-
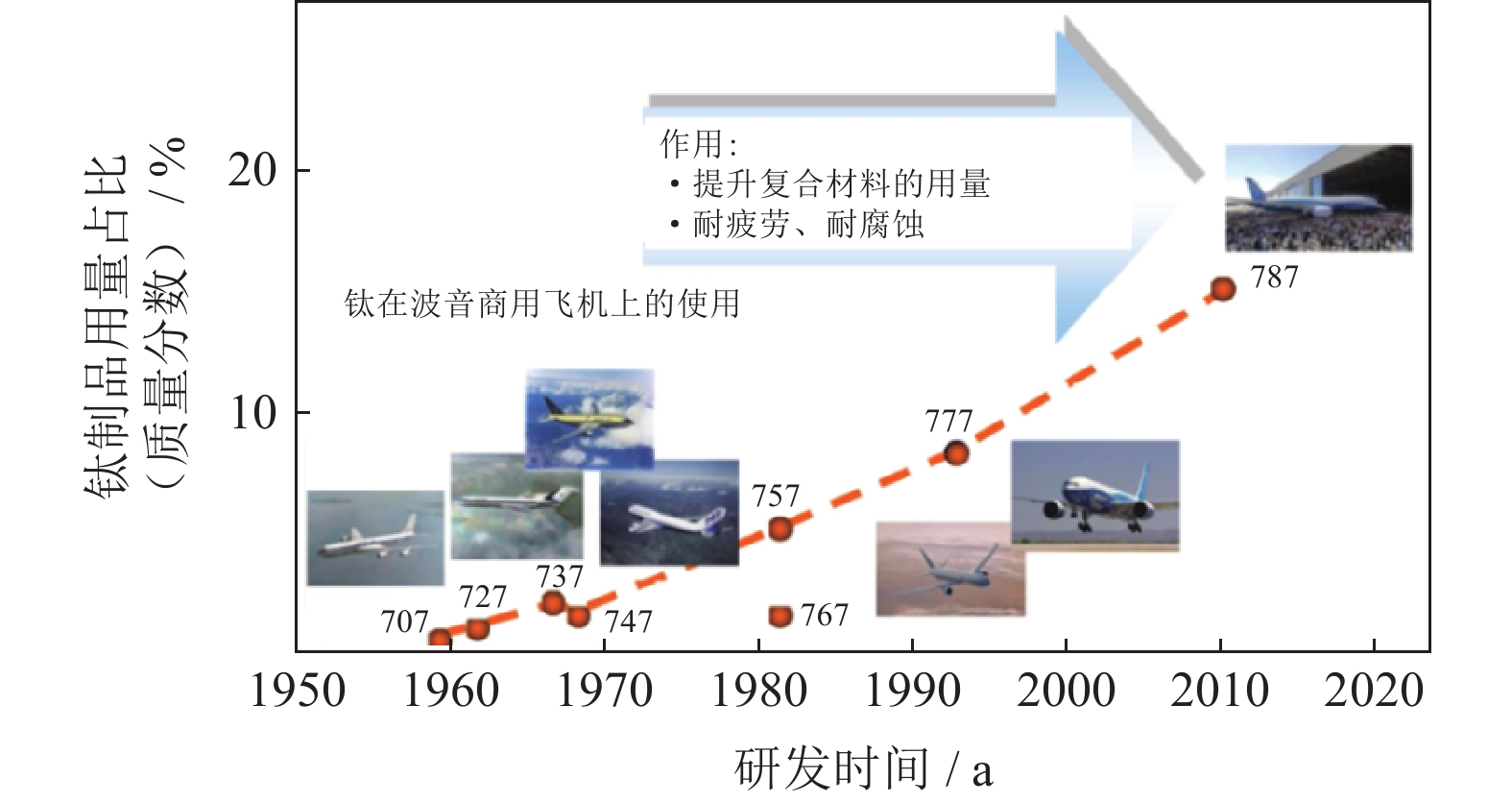
摘要: 钛及钛合金具有低比重、高比强度、优异的生物相容性以及良好的耐腐蚀性等特点,在航空航天、生物医疗、化工、船舶、汽车等领域极具应用潜力。钛合金粉末注射成形技术(powder injection molding,PIM)提高了材料的利用率,实现了中小型复杂形状钛产品的大批量、低成本制备,显著地推动了钛及钛合金产品的生产及应用。目前关于粉末注射成形钛合金粘结剂体系的相关文献报道十分有限,新型粉末注射成形钛合金粘结剂体系的开发处于停滞不前的状态。本文分析总结了不同粉末注射成形钛合金粘结剂体系的研究现状,并针对目前存在的问题提出改进措施。Abstract: Titanium and titanium alloys have the low specific gravity, high specific strength, excellent biocompatibility, and good corrosion resistance, showing the great application potential in the aerospace, biomedicine, chemical engineering, shipbuilding, automobile, and other fields. The powder injection molding (PIM) technology used for titanium alloys increases the utilization rate of materials, realizes the large-scale and low-cost preparation of small and medium-sized titanium products with complex shape, and significantly promotes the development of titanium and its alloys. At present, there are few reports about the titanium alloy binder system for powder injection molding, and the development of new type titanium alloy binder system for powder injection molding is in a stagnating state. The research status of the different titanium alloy binder systems for powder injection molding was introduced in this paper, and some improvements for the existing problems were suggested as the reference for researchers.
-
Key words:
- titanium alloys /
- powder injection molding /
- binders /
- debinding
-
图 2 部分粉末注射成形钛合金产品:(a)德国TiJet公司制备的工程应用零部件;(b)德国TiJet公司制备生物医用零部件;(c)Ti‒6Al‒7Nb合金骨螺钉;(d)CP-Ti人工镫骨;(e)钛合金眼镜架;(f)Ti‒6Al‒4V表壳实物
Figure 2. Parts of titanium alloy products by powder injection molding: (a) parts of engineering applications prepared by TiJet; (b) parts of biomedical applications prepared by TiJet; (c) Ti‒6Al‒7Nb bone screws; (d) CP-Ti artificial stapes; (e) titanium alloy spectacle frames; (f) Ti‒6Al‒4V watchcase
表 1 粉末注射成形钛合金常用粘结剂骨架剂组元的热力学性质
Table 1. Thermodynamic properties of the skeleton components of titanium alloys by powder injection molding
聚合物组元 结构 热分解行为 热分解起始
温度 / ℃热分解结束
温度 / ℃分解原理 产物类型 高密度聚乙烯(HDPE) 
368 498 随机断链 烷烃、烯烃、少量单体 低密度聚乙烯(LDPE) 
355 467 随机断链 烷烃、烯烃、少量单体 聚丙烯(PP) 
304 420 随机断链 烷烃、烯烃、少量单体 聚苯乙烯(PS) 
236 426 随机断链 苯乙烯单体、二聚体及三聚体 聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯(PMMA) 
278 428 端链断裂 单体(约90%~100%) 乙烯—醋酸乙烯共聚物(EVA) 
306 491 链式剥离 乙酸、1-丁烯、CO2、
CO、乙烯、甲烷聚甲醛(POM) 
180 395 端链断裂 甲醛单体 注:以上各聚合物的热分解温度都是通过热分析曲线获得。 -
[1] Dehghan-Manshadi A, Stjohn D, Dargusch M S, et al. Metal injection moulding of non-spherical titanium powders: Processing, microstructure and mechanical properties. J Manuf Process, 2018, 31: 416 doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2017.12.004 [2] Xu W, Lu X, Wang L N, et al. Mechanical properties, in vitro corrosion resistance and biocompatibility of metal injection molded Ti− 12Mo alloy for dental applications. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater, 2018, 88: 534 doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2018.08.038 [3] Zhang B Z, Sun J Q. Recent applications of titanium alloys in typical commercial aircraft fuselage structure. Adv Aeronaut Sci Eng, 2014, 5(3): 275张宝柱, 孙洁琼. 钛合金在典型民用飞机机体结构上的应用现状. 航空工业进展, 2014, 5(3): 275 [4] Dehghan-Manshadi A, Bermingham M, Dargusch M, et al. Metal injection moulding of titanium and titanium alloys: Challenges and recent development. Powder Technol, 2017, 319: 289 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.06.053 [5] Liu C, Kong X J, Wu S W, et al. Research progress on metal injection molding of titanium and titanium alloys. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(2): 150 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.012刘超, 孔祥吉, 吴胜文, 等. 钛及钛合金金属粉末注射成形技术的研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(2): 150 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2017.02.012 [6] Aust E, Limberg W, Gerling R, et al. Advanced TiAl6Nb7 bone screw implant fabricated by metal injection moulding. Adv Eng Mater, 2006, 8(5): 365 doi: 10.1002/adem.200500134 [7] Fu G, Loh N H, Tor S B, et al. Replication of metal microstructures by micro powder injection molding. Mater Des, 2004, 25(8): 729 doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2004.01.013 [8] Ye S, Mo W, Lü Y, et al. Metal injection molding of thin-walled titanium glasses arms: A case study. JOM, 2018, 70(5): 616 doi: 10.1007/s11837-018-2788-1 [9] Ye S, Mo W, Lü Y, et al. The technological design of geometrically complex Ti−6Al−4V parts by metal injection molding. Appl Sci, 2019, 9: 1339 doi: 10.3390/app9071339 [10] Lu X, Liu C C, Qu X H. Research progresses of powder injection molding for titanium alloys. Powder Metall Technol, 2013, 31(2): 139 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2013.02.011路新, 刘程程, 曲选辉. 钛及钛合金粉末注射成形技术研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2013, 31(2): 139 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2013.02.011 [11] Wen G, Cao P, Gabbitas B, et al. Development and design of binder systems for titanium metal injection molding: an overview. Metall Mater Trans A, 2013, 44(3): 1530 doi: 10.1007/s11661-012-1485-x [12] Froes F H S. Advances in titanium metal injection molding. Powder Metall Met Ceram, 2007, 46(5-6): 303 doi: 10.1007/s11106-007-0048-y [13] Nyberg E, Miller M, Simmons K, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium components fabricated by a new powder injection molding technique. Mater Sci Eng C, 2005, 25(3): 336 doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2005.04.006 [14] Gerling R, Aust E, Limberg M, et al. Metal injection moulding of gamma titanium aluminide alloy powder. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 423(1-2): 262 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.02.002 [15] Obasi G C, Ferri O M, Ebel T, et al. Influence of processing parameters on mechanical properties of Ti− 6Al− 4V alloy fabricated by MIM. Mater Sci Eng A, 2010, 527(16-17): 3929 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.02.070 [16] Guo S B, Duan B H, He X B, et al. Powder injection molding of pure titanium. Rare Met, 2009, 28(3): 261 doi: 10.1007/s12598-009-0052-0 [17] Liu C C, Lu X, Yang F, et al. Metal injection moulding of high Nb-containing TiAl alloy and its oxidation behaviour at 900 ℃. Metals, 2018, 8(3): 163 doi: 10.3390/met8030163 [18] Friederici V, Bruinink A, Imgrund P, et al. Getting the powder mix right for design of bone implants. Met Powder Rep, 2010, 65(7): 14 doi: 10.1016/S0026-0657(11)70041-8 [19] Wang J H, Shi Q N, Wu C L, et al. Rheological characteristics of injection molded titanium alloys powder. Trans Nonferrous Met Soc China, 2013, 23(9): 2605 doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62774-0 [20] Li Y, Zhang X Q, Zhu J, et al. Study on debinding process of Ti− Mo getter material by powder injection molding. J Funct Mater, 2014, 45(2): 2110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2014.02.023李洋, 张心强, 朱君, 等. Ti− Mo吸气材料注射成形脱脂工艺的研究. 功能材料, 2014, 45(2): 2110 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2014.02.023 [21] Carrño-Morelli E, Bidaux J E, Rodríguez-Arbaizar M, et al. Production of titanium grade 4 components by powder injection moulding of titanium hydride. Powder Metall, 2014, 57(2): 89 doi: 10.1179/0032589914Z.000000000165 [22] Krug S, Evans J R G, Maat J H H T. Residual stresses and cracking in large ceramic injection mouldings subjected to different solidification schedules. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2000, 20(14-15): 2535 doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(00)00120-5 [23] Krug S, Evans J R G, Maat J H H T. Transient effects during catalytic binder removal in ceramic injection moulding. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2001, 21(12): 2275 doi: 10.1016/S0955-2219(00)00312-5 [24] Zhang C, Liu C L. Rheological behavior and degreasing process of polyformaldehyde/polypropylene/titanium catalytic degreasing material for metal powder injection molding. Hot Working Technol, 2017, 46(24): 45章诚, 刘春林. 金属粉末注射成型催化脱脂料POM/PP/Ti的流变行为及脱脂工艺. 热加工工艺, 2017, 46(24): 45 [25] Luo H, Zong W, Zhou W Z, et al. Analysis of rheological behavior of catalytic debinding feedstocks for In713C superalloy metal injection molding. Mater Res Appl, 2016, 10(3): 205 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2016.03.011罗浩, 宗伟, 周晚珠, 等. 注射成形聚甲醛基In713C高温合金喂料流变行为的研究. 材料研究与应用, 2016, 10(3): 205 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9981.2016.03.011 [26] Zhu H Y, Zhou S Q, Song S H, et al. Rheological properties of new type POM/PE alloy feedstocks. J Mater Sci Eng, 2018, 36(1): 103朱海洋, 周淑千, 宋善寒, 等. 新型POM/PE合金喂料的流变特性. 材料科学与工程学报, 2018, 36(1): 103 [27] Gonzalez-Gutierrez J, Stringari G B, Megen Z M, et al. Selection of appropriate polyoxymethylene based binder for feedstock material used in powder injection moulding. J Phys Conf Ser, 2015, 602(1): 012001 [28] Sidambe A T, Figueroa I A, Hamilton H, et al. Metal injection moulding of Ti-64 components using a water soluble binder. PIM Int, 2010, 4(4): 56 [29] Hayat M D, Wen G, Zulkifli M F, et al. Effect of PEG molecular weight on rheological properties of Ti-MIM feedstocks and water debinding behaviour. Powder Technol, 2015, 270: 296 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.10.035 [30] Hayat M D, Li T, Cao P. Incorporation of PVP into PEG/PMMA based binder system to minimize void nucleation. Mater Des, 2015, 87: 932 doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.08.131 [31] Hayat M D, Goswami A, Matthews S, et al. Modification of PEG/PMMA binder by PVP for titanium metal injection moulding. Powder Technol, 2017, 315: 243 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.04.004 [32] Thavanayagam G, Pickering K L, Swan J E, et al. Analysis of rheological behaviour of titanium feedstocks formulated with a water-soluble binder system for powder injection moulding. Powder Technol, 2015, 269: 227 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2014.09.020 [33] Thavanayagam G, Swan J E. Aqueous debinding of polyvinyl butyral based binder system for titanium metal injection moulding. Powder Technol, 2018, 326: 402 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2017.11.069 [34] Hayat M D, Jadhav P P, Zhang H, et al. Improving titanium injection moulding feedstock based on PEG/PPC based binder system. Powder Technol, 2018, 330: 304 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.02.043 [35] Guo S B, Quan X H. Research progress in binders used for metal injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2004, 3: 178 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2004.03.012郭世柏, 曲选辉. 金属注射成形粘结剂的研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2004, 3: 178 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2004.03.012 [36] He Y Q, Qiao B, Yang J M, et al. Research status and developing of metal injection molding. Adv Mater Res, 2013, 629(105): 100 [37] Li Y M, Li Y P. Theory and Application of Metal Injection Molding. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2004.李益民, 李云平. 金属注射成形原理与应用. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2004. [38] Chen G, Cao P, Wen G, et al. Debinding behaviour of a water soluble PEG/PMMA binder for Ti metal injection moulding. Mater Chem Phys, 2013, 139(2-3): 557 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2013.01.057 [39] Zheng L Q. Catalytic Debinding for Powder Injection Molding [Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2009.郑礼清. 粉末注射成形催化脱脂研究[学位论文]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2009. [40] German R M. Powder Injectin Molding. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2001.German R M. 粉末注射成形. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2001. [41] Guo S B, Zhang H A, Zhang R F, et al. Research on solvent debinding process of titanium alloy compacts by metal injection molding. Rare Metal Mater Eng, 2007, 36(3): 537 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2007.03.040郭世柏, 张厚安, 张荣发, 等. 钛合金粉末注射成形溶剂脱脂工艺研究. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(3): 537 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2007.03.040 [42] Liu C, Kong X J, Kuang C J. Research on powder injection molding of grade 2 cp-titanium for biomedical application. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(4): 281 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.04.009刘超, 孔祥吉, 况春江, 等. 生物医用二级纯钛注射成形研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(4): 281 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.04.009 -




 下载:
下载: