Effect of aging treatment on the behavior of room temperature tensile of P/M superalloys used for inertia friction welding joints
-
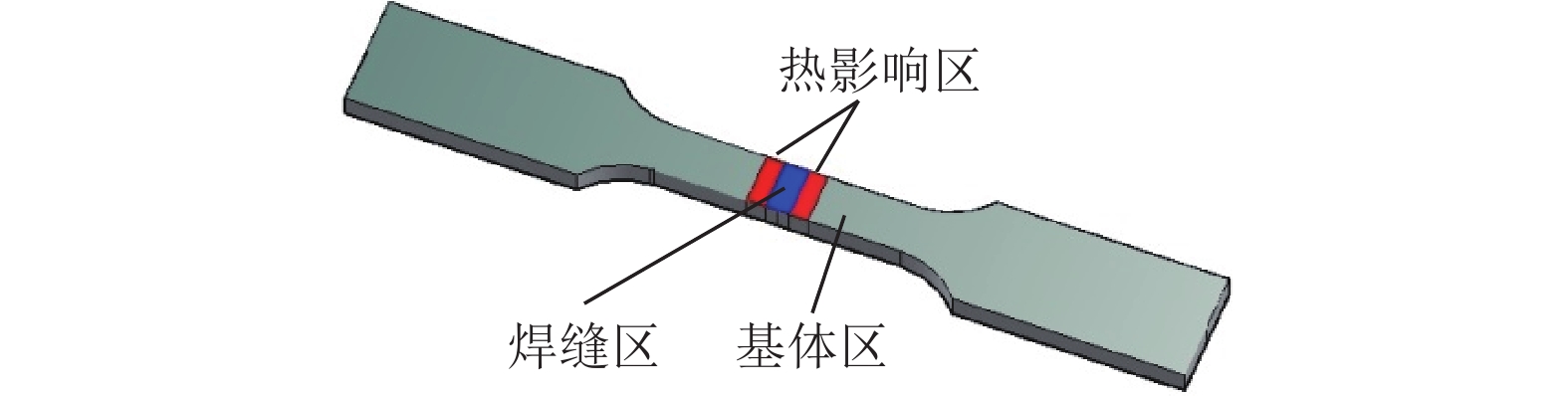
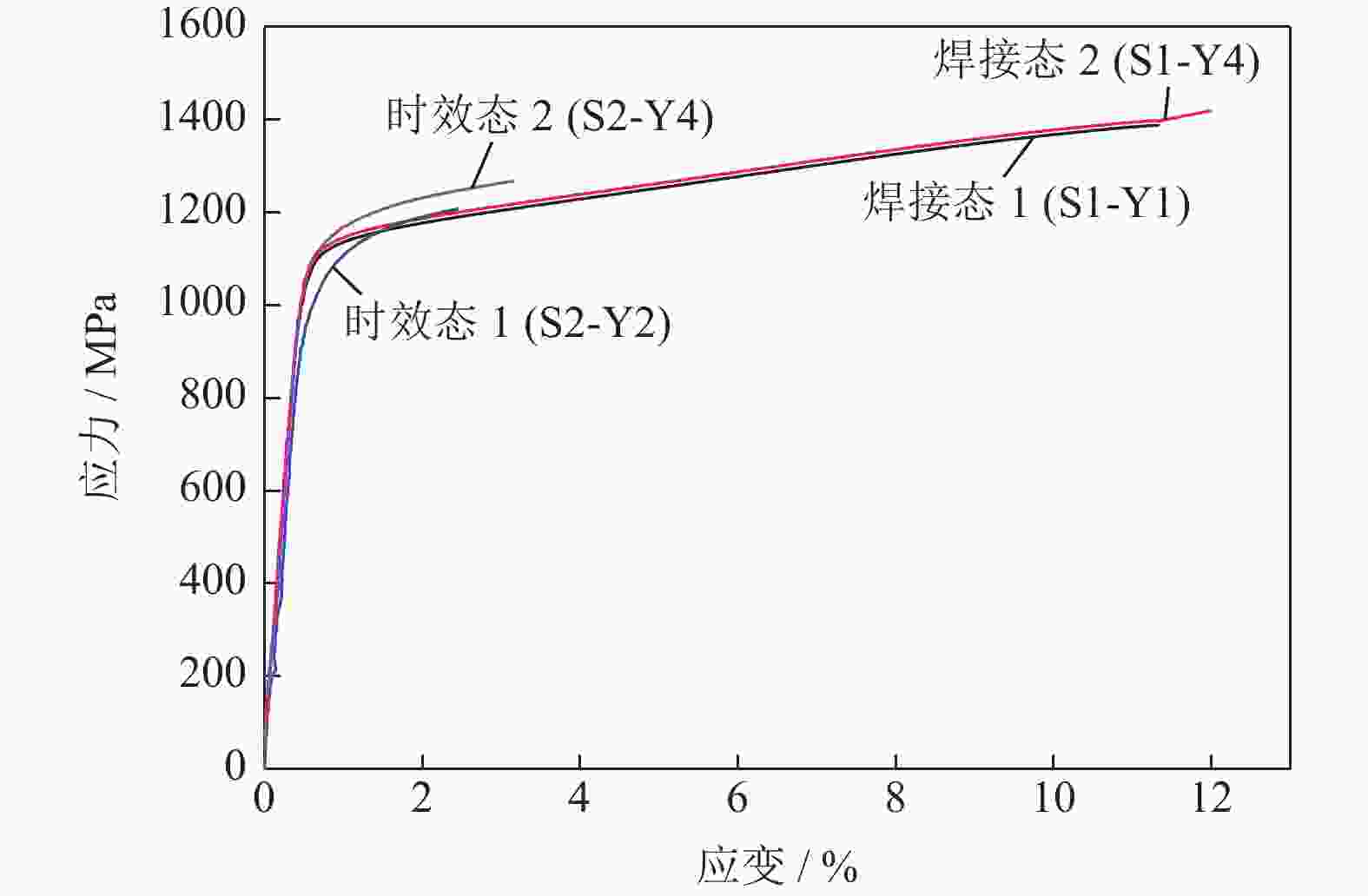
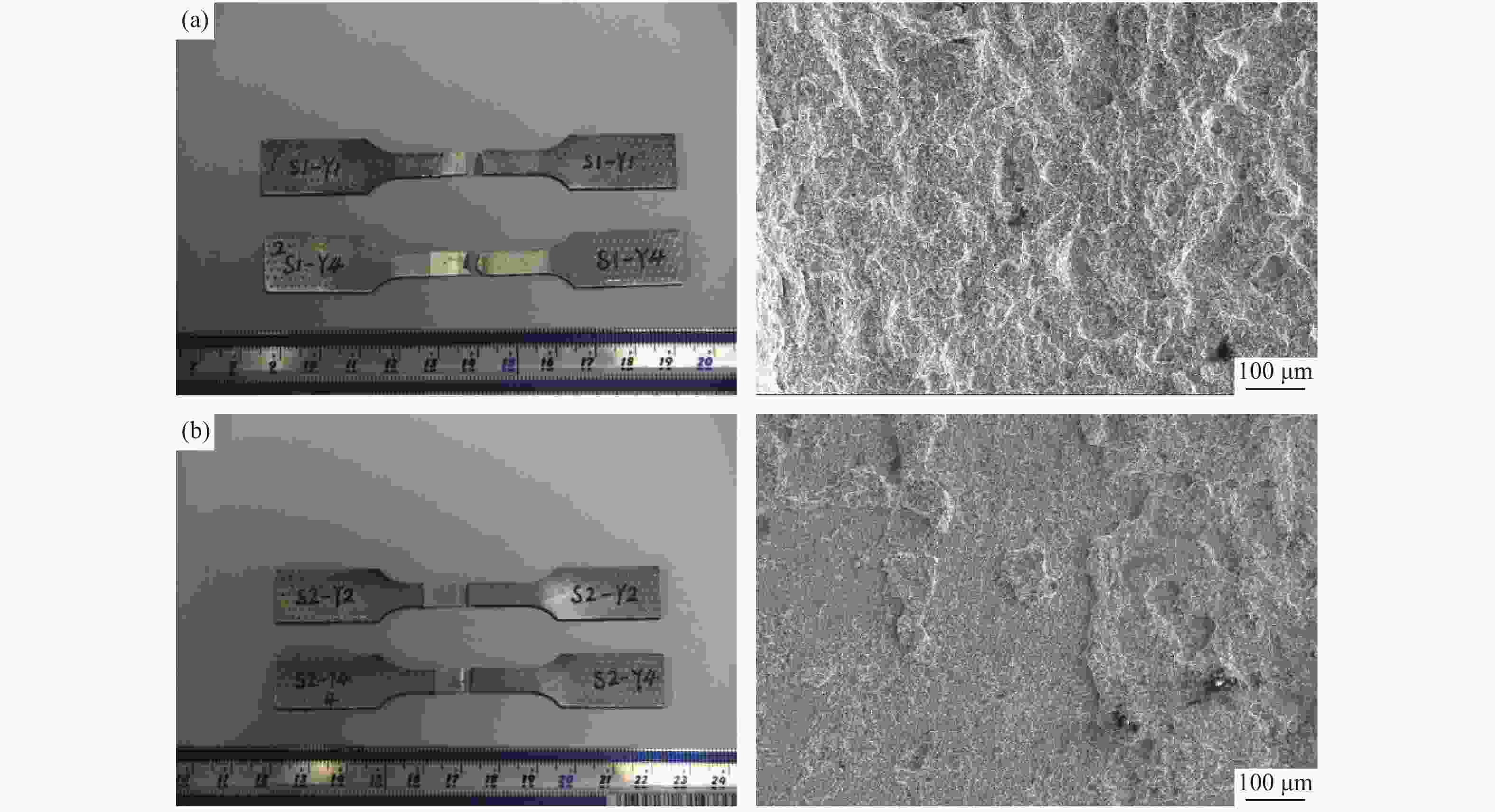
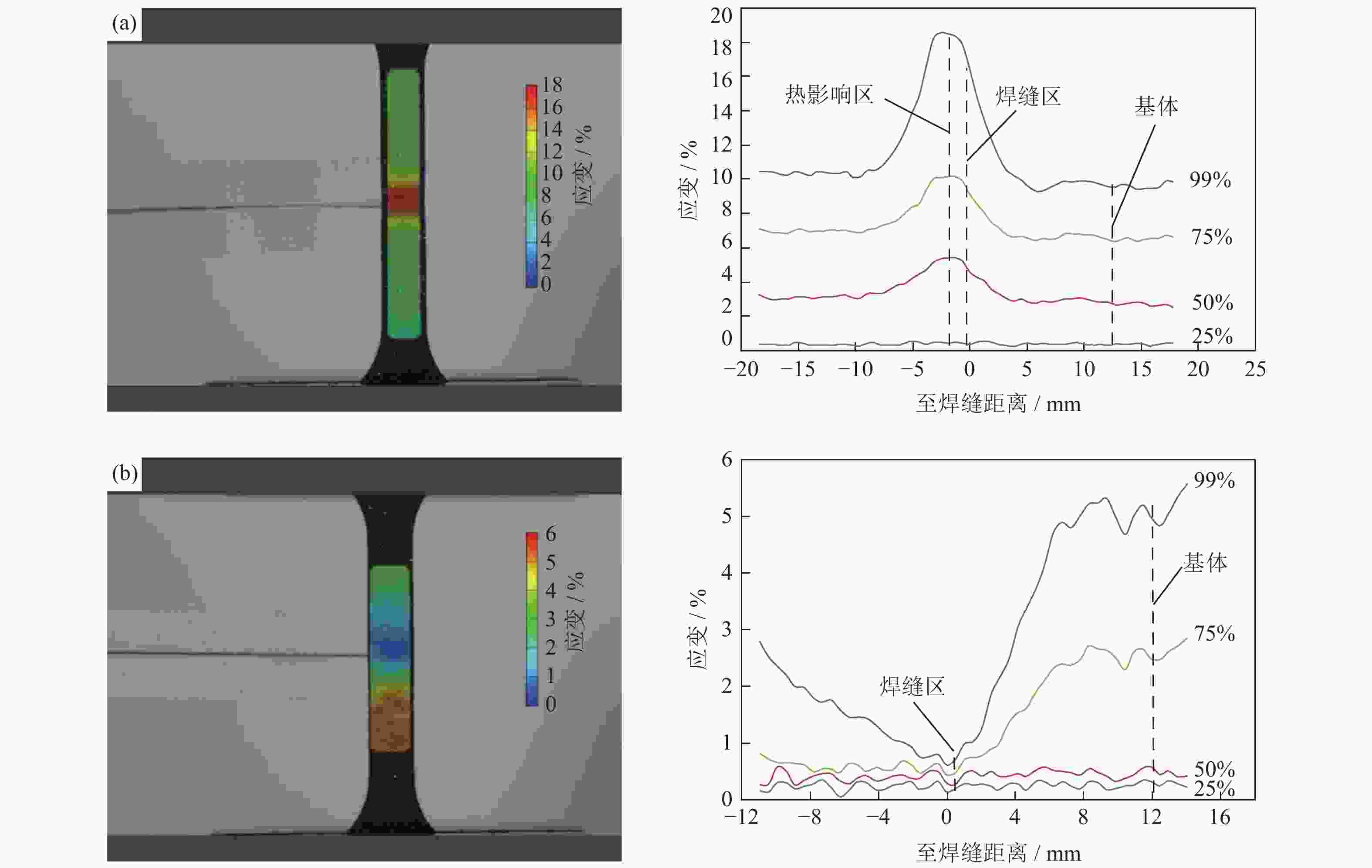
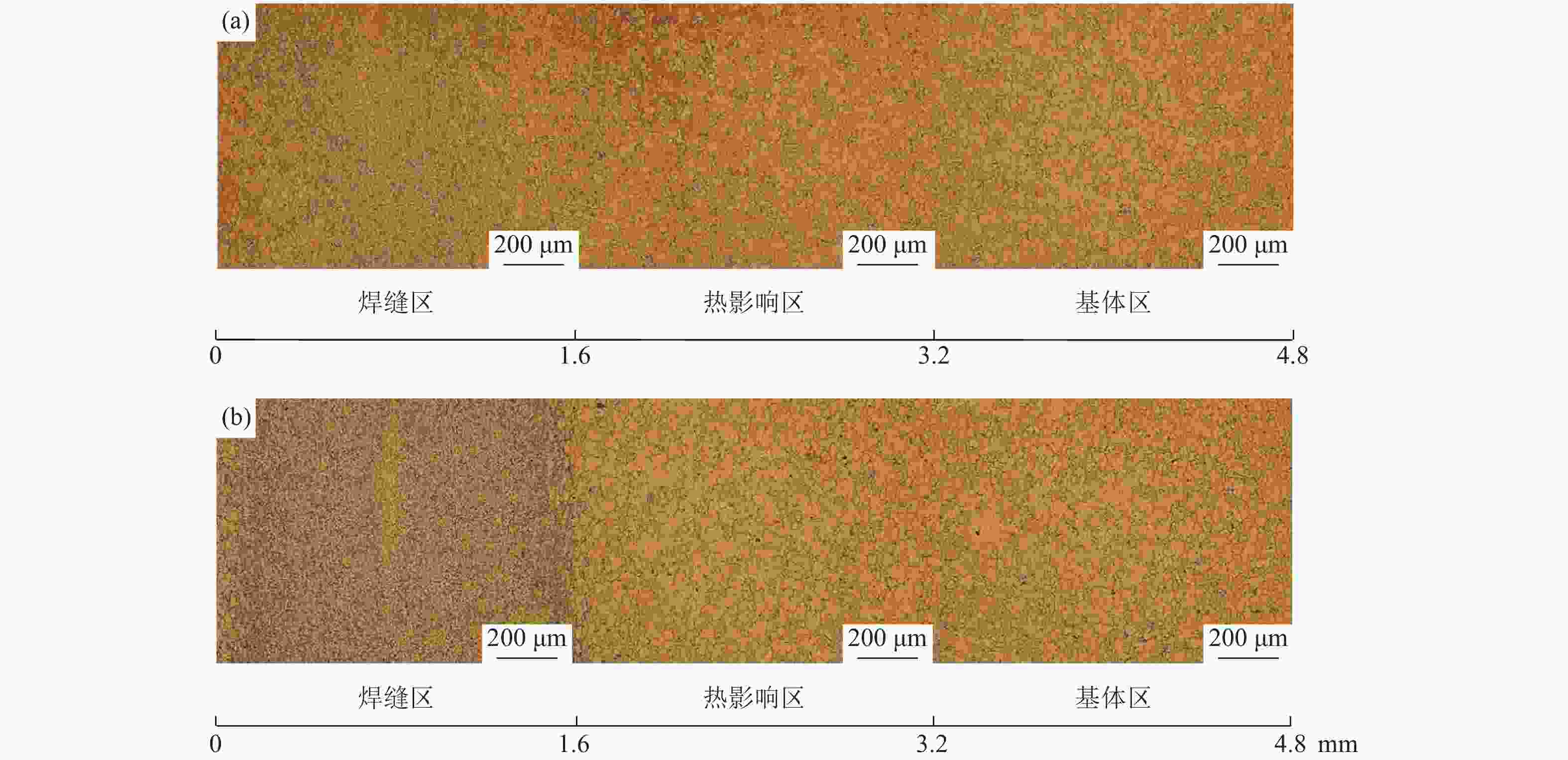
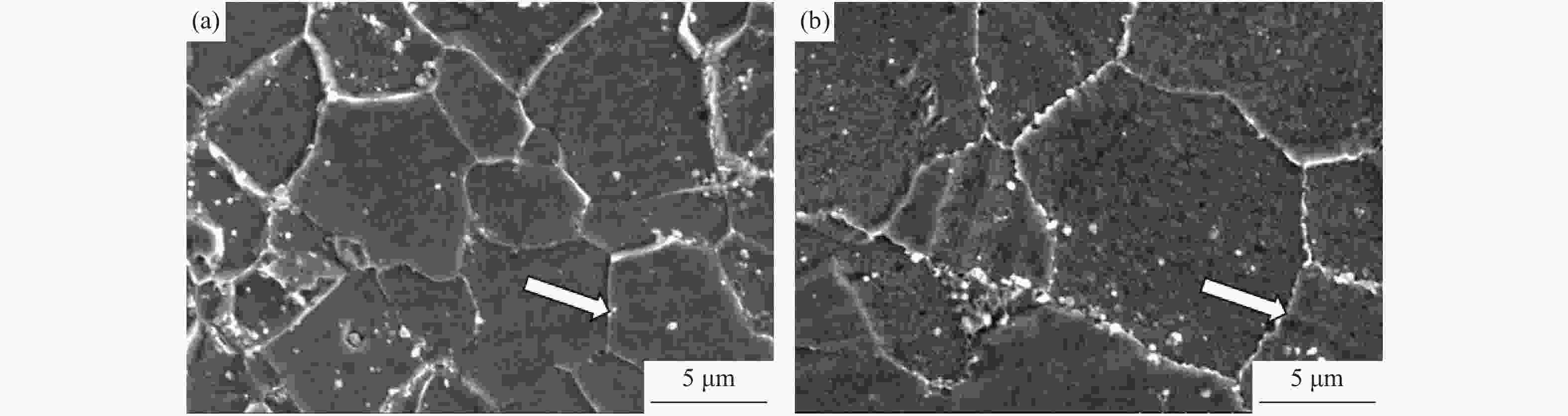
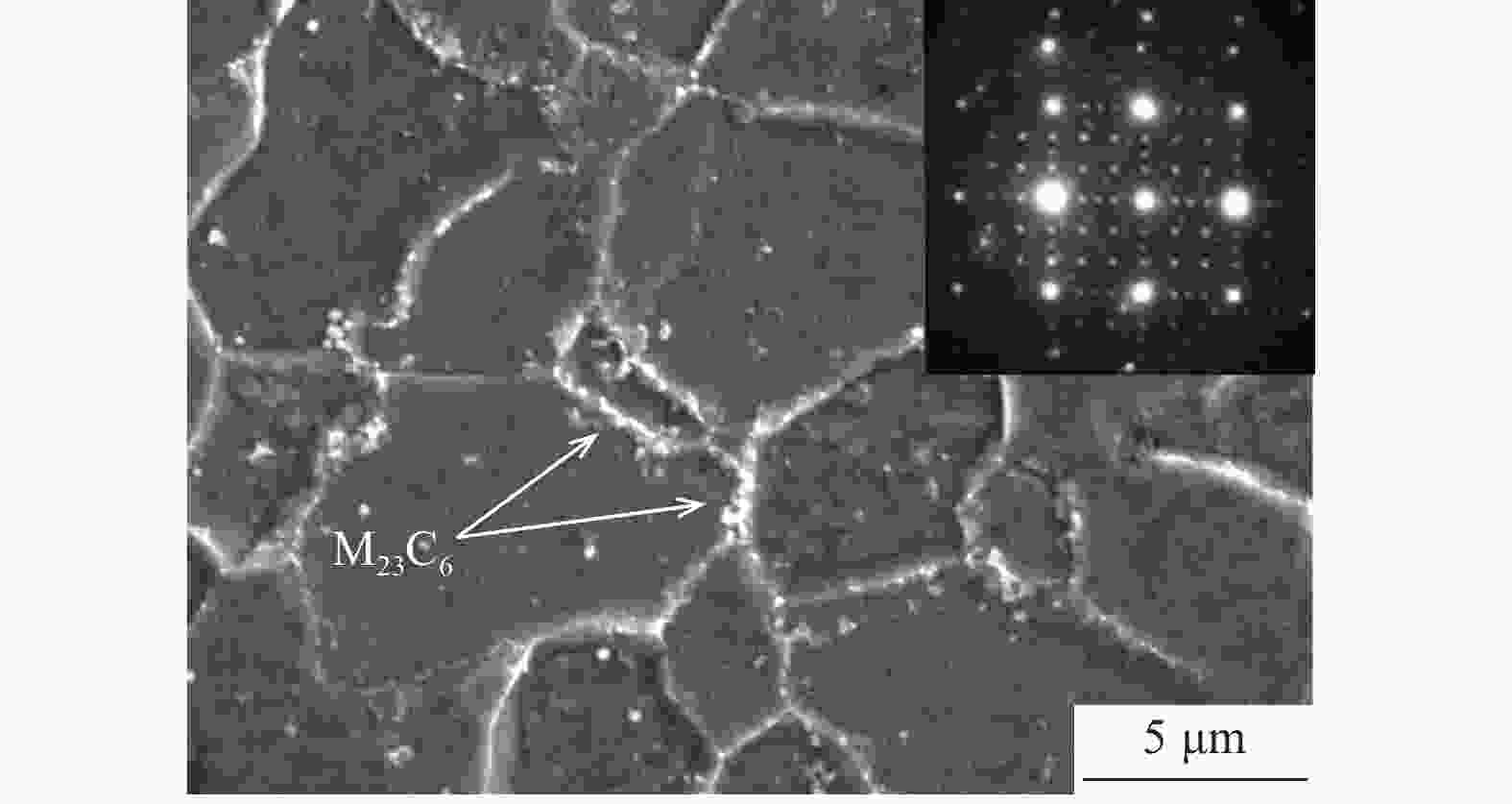
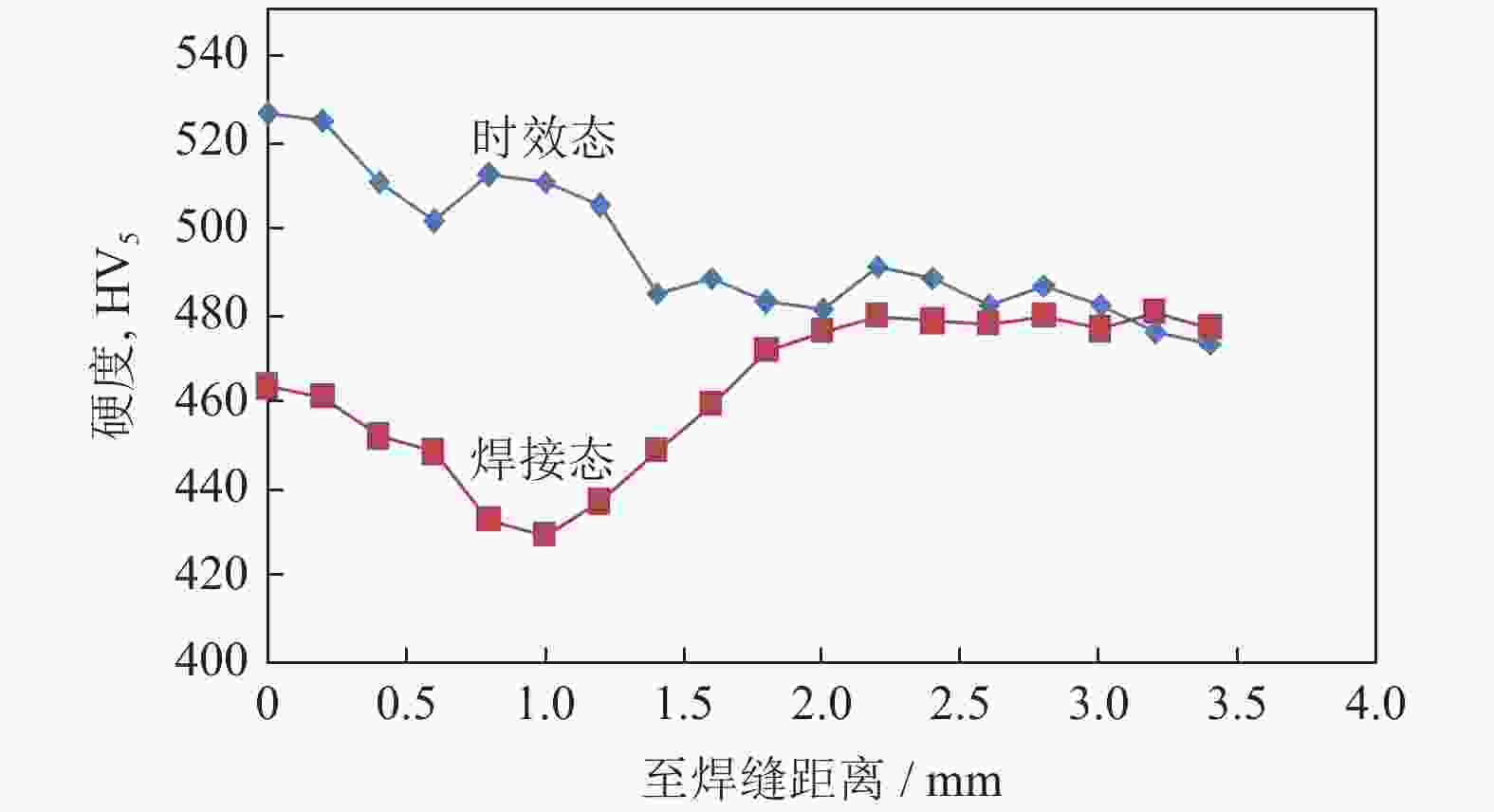
摘要: 对惯性摩擦焊扩散连接的FGH96合金试样经时效处理前后的室温拉伸行为进行了研究,并对其失效机制进行了评估。结果表明,对于焊接态(原状态)FGH96合金试样,由于焊缝区和热影响区的γ′相综合强化效果弱,晶界平直化,导致焊缝区和热影响区的强度低于基体,在室温拉伸过程中塑性应变量大;由于热影响区的晶粒尺寸大,晶界强化效果弱,且位错强化效果低于焊缝区,使热影响区成为整个试样强度的最薄弱区域,裂纹从该处萌生,断口表现出一定的塑性特征。对于时效处理后的FGH96合金试样,由于γ′相的粗化,强化相体积分数的提高,及γ′/γ之间错配度的增加,提高了γ′相的综合强化效果,使焊缝区和热影响区的强度较焊接态试样显著提高,并高于基体,在室温拉伸过程中基体的塑性应变量相对较大。连续或半连续析出的M23C6型碳化物弱化了焊缝区晶界的结合强度,导致试样从该处断裂,并出现了脆性断裂的特征。显微硬度的测试结果较好验证了焊接态和时效态试样强度的分布情况。Abstract: The behavior of the room temperature tensile of the FGH96 P/M superalloys connected by the inertia friction welding before and after the aging treatment was investigated, and the failure mechanism of the FGH96 P/M superalloys was evaluated. The results show that, for the FGH96 P/M superalloy samples in the as-welded (original) state, the strength of the superalloy samples in the welding line zone (WLZ) and the heat affected zone (HAZ) is lower than that of the parent alloys, and the plastic strain is the largest during the room temperature tensile process, due to the weak comprehensive strengthening effect of γ′ phase and the straight grain boundaries in WLZ and HAZ. Because of the large grain size in HAZ, the weak strengthening effect of grain boundaries, and the lower dislocation density than that of WLZ, the strength of the superalloy samples in HAZ becomes the weakest, where the cracks originate and show a certain plastic characteristic of the fracture. For the FGH96 P/M superalloy samples after the aging treatment, the comprehensive strengthening effect of γ′ phase is improved, due to the coarsening of γ′ phase, the increase of the strengthened phase volume fraction, and the mismatch increase between γ and γ′, compared with the superalloy samples in the as-welded state, the strength of the superalloy samples after the aging treatment in WLZ and HAZ is higher than that of the parent alloys, and the plastic strain of the parent alloys is larger during the room temperature tensile process. The M23C6 carbide precipitated continuously or semi-continuously weakens the bonding strength of grain boundary in the as-welded state, leading to the sample fracture and showing the characteristic of brittle fracture. The results of microhardness test verify the strength distribution of the FGH96 P/M superalloy samples in the as-welded state and after the aging treatment.
-
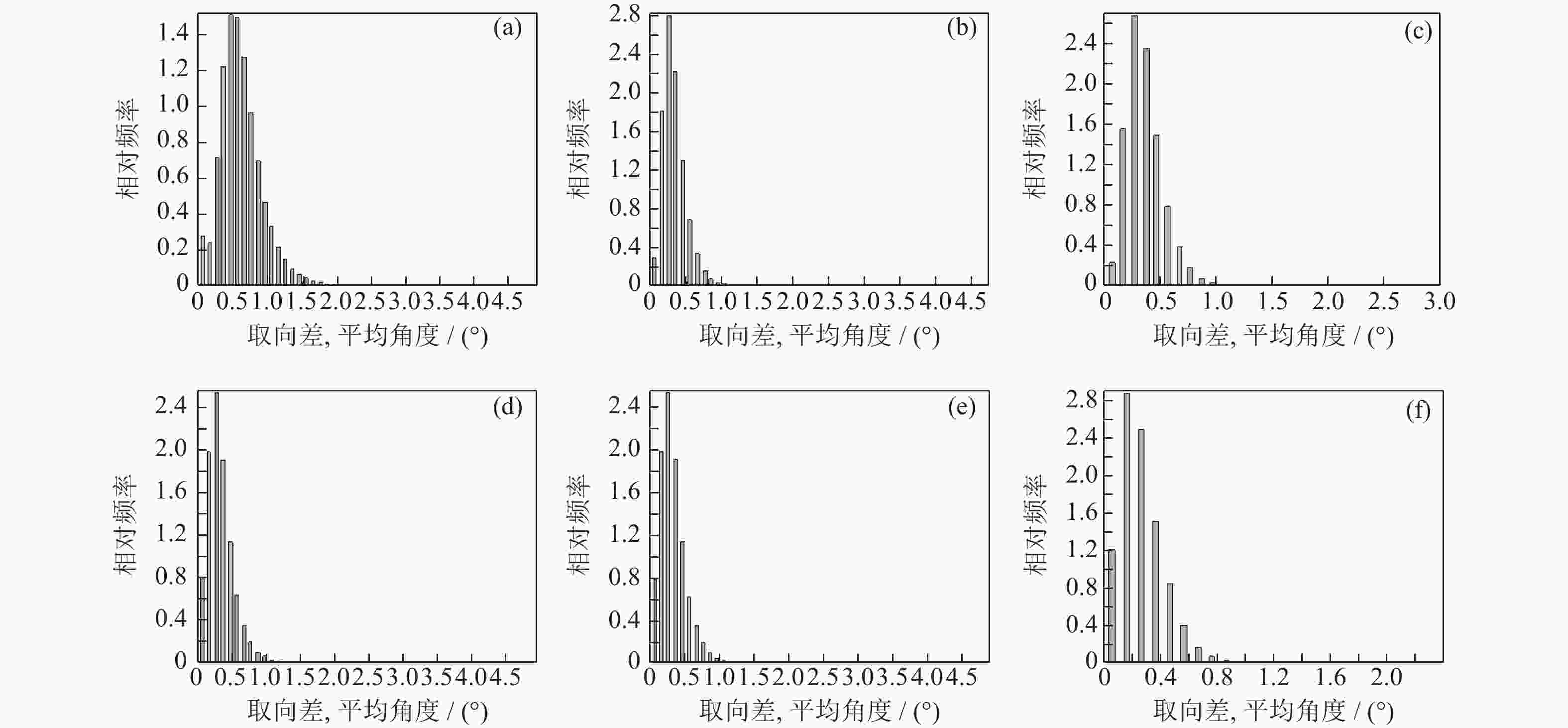
图 9 试样部位及时效处理对晶体取向差的影响:(a)焊接态焊缝区;(b)焊接态热影响区;(c)焊接态基体区;(d)时效态焊缝区;(e)时效态热影响区;(f)时效态基体区
Figure 9. Influence of the sample zones and ageing treatment on the grain misorientation: (a) WLZ in as-welded state; (b) HAZ in as-welded state; (c) PAZ in as-welded state; (d) WLZ by PWHT; (e) HAZ by PWHT; (f) PAZ by PWHT
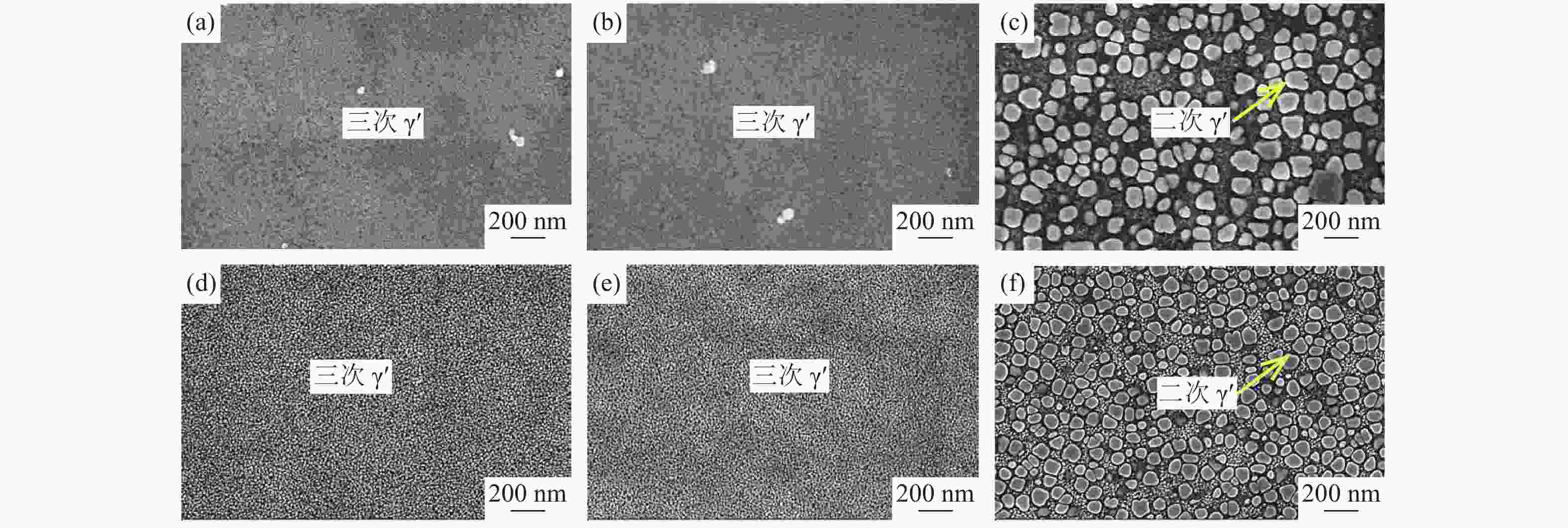
图 10 试样部位及时效处理对三次γ′相尺寸的影响:(a)焊接态焊缝区;(b)焊接态热影响区;(c)焊接态基体区;(d)时效态焊缝区;(e)时效态热影响区;(f)时效态基体区
Figure 10. Influence of the sample zones and ageing treatment on the grain size of tertiary γ′: (a) WLZ in as-welded state; (b) HAZ in as-welded state; (c) PAZ in as-welded state; (d) WLZ by PWHT; (e) HAZ by PWHT; (f) PAZ by PWHT
表 1 FGH96合金化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of the FGH96 alloys
% Co Cr Mo W Al Ti Nb C B Zr Ni 12.960 16.170 4.040 4.010 2.200 3.780 0.690 0.050 0.016 0.042 余量 -
[1] Zou J W, Wang W X. Development and application of P/M superalloy. J Aeronaut Mater, 2006, 26(3): 244 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.03.051邹金文, 汪武祥. 粉末高温合金研究进展与应用. 航空材料学报, 2006, 26(3): 244 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.03.051 [2] Wang W X, He F, Zou J W. The application and development of P/M superalloys. Aviat Mainten Eng, 2002(6): 26汪武祥, 何峰, 邹金文. 粉末高温合金的应用与发展. 航空工程与维修, 2002(6): 26 [3] Tu W J, Pollock T M. Deformation and strain storage mechanisms during high-temperature compression of a powder metallurgy nickel-base superalloy. Metall Mater Trans A, 2010, 41: 2002 doi: 10.1007/s11661-010-0251-1 [4] Han F L. Welding of PM structure parts. Powder Metall Technol, 2011, 29(3): 224韩凤麟. 粉末冶金结构零件焊接. 粉末冶金技术, 2011, 29(3): 224 [5] Wang H J, Cui Z W, Sun F, et al. Superalloy GH4169 complicated components prepared by selective laser melting forming technique. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(5): 368 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.05.009王会杰, 崔照雯, 孙峰, 等. 激光选区熔化成形技术制备高温合金GH4169复杂构件. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(5): 368 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.05.009 [6] Fukumoto S, Yamamoto D, Tomita T, et al. Effect of post weld heat treatment on microstructures and mechanical properties of AZ31B friction welded joint. Mater Trans, 2007, 48(1): 44 doi: 10.2320/matertrans.48.44 [7] Baxter G J, Preuss M, Withers P J. Inertia friction welding of nickel base superalloys for aerospace applications. Miner Met Mater Ser, 1992: 437 [8] Preuss M, Withers P J, Pang J W L, et al. Inertial welding nickel-based superalloy: Part II. Residual stress characterization. Metall Mater Trans A, 2002, 33(10): 3227 doi: 10.1007/s11661-002-0308-x [9] Preuss M, Withers P J, Pang J W L, et al. Inertial welding nickel-based superalloy: Part I. Metallurgical characterization. Metall Mater Trans A, 2002, 33(10): 3215 doi: 10.1007/s11661-002-0307-y [10] Karadge M, Grant B, Withers P J, et al. Thermal relaxation of residual stresses in nickel-based superalloy inertia friction welds. Metall Mater Trans A, 2011, 42(8): 2301 doi: 10.1007/s11661-011-0613-3 [11] Loyer Danflou H, Marty M, Walder A. Formation of serrated grain boundaries and their effect on the mechanical properties in a P/M nickel base superalloy // Superalloys 1992. Pennsylvania, 1992: 63 [12] He S C, Zhang T C, Guo D L, et al. Normal mechanical property analysis of P/M superalloy FGH96 inertia friction welding joint. J Aeronaut Mater, 2006, 26(3): 122 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.03.025何胜春, 张田仓, 郭德伦, 等. 粉末高温合金FGH96惯性摩擦焊接头常温力学性能分析. 航空材料学报, 2006, 26(3): 122 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.03.025 [13] Wang B, Huang J H, Zhang T C, et al. Microstructure and evolution process during inertia friction welding of FGH96/GH4169 superalloy. Aeronaut Manuf Technol, 2015(11): 83王彬, 黄继华, 张田仓, 等. FGH96/GH4169高温合金惯性摩擦焊微观组织及演变过程. 航空制造技术, 2015(11): 83 [14] Ji S D, Liu W, Zhang L G, et al. Numerical simulation of material flow behavior in inertia friction welding of FGH96 alloy. Mater Sci Technol, 2013, 21(1): 109 doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20130119姬书得, 刘伟, 张利国, 等. FGH96合金惯性摩擦焊过程材料流动行为的数值模拟. 材料科学与工艺, 2013, 21(1): 109 doi: 10.11951/j.issn.1005-0299.20130119 [15] Wang X F, Zou J W, Yang J, et al. Microstructure characterization of inertia friction bonding region for nickel-based superalloy FGH96. Mater China, 2019, 38(8): 806王晓峰, 邹金文, 杨杰, 等. FGH96合金惯性摩擦焊焊区的微观组织表征. 中国材料进展, 2019, 38(8): 806 [16] Viswanathan G B, Sarosi P, Henry M, et al. Deformation mechanisms at intermediate creep temperature in Rene88 DT // Superalloys 2004. Pennsylvania, 2004: 173 [17] Siems C T. Superalloy. Translated by Zhao J. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology Press, 1992C T 西姆斯. 高温合金. 赵杰, 译. 大连: 大连理工大学出版社, 1992 [18] Huang Z W, Li H Y, Baxter G, et al. Electron microscopy characterization of the weld line zones of an inertial friction welded superalloy. J Mater Process Technol, 2011, 211(12): 1927 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.06.019 -



 下载:
下载: