Microstructure and failure mechanism of FGH96 solid-state diffusion bonding interface
-
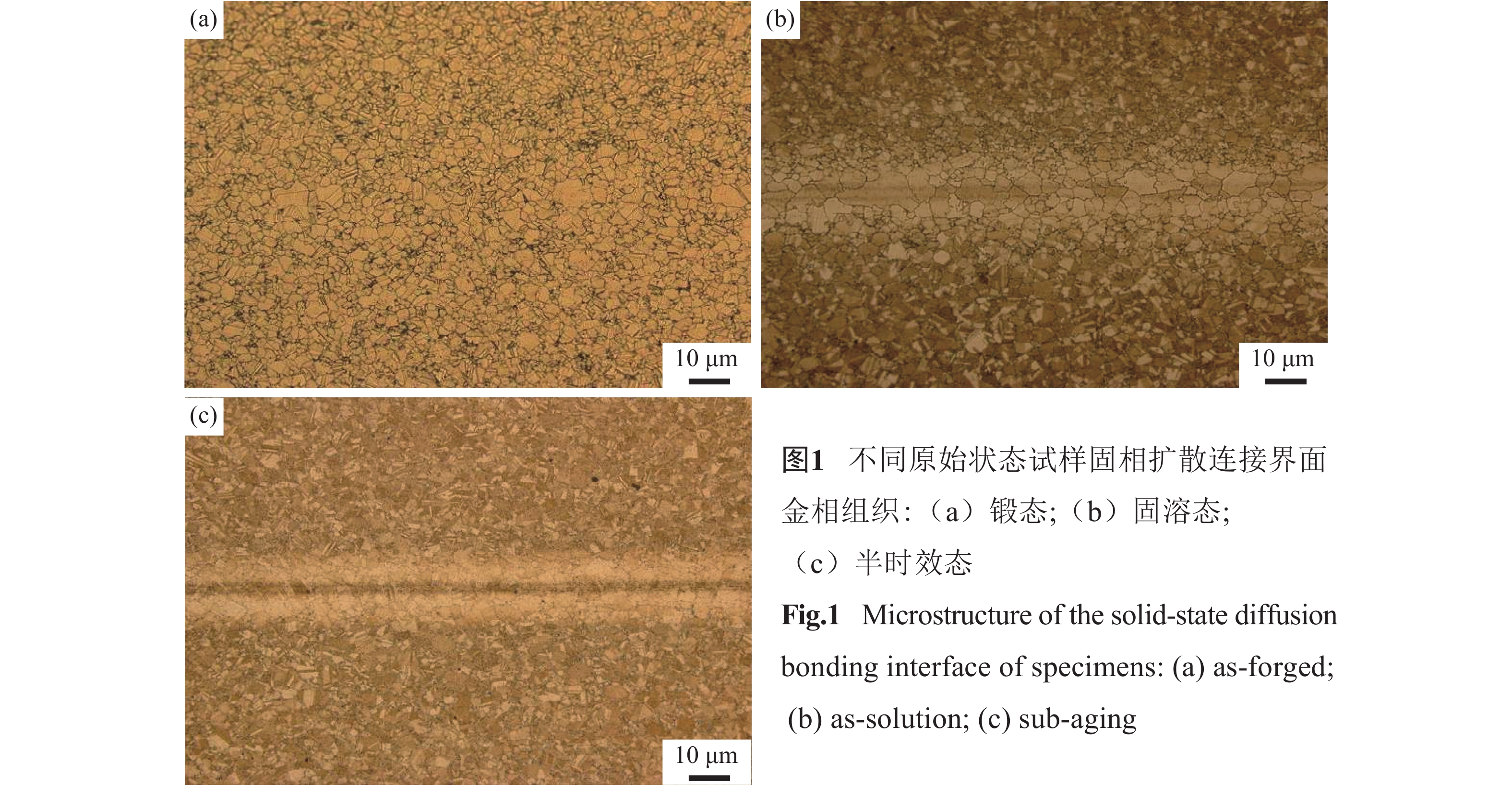
摘要: 对原始状态分别为锻态、固溶态和半时效态的FGH96合金固相扩散连接界面显微组织进行表征,并对连接界面的拉伸性能进行测试,对失效行为进行研究。结果表明,锻态、固溶态和半时效态试样经固相扩散连接后界面均实现了良好的冶金结合,连接界面无孔洞和缝隙等缺陷。锻态试样界面扩散更为充分,组织过渡更为平缓;固溶态和半时效态试样界面存在明显的连接影响区。锻态试样经固相扩散连接和标准热处理后,二次γʹ相细小、均匀且呈典型椭球状;固溶态和半时效态试样因固相扩散连接热循环的作用导致γʹ相发生长大和分化。二次γʹ相尺寸及形貌的不同决定了界面区域性能水平的差异。电子背散射衍射测试结果表明,连接界面处大晶粒的择优取向为{100},距离固相扩散连接界面越近,晶粒的择优取向越明显。拉伸试验结果表明,锻态试样经固相扩散连接和标准热处理后,连接界面处的强度达到基体强度的99%以上。拉伸裂纹主要萌生于连接界面大晶粒及γʹ相粗化聚集区域,体现为穿晶的韧窝型断裂。Abstract: The microstructure on the solid-state diffusion bonding interfaces of the initially as-forged, as-solution, and sub-aging FGH96 was characterized, the tensile properties of the bonding interfaces were tested, and the failure behavior was studied. It is found that the good metallurgical bonding is achieved at the bonding interfaces of all the three primitive state specimens after the solid-state diffusion, and no cracks and cavities are found. The interfaces of the as-forged specimens show more sufficient diffusion of elements and smoother transition of microstructure, while the interfaces of both the as-solution and sub-aging specimens exhibit an obvious bonding effecting zone. After the solid-state diffusion bonding and the standard heat treatment, the second γʹ phases in the as-forged specimens are fine, uniform, and spherical. However, the second γʹ phases in the as-solution and sub-aging specimens grow up and split up because of the solid-state diffusion bonding thermal cycle. Different morphology of the second γʹ phases causes the difference of properties in the bonding interface regions. Results of the electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) show that the preferred orientation of large grains is {100}, and the grain orientation is more obvious as the closer distance to the solid diffusion interface. The tensile test results show that the strength at the interfaces of the forged specimens after the solid-state diffusion bonding and the standard heat treatment is more than 99% of that of the matrix. The tensile cracks mainly initialize from the aggregated area of the large grains and the coarse γʹ phases, which show the transgranular dimple fracture behavior.
-
Key words:
- FGH96 superally /
- solid-state diffusion bonding /
- microstructure /
- failure mechanism
-
图 4 不同原始状态试样距离固相扩散连接界面不同位置γʹ强化相:(a)锻态,Zone1;(b)固溶态,Zone1;(c)半时效态,Zone1;(d)锻态,Zone2;(e)固溶态,Zone2;(f)半时效态,Zone2;(g)锻态,Zone3;(h)固溶态,Zone3;(i)半时效态,Zone3
Figure 4. Microstructure of γʹ phases in the different distance from the solid-state diffusion bonding interface of specimens: (a) as-forged, Zone1; (b) as-solution, Zone1; (c) sub-aging, Zone1; (d) as-forged, Zone2; (e) as-solution, Zone2; (f) sub-aging, Zone2; (g) as-forged, Zone3; (h) as-solution, Zone3; (i) sub-aging, Zone3
图 6 固溶态试样连接界面区域电子背散射衍射晶粒取向分析:(a)连接界面处;(b)距连接界面100~200 μm处;(c)距连接界面200~300 μm处
Figure 6. EBSD analysis of the grain orientation at the bonding interface of the solid solution specimens: (a) bonding interface; (b) 100~200 μm away from the bonding interface; (c) 200~300 μm away from the bonding interface
图 9 固溶态连接试样拉伸断口形貌:(a)室温宏观形貌;(b)室温扩展区形貌;(c)650 ℃宏观形貌;(d)650 ℃扩展区形貌
Figure 9. Tensile fracture morphology of the solid solution specimens: (a) macro morphology at room temperature; (b) extended region morphology at room temperature; (c) macro morphology at 650 ℃; (d) extended region morphology at 650 ℃
表 1 FGH96镍基粉末高温合金化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of the nickel-based powder metallurgy superalloy FGH96
% C Cr Co Mo W Al Ti Nb B Zr Ni 0.02~0.05 15.5~16.5 12.5~13.5 3.8~4.2 3.8~4.2 2.0~2.4 3.5~3.9 0.6~1.0 0.006~0.015 0.025~0.050 余量 -
[1] Reed R C. The Superalloys: Fundamentals and Applications. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2006 [2] Wang W X, He F, Zou J W. The application and development of P/M superalloys. Aviat Maint Eng, 2002(6): 26汪武祥, 何峰, 邹金文. 粉末高温合金的应用与发展. 航空工程与维修, 2002(6): 26 [3] Guo W M, Dong J X, Wu J T, et al. Microstructure and properties of PM superalloys FGH96. J Iron Steel Res, 2005, 17(1): 59 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2005.01.015国为民, 董建新, 吴剑涛, 等. FGH96镍基粉末高温合金的组织和性能. 钢铁研究学报, 2005, 17(1): 59 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0963.2005.01.015 [4] Preuss M, Withers P J, Pang J W L, et al. Inertia welding nickel-based superalloy: Part 1. Metalurgical characterization. Metall Mater Trans A, 2002, 33: 3215 doi: 10.1007/s11661-002-0307-y [5] Senkov O N, Mahaffey D W, Semiatin S L. A comparison of the inertia friction welding behavior of similar and dissimilar nickel-based superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A, 2018, 49: 5428 doi: 10.1007/s11661-018-4853-3 [6] Li H Y, Huang Z W, Bray S, et al. High temperature fatigue of friction welded joints in dissimilar nickel based superalloys. Mater Sci Technol, 2007, 23(12): 1408 doi: 10.1179/174328407X243933 [7] Gale W F, Butts D A. Transient liquid phase bonding. Sci Technol Weld Joining, 2004, 9(4): 283 doi: 10.1179/136217104225021724 [8] Yuan L, Xiong J T, Peng Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties in the solid-state diffusion bonding joints of Ni3Al based superalloy. Mater Sci Eng A, 2020, 772: 138670 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2019.138670 [9] Chamanfar A, Jahazi M, Cormier J. A review on inertia and linear friction welding of Ni-based superalloys. Metall Mater Trans A, 2015, 46: 1639 doi: 10.1007/s11661-015-2752-4 [10] Pouranvari M, Ekrami A, Kokabi A H. Microstructure evolution mechanism during post-bond heat treatment of transient liquid phase bonded wrought IN718 superalloy: An approach to fabricate boride-free joints. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 723: 84 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.206 [11] Shirzadi A. Solid-State Diffusion Bonding. Microjoining and Nanojoining. Cambridge: Woodhead Publishing Limited, 2004 [12] Zhang G, Chandel R S, Seow H P. Solid state diffusion bonding of Inconel 718. Sci Technol Weld Joining, 2001, 6(4): 235 doi: 10.1179/136217101101538820 [13] Li Z R, Feng G J, Xu K, et al. Vacuum diffusion bonding process of GH4169 superalloy. Trans China Weld Inst, 2013, 34(6): 21李卓然, 冯广杰, 徐慨, 等. 高温合金GH4169真空扩散连接工艺. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(6): 21 [14] Zhu Y, Zhang H, Cheng X T, et al. Effect of nickel interlayer thickness on solid-state diffusion bonding quality of superalloy GH4099. Trans China Weld Inst, 2018, 39(4): 93 doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390103朱源, 张昊, 程晓瞳, 等. 镍箔中间层厚度对GH4099合金固相扩散焊质量的影响. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(4): 93 doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390103 [15] Cui Z Q, Qin Y C. Metallurgy and Heat Treatment. 2nd Ed. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2007崔忠圻, 覃耀春. 金属学与热处理. 2版. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2007 -




 下载:
下载: