Effect of hot rotary swaging deformation on microstructure and properties of ASP30 grade powder metallurgical high speed steels strengthened by TiCN
-
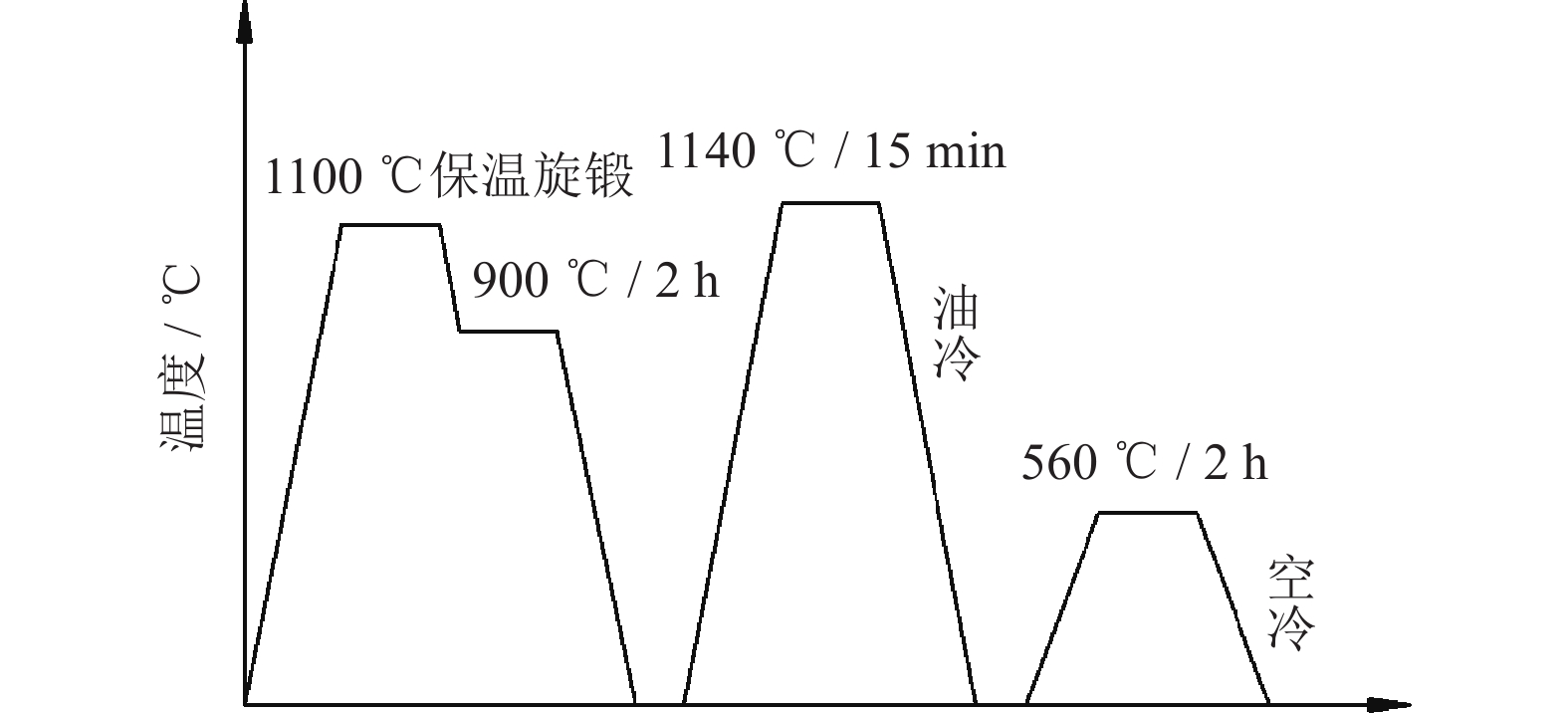
摘要: 采用粉末冶金法制备TiCN强化ASP30粉末冶金高速钢棒料,研究TiCN及旋锻变形量对ASP30高速钢力学性能与显微组织的影响,并研究其摩擦磨损行为。结果表明,添加质量分数5%的TiCN可明显提高ASP30的耐磨性。旋锻变形量为56%的ASP30+5%TiCN合金棒料经淬火-回火处理后,抗弯强度达到4084.99 N·mm‒2,抗冲击韧性达到14.55 J·cm‒2,相较于未旋锻态,其强韧性得到明显提升。在反复径向旋锻变形作用下,TiCN硬质相明显破碎,呈弥散颗粒状分布,且旋锻可以促进TiCN生成核壳结构,硬质相与基体之间的润湿性与结合能力得到提高,抑制了磨削过程中硬质相/基体间裂纹的产生。Abstract: The ASP30 powder metallurgy (PM) high speed steels strengthened by TiCN were fabricated by powder metallurgy process, the effects of TiCN and rotary awaging deformation on the mechanical properties, microstructure, and tribological behaviors of the ASP30 steels were investigated. The results show that, adding TiCN with the mass fraction of 5% can effectively improve the wear resistance of ASP30. After the quenching-tempering treatment, the bending strength of ASP30+5%TiCN with the 56% swaging deformation is 4084.99 N·mm‒2, and the impact toughness is 14.55 J·cm‒2. The strength and toughness of the ASP30 steels after swaging are effectively improved. After the repeated radial swaging deformation, the TiCN phases are obviously broken and distribute as the dispersion particles. Besides, the rotary swaging can promote the formation of TiCN core-rim structure and improve the wettability and bonding ability between the hard phase and the matrix, inhibiting the generation of cracks between the hard phase and the matrix during grinding.
-
Key words:
- TiCN /
- powder metallurgy /
- high speed steels /
- rotary swaging /
- mechanical properties /
- friction wear tests
-
表 1 ASP30高速钢化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of the ASP30+5%TiCN high speed steels
% C W Mo Cr V Co Si Mn Fe 1.28 6.40 5.00 4.20 3.10 8.50 0.30 0.30 余量 表 2 旋锻变形量对合金力学性能的影响
Table 2. Effect of rotary swaging deformation on the mechanical properties of alloys
变形量 /
%冲击韧性 /
(J·cm‒2)抗弯强度 /
(N·mm‒2)硬度,
HRC0 7.68 2011.42 66.30 21 11.22 3402.90 62.26 40 12.36 3734.61 62.26 56 14.55 4084.99 62.74 73 13.44 3842.56 61.89 -
[1] Chatterjee D, Sutradhar G, Oraon B. Fuzzy rule-based prediction of hardness for sintered HSS components. J Mater Process Technol, 2008, 200(1-3): 212 doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.09.057 [2] Badger J. Grindability of conventionally produced and powder-metallurgy high-speed steel. CIRP Ann, 2007, 56(1): 353 doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2007.05.081 [3] Wu Y C. Evolution of technology of powder metallurgy high speed steel. Powder Metall Ind, 2007, 17(2): 30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2007.02.007吴元昌. 粉末冶金高速钢生产工艺的发展. 粉末冶金工业, 2007, 17(2): 30 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2007.02.007 [4] Jia C C, Wu L Z. Powder metallurgy high speed steel. Met World, 2012(2): 5 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6826.2012.02.002贾成厂, 吴立志. 粉末冶金高速钢. 金属世界, 2012(2): 5 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6826.2012.02.002 [5] Lan D F. Study on Preparation and Heat Treatment of Ti(C, N) Based Steel Bonded Carbide [Dissertation]. Zhuzhou: Hunan University of Technology, 2016兰登飞. TiCN基钢结硬质合金制备及热处理的研究[学位论文]. 株洲: 湖南工业大学, 2016 [6] Velasco F, Isabel R, Antón N, et al. TiCN—high speed steel composites: sinterability and properties. Composites Part A, 2002, 33(6): 819 doi: 10.1016/S1359-835X(02)00024-6 [7] Liu H W, Chen K H, Lü H B. Wettability of Ti(C, N)-based cermets. Powder Metall Technol, 2000, 18(3): 167 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2000.03.002刘红卫, 陈康华, 吕海波. Ti(C, N)基硬质合金中的润湿性研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2000, 18(3): 167 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2000.03.002 [8] Zhang H B, Shen W J, Zhuang Q M, et al. Novel powder metallurgy high speed steel with high-performance and its near-net shaping technology. J Netshape Form Eng, 2017, 9(2): 14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6457.2017.02.003张惠斌, 沈玮俊, 庄启明, 等. 新型高性能粉末冶金高速钢及其近净成形制备技术. 精密成形工程, 2017, 9(2): 14 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6457.2017.02.003 [9] Ghaei A, Taheri A K, Movahhedy M R. A new upper bound solution for analysis of the radial forging process. Int J Mech Sci, 2006, 48(11): 1264 doi: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2006.06.002 [10] Frank G, Christine K. Rotary swaging technology-applications of a versatile process. Sheet Met Ind, 1998, 75(8): 22 [11] Zhou X F, Fang F, Jiang J Q, et al. Study on property and morphology of M2C eutectic carbides in M2 high speed steel. Iron Steel, 2009, 44(9): 76 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2009.09.018周雪峰, 方峰, 蒋建清, 等. 高速钢M2中共晶碳化物M2C的性质和形态. 钢铁, 2009, 44(9): 76 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0449-749X.2009.09.018 [12] Akhtar F. A new method to process high strength TiCN stainless steel matrix composites. Powder Metall, 2007, 50(3): 250 doi: 10.1179/174329007X178038 [13] Li Q, Li Z D, Lin C G, et al. Research on hot-swage deformation of Mo70Cu30 alloy sintered bar. Powder Metall Technol, 2015, 33(5): 355 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.05.008李卿, 李增德, 林晨光, 等. Mo70Cu30合金烧结棒坯热旋锻变形研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2015, 33(5): 355 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.05.008 [14] Fredriksson H, Hillert M, Nica M. Decomposition of the M2C carbide in high speed steel. Scand J Metall, 1979, 8(3): 115 [15] Mao S W. Research of characteristics and mechanism on WC grain diffusion-dissolution-precipitation during sintering of ultrafine cemented carbide. Cement Carb, 2014, 31(2): 67毛善文. 超细硬质合金烧结过程中WC扩散-溶解-析出特征与机理研究. 硬质合金, 2014, 31(2): 67 [16] Wang Q, Wang W Z, Zhang H X. Growth kinetics of ceramet particles in the form of dissolve-separation. J Northeast Univ Nat Sci, 1996, 17(5): 32王群, 王文忠, 张洪绪, 等. 金属陶瓷中的颗粒的溶解-析出生长机制动力学. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 1996, 17(5): 32 [17] Wang D Z, Liu X Y, Zhou M L. Study on toughening mechanism of Mo-La2O3 sintered bars. Powder Metall Technol, 2002, 20(2): 75 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2002.02.003王德志, 刘心宇, 周美玲. Mo-La2O3烧结坯的韧化机制研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2002, 20(2): 75 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2002.02.003 [18] Li R, Wang X X. Effect of Ti content and ageing on microstructure and hardness of 00Cr12Ni9Mo4Cu maraging stainless steel. Trans Mater Heat Treat, 2009, 30(3): 137李蓉, 王小祥. Ti含量及时效工艺对00Cr12Ni9Mo4Cu合金组织和硬度的影响. 材料热处理学报, 2009, 30(3): 137 [19] Ma L X, Liu Y X, Li W X. Study on adherence abrasion and influenced factors. J Harbin Univ Comm Nat Sci, 2001, 17(1): 74马丽心, 刘义翔, 李文新. 粘着磨损及影响因素的研究. 哈尔滨商业大学学报(自然科学版), 2001, 17(1): 74 [20] Sun Y. Sliding wear behaviour of surface mechanical attrition treated AISI 304 stainless steel. Tribol Int, 2013, 57(4): 67 -




 下载:
下载: