liu J T. Development in powder metallurgy superalloy. Mater China, 2013, 32(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJKB201301003.htm张义文, 刘建涛. 粉末高温合金研究进展. 中国材料进展, 2013, 32(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XJKB201301003.htm [9] Fu H, Wang M Y, Ji Z, et al. Effect of thermal deformation on prior particle boundary of FGH96 superalloy. Powder Metall Technol, 2018, 36(3): 201 doi: 10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2018.03.007傅豪, 王梦雅, 纪箴, 等. 热变形对FGH96高温合金原始颗粒边界的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2018, 36(3): 201 doi: 10.19591/j.cnki.cn11-1974/tf.2018.03.007 [10] Ma W B, Liu G Q, Hu B F, et al. Formation of previous particle boundaries of nickel base PM superalloy FGH96. Acta Metall Sinica, 2013, 49(10): 1248 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXB201310013.htm马文斌, 刘国权, 胡本芙, 等. 镍基粉末高温合金FGH96中原始粉末颗粒边界的形成机理. 金属学报, 2013, 49(10): 1248 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JSXB201310013.htm [11] Qin Z J, Liu C Z, Wang Z, et al. Formation and microstructure evolution of precipitation on prior particle boundaries in P/M nickel-base superalloys. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2016, 26(1): 50 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201601007.htm秦子珺, 刘琛仄, 王子, 等. 镍基粉末高温合金原始颗粒边界形成及组织演化特征. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(1): 50 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXZ201601007.htm [12] Gao Z J, Zhang G Q, Li Z, et al. Surface segregation and oxidation behavior of superalloy powders fabricated by argon atomization. Mater Sci Forum, 2013, 747-748: 518 http://www.istic.ac.cn/suoguan/detailed.htm?dbname=xw_qk&wid=0220130700359916 [13] Gao Z J, Zhang G Q, Li Z, et al. Effect of size distribution and oxygen content of powder on microstructure of HIPed superalloy FGH96. Chin J Rare Met, 2012, 36(4): 665 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2012.04.026高正江, 张国庆, 李周, 等. 粉末粒度和氧含量对HIP态FGH96合金组织的影响. 稀有金属, 2012, 36(4): 665 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2012.04.026 [14] Liu N, Li Z, Zhang G Q, et al. Oxidation characteristics of nickel-based superalloy powders prepared by argon gas atomization. Chin J Rare Met, 2011, 35(4): 481 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2011.04.002刘娜, 李周, 张国庆, 等. 氩气雾化镍基高温合金粉末的氧化特性研究. 稀有金属, 2011, 35(4): 481 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2011.04.002 [15] Appa Rao G, Srinivas M, Sarma D S. Effect of oxygen content of powder on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot isostatically pressed superalloy Inconel 718. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 435-436: 84 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.07.053 [16] Xu W Y, Liu Y F, Yuan H, et al. Surface characterization of nickel-base superalloy powder//CMC 2018: Physics and Engineering of Metallic Materials. Xiamen, 2018: 561 [17] Nesbitt H W, Legrand D, Bancroft G M, et al. Interpretation of Ni2p XPS spectra of Ni conductors and Ni insulators. Phys Chem Miner, 2000, 27: 357 doi: 10.1007/s002690050265 [18] Watts J F, Wolstenholme J. An Introduction to Surface Analysis by XPS and AES. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2003 [19] Chasoglou D, Hryha E, Norell M, et al. Characterization of surface oxides on water-atomized steel powder by XPS/AES depth profiling and nano-scale lateral surface analysis. Appl Surf Sci, 2013, 268: 496 doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2012.12.155 [20] Shvab R, Leicht A, Hryha E, et al. Characterization of the virgin and recycled nickel alloy HX powder used for selective laser melting//Proceedings of World PM2016 Congress & Exhibition 2016. Hamburg, 2016: 1692 -




 下载:
下载: