Research on catalyst debinding process of 316L/POM composite parts fabricated by fused deposition modeling
-
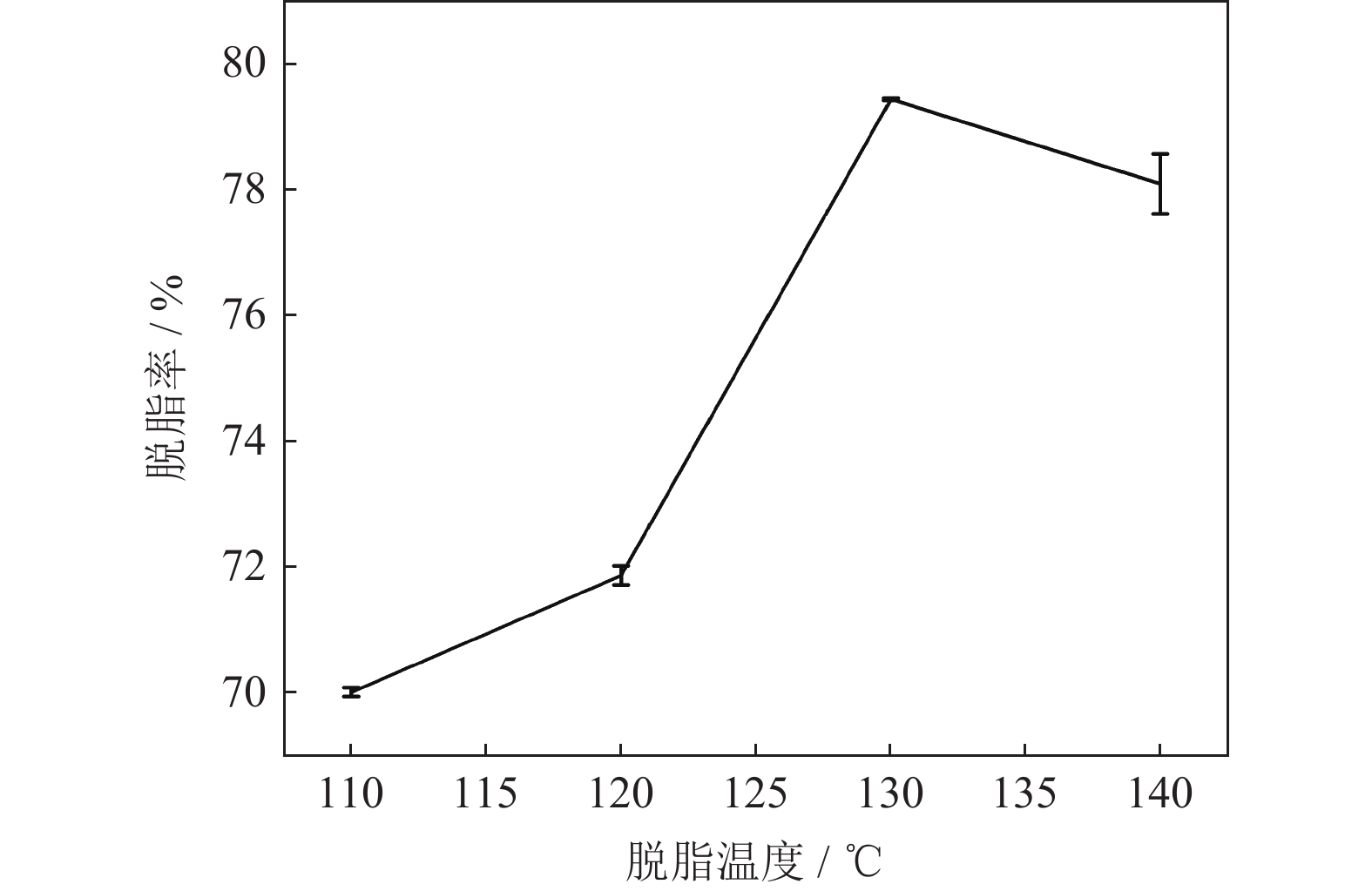
摘要: 采用熔融沉积成型制备了316L/POM复合材料成型坯,研究了脱脂温度、催化剂流量、脱脂时间、试样尺寸和填充率等参数对熔融沉积成型坯脱脂率的影响。结果表明:随着脱脂温度的增大,脱脂率升高,但在130~140 ℃时有所下降。随着催化剂流量和脱脂时间的增大,脱脂率升高。随着试样厚度和填充率的增大,脱脂率降低,但试样的平面尺寸对脱脂率的影响不大。通过对熔融沉积成型坯的计算机断层扫描和扫描电子显微镜观察发现,在熔融沉积成型打印时,熔融丝料间隙形成的气体交换通道网可以加快脱脂速率。
-
关键词:
- 熔融沉积成型 /
- 催化脱脂 /
- 脱脂率 /
- 316L/POM复合材料 /
- 3D打印
Abstract: 316L/POM composite parts were prepared by fused deposition modeling (FDM). The effects of debinding temperature, catalyst flow rate, debinding time, sample size, and filling rate on the debinding rate of FDM parts were studied. The results show that, the debinding rate increases with the increase of debinding temperature but decreases at 130~140 ℃. The increases of the catalyst flow rate and debinding time aggrandize the bebinding rate. The debinding rate decreases with the increase of the sample thickness and filling rate, but the plane size of the samples has little impact on the debinding rate. The computed tomography (CT) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) of FDM parts reveal that the gas exchange channel network formed in the large fuse gaps during FDM printing can accelerate the debinding rate.-
Key words:
- fused deposition modeling /
- catalytic debinding /
- debinding ratio /
- 316L/POM composites /
- 3D printing
-
表 1 实验材料配比(质量分数)
Table 1. Experimental material composition
% 316L不锈钢粉末(气雾化) 聚甲醛(POM) 聚丙烯(PP) 氧化锌 邻苯二甲酸二辛酯和邻苯二甲酸二丁酯混合物
(质量比0.3:10.0)86 11 1 1 1 表 2 熔融沉积成型打印参数
Table 2. Printing parameters of the fused deposition modeling
层高 / mm 打印速度 /
(mm∙s‒1)喷嘴直径 / mm 填充方式 线宽 / mm 打印平台温度 / ℃ 喷嘴温度 / ℃ 外壳层数 /
外壳形式0.2 20 0.6 往复直线填充 0.7 130 230 3层/偏置挤出 表 3 对比实验中催化脱脂条件
Table 3. Experimental scheme of the catalytic degreasing conditions
脱脂温度 / ℃ 催化剂流量 / (mL∙min‒1) 脱脂时间 / h 试样尺寸 / mm 填充率 / % 氮气流量 / (m3∙h‒1) 催化剂 110、120、
130、1400.05、0.15、
0.25、0.350.5、1.0、2.0、
3.0、4.0(0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2、1.4)×(25×20)×6
25×20×(4、6、8、10)30、40、50、60、
70、80、90、1000.25 68硝酸 -
[1] Liu B, Wang Y, Lin Z, et al. Creating metal parts by fused deposition modeling and sintering. Mater Lett, 2020, 263: 127252 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2019.127252 [2] Lengauer W, Duretek I, Fürst M, et al. Fabrication and properties of extrusion-based 3D-printed hardmetal and cermet components. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2019, 82: 141 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2019.04.011 [3] Gong H, Snelling D, Kardel K, et al. Comparison of stainless steel 316L parts made by FDM and SLM-based additive manufacturing processes. JOM, 2019, 71(3): 880 doi: 10.1007/s11837-018-3207-3 [4] Thompson Y, Gonzalez-Gutierrez J, Kukla C, et al. Fused filament fabrication, debinding and sintering as a low cost additive manufacturing method of 316L stainless stee. Addit Manuf, 2019, 30: 100861 [5] Miao J F, Li F, He X T, et al. Analysis of molding quality of 3D printing metal powder/PVA composite slurry. Plastics, 2019, 48(2): 119苗剑飞, 李飞, 何雪涛, 等. 3D打印金属粉末/PVA复合浆料的成型质量分析. 塑料, 2019, 48(2): 119 [6] Cheng Y H, Bian H G, Wang C S, et al. A new 3D printing molding‒degreasing‒sintering process. Chin J Process Eng, 2020, 20(6): 687 doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.219304程耀华, 边慧光, 汪传生, 等. 一种新型3D打印成型‒脱脂‒烧结工艺. 过程工程学报, 2020, 20(6): 687 doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.219304 [7] Attia U M, Alcock J R. Fabrication of hollow, 3D, micro-scale metallic structures by micro-powder injection moulding. J Mater Process Technol, 2012, 212(10): 2148 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.05.022 [8] Jing X L, Chen H, Liu B, et al. Research on preparation and application of the catalytic debinding feedstock for 304 stainless steel. Powder Metall Ind, 2017, 27(3): 31 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.20160068敬小龙, 陈慧, 刘兵, 等. 304不锈钢注射成形用催化脱脂型喂料制备及其应用研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2017, 27(3): 31 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.20160068 [9] Yu J, Li Y M, Li D Y, et al. Effect of powder loading on mechanical properties of metal injection molding 17-4PH stainless steel. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2018, 23(1): 32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2018.01.005喻建, 李益民, 李东阳, 等. 粉末装载量对金属注射成形17-4PH不锈钢力学性能的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2018, 23(1): 32 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2018.01.005 [10] Xu X M, Li D X, Wu W, et al. The modified catalytic debinding binder and its application research. Powder Metall Ind, 2015, 25(5): 36 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.20140093徐小明, 李笃信, 吴谓, 等. 改进型催化脱脂型粘结剂及其应用研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2015, 25(5): 36 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-6543.20140093 [11] Zhang C, Liu C L. Rheological behaviors and degreasing process of polyformaldehyde/polypropylene/titanium catalytic degreasing metarials used for metal powder injection molding. Hot Working Technol, 2017, 46(24): 45章诚, 刘春林. 金属粉末注射成型催化脱脂料POM/PP/Ti的流变行为及脱脂工艺. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(24): 45 [12] Chen H, Jing X L, Liu B, et al. Catalytic debinding for 304L powder injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(6): 440 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.06.008陈慧, 敬小龙, 刘兵, 等. 304L不锈钢粉末注射成形研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(6): 440 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.06.008 [13] Zheng L Q. Study on Catalytic Degreasing in Powder Injection Molding [Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2009郑礼清. 粉末注射成形催化脱脂研究[学位论文]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2009 [14] Zhou R. Research on Catalytic Debinding of Titanium and Effect of Oxygen on Mechanical Properties and Microscopic Deformation Mechanisms of Metal Injection Molding Titanium [Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2014周蕊. 纯钛催化脱脂工艺及氧对注射成形纯钛力学行为及变形微观机制的影响研究[学位论文]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014 [15] Zhou S Y, Cai Y X, Luo T G, et al. Research on preparation and properties of catalytic debinding feedstock for Titanium metal injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2015, 33(2): 95周时宇, 蔡一湘, 罗铁钢, 等. 钛注射成形用催化脱脂型喂料的制备与性能研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2015, 33(2): 95 -




 下载:
下载: