Study on preparation technology of spherical TiAl alloy powders used for additive manufacturing
-
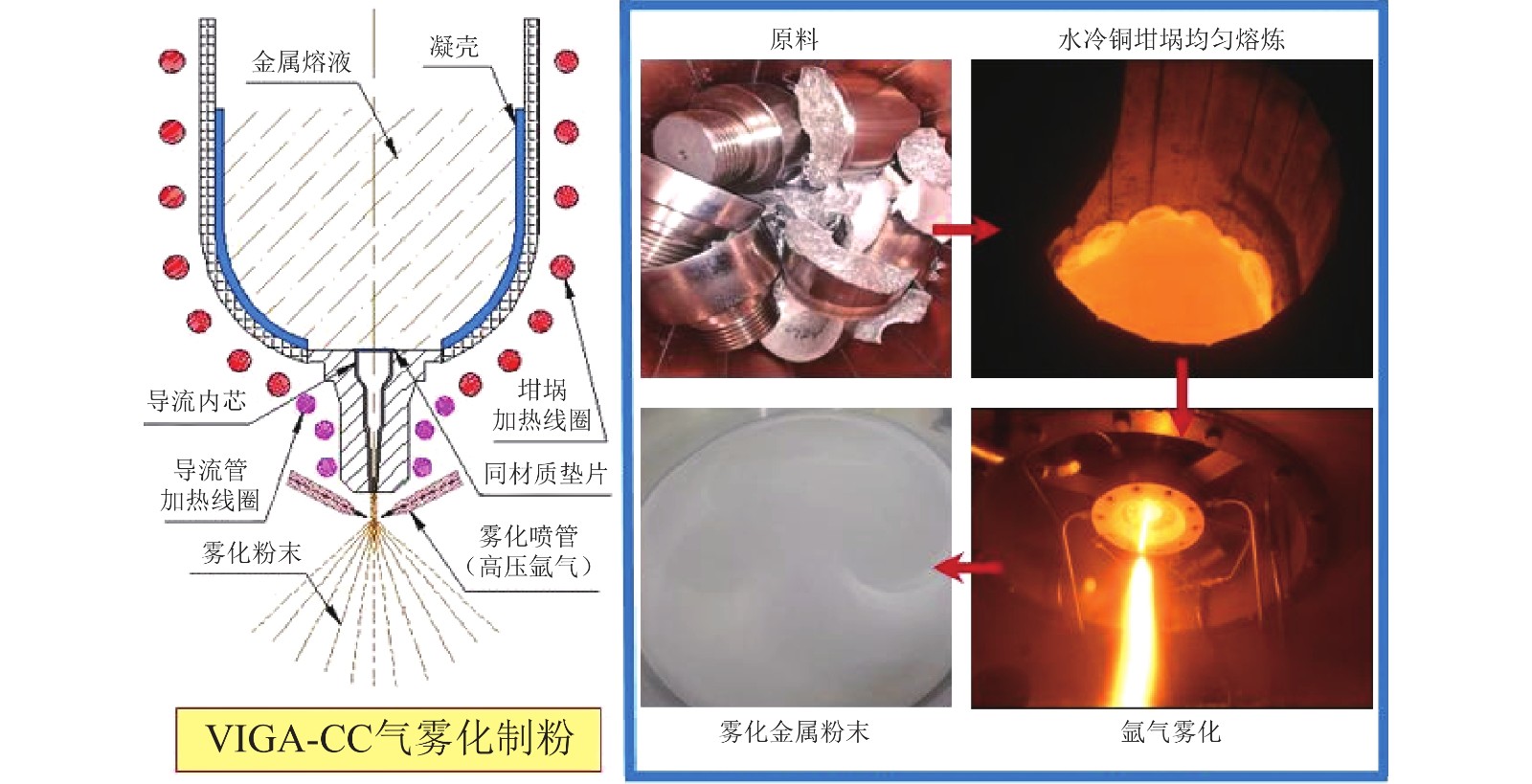
摘要: 以TiAl合金块为原料,利用水冷铜坩埚真空感应熔炼气雾化技术制粉,通过对导流系统和雾化器的优化改进,制备出氧含量低、细粉收率高的球形TiAl合金粉末。结果表明,将导热性好的石墨导流基座和耐冲刷的BN材质陶瓷导流内芯配合使用,既可以保证导流管加热,也可以有效阻止金属熔液的冲刷;螺旋喷管雾化器使雾化点下移,回流区位置远离导流管出口,解决了液柱反流的问题。螺旋分布管能够有效约束雾化气体,动能损失小,能够显著提高细粉收率达20%以上。实验制备的球形TiAl合金粉末流动性为27.7 [s·(50 g)‒1],球形度>90%,粉末氧增量小,适用于3D打印和注射成型工艺用粉。Abstract: Through optimizing and improving the guide system and atomizer, the spherical TiAl alloy powders with low oxygen content and high fine powder yield were prepared by water-cooled copper crucible vacuum induction melting gas atomizing technology, using the TiAl alloy blocks as the raw materials. In the results, the graphite guide base with good thermal conductivity and the BN ceramic guide core with erosion resistance can not only ensure the heating of guide pipe, but also effectively prevent the erosion of molten metal. The spiral nozzle atomizer moves the atomization point downward, and the position of reflux area is far away from the outlet of guide pipe, which solves the problem of liquid column backflow. The spiral distribution tube can effectively restrain the atomized gas, reduce the kinetic energy loss, and significantly improve the yield of fine powders by more than 20%. The fluidity of the spherical TiAl alloy powders prepared in the experiment is 27.7 [s·(50 g)‒1], the sphericity is more than 90%, and the oxygen incremental is small, which are suitable for the 3D printing and injection molding.
-
Key words:
- additive manufacturing /
- gas atomization /
- TiAl alloys /
- diversion inner core /
- atomizing nozzle
-
表 1 改进后VIGA-CC制备的TiAl粉末物理性能
Table 1. Physical properties of the TiAl powders prepared by the modified VIGA-CC
流动性 / [s·(50 g)‒1] 松装密度 / (g·cm‒3) 振实密度 / (g·cm‒3) 球形度 / % 27.7 2.22 2.49 >90 表 2 改进后VIGA-CC所制TiAl粉末的化学成分(质量分数)
Table 2. Chemical composition of the TiAl powders prepared by the modified VIGA-CC
% Al Cr Fe Nb C H N O O(原料) 34.000 2.420 0.100 4.750 0.014 0.001 0.006 0.066 0.060 -
[1] Qin R Y, Zhang G D, Li N, et al. Research progress on additive manufacturing of TiAl-based alloys. J Mech Eng, 2021, 57(8): 115 doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.08.115秦仁耀, 张国栋, 李能, 等. TiAl基合金的增材制造技术研究进展. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(8): 115 doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.08.115 [2] Wang L, Shen C, Zhang C, et al. Research progress and prospects of TiAl alloy produced by additive manufacturing technology. Electr Weld Mach, 2020, 50(4): 1 doi: 10.7512/j.issn.1001-2303.2020.04.01王林, 沈忱, 张弛, 等. 增材制造TiAl合金的研究现状及展望. 电焊机, 2020, 50(4): 1 doi: 10.7512/j.issn.1001-2303.2020.04.01 [3] Zhang G Q, Liu Y F, Liu N, et al. Progress in powder metallurgy TiAl-based intermetallics. Aeronaut Manuf Technol, 2019, 62(22): 38张国庆, 刘玉峰, 刘娜, 等. TiAl金属间化合物粉末冶金工艺研究进展. 航空制造技术, 2019, 62(22): 38 [4] Sun S J. TiAl alloy parts produced by additive manufacturing method will be used in turbine blade of aircraft engine, Powder Metall Ind, 2015, 25(1): 65孙世杰. 增材制造方法生产的TiAl合金零件将被应用于飞机发动机涡轮叶片. 粉末冶金工业, 2015, 25(1): 65 [5] Du Y L, Ou Y Y, Lu X X, et al. Research progress on additive manufacturing of TiAl intermetallic compound. J Xuzhou Inst Technol Nat Sci, 2016, 31(2): 1杜宇雷, 欧园园, 卢晓阳, 等. TiAl金属间化合物的增材制造研究进展. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版), 2016, 31(2): 1 [6] Liu N, Li Z, Yuan H, et al. Fabrication and characterization of gas atomized TiAl alloy powders. J Iron Steel Res, 2011, 23(Suppl 2): 537 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.2011.s2.140刘娜, 李周, 袁华, 等. 气雾化TiAl合金粉末的制备及表征. 钢铁研究学报, 2011, 23(增刊 2): 537 doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1001-0963.2011.s2.140 [7] Liu Y J, Hu Q, Zhao X M, et al. Investigation of centrifugal atomization technology of high fluidity aluminium alloy powder for additive manufacturing. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2021, 50(5): 1767刘英杰, 胡强, 赵新明, 等. 增材制造用高流动性铝合金粉末制备技术研究. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2021, 50(5): 1767 [8] He W W, Tang H P, Chen B K, et al. Study on process and particle size prediction on high-NbTiAl powder produced by PREP. Titanium Ind Prog, 2019, 36(3): 26贺卫卫, 汤慧萍, 陈斌科, 等. PREP法制备高铌TiAl粉末工艺研究及粒度预测. 钛工业进展, 2019, 36(3): 26 [9] Yang X, Xi Z P, Liu Y, et al. Characterization of TiAl powders prepared by plasma rotating electrode processing. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2010, 39(12): 2251杨鑫, 奚正平, 刘咏, 等. 等离子旋转电极法制备钛铝粉末性能表征. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2010, 39(12): 2251 [10] He W W, Tang H P, Liu Y, et al. Preparation of high-temperature TiAI pre-alloyed powder by PREP and its densification microstructure research. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2014, 43(11): 2768贺卫卫, 汤慧萍, 刘咏, 等. PREP法制备高温TiAl预合金粉末及其致密化坯体组织研究. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2014, 43(11): 2768 [11] Yang G Y, Jia W P, Zhao P, et al. Ti‒47Al‒2Nb‒2Cr alloy produced by selective electron beam melting. Rare Met Mater Eng, 2016, 45(7): 1683 doi: 10.1016/S1875-5372(16)30140-0 [12] Li X G, Zhu Q, Shu S, et al. Fine spherical powder production during gas atomization of pressurized melts through melt nozzles with a small inner diameter. Powder Technol, 2019, 356: 759 doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.09.023 [13] Lubanska H. Correction of spray ring data for gas atomization of liquid metals. JOM, 1970, 22: 45 [14] Dong H Q, Guo Z M, Mao X M, et al. Prospect of development trend of melting technology of titanium and/or its alloys with high efficiency and low energy consumption. Mater Rev, 2008, 22(5): 68 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2008.05.017董和泉, 国子明, 毛协民, 等. 低能耗节约型钛及钛合金熔炼技术的发展趋势. 材料导报, 2008, 22(5): 68 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-023X.2008.05.017 [15] Chen Y C, Han J C, Xiao S L, et al. Research progress of rare earth yttrium application in γ-TiAl based alloy and precision thermal forming. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2014, 24(5): 1241陈玉勇, 韩建超, 肖树龙, 等. 稀土Y在γ-TiAl基合金及其精密热成形中应用的研究进展. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(5): 1241 [16] Kostov A, Friedrich B. Predicting thermodynamic stability of crucible oxides in molten titanium and titanium alloys. Compos Mater Sci, 2006, 38(2): 374 doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2006.03.006 [17] Zhao S Y, Chen G, Tan P, et al. Characterization of spherical TC4 powders by gas atomization and its interstitial elemental control. Chin J Nonferrous Met, 2016, 26(5): 980赵少阳, 陈刚, 谈萍, 等. 球形TC4粉末的气雾化制备、表征及间隙元素控制. 中国有色金属学报, 2016, 26(5): 980 [18] Sadrnezhaad S K, Raz S B. Interaction between refractory crucible materials and the melted NiTi shape-memory alloy. Metall Mater Trans B, 2005, 36: 395 doi: 10.1007/s11663-005-0068-2 [19] Kartavykh A V, Tcherdyntsev V V, Zollinger J. TiAl‒Nb melt interaction with AlN refractory crucibles. Mater Chem Phys, 2009, 116(1): 300 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.03.032 [20] Kartavykh A V, Cherdyntsev V V. Chemical compatibility of a TiAl‒Nb melt with oxygen-free crucible ceramics made of aluminum nitride. Russ Metall, 2008, 6: 491 [21] Kartavykh A V, Tcherdyntsev V V, Zollinger J. TiAl‒Nb melt interaction with pyrolytic boron nitride crucibles. Mater Chem Phys, 2010, 119(3): 347 doi: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2009.09.021 [22] Lee E S, Ahn S. Solidification progress and heat transfer analysis of GAS-atomized alloy droplets during spray forming. Acta Metall Mater, 1994, 42(9): 3231 doi: 10.1016/0956-7151(94)90421-9 -




 下载:
下载: