| [1] |
Fang S X, Zhao H L, Zhang Q J. The application status and development trends of ultrasonic machining technology. J Mech Eng, 2017, 53(19): 22 doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.19.022房善想, 赵慧玲, 张勤俭. 超声加工技术的应用现状及其发展趋势. 机械工程学报, 2017, 53(19): 22 doi: 10.3901/JME.2017.19.022
|
| [2] |
Shang B, Jiang R P, Li X Q, et al. Effect of ultrasonic outfield on solidification rules of ZL205A aluminum alloy under different temperature-control states. Chin J Eng, 2019, 41(8): 1007商兵, 蒋日鹏, 李晓谦, 等. 超声外场对不同温控状态下ZL205A铝合金凝固规律的影响. 工程科学学报, 2019, 41(8): 1007
|
| [3] |
Eskin D G, Wang F. Joint effect of ultrasonic vibrations and solid metal addition on the grain refinement of an aluminium alloy. Metals, 2019, 9(2): 161 doi: 10.3390/met9020161
|
| [4] |
Liu X Y. Simulation on Microstructure Evolution of Al2O3/SiC Ceramic Cutting Tool Materials [Dissertation]. Tianjin: Hebei University of Technology, 2015.刘曦阳. Al2O3/SiC陶瓷刀具材料微观组织演变的模拟[学位论文]. 天津: 河北工业大学, 2015.
|
| [5] |
Wang X M, Huang L X, Qin X G. Kinetic Monte Carlo simulation of soild-state sintering of powder. Chin J Stereol Image Anal, 2017, 22(2): 151王晓勉, 黄龙霄, 秦湘阁. 粉末固相烧结的动力学蒙特卡洛模拟. 中国体视学与图像分析, 2017, 22(2): 151
|
| [6] |
Shao X, Zheng Y, Wang S W, et al. Monte Carlo simulation on grain growth of the ceramic phase in Mo2FeB2-based cermets during the liquid phase sintering. Cem Carbide, 2018, 35(3): 147邵想, 郑勇, 王守文, 等. Mo2FeB2基金属陶瓷液相烧结过程中硬质相晶粒生长的蒙特卡罗模拟. 硬质合金, 2018, 35(3): 147
|
| [7] |
Ma L, Yu J C, Guo X, et al. Pressureless densification and properties of TiB2–B4C composite ceramics with Ni as additives. Micro Nano Lett, 2018, 13(7): 947 doi: 10.1049/mnl.2017.0709
|
| [8] |
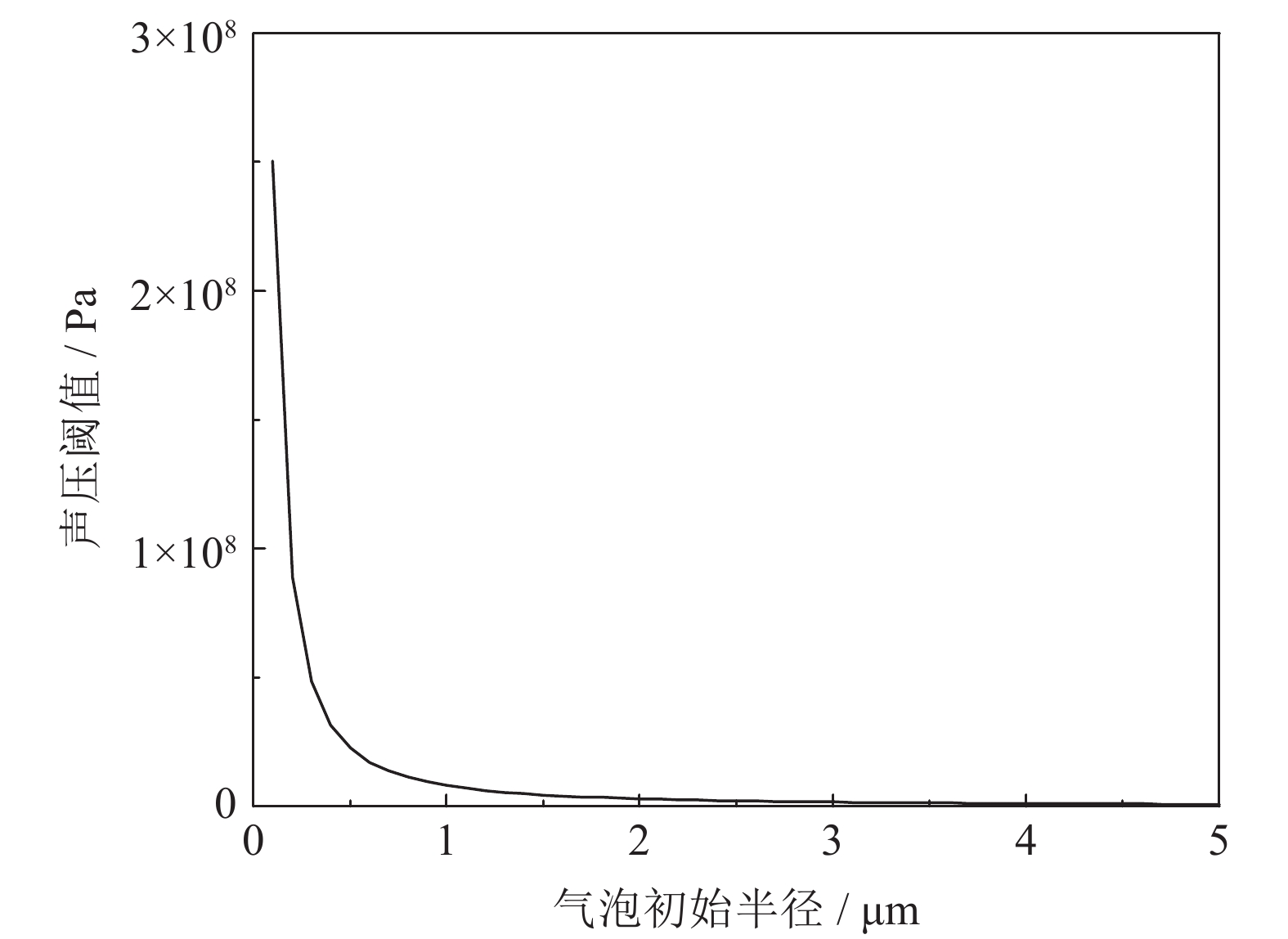
Zhang C B. Numerical Analysis of Cavitation Bubbles Kinematics in Tumor Ultrasound Therapy [Dissertation]. Dalian: Dalian Jiaotong University, 2016.张晨博. 肿瘤超声治疗中气泡空化运动学数值分析[学位论文]. 大连: 大连交通大学, 2016.
|
| [9] |
Bao R, Li L B, Yi J H, et al. The fabrication of carbon nanotube reinforced copper matrix powder. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(6): 454 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.06.011鲍瑞, 李澜波, 易健宏, 等. CNTs增强铜基复合粉末制备的研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(6): 454 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.06.011
|
| [10] |
Cai C L, Tu J, Guo X S, et al. The impacts of encapsulating shell properties and acoustic driving parameters on the dynamic behavior of interacting microbubbles. Acta Acust, 2019, 44(4): 772蔡晨亮, 屠娟, 郭霞生, 等. 包膜黏弹特性及声驱动参数对相互作用微泡动力学行为的影响. 声学学报, 2019, 44(4): 772
|
| [11] |
Hu Q Q, Zhang L H. Effects of ultrasonic cavitation behavior on grain refinement of 7050 aluminum alloy. Spec Cast Nonferrous Alloys, 2012, 32(4): 387胡谦谦, 张立华. 超声空化对7050铝合金的细晶分析. 特种铸造及有色合金, 2012, 32(4): 387
|
| [12] |
Li Z W, Xu Z W, Ma L, et al. Cavitation at filler metal/substrate interface during ultrasonic-assisted soldering. Part II: Cavitation erosion effect. Ultrason Sonochem, 2019, 50: 278 doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2018.09.027
|
| [13] |
Guan Z D, Zhang Z T, Jiao J S. Physical Properties of Inorganic Materials. 2nd Ed. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011.关振铎, 张中太, 焦金生. 无机材料物理性能. 2版. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011.
|
| [14] |
Wang X, Atkinson A. Combining densification and coarsening in a Cellular Automata-Monte-Carlo simulation of sintering: Methodology and calibration. Comput Mater Sci, 2018, 143: 338 doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2017.11.023
|
| [15] |
Yan S W, Huang S Y, Hu J H, et al. Development and application of numerical simulation in powder metallurgy manufacturing. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(1): 57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.01.010颜士伟, 黄尚宇, 胡建华, 等. 数值仿真技术在粉末冶金零件制造中的应用及研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(1): 57 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.01.010
|
| [16] |
Zhang D L, Weng G A, Gong S P, et al. Computer simulation of grain growth of intermediate and final-stage sintering and Ostwald ripening of BaTiO3-based PTCR ceramics. Mater Sci Eng B, 2003, 99(1-3): 428 doi: 10.1016/S0921-5107(02)00449-X
|




 下载:
下载: