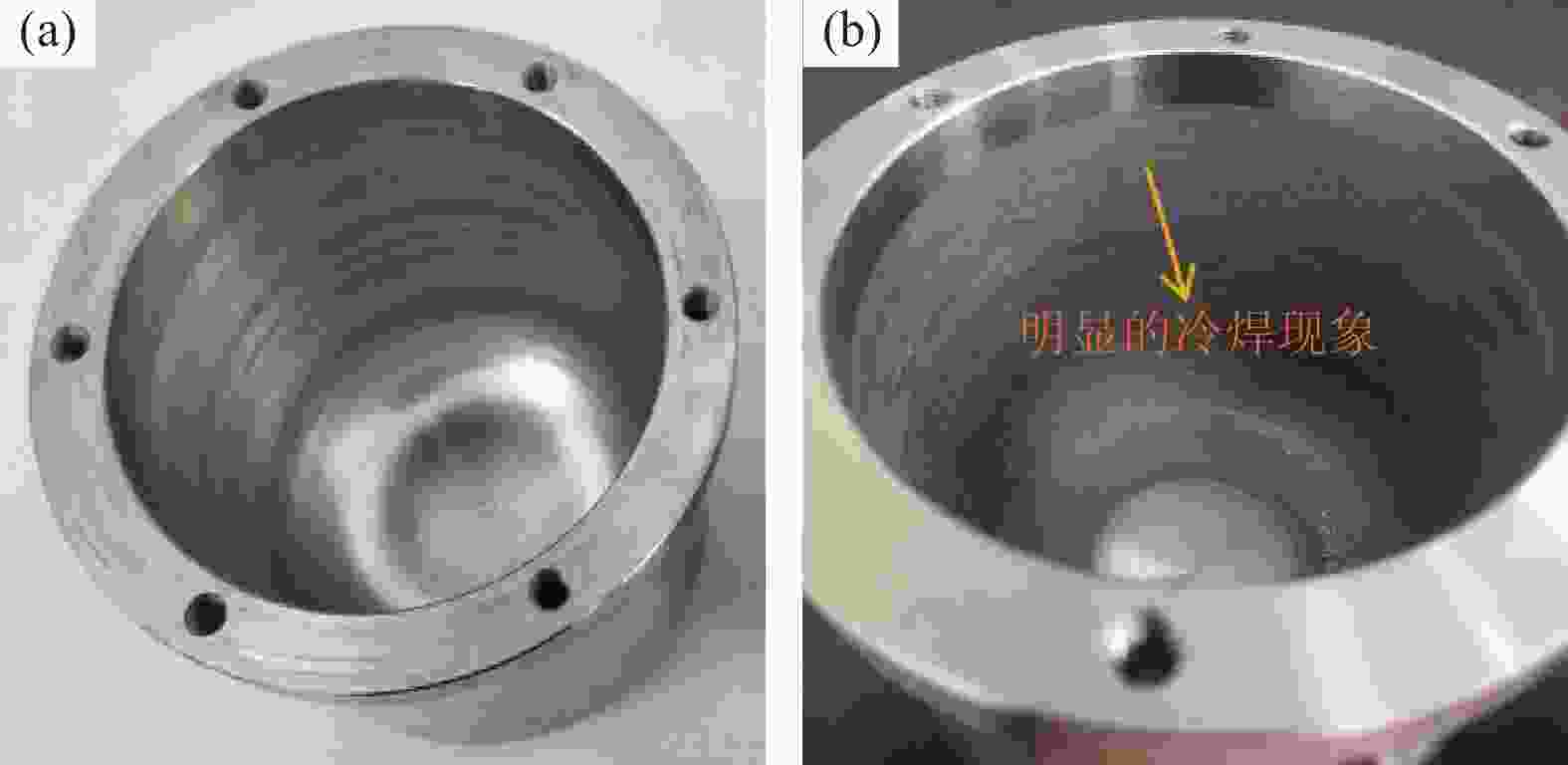
Effect of ball milling process on mechanical properties of medical Ti–Mg composites
-
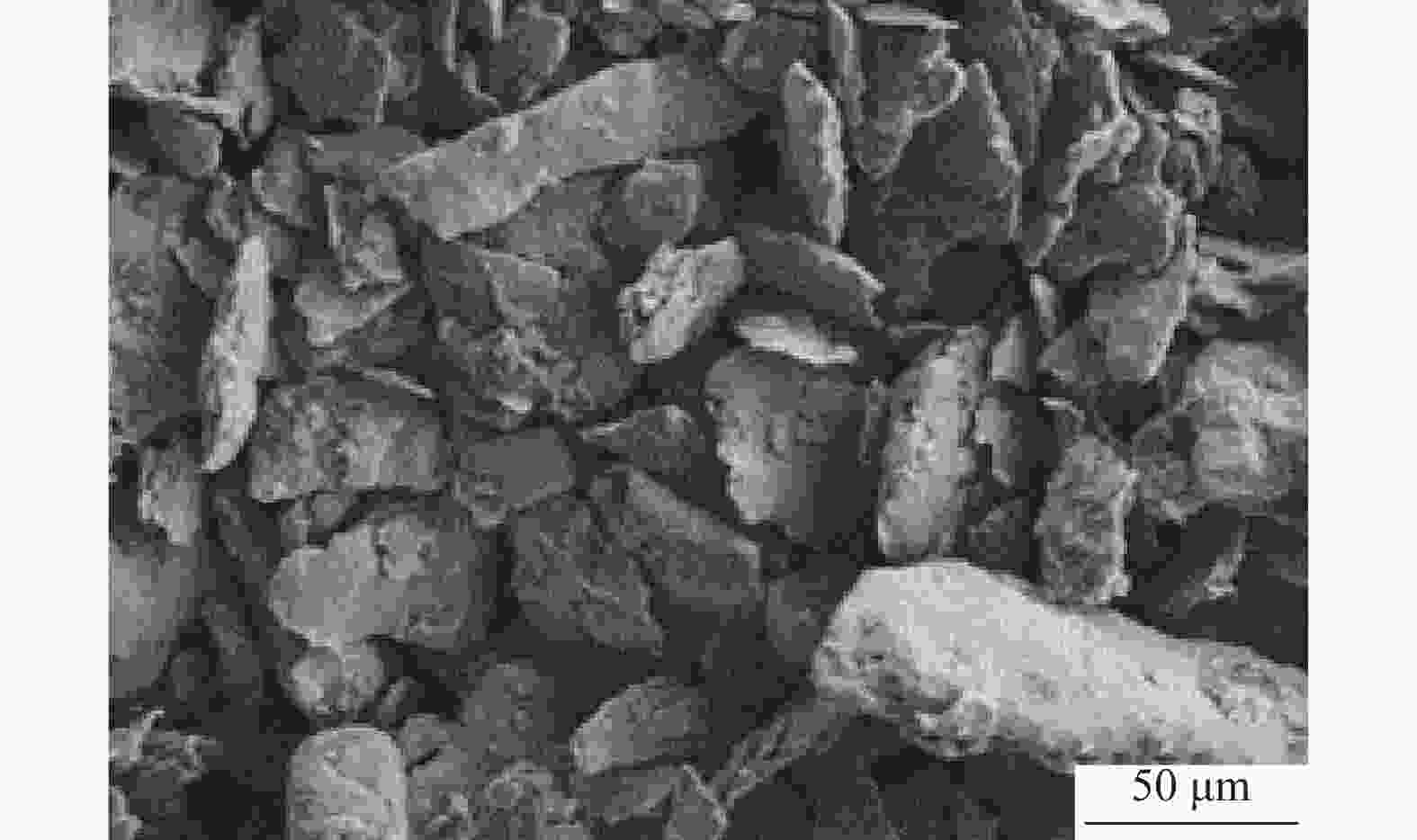
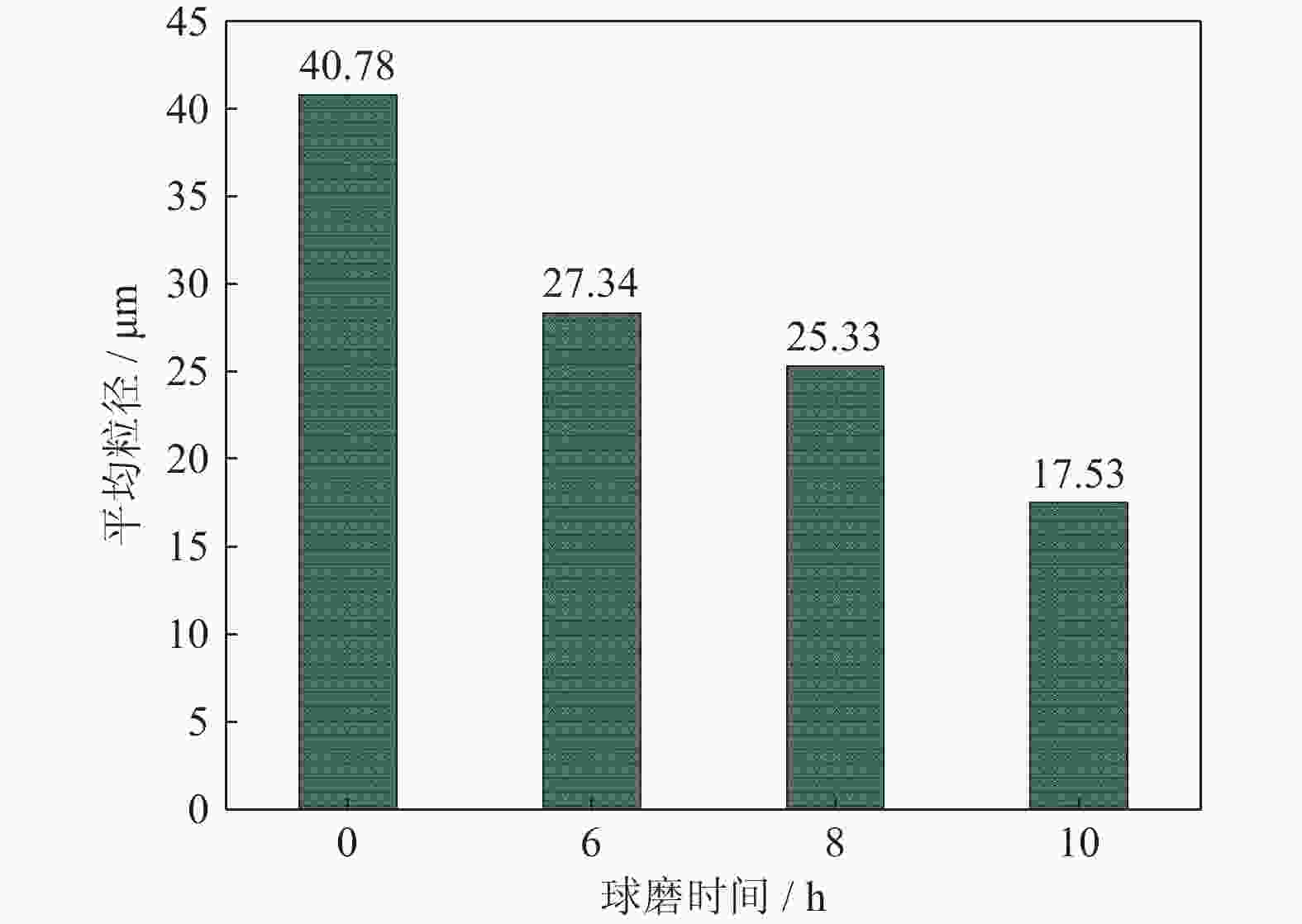
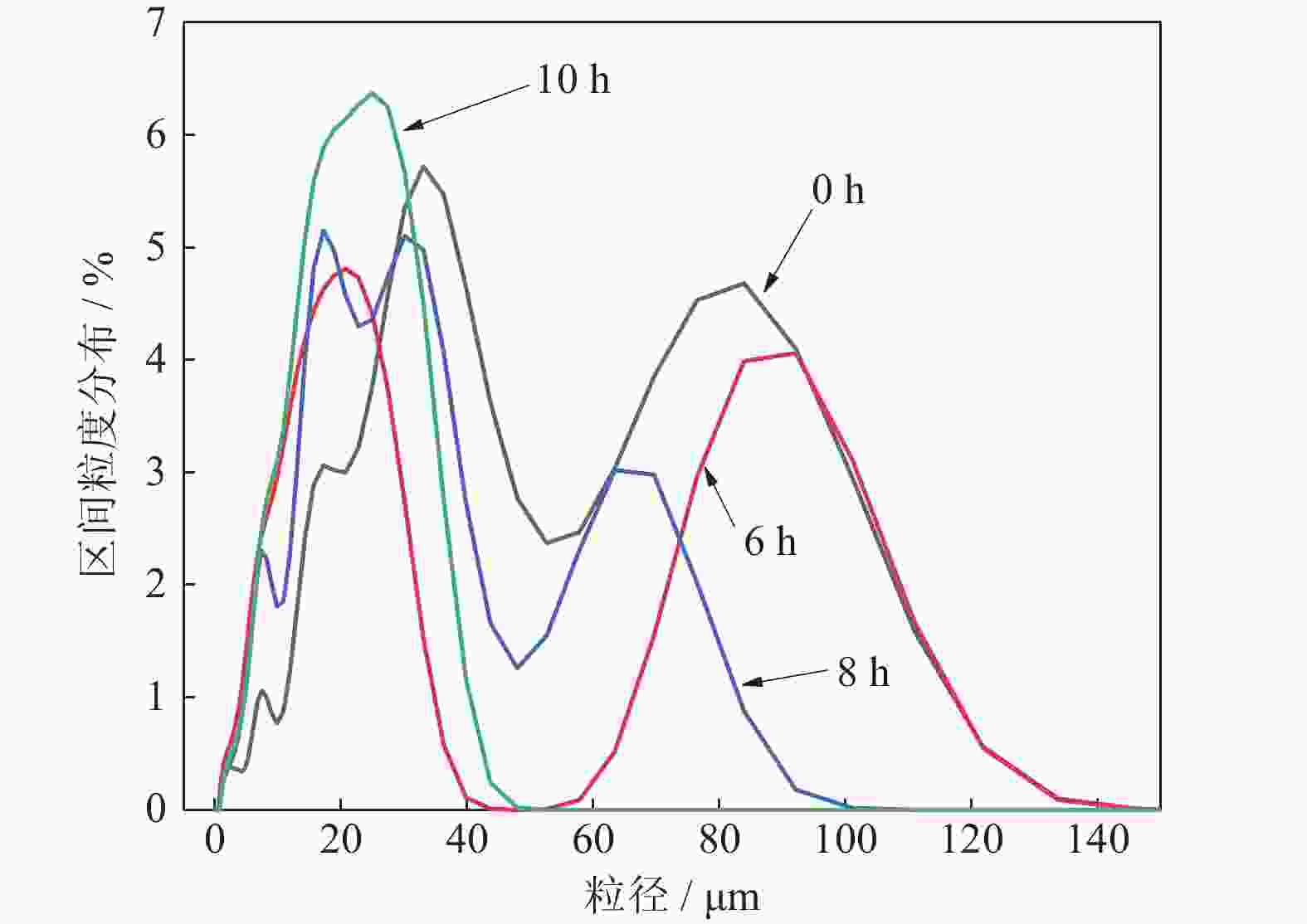
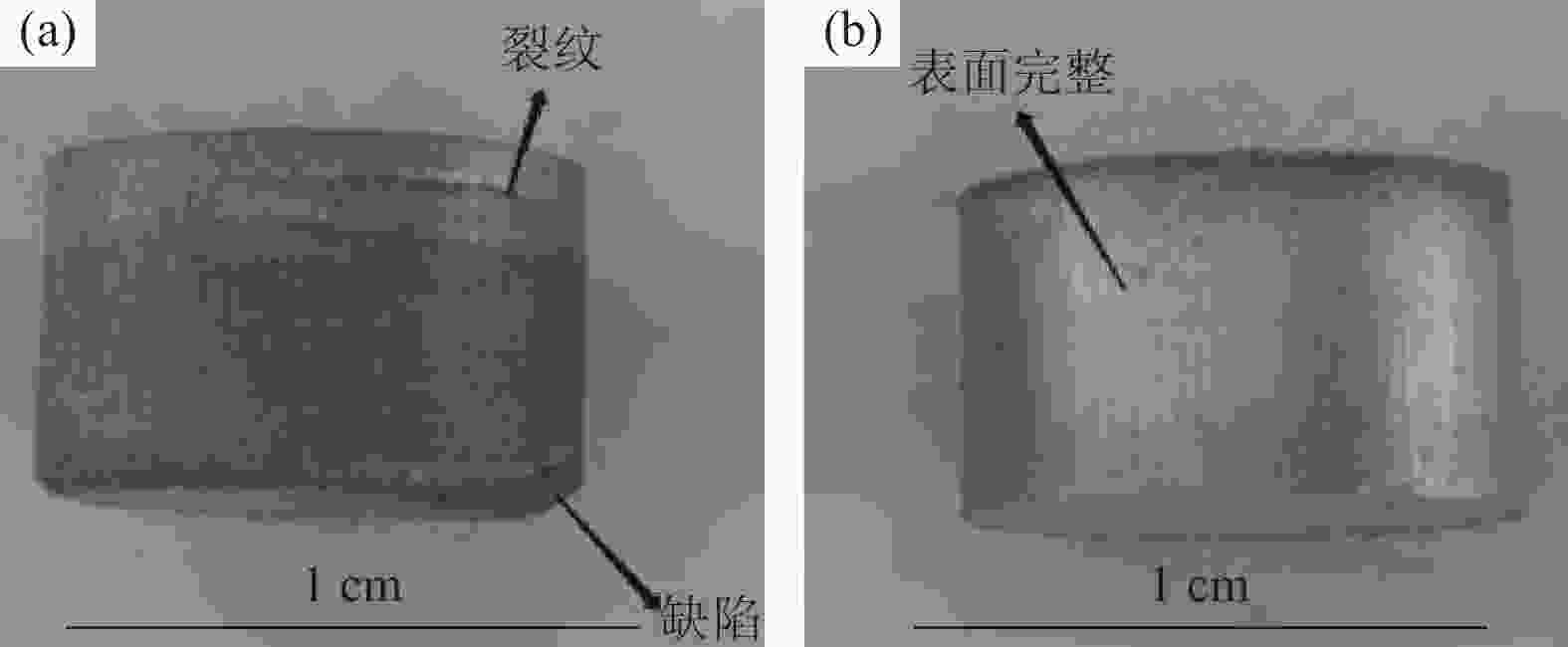
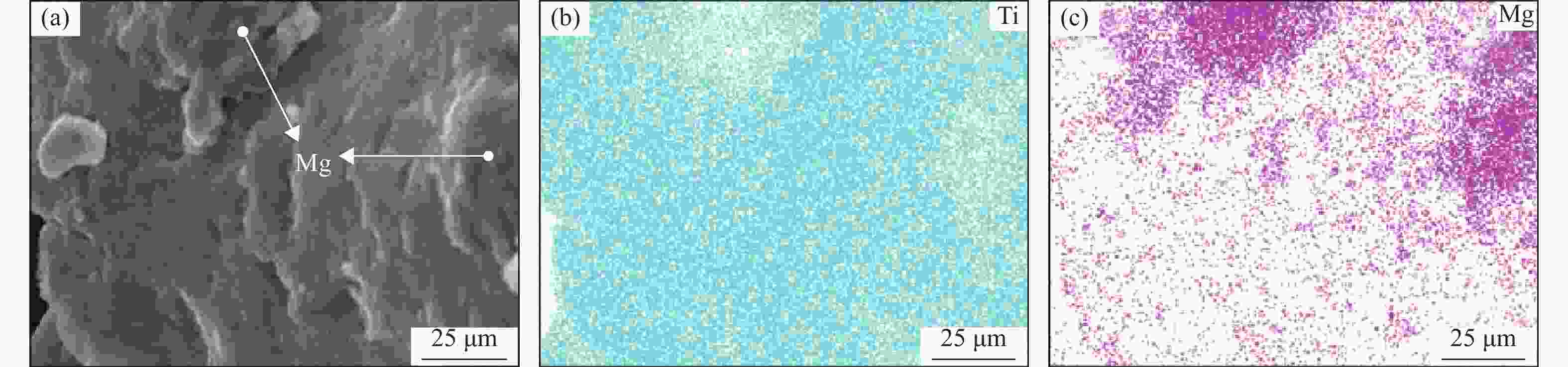
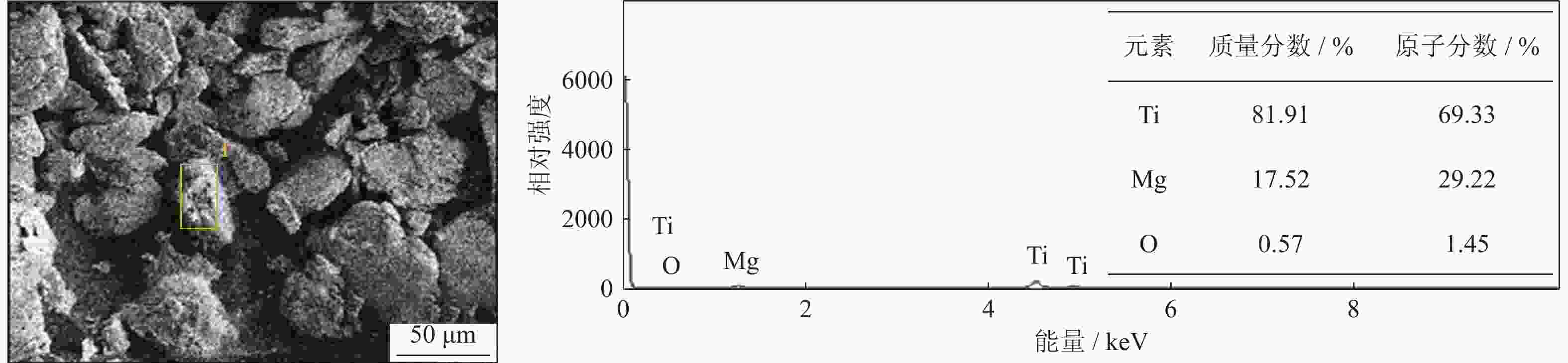
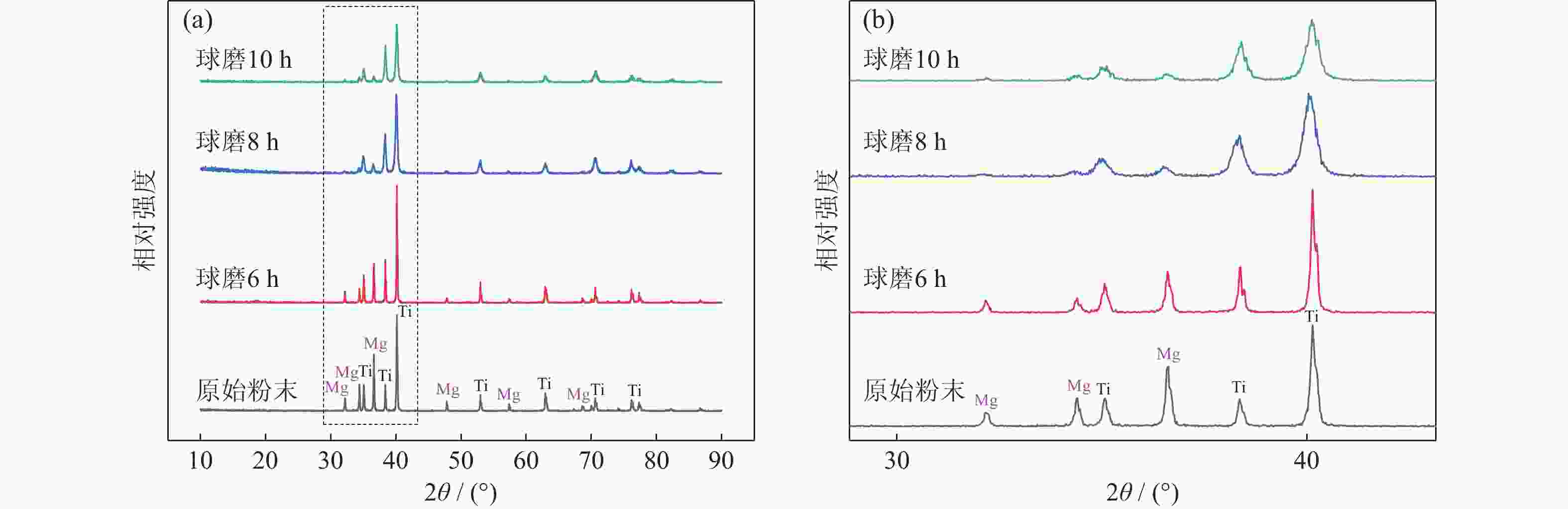
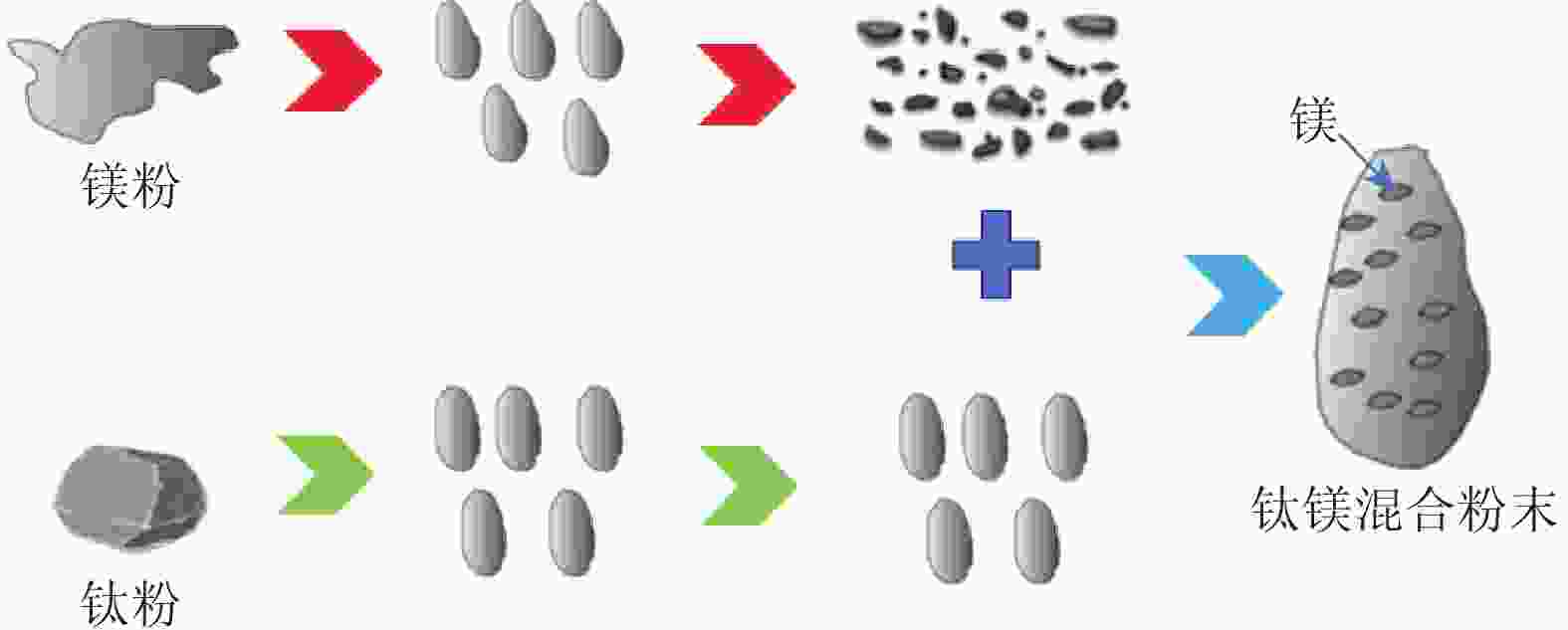
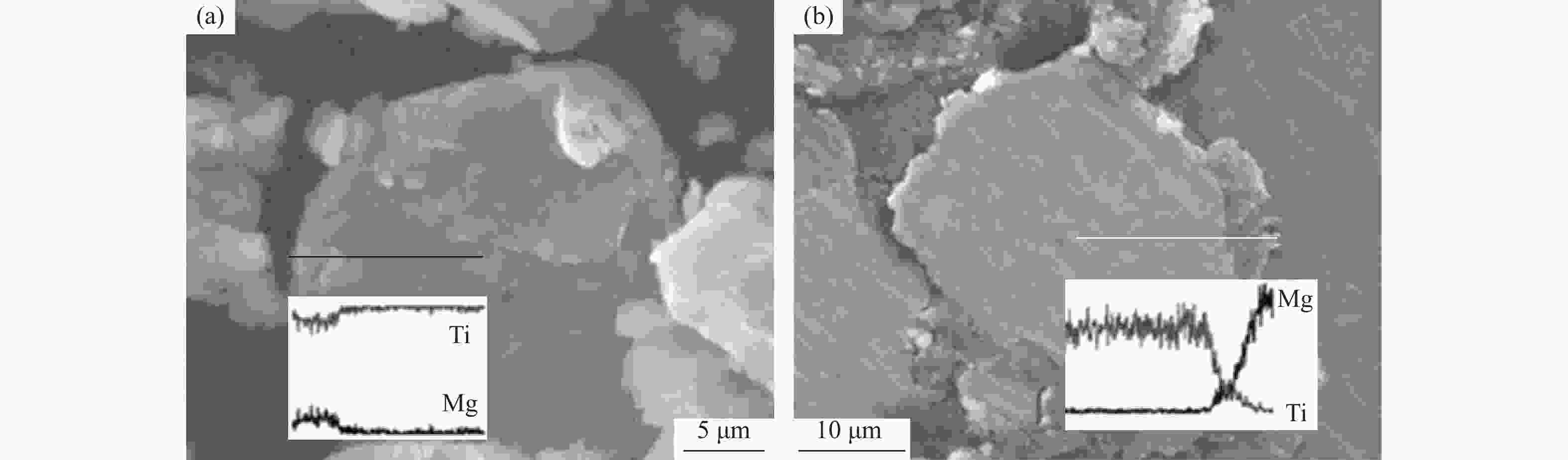
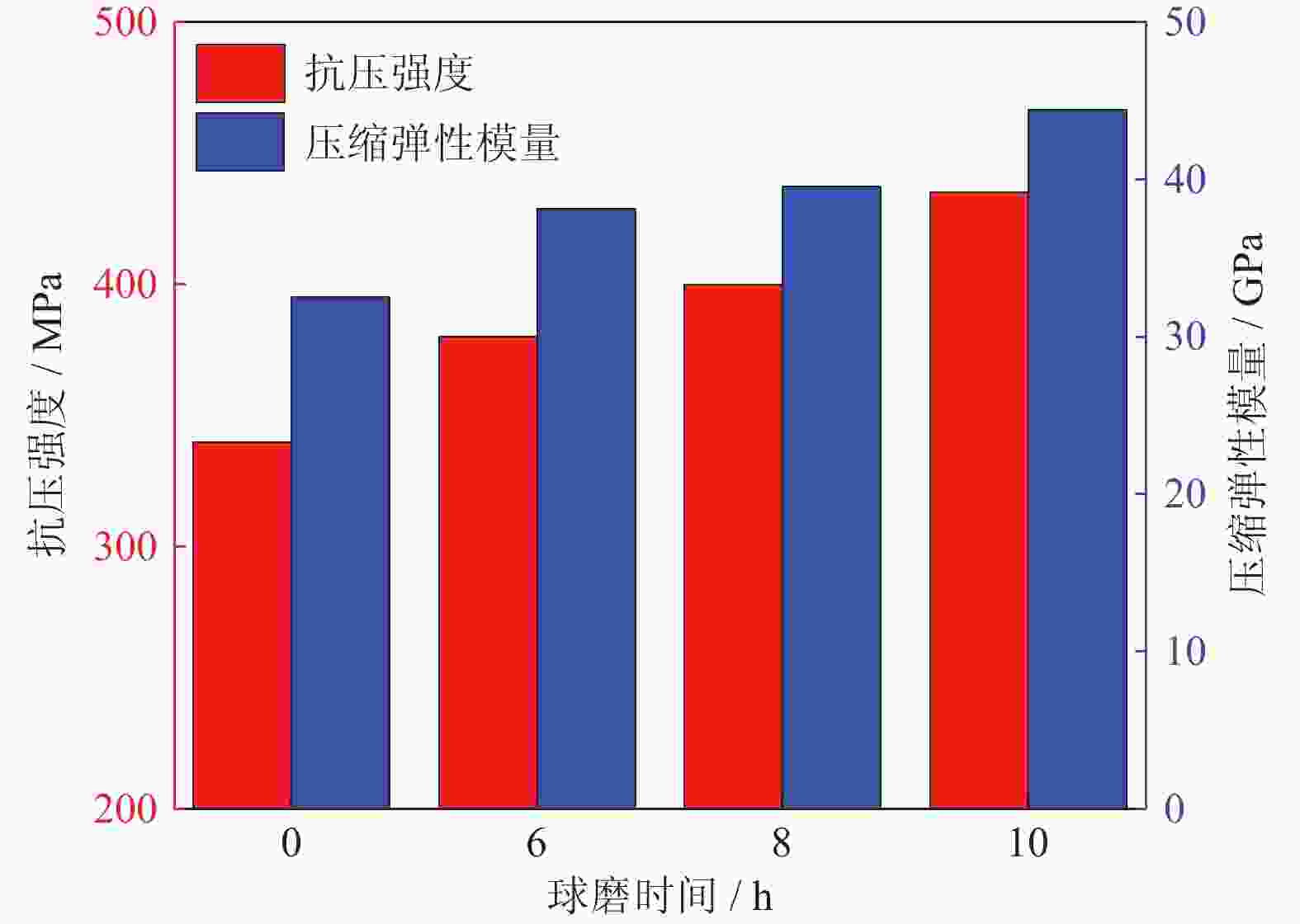
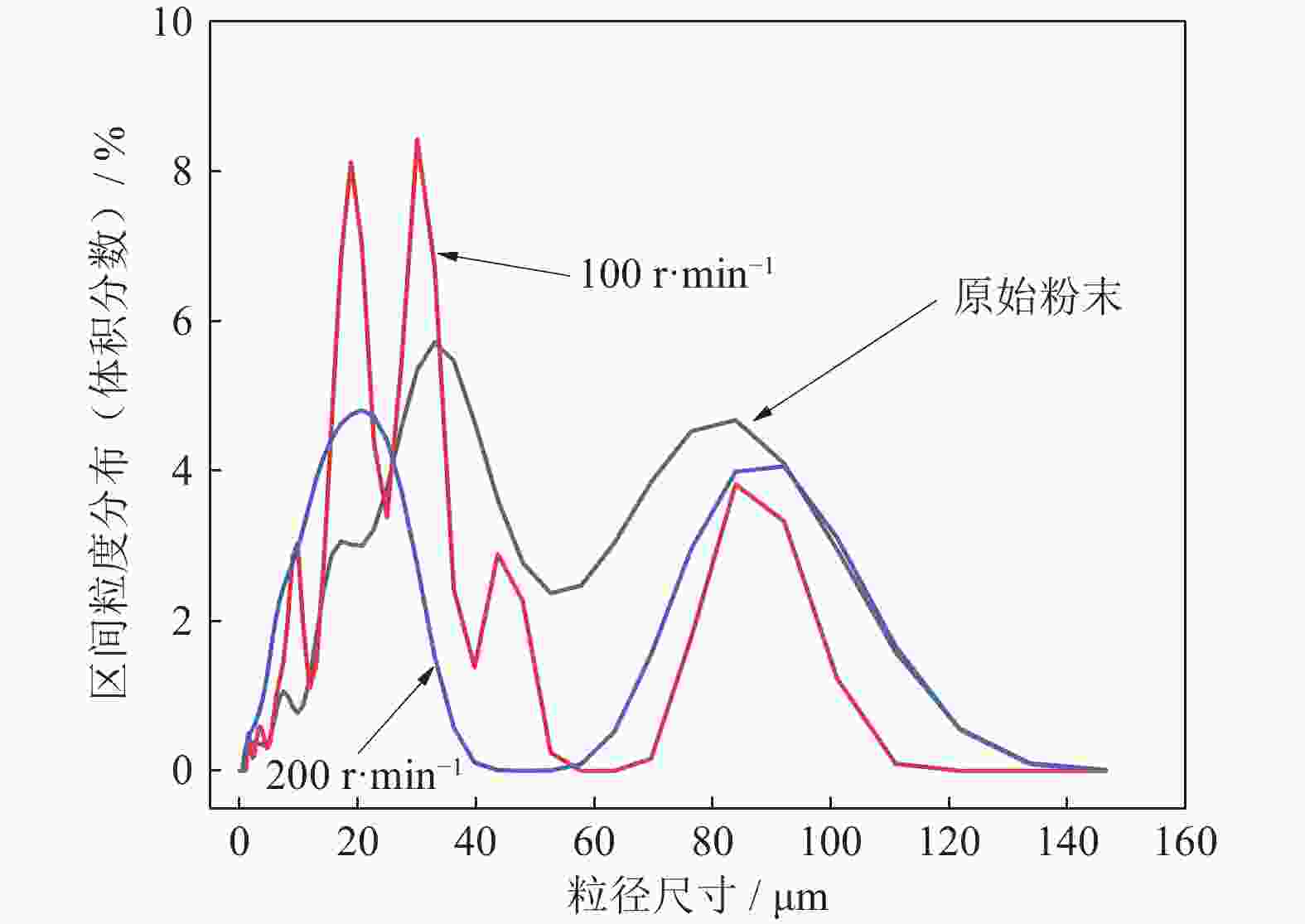
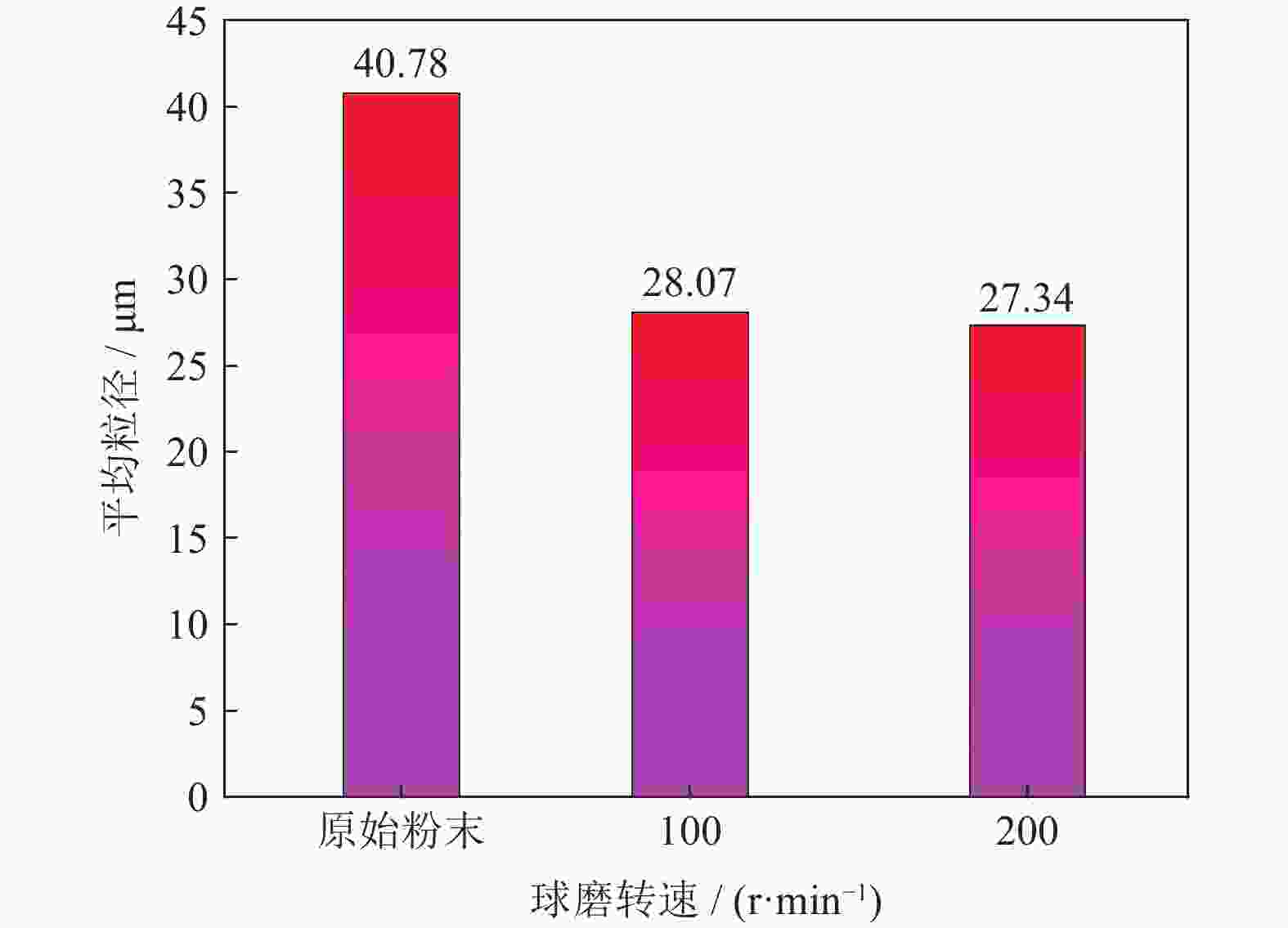
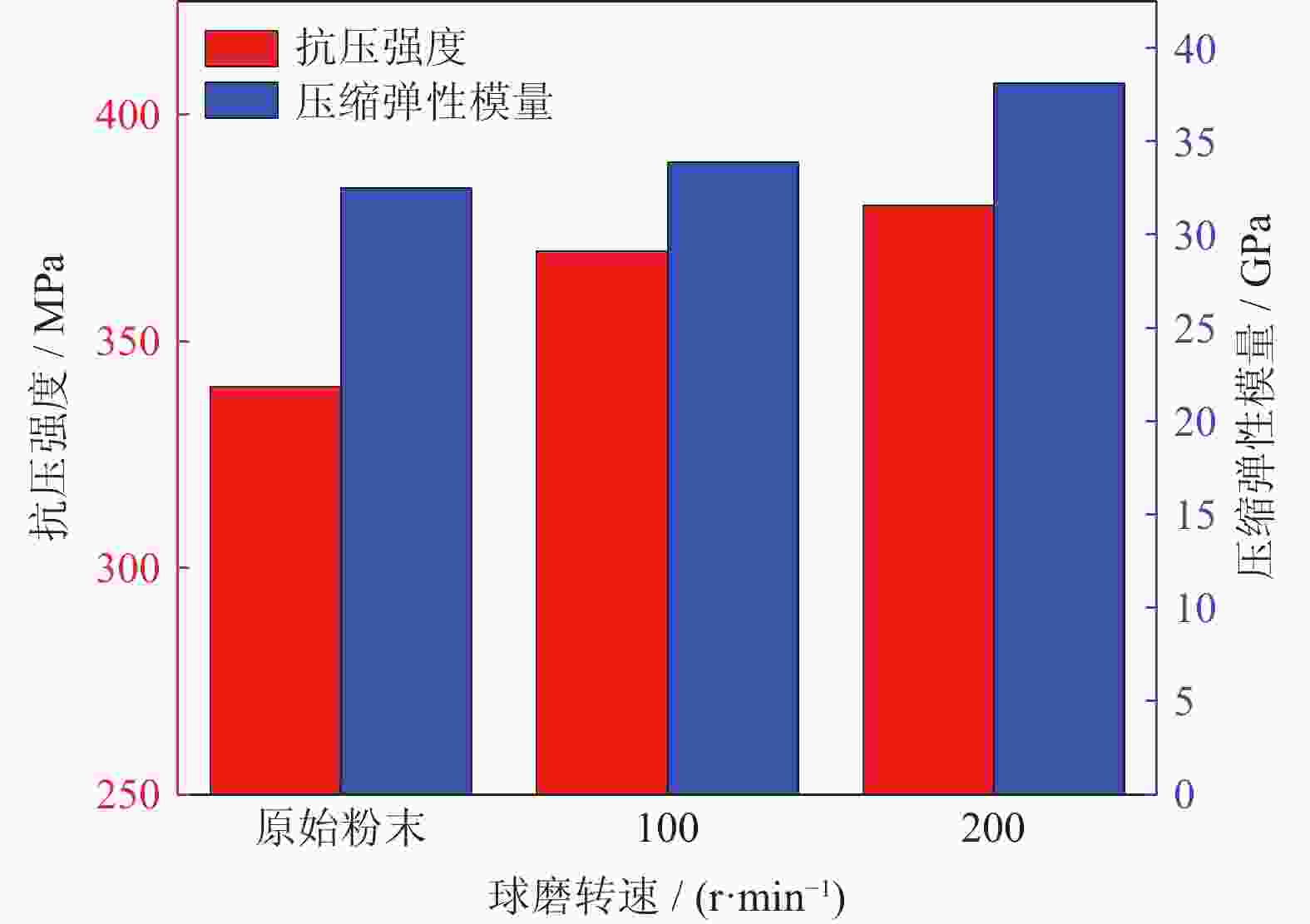
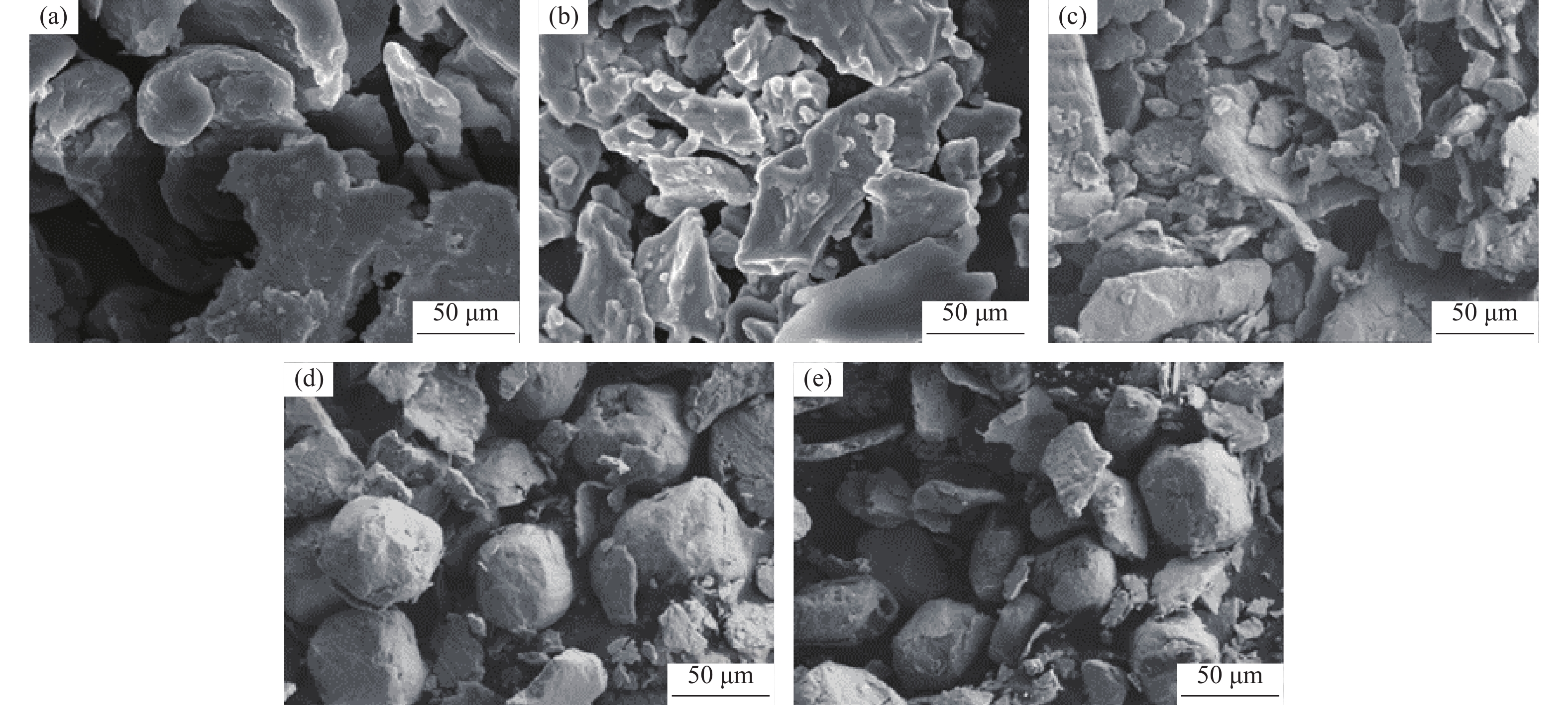
摘要: 采用球磨+冷压制坯+微波加热烧结工艺制备Ti–15Mg复合材料,研究球磨工艺对Ti–15Mg混合粉末性能以及烧结后复合材料力学性能的影响。结果表明:以200 r·min−1球磨转速球磨8~10 h,随着球磨时间延长,混合粉末的平均粒径明显变小,粉末粒度分布逐渐集中在10~45 μm区间,粉末的球形度增加。在长时间球磨过程中,软质镁颗粒受到强烈撞击、研磨,引起表面破碎,钛颗粒出现了体积破碎和表面破碎,最终导致软质镁颗粒包裹脆性钛颗粒。球磨8 h后,混合粉末未出现明显的氧化,混合粉末中钛、镁粉末分布较为均匀,复合材料的力学性能较为优良,符合作为医用材料的力学性能要求。在低球磨转速下,球磨转速的提高不会导致粉末性能和烧结后复合材料性能出现明显变化。最佳球磨工艺参数为球磨时间8 h、球磨速度200 r·min−1,过程控制剂为正己烷。Abstract: Ti–15Mg composites were prepared by ball milling, cold pressing, and microwave heating sintering. The effects of ball milling parameters on the properties of the Ti–15Mg mixed powders and the mechanical properties of the sintered composites were studied. The results show that, the average particle size of the mixed powders decreases significantly with the extension of the milling time at the ball milling speed of 200 r·min−1 for 8~10 h, the particle size distribution gradually concentrates in the range of 10~45 μm, and the sphericity of the powders increases. In the process of long-time ball milling, the soft Mg particles are subjected to the strong impact and ground, eventually leading to the soft Mg particles wrapped in the brittle Ti particles. After ball milling for 8 h, there are no obvious oxidations in the mixed powders. The distribution of Ti and Mg powders in the mixed powders are relatively uniform, and the mechanical properties of the composites are relatively excellent, which meets the requirements of medical materials. At low milling speed, the increase of milling speed can not lead to the significant change in the powder’s properties and the sintered composite properties. The optimal ball milling parameters are obtained as the ball milling time of 8 h and the milling speed of 200 r·min−1 with n-hexane as the process control agent.
-
Key words:
- mechanical milling /
- medical metal materials /
- Ti–Mg composites /
- mechanical properties
-
表 1 球磨过程中实验参数
Table 1. Experimental parameters during the ball milling
球料比 过程控制剂 球磨时间 / h 球磨转速 / (r·min−1) 10:1 正己烷 6 200 8 200 10 200 6 100 表 2 不同球磨时间下混合粉末的粉末收回率
Table 2. Powder recovery of the mixed powders under the different ball milling parameters
球磨时间 / h 球磨转速 / (r·min−1) 粉末收回率 / % 6 200 94.13 8 200 85.38 10 200 60.48 表 3 不同球磨转速球磨6 h后混合粉末的粉末收回率
Table 3. Powder recovery rate of the mixed powders after ball milling for 6 h with different ball milling speeds
球磨转速 / (r·min−1) 粉末收回率 / % 200 94.13 100 96.67 -
[1] Liu J Q, Liu J, Tang Y J, et al. Research progress in titanium alloy in the field of orthopaedic implants. J Mater Eng, 2021, 49(8): 11 doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2020.000380刘剑桥, 刘佳, 唐毓金, 等. 钛合金在骨科植入领域的研究进展. 材料工程, 2021, 49(8): 11 doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2020.000380 [2] Yu Z T, Yu S, Cheng J, et al. Development and application of novel biomedical titanium alloy materials. Acta Metall Sinica, 2017, 53(10): 1238 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00288于振涛, 余森, 程军, 等. 新型医用钛合金材料的研发和应用现状. 金属学报, 2017, 53(10): 1238 doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00288 [3] Liu F, Zhou C K, Liu Y. Effect of milling process on properties of Ti/HA biomedical composites. Powder Metall Technol, 2005, 23(2): 116 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2005.02.009刘芳, 周科朝, 刘咏. 原始粉料的球磨工艺对Ti/HA生物复合材料性能的影响. 粉末冶金技术, 2005, 23(2): 116 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-3784.2005.02.009 [4] Xia P Z, Xu Y, Zhao S T, et al. Research progress of preparation technology of Ti–Mg composite materials. Titanium Ind Prog, 2021, 38(3): 41夏朋昭, 许莹, 赵思坛, 等. Ti–Mg复合材料制备技术研究进展. 钛工业进展, 2021, 38(3): 41 [5] Tian Y Q, Zhao G Z, Liu Y, et al. Research progress in degradation behavior of biodegradable medical Mg-based alloys in vivo and in vitro. J Mater Eng, 2021, 49(5): 24 doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2020.000338田亚强, 赵冠璋, 刘芸, 等. 生物可降解医用镁合金体内外降解行为研究进展. 材料工程, 2021, 49(5): 24 doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2020.000338 [6] Ouyang S H, Huang Q L, Liu Y, et al. Powder metallurgical Ti–Mg metal-metal composites facilitate osteoconduction and osseointegration for orthopedic application. Bioact Mater, 2019, 4(1): 37 [7] Zhang J L. Preparation and Micro-Arc Oxidation Modification of the Microwave Sintered Ti–Mg Composites [Dissertation]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2019张金龙. 医用Ti–Mg复合材料的微波烧结制备及表面微弧氧化改性研究 [学位论文]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2019 [8] Wang Q. Degradation Behavior of Biomedical Porous Ti–Mg Composites Prepared by Microwave Sintered [Dissertation]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2016王巧. 生物医用多孔Ti–Mg复合材料的微波烧结制备及降解行为研究[学位论文]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2016 [9] Jiang S. Design, Fabrication and Characterization of Bicontinuous Titanium-Magnesium Composites [Dissertation]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017姜山. 双连续钛–镁复合材料设计制备与表征[学位论文]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017 [10] Jiang G F, Wang C L, Li Q Y, et al. Porous titanium with entangled structure filled with biodegradable magnesium for potential biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng C, 2015, 47: 142 doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2014.11.014 [11] Li Q Y, Jiang G F, Wang C L, et al. Mechanical degradation of porous titanium with entangled structure filled with biodegradable magnesium in Hanks’ solution. Mater Sci Eng C, 2015, 57: 349 doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.08.008 [12] Esen Z, Dikici B, Duygulu O, et al. Titanium-magnesium based composites: Mechanical properties and invitro corrosion response in Ringer's solution. Mater Sci Eng A, 2013, 573: 119 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2013.02.040 [13] Kumar A, Pandey P M. Study of the influence of microwave sintering parameters on the mechanical behaviour of magnesium-based metal matrix composite. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part C, 2021, 235(13): 2416 doi: 10.1177/0954406220951236 [14] Chen Q. Fabrication and Property of Aluminum Matrix Composites Reinforced by High Entropy Alloy [Dissertation]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2016陈奇. 高熵合金增强铝基复合材料的制备及性能研究[学位论文]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2016 [15] Wang Y Q. Preparation and Properties of Porous Ti–Mg Matrix Bio-Composites with Low Elastic Modulus [Dissertation]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010王月勤. 低模量多孔Ti–Mg系生物复合材料的制备与性能研究[学位论文]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010 [16] Huang P Y. Theory of Power Metallurgy. 2nd Ed. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2004黄培云. 粉末冶金原理. 2版. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2004 [17] Leung Kishev H Π. Handbook of Metal Binary Phase Diagrams. Transl by Guo Q W. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008梁基谢夫 H П. 金属二元系相图手册. 郭青蔚 等译. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008 [18] Cheng M, Liu Y, Wu H, et al. Effects of parameters of high-energy ball-milling on properties of TiH2 and Mg powder. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metal, 2016, 21(4): 626 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.04.017程铭, 刘咏, 吴宏, 等. 高能球磨工艺参数对氢化钛粉和镁粉性能的影响. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2016, 21(4): 626 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2016.04.017 [19] Li Y H, Chen N, Cui H T, et al. Fabrication and characterization of porous Ti–10Cu alloy for biomedical application. J Alloys Compd, 2017, 723: 967 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.06.321 -



 下载:
下载: