Effect of oxidation time on microstructure and electromagnetic properties of FeSiAl alloy powders
-
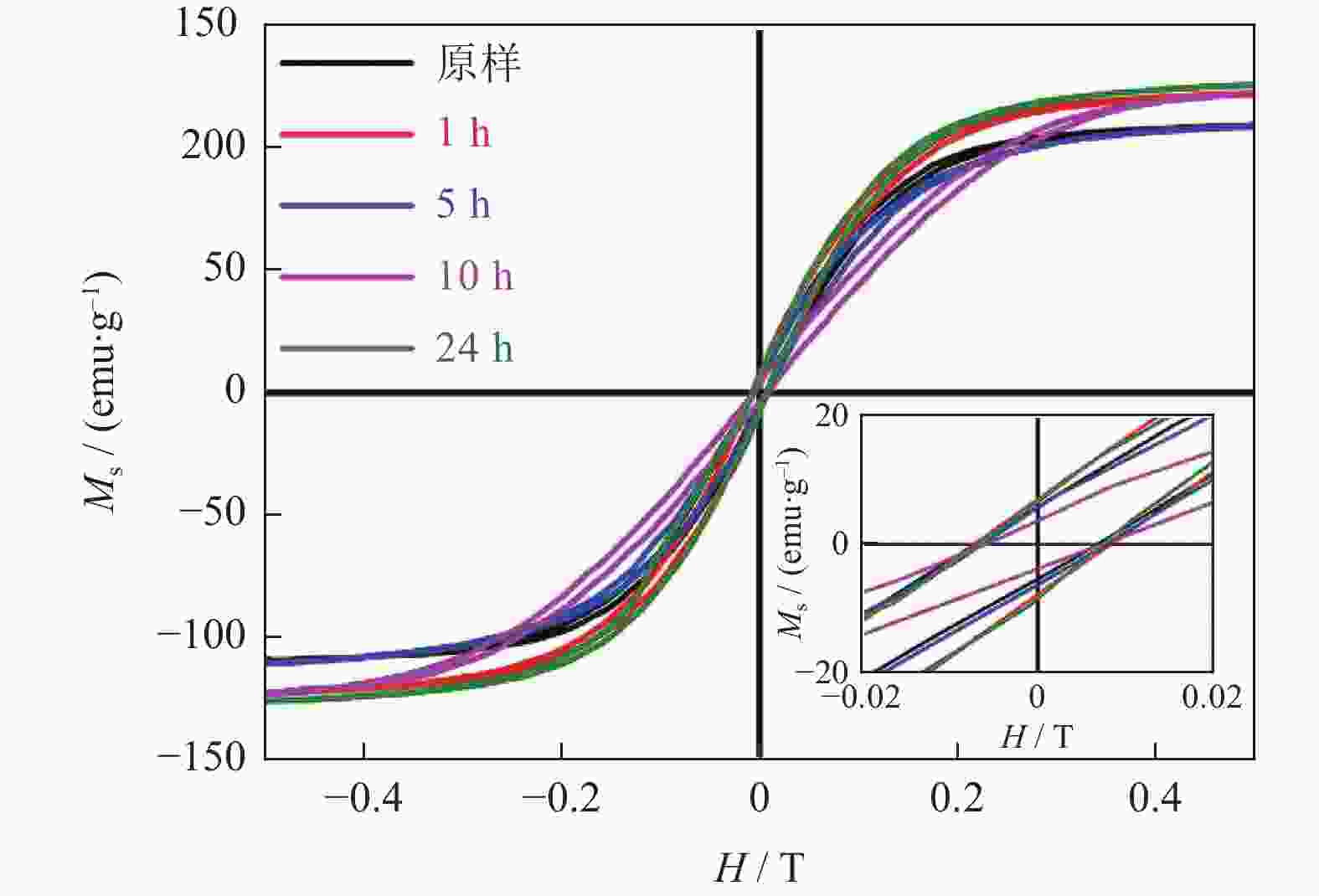
摘要: 以FeSiA合金粉末为原料,研究空气中500 ℃下不同氧化时间对FeSiAl合金粉末微观组织和电磁性能的影响。结果表明:随着氧化时间的延长,FeSiAl合金粉末颜色由深灰色向土黄色转变,表面微观形貌无明显改变。氧化5 h后,粉末表面出现Fe3O4,随着氧化时间进一步增加至10 h,Fe3O4逐渐转变为Fe2O3。FeSiAl合金粉末表面氧化层主要包含Fe2O3、SiO2和Al2O3。粉末介电常数和磁导率的实部随着氧化时间的增加呈上升趋势,介电常数的虚部和磁导率虚部无明显变化。
-
关键词:
- FeSiAl合金粉末 /
- 氧化时间 /
- 微观组织 /
- 电磁性能
Abstract: The effect of oxidation time on the microstructure and electromagnetic properties of the FeSiAl alloy powders was investigated at 500 ℃ in air, using FeSiAl alloy powders as the raw materials. The results show that, the surface color of the FeSiAl alloy powders changes from gray to yellow with the increase of oxidation time, and there is no significant change of the surface microstructure. After the oxidation time reaches 5 h, Fe3O4 can be found and gradually transforms into Fe2O3 as the oxidation time up to 10 h. The surface oxide layer of the FeSiAl alloy powders is mainly composed of Fe2O3, SiO2, and Al2O3. The real part of the permittivity and permeability of the powders show an upward trend with the oxidation time increasing, and there is no obvious change in the imaginary part of the permittivity and permeability.-
Key words:
- FeSiAl alloy powders /
- oxidation time /
- microstructure /
- electromagnetic properties
-
图 4 空气中500 ℃氧化不同时间FeSiAl合金粉末表面O1s高分辨能谱分析:(a)原样表面全谱;(b)原样;(c)1 h;(d)5 h;(e)10 h;(f)24 h
Figure 4. High-resolution O1s XPS spectra of the FeSiAl alloy powders oxidized for the different time at 500 ℃ in air: (a) survey spectra of the as-received sample; (b) as-received sample; (c) 1 h; (d) 5 h; (e) 10 h; (f) 24 h
图 6 空气中500 ℃下氧化不同时间后FeSiAl合金电磁参数:(a)介电常数实部(ε′);(b)介电常数虚部(ε″);(c)磁导率实部(μ′);(d)磁导率虚部(μ″)
Figure 6. Electromagnetic parameters of the FeSiAl alloy powders oxidized for the different time at 500 ℃ in air: (a) real part of complex permittivity (ε′); (b) imaginary part of complex permittivity (ε″); (c) real part of complex permeability (μ′); (d) imaginary part of complex permeability (μ″)
-
[1] Han C, Zhang M, Cao W Q, et al. Electrospinning and in-situ hierarchical thermal treatment to tailor C-NiCo2O4 nanofibers for tunable microwave absorption. Carbon, 2021, 171: 953 doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.09.067 [2] Liu P, Gao S, Chen C, et al. Vacancies-engineered and heteroatoms-regulated N-doped porous carbon aerogel for ultrahigh microwave absorption. Carbon, 2020, 169: 276 doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.07.063 [3] Guo Y, Jian X, Zhang L, et al. Plasma-induced FeSiAl@Al2O3@SiO2 core-shell structure for exceptional microwave absorption and anti-oxidation at high temperature. Chem Eng J, 2020, 384: 123371 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123371 [4] Huo Y, Zhao K, Miao P, et al. Microwave absorption performance of SiC/ZrC/SiZrOC hybrid nanofibers with enhanced high-temperature oxidation resistance. ACS Sustain Chem Eng, 2020, 8(28): 10490 doi: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c02789 [5] Wei H, Yin X, Jiang F, et al. Optimized design of high-temperature microwave absorption properties of CNTs/Sc2Si2O7 ceramics. J Alloys Compd, 2020, 823: 153864 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.153864 [6] Jian X, Tian W, Li J, et al. High-temperature oxidation resistant ZrN0.4B0.6-SiC nanohybrid for enhanced microwave absorption. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2019, 11(17): 15869 doi: 10.1021/acsami.8b22448 [7] Gao P, Jia C C, Cao W B, et. al. Effects of SiC content on the dielectric properties of AlN‒SiC composite ceramics. Powder Metall Technol, 2014, 32(4): 248高鹏, 贾成厂, 曹文斌, 等. SiC含量对氮化铝基微波衰减复合陶瓷性能的影响研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2014, 32(4): 248 [8] Song W L, Cao M S, Hou Z L, et al. High-temperature microwave absorption and evolutionary behavior of multiwalled carbon nanotube nanocomposite. Scr Mater, 2009, 61(2): 201 doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2009.03.048 [9] Sengupta A, Rao B B, Sharma N, et al. Comparative evaluation of MAX, MXene, NanoMAX, and NanoMAX-derived-MXene for microwave absorption and Li ion battery anode applications. Nanoscale, 2020, 12(15): 8466 doi: 10.1039/C9NR10980C [10] Han T, Luo R, Cui G, et al. Effect of SiC nanowires on the high-temperature microwave absorption properties of SiCf/SiC composites. J Eur Ceram Soc, 2019, 39(5): 1743 doi: 10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2019.01.018 [11] Xu H, Yin X, Li M, et al. Mesoporous carbon hollow microspheres with red blood cell like morphology for efficient microwave absorption at elevated temperature. Carbon, 2018, 132: 343 doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.02.040 [12] Ji Z, Chen K, Zhang Y F, et al. Progress on ferrite wave-absorbing materials. Powder Metall Technol, 2015, 33(5): 378 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.05.012纪箴, 陈珂, 张一帆, 等. 铁氧体磁性材料吸波性能研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2015, 33(5): 378 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.05.012 [13] Liu J, Cao M S, Luo Q, et al. Electromagnetic property and tunable microwave absorption of 3D nets from nickel chains at elevated temperature. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016, 8(34): 22615 doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b05480 [14] Li Y, Fang X, Cao M. Thermal frequency shift and tunable microwave absorption in BiFeO3 family. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 24837 doi: 10.1038/srep24837 [15] Sharma V, Saha J, Patnaik S, et al. YIG based broad band microwave absorber: A perspective on synthesis methods. J Magn Magn Mater, 2017, 439: 277 doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2017.04.098 [16] Legarra E, Apiñaniz E, Plazaola F. Study of the enhancement of the magnetic properties of Fe70Al30‒xSix alloys in the order-disorder transition. J Alloys Compd, 2016, 682: 495 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.04.294 [17] Li L, Gao Z, Li A, et al. Fabrication of carbonyl iron powder/SiO2-reduced iron powder/SiO2 soft magnetic composites with a high resistivity and low core loss. J Magn Magn Mater, 2018, 464: 161 doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.05.053 [18] Gawlińska-Nęcek K, Wlazło M, Socha R, et al. Influence of conditioning temperature on defects in the double Al2O3/ZnO layer deposited by the ALD method. Materials, 2021, 14(4): 1038 doi: 10.3390/ma14041038 [19] Fan Z, Shi J W, Gao C, et al. Rationally designed porous MnOx‒FeOx nanoneedles for low-temperature selective catalytic reduction of NOx by NH3. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2017, 9(19): 16117 doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b00739 [20] Yang J, Zhang Q, Wang Z, et al. Rational construction of self-standing sulfur-doped Fe2O3 anodes with promoted energy storage capability for wearable aqueous rechargeable NiCo-Fe batteries. Adv Energy Mater, 2020, 10(33): 2001064 doi: 10.1002/aenm.202001064 [21] Bahadur N M, Chowdhury F, Obaidullah M, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic application of SiO2@TiO2 core-shell nanocomposite particles. J Nanomater, 2019, 2019: 1 [22] Liu T, Sun X, Sun S, et al. A robust and low-cost biomass carbon fiber@SiO2 interlayer for reliable lithium-sulfur batteries. Electrochim Acta, 2019, 295: 684 doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.10.168 [23] Hemmati I, Hosseini H M, Kianvash A. The correlations between processing parameters and magnetic properties of an iron-resin soft magnetic composite. J Magn Magn Mater, 2006, 305(1): 147 doi: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.12.004 [24] Jiang Z, Huang W, Zhang Z, et al. Thermal decomposition of Mo(CO)6 on thin Al2O3 film: A combinatorial investigation by XPS and UPS. Surf Sci, 2007, 601(3): 844 doi: 10.1016/j.susc.2006.11.016 [25] Kouotou P M, Tian Z Y. Controlled synthesis of α-Fe2O3@Fe3O4 composite catalysts for exhaust gas purification. Proc Combust Inst, 2019, 37(4): 5445 doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2018.05.172 [26] Liu J, Liang H, Wu H J, et al. Hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4/MoS2 composites for selective broadband electromagnetic wave absorption performance. Composites Part A, 2020, 130: 105760 doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105760 [27] Deng X, Herranz T, Weis C, et al. Adsorption of water on Cu2O and Al2O3 thin films. J Phys Chem C, 2008, 112(26): 9668 doi: 10.1021/jp800944r -




 下载:
下载: