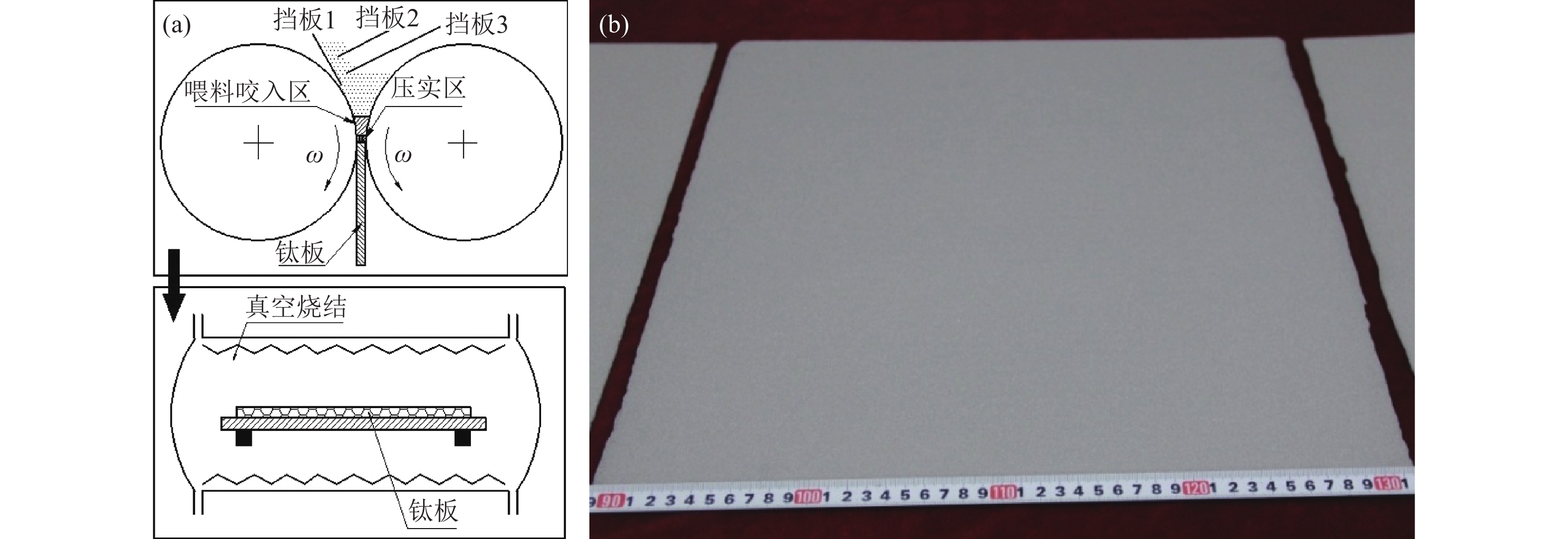
Effect of rolling direction on mechanical properties of powder-rolled porous titanium plates
-
摘要: 以氢化脱氢钛粉为原料,采用粉末轧制和真空烧结工艺制备出两种不同厚度的多孔钛板。利用孔径及孔径分布分析、扫描电镜观察、拉伸实验、三点弯曲实验、剪切强度测试等手段,对垂直于轧制方向和平行于轧制方向的板材力学性能进行了研究,并从孔径分布和烧结颈发育方面对其进行了解释。结果表明,1.96 mm厚的多孔钛板比1.32 mm厚多孔钛板的最大孔径小,且其孔径分布相对均匀;对于厚度相同的粉末轧制多孔钛板,垂直于轧制方向的板材平均抗拉强度比平行于轧制方向的增大25%、弯曲强度增大45%;随着轧制多孔钛板厚度的增加,其抗拉强度、弯曲强度、剪切强度等均显著增大,粉末轧制多孔钛板力学性能的方向差异与轧制致密板材的方向差异完全相反。Abstract: Two types of porous titanium plates with the various thicknesses were prepared by powder rolling followed by vacuum sintering in this study, using the hydrogenated dehydrogenated titanium powders as the raw materials. The mechanical properties of the porous titanium plates either perpendicular or paralleled to the rolling direction were studied by the analysis of pore size and pore size distribution, scanning electron microscopy, tension test, three-point bending test, and shearing strengh test, which were also explained from the aspects of pore size distribution and sintering necking development. The results show that, the maximum pore size of the 1.96 mm-thick porous titanium plate is smaller than that of the 1.32 mm-thick plate, while the pore size distributions are relatively uniform. For the powder-rolled porous titanium plates in the same thickness, the average tensile strength and bending strength of the porous titanium plate perpendicular to the rolling direction are 25% and 45% higher than that paralleled to the rolling direction, respectively. With the thickness increasing, the tensile strength, bending strength, and shear strength all rise significantly. It is found that the effect of rolling direction on the mechanical properties of the powder-rolled porous titanium plates exhibits contrary to that of the densified titanium plates.
-
Key words:
- powder rolling /
- porous titanium plates /
- rolling direction /
- mechanical properties
-
图 5 1.96 mm厚粉末轧制钛板断口形貌:(a)平行于轧制方向;(b)垂直于轧制方向;(c)图5(a)局部放大;(d)图5(b)局部放大
Figure 5. Fracture morphology of the 1.96 mm-thick powder rolled titanium plates: (a) parallel to rolling direction; (b) perpendicular to rolling direction; (c) local magnification of Fig. 5(a); (d) local magnification of Fig. 5(b)
图 6 1.32 mm厚粉末轧制钛板拉伸应力‒应变曲线(a),1.96 mm厚粉末轧制钛板拉伸应力‒应变曲线(b),1.32 mm厚粉末轧制钛板弯曲应力‒应变曲线(c),1.96 mm厚粉末轧制钛板弯曲应力‒应变曲线(d)
Figure 6. Tensile stress-strain curves of the 1.32 mm-thick powder rolled titanium plates (a), the tensile stress-strain curves of the 1.96 mm-thick powder rolled titanium plates (b), the bending stress-strain curves of the 1.32 mm-thick powder rolled titanium plates (c), the bending stress-strain curves of the 1.96 mm-thick powder rolled titanium plates (d)
表 1 氢化脱氢钛粉化学成分(质量分数)
Table 1. Chemical composition of the hydrogenated titanium powders
% C H O N Fe Si Ti 0.013 0.019 0.250 0.014 0.020 0.020 余量 表 2 不同厚度多孔钛板的密度、孔隙率、透气度
Table 2. Density, porosity, and air permeability of the porous titanium plates with various thicknesses
样品厚度 / mm 密度 / (g·cm‒3) 孔隙率 / % 透气度 / [m3∙(h·kPa·m2)‒1] 1.32 3.05±0.01 32.2±0.2 301.30±17.60 1.96 3.17±0.05 29.5±1.2 171.66±6.30 表 3 不同厚度多孔钛板的抗拉强度和抗弯强度
Table 3. Tensile strength and flexural strength of the porous titanium plates with various thickness
样品厚度 / mm 抗拉强度 / MPa 拉伸应变 / % 抗弯强度 / MPa 弯曲应变/ % 1.32(PX) 58.7±3.8 1.3±0.1 88.8±7.6 1.4±0.2 1.32(CZ) 78.7±2.4 1.6±0.1 134.5±15.5 1.6±0.1 1.96(PX) 76.4±4.2 1.7±0.2 130.8±22.2 1.5±0.3 1.96(CZ) 106.4±3.8 3.5±0.4 191.2±11.5 1.8±0.1 表 4 不同厚度多孔钛板的剪切强度
Table 4. Shear strength of the porous titanium plates with various thickness
样品厚度 / mm 剪切应力 / MPa 剪切应变 / % 1.32 9.90±0.70 27.05±1.06 1.96 13.50±0.85 28.37±3.15 -
[1] Huang P Y. Theory of Power Metallurgy. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1997黄培云. 粉末冶金原理. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1997 [2] Zhou Z D. Powder rolling. Powder Metall Ind, 2001, 11(1): 36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2001.01.007周志德. 金属粉末轧制. 粉末冶金工业, 2001, 11(1): 36 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2001.01.007 [3] Sun C F. 200 Powder mill and its application. Powder Metall Technol, 1990, 8(3): 139宋春福. 200粉末轧机及其应用. 粉末冶金技术, 1990, 8(3): 139 [4] Govender A, Bemont C, Chikosha S. Sintering high green density direct powder rolled titanium strips in argon atmosphere. Metals, 2021, 11(6): 936 doi: 10.3390/met11060936 [5] Kunene K, Bemont C P, Cornish L A, et al. The influence of direct powder rolling parameters on the properties of aluminium strip. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng, 2021, 1147(1): 012017 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/1147/1/012017 [6] Akihide H, Natsuki Y, Isao N, et al. Production of anisotropic Sm‒Fe‒N magnet sheets by modified powder rolling. Mater Lett, 2021, 294: 129815 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.129815 [7] Tang H P, Tan P, Xi Z P, et al. Research progress of sintered porous metal. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2006, 35(Suppl 2): 428汤慧萍, 谈萍, 奚正平, 等. 烧结金属多孔材料研究进展. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2006, 35(增刊2): 428 [8] Jia C C, Jin C H. Powder metallurgy porous materials. Met World, 2013, 4(1): 10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6826.2013.01.05贾成厂, 金成海. 粉末冶金多孔材料. 金属世界, 2013, 4(1): 10 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6826.2013.01.05 [9] Luo X, Wu M, Fang C, et al. The current status and development of semi-solid powder forming (SPF). JOM, 2019, 71(12): 4349 doi: 10.1007/s11837-019-03419-6 [10] Mothopeng N, Maledi N, Maminza M, et al. A comparative corrosion study of titanium strips produced by wrought and direct powder rolling processes. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng, 2018, 430: 012041 doi: 10.1088/1757-899X/430/1/012041 [11] Zuo B Q, Ding W H, He W J, et al. Study on rolling process of titanium powder. Powder Metall Ind, 2019, 29(3): 13左碧强, 丁文红, 贺文健, 等. 钛粉轧制成型工艺研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2019, 29(3): 13 [12] Zhao S Y, Tan P, Li G Z, et al. Fabrication and tensile properties of large-scale porous Ti sheet by powder rolling. Tanium Ind Prog, 2021, 38(2): 20赵少阳, 谈萍, 李广忠, 等. 粉末轧制大尺寸多孔钛板制备工艺研究. 钛工业进展, 2021, 38(2): 20 [13] Polyakova M, Golubchik E. Methodology of technological adaptation applied to powder rolling. Key Eng Mater, 2018, 779: 174 doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.779.174 [14] Li Z F, Tan P, Ge Y, et al. Study on the properties of the powder-rolled porous tisheets with different powder sizes. Mater China, 2020, 39(3): 243李增峰, 谈萍, 葛渊, 等. 不同粉末粒度的粉末轧制多孔钛板的孔隙性能研究. 中国材料进展, 2020, 39(3): 243 [15] Sun X D, Zhang J, Xu P M, et al. Static tensile strength of porous titanium plates. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2009, 38(Suppl 1): 443孙旭东, 张健, 许佩敏, 等. 多孔钛板静态抗拉强度的研究. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(增刊1): 443 [16] Liu P S, Fu C, Li T F. Tensile strength of high-porosity metals. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2000, 29(2): 94 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2000.02.006刘培生, 付超, 李铁藩. 高孔率金属材料的抗拉强度. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2000, 29(2): 94 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2000.02.006 [17] Zhao S Y, Tan P, Chen G, et al. Fabrication and tensile properties of large-scale porous Ti sheet by powder rolling. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2015, 20(5): 753 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2015.05.014赵少阳, 谈萍, 陈刚, 等. 大规格粉末轧制多孔钛板的制备及拉伸性能研究. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2015, 20(5): 753 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2015.05.014 [18] Yang B J, Wang Q B, Tang H P, et al. The relationship between rolling force and pore properties of porous stainless steel plate. Chin Mater Sci Technol Equip, 2014, 10(6): 47杨保军, 汪强兵, 汤慧萍, 等. 轧制力与不锈钢多孔板孔隙性能的关系. 中国材料科技与设备, 2014, 10(6): 47 [19] Zang C Y, Tang H P, Wang J Y, et al. Research progress on mechanical properties of sintered metallic porous materials. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2009, 38(Suppl 1): 437臧纯勇, 汤慧萍, 王建永, 等. 烧结金属多孔材料力学性能的研究进展. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2009, 38(增刊1): 437 [20] Hu Z Y, Li M H, Xu W, et al. Fabrication and mechanical properties of porous titanium foam. Titanium Ind Prog, 2010, 27(4): 12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2010.04.004胡紫英, 李美姮, 徐威, 等. 多孔钛的粉末冶金法制备及其力学性能研究. 钛工业进展, 2010, 27(4): 12 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2010.04.004 [21] Xi Z P, Tang H P, Wang J Y, et al. Study on the mechanical properties of porous metals. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2007, 36(Suppl 3) : 555奚正平, 汤慧萍, 王建永, 等. 金属多孔材料力学性能的研究. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2007, 36(增刊3): 555 [22] Qiao J C, Xi Z P, Tang H P, et al. Current status of metal porous materials by powder metallurgy technology. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2008, 37(11): 2054 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2008.11.040乔吉超, 奚正平, 汤慧萍, 等. 粉末冶金技术制备金属多孔材料研究进展. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2008, 37(11): 2054 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2008.11.040 [23] Gao J M. Material Mechanics Performance. Wuhan: Wuhan Univeristy of Technoloyg Press, 2007高建明. 材料力学性能. 武汉: 武汉理工大学出版, 2007 [24] Xu P M, Zhang J, Sun X D, et al. Characterization technology of pore structure metallic porous materials. Mater Heat Treat, 2009, 38(12): 50许佩敏, 张健, 孙旭东, 等. 金属多孔材料孔结构表征技术. 材料热处理技术, 2009, 38(12): 50 -




 下载:
下载: