Effect of Y2O3–CeO2 two-phase dispersion strengthening on the grain size and tensile properties of Mo alloys
-
摘要: 采用纳米喷雾掺杂技术和粉末冶金方法制备了含不同质量分数氧化钇(Y2O3)和氧化铈(CeO2)的Mo–Y–Ce合金,分析了Y2O3和CeO2双相弥散强化对Mo合金晶粒度和室温力学性能的影响。结果表明,Y2O3可抑制个别晶粒异常长大,并具有沉淀强化效果。Mo–Y合金丝的力学性能与Y2O3掺杂量密切相关,当Y2O3质量分数为0.60%时,ϕ1.8-mm Mo–Y合金丝抗拉强度为1050 MPa,屈服强度为923 MPa;CeO2因与Mo基体具有半共格关系而具有较好的韧化效果,当CeO2质量分数为0.06%~0.08%时,Mo–Y–Ce合金烧结态晶粒尺寸达10 μm以下,ϕ1.8-mm Mo–Y–Ce合金丝抗拉强度为1130 MPa,屈服强度为1018 MPa,延伸率达到28.5%。ϕ0.18-mm Mo–Y–Ce合金丝抗拉强度达2510 MPa。实验优化出Mo–Y–Ce双相弥散强化Mo合金的最优成分为Mo–0.6Y2O3–(0.06~0.08)CeO2。Abstract: Mo–Y–Ce alloys doped by yttrium oxide (Y2O3) and cerium oxide (CeO2) in different mass fraction were prepared by the nanometer spray doping technology and the powder metallurgy method. The two-phase dispersion strengthening effect of Y2O3 and CeO2 on the grain size and mechanical properties of Mo alloys at room temperature was studied. The results show that Y2O3 restrains the abnormal growth of the individual grains and has the effect of precipitation strengthening. The mechanical properties of the Mo–Y alloy wires are closely related to the doping amount of Y2O3. When the mass fraction of Y2O3 is 0.60%, the tensile strength and yield strength of the ϕ1.8-mm Mo–Y alloy wires reach 1050 and 923 MPa, respectively. Because of the semi-coherent relationship between CeO2 and the Mo matrix, CeO2 has the good toughening effect. When the mass fraction of CeO2 is 0.06%~0.08%, the grain size of the sintered Mo–Y–Ce alloys is smaller than 10 μm, the tensile strength and yield strength of the ϕ1.8-mm Mo–Y–Ce alloy wires are 1130 and 1018 MPa, respectively, the elongation reaches 28.5%. The tensile strength of ϕ0.18-mm Mo–Y–Ce alloy wires reaches 2510 MPa. The optimal composition of the Mo–Y–Ce two-phase dispersion strengthening Mo alloys is Mo–0.6Y2O3–(0.06~0.08)CeO2.
-
Key words:
- two-phase dispersion strengthening /
- Mo alloys /
- alloy wires /
- grain size /
- mechanical properties
-
表 1 Mo–Y合金丝中Y2O3设计成分
Table 1. Composition of Y2O3 in the Mo–Y alloy wires
编号 1# 2# 3# 4# Y2O3质量分数 / % 0.47 0.60 0.80 1.00 表 2 Mo–0.6Y2O3–Ce合金丝中CeO2设计成分
Table 2. Composition of CeO2 in the Mo–0.6Y2O3–Ce alloy wires
编号 1# 2# 3# 4# 5# CeO2质量分数 / % 0.03 0.06 0.08 0.12 0.15 表 3 ϕ1.8-mm Mo–Y合金丝室温力学性能
Table 3. Mechanical properties of the ϕ1.8-mm Mo–Y alloy wires at the room temperature
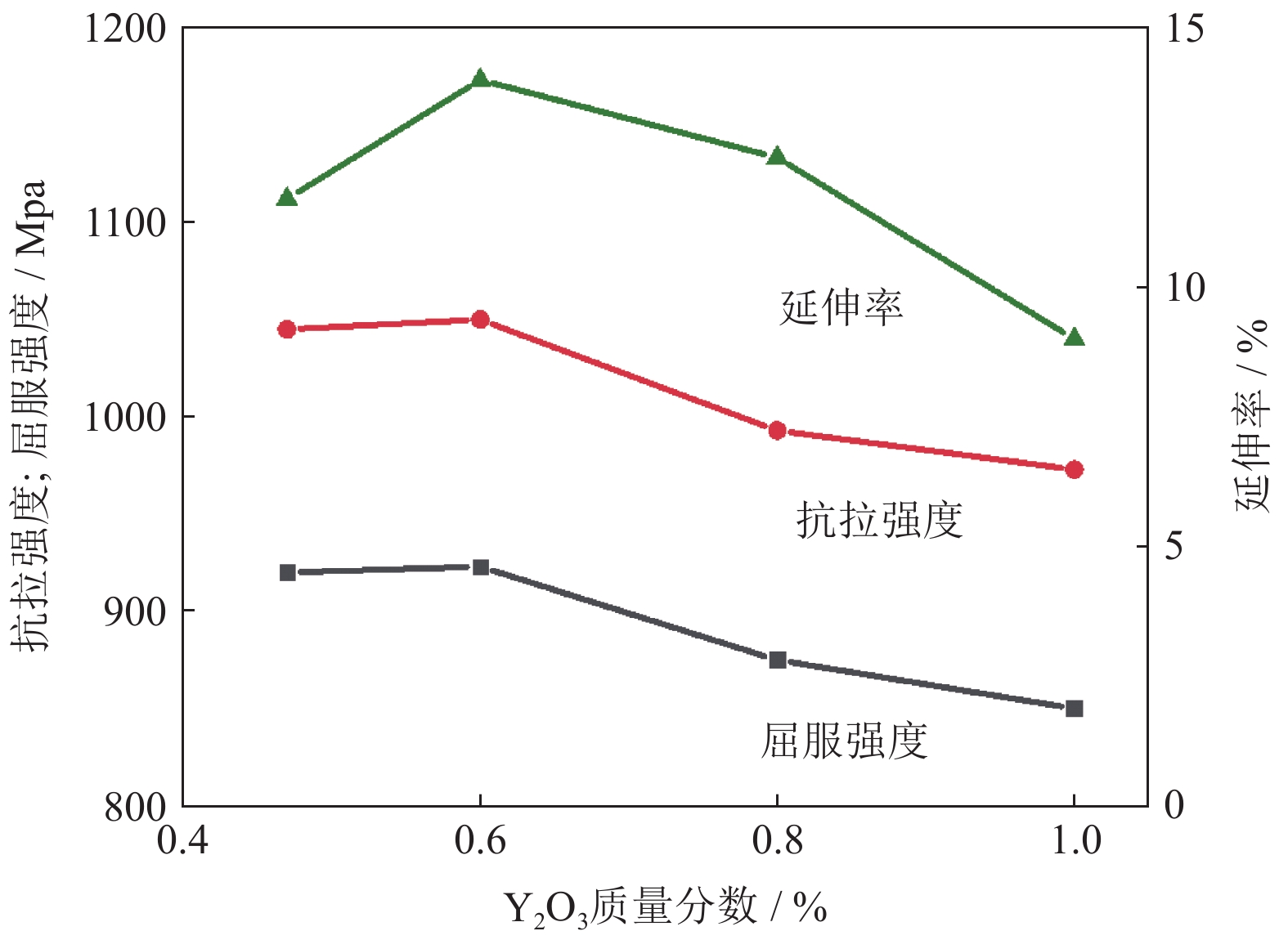
Mo–Y合金 屈服强度 / MPa 抗拉强度 / MPa 延伸率 / % 屈强比 Mo–0.47Y2O3 920 1045 11.7 0.88 Mo–0.6Y2O3 923 1050 14.0 0.90 Mo–0.8Y2O3 875 993 12.5 0.88 Mo–1.0Y2O3 850 973 9.0 0.87 表 4 ϕ0.18-mm Mo–Y合金丝的抗拉强度
Table 4. Tensile strength of the ϕ0.18-mm Mo–Y alloy wires
Mo–Y合金 抗拉强度 / MPa Mo–0.47Y2O3 2226 Mo–0.6Y2O3 2363 Mo–0.8Y2O3 2226 Mo–1.0Y2O3 2120 表 5 ϕ1.8-mm Mo–Y–Ce合金丝室温力学性能
Table 5. Mechanical properties of the ϕ1.8-mm Mo–Y–Ce alloy wires at the room temperature
Mo–Y–Ce合金 屈服强度 / MPa 抗拉强度 / MPa 延伸率 / % 屈强比 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.03CeO2 883 1005 22.7 0.88 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.06CeO2 1018 1130 24.0 0.90 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.08CeO2 868 968 28.5 0.89 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.12CeO2 975 1087 25.8 0.90 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.15CeO2 890 987 25.0 0.91 表 6 ϕ0.18-mm Mo–Y–Ce合金丝抗拉强度
Table 6. Tensile strength of the ϕ0.18-mm Mo–Y–Ce alloy wires
Mo–Y–Ce合金 抗拉强度 / MPa Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.03 CeO2 2075 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.06 CeO2 2235 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.08 CeO2 2510 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.12 CeO2 2510 Mo–0.6Y2O3–0.15 CeO2 2320 -
[1] Chen Y F, Xie J P, Wang A Q, et al. Research status and development trend of molybdenum and molybdenum alloy sputtering target materials. Powder Metall Technol, 2018, 36(5): 393陈艳芳, 谢敬佩, 王爱琴, 等. 钼及钼合金溅射靶材的研究现状与发展趋势. 粉末冶金技术, 2018, 36(5): 393 [2] Xu K D. The Material Science and Engineering of Molybdenum. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2014徐克玷. 钼的材料科学与工程. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2014 [3] Hu B L, Wang K S, Hu P, et al. Fracture behavior of the La-doped molybdenum-titanium-zirconium alloy. Mater Sci Eng A, 2019, 759: 167 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.05.031 [4] Iorio L E, Bewlay B P, Larsen M. Analysis of AKS- and lanthanum-doped molybdenum wire. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2006, 24(4): 306 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2005.10.004 [5] Guo L, Song R, Dan X G, et al. Present research status of preparation technology of rare earth molybdenum alloys and strengthening-toughening mechanism. China Molybdenum Ind, 2017, 41(2): 45郭磊, 宋瑞, 淡新国, 等. 稀土钼合金制备工艺及强韧化机理研究现状. 中国钼业, 2017, 41(2): 45 [6] Zhao H. Research and development on the sintering techniques of molybdenum and molybdenum alloys. Powder Metall Technol, 2019, 37(5): 382赵虎. 钼及钼合金烧结技术研究及发展. 粉末冶金技术, 2019, 37(5): 382 [7] Zhang G J, Liu G, Sun Y J, et al. Microstructure and strengthening mechanisms of molybdenum alloy wires doped with lanthanum oxide particles. Int J Refract Met Hard Mater, 2009, 27(1): 173 doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2008.06.007 [8] Wang X G, Han Q, Zhao B H. Study on the room-temperature plasticity and toughness of rare earth oxide-doped molybdenum sheet. Chin J Rare Met, 2003, 27(1): 80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2003.01.017王新刚, 韩强, 赵宝华. 稀土高温钼板室温塑韧性研究. 稀有金属, 2003, 27(1): 80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2003.01.017 [9] Zhang G J, Sun Y J, Zuo C. Microstructure and mechanical properties of multi-components rare earth oxide-doped molybdenum alloys. Mater Sci Eng A, 2006, 483-484: 350 [10] He B H, Yang H L, Ruan J M. Effect of Y2O3 content on microstructure and properties of molybdenum alloys. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2012, 17(2): 234 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2012.02.016何斌衡, 杨海林, 阮建明. Y2O3含量对钼合金组织和性能的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2012, 17(2): 234 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2012.02.016 [11] Chen D J, Wu H L, Li Z S, et al. Effects of the high content La2O3/Y2O3 on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mo-alloy. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(1): 26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.01.005陈大军, 吴护林, 李忠盛, 等. 高含量La2O3/Y2O3对钼合金微观组织与性能的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(1): 26 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.01.005 [12] Li N, Xu L J, Dou C H, et al. High temperature mechanical properties of molybdenum alloys doped yttrium oxide. Chin J Rare Met, 2020, 44(6): 578李娜, 徐流杰, 窦彩虹, 等. 氧化钇掺杂对钼合金高温力学性能的影响. 稀有金属, 2020, 44(6): 578 [13] Yang Q L, Feng P F, Zhao H, et al. Occurrence status of Ce element in Mo alloy and its effects on the mechanical properties of Mo alloy. China Molybdenum Ind, 2011, 35(3): 44 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2602.2011.03.011杨秦莉, 冯鹏发, 赵虎, 等. Ce在钼合金中的存在形态及其对力学性能的影响. 中国钼业, 2011, 35(3): 44 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2602.2011.03.011 [14] Yang D X, Wang P, Wei S Z, et al. Study on structures and properties of Mo products doped with rare earth. Chin Rare Earths, 2011, 32(6): 62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2011.06.013杨涤心, 王攀, 魏世忠, 等. 稀土掺杂钼制品的组织和性能研究. 稀土, 2011, 32(6): 62 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0277.2011.06.013 [15] Dong D, Wang C Y. Research progress on preparation technology of molybdenum alloy. Powder Metall Technol, 2017, 35(4): 304董帝, 王承阳. 钼合金制备工艺的研究进展. 粉末冶金技术, 2017, 35(4): 304 [16] Feng P F, Yang Q L, Zhao H, et al. Nano Second Phase Particles Doped with Molybdenum Alloy Powder and Preparation Method of Products: China Patent, CN103273071A, 2013-09-04冯鹏发, 杨秦莉, 赵虎, 等. 纳米第二相颗粒掺杂钼合金粉末及制品的制备方法: 中国专利, CN103273071A, 2013-09-04 [17] Feng P F, Yang Q L, Dang X M, et al. Nanosized powder spray doping technology of molybdenum alloys. Chin J Rare Met, 2017, 41(1): 57冯鹏发, 杨秦莉, 党晓明, 等. 钼合金纳米喷雾掺杂工艺研究. 稀有金属, 2017, 41(1): 57 -




 下载:
下载: