-
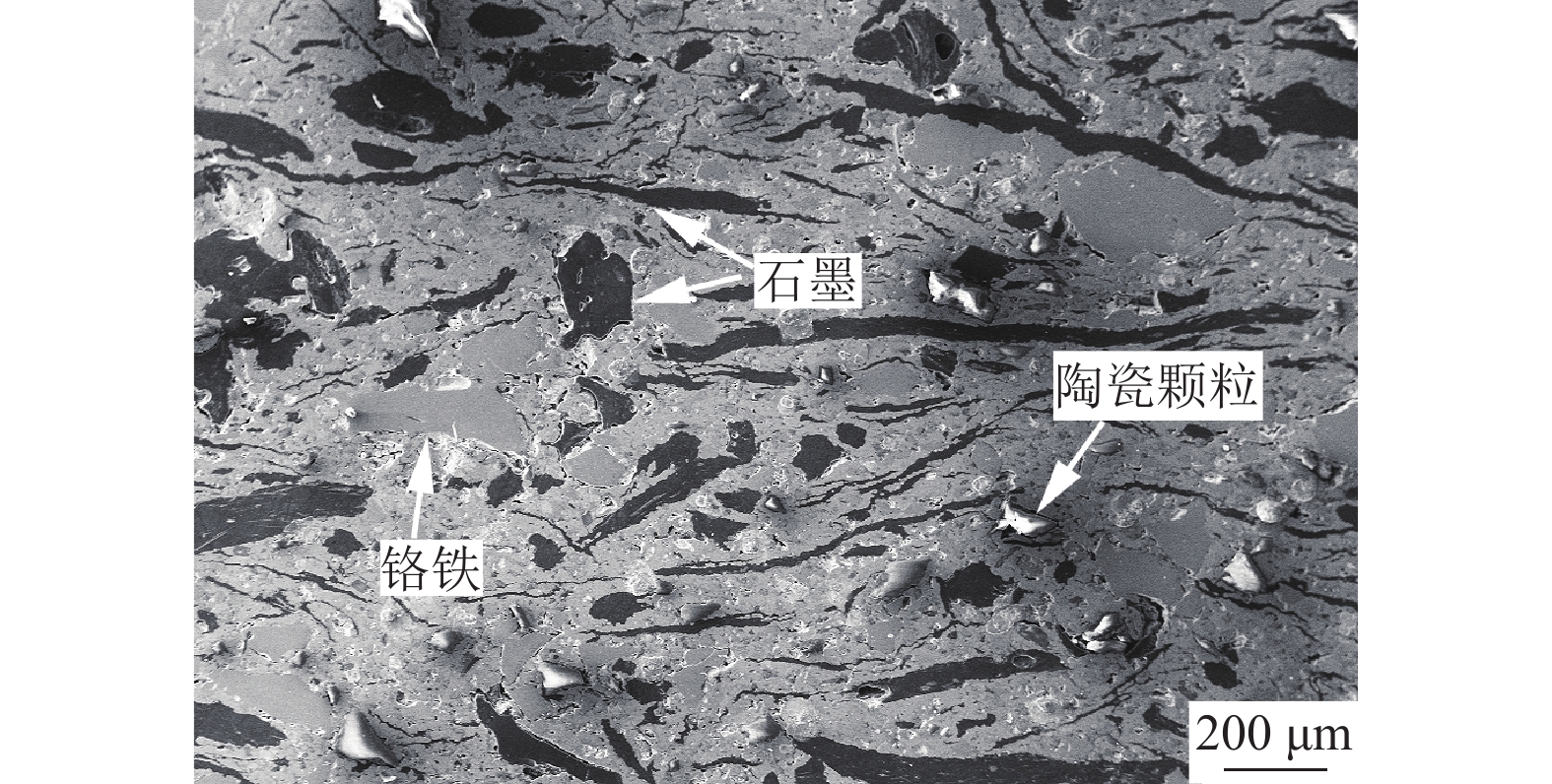
摘要: Cu基粉末冶金闸片在高速制动时受温度的影响易发生摩擦系数的衰退,直接影响列车制动的有效性。利用1:1制动试验台进行不同速度下Cu基粉末冶金闸片的高速制动试验,分析试验后的摩擦材料和磨屑组织。结果表明:制动速度为350 km·h−1和380 km·h−1产生的高温使摩擦材料表层的金属基体发生软化熔融,降低了摩擦副表面微凸点的剪切阻力,导致摩擦系数下降。摩擦表面形成的金属氧化膜具有减磨作用,造成摩擦系数的进一步衰退。在380 km·h−1制动时,石墨在高温下被氧化,摩擦表面失去稳定的润滑膜,出现粘着磨损和材料转移,磨耗量大幅增加。Abstract: Friction coefficients of the Cu-based powder metallurgical brake pads decline due to the high temperature during the high-speed braking, which will directly affect the train braking effectiveness. The 1:1 high-speed braking tests of Cu-based powder metallurgical brake pads were carried out under the different speeds, and the friction materials and abrasive texture after the tests were analyzed. The results show that, the metal matrix on the surface of friction materials melts due to the high temperature under the braking speeds of 350 km·h−1 and 380 km·h−1, decreases the shear resistance of the micro bumps on the friction surface, and causes the decline of friction coefficient. The metal oxide films formed on the friction surface reduce the wear, resulting in the further decline of friction coefficient. The friction surface lost the stable lubricant film when the graphite is oxidized under the high temperature generated by 380 km·h−1 braking, and the wear loss increases significantly due to the adhesive wear and material transfer behavior.
-
Key words:
- Cu-based powder metallurgy brake pads /
- friction materials /
- wear loss /
- high speed braking /
- fading
-
表 1 制动摩擦试验方案
Table 1. Scheme of the brake friction test
制动次序 制动速度 / (km·h−1) 双侧闸片压力 / kN 初始温度 / ℃ 备注 1~3 120 30 50~60 第3闸结束后闸片称重,收集磨屑 4~6 300 30 50~60 第6闸结束后闸片称重,收集磨屑 7~9 350 30 50~60 第9闸结束后闸片称重,收集磨屑 10~12 380 30 50~60 第12闸结束后闸片称重,收集磨屑 表 2 摩擦材料的物理和力学性能
Table 2. Physical and mechanical properties of the friction materials
硬度,HBW 密度 / (g·cm−3) 摩擦体剪切强度 / MPa 摩擦体与粘接面剪切强度 / MPa 摩擦体抗压强度 / MPa 16 4.6 10 13 93 表 3 图6中不同位置磨屑能谱分析
Table 3. EDS analysis of abrasive in Fig.6
位置 质量分数 / % C O Cr Fe Cu 位置1 14.19 18.98 5.49 21.33 39.41 位置2 16.95 14.96 4.07 22.75 33.52 位置3 5.17 16.95 1.10 5.26 70.96 位置4 3.60 13.94 — 5.11 77.35 表 4 图7中磨屑断面能谱分析
Table 4. EDS analysis of the abrasive fracture surface in Fig.7
-
[1] Zhou H B. Research on the Effects of Characteristic Friction Components/Cu Matrix Interface on Friction and Wear Mechanism of Powder Metallurgy Friction Materials [Dissertation]. Changsha: Central South University, 2014周海滨. 粉末冶金摩擦材料特征摩擦组元与铜基体的界面及其对摩擦磨损机理影响研究[学位论文]. 长沙: 中南大学, 2014 [2] Wang X Y, Ru H Q Braking properties of Cu–Fe based powder metallurgy braking materialsPowder Metall Ind2015 25 6 48 王晓阳, 茹红强 Cu–Fe基粉末冶金闸片制动特性的研究粉末冶金工业2015 25 6 48 [3] Dai Z D, Xue Q J Thermodynamic study of friction and wear: present situation and expectationSci China2009 39 7 1211 戴振东, 薛群基 摩擦磨损的热力学研究: 现状和展望中国科学2009 39 7 1211 [4] Duan H T, Du S M, Zhang Y Z, et al Study on the friction heat rule under high-speed dry sliding conditionsLubr Eng2007 32 10 40 段海涛, 杜三明, 张永振, 等 高速干滑动条件下钢/铜摩擦副摩擦磨损表面摩擦热规律研究润滑与密封2007 32 10 40 [5] Liu J X, Guo Y Q, Han C S, et al Study of high temperature fatigue wear of copper powder metallurgy (Cu-PM) friction materialLubr Eng2004 29 3 1 刘建秀, 郭炎强, 韩长生, 等 铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料高温疲劳磨损规律润滑与密封2004 29 3 1 [6] Liu L J, Li L, Wu Q J, et al Effects of braking velocity on friction properties of Cu-based powder metallurgy friction materialPowder Metall Technol2018 36 2 83 刘联军, 李利, 吴其俊, 等 刹车速度对铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料性能的影响粉末冶金技术2018 36 2 83 [7] Liu Y T. Research on Morphological Control and Performance Impact of Lubrication Component of CuFe Based Friction Materials [Dissertation]. Shenyang: Northeastern University, 2015刘倚天. Cu–Fe基摩擦材料中润滑组元形态的控制及其影响[学位论文]. 沈阳: 东北大学, 2015 [8] Zhu X G, Sun L M, Chen Y, et al Effect of braking conditions on tribological performance of Cu-based powder metallurgy brake padsJ Henan Univ Sci Technol Nat Sci2015 36 4 1 朱旭光, 孙乐民, 陈跃, 等 制动条件对Cu基闸片材料摩擦磨损性能的影响河南科技大学学报: 自然科学版2015 36 4 1 [9] Zhu X G, Sun L M, Chen Y, et al Tribological performances of Cu-based powder metallurgy brake pads under high-speed braking conditionLubr Eng2015 40 11 52 朱旭光, 孙乐民, 陈跃, 等 高速制动工况下Cu基粉末冶金闸片材料摩擦磨损性能润滑与密封2015 40 11 52 [10] Han Y. Performance and Tribology Research of Ceramic Friction Material [Dissertation]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2008韩野. 陶瓷纤维摩擦材料的制备及摩擦机制研究[学位论文]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008 [11] Wang K, Li H B, Liu X D Effects of brake temperature on brake performanceNew Technol New Prod China2013 12 82 王坤, 李海斌, 刘晓东 制动器制动温度对制动性能的影响中国新技术新产品2013 12 82 [12] Bi Y Q. Preparation Parameters and Friction and Wear Properties of Cu-based Powder Metallurgy Friction Material for Wind Turbine [Dissertation]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2015毕勇强. 风电用铜基粉末冶金摩擦材料制备工艺参数及其摩擦磨损性能[学位论文]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2015 [13] Zhuang T Y, Zhang J L, Wang F, et al Research progress on the microwave sintering mechanism of metal powdersPowder Metall Technol2019 37 5 392 庄天涯, 张际亮, 王霏, 等 金属粉末微波烧结机理研究进展粉末冶金技术2019 37 5 392 [14] Xiao Y L, Zhang Z Y, Yao P P, et al Mechanical and tribological behaviors of copper metal matrix composites for brake pads used in high-speed trainsTribol Int2018 119 585 [15] Demirskyi D, Agrawal D, Ragulya A Neck growth kinetics during microwave sintering of nickel powderJ Alloys Compd2011 509 5 1790 [16] Zhang Y Z, Zhang G D The role of graphite particles in the high temperature wear of copper hybrid composites against steelMater Des2006 27 79 [17] Wang J Y, Shan Y, Wang W Z, et al Effects of graphite addition on tribological properties of NiCr–W–Ti self-lubricating composites at elevated temperaturesJ Mater Sci Eng2017 35 3 358 汪建义, 陕钰, 王文珍, 等 石墨的添加对NiCr–W–Ti自润滑复合材料高温摩擦学性能的影响材料科学与工程学报2017 35 3 358 [18] Gu S C, Zhu L H, Duan Y M, et al Friction and wear behavior of M2 high speed steel at elevated temperatureShanghai Met2020 42 4 50 顾绳初, 朱丽慧, 段元满, 等 M2高速钢的高温摩擦磨损行为上海金属2020 42 4 50 [19] Yin C H, Li S B, Liang Y L A review on microstructure evolution in a friction-induced layer and the self-lubricating behavior during dry sliding friction of steelsMater Rep2020 34 10 19134 尹存宏, 李少波, 梁益龙 钢铁材料摩擦层结构演变与干摩擦自润滑行为研究进展材料导报2020 34 10 19134 -




 下载:
下载: