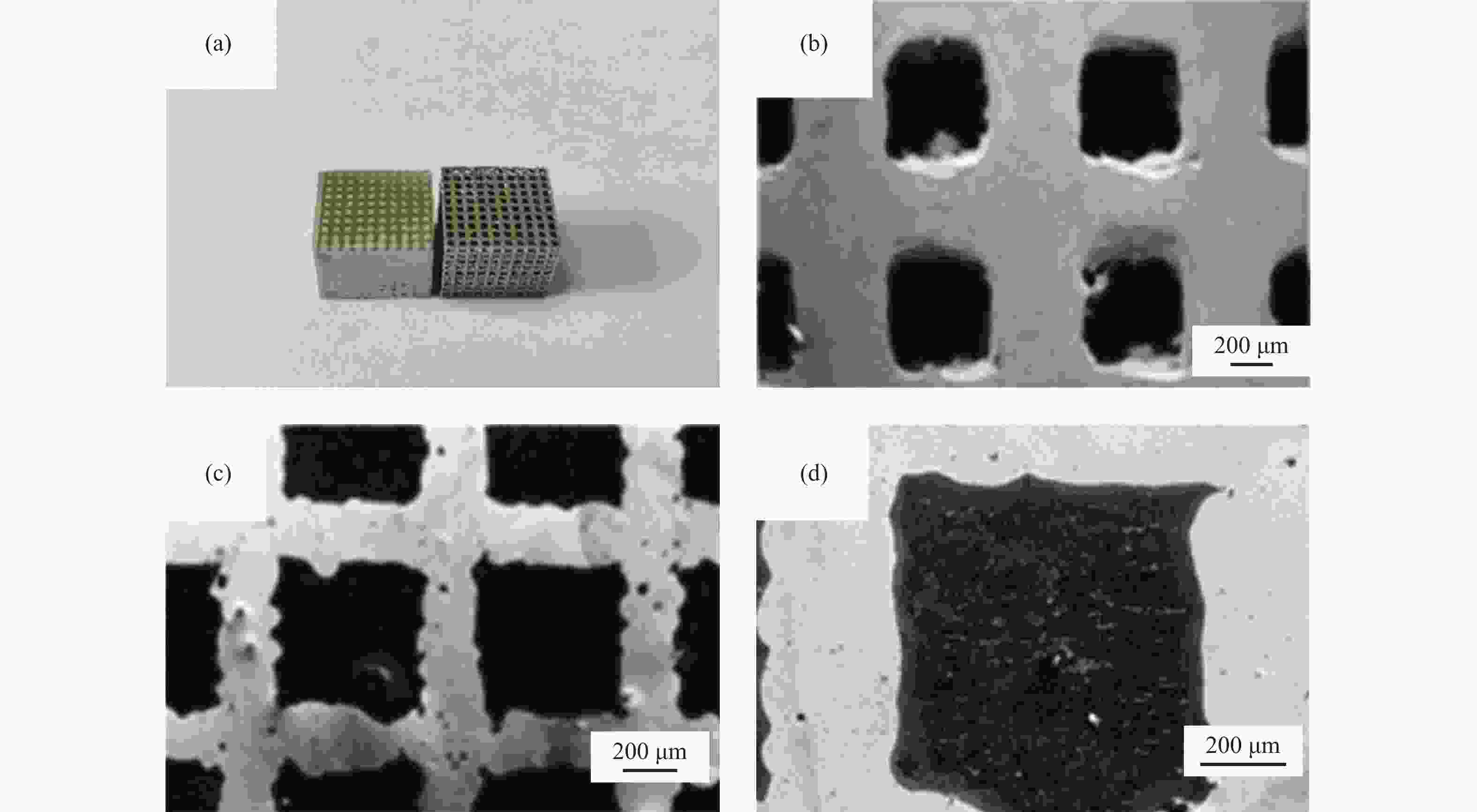
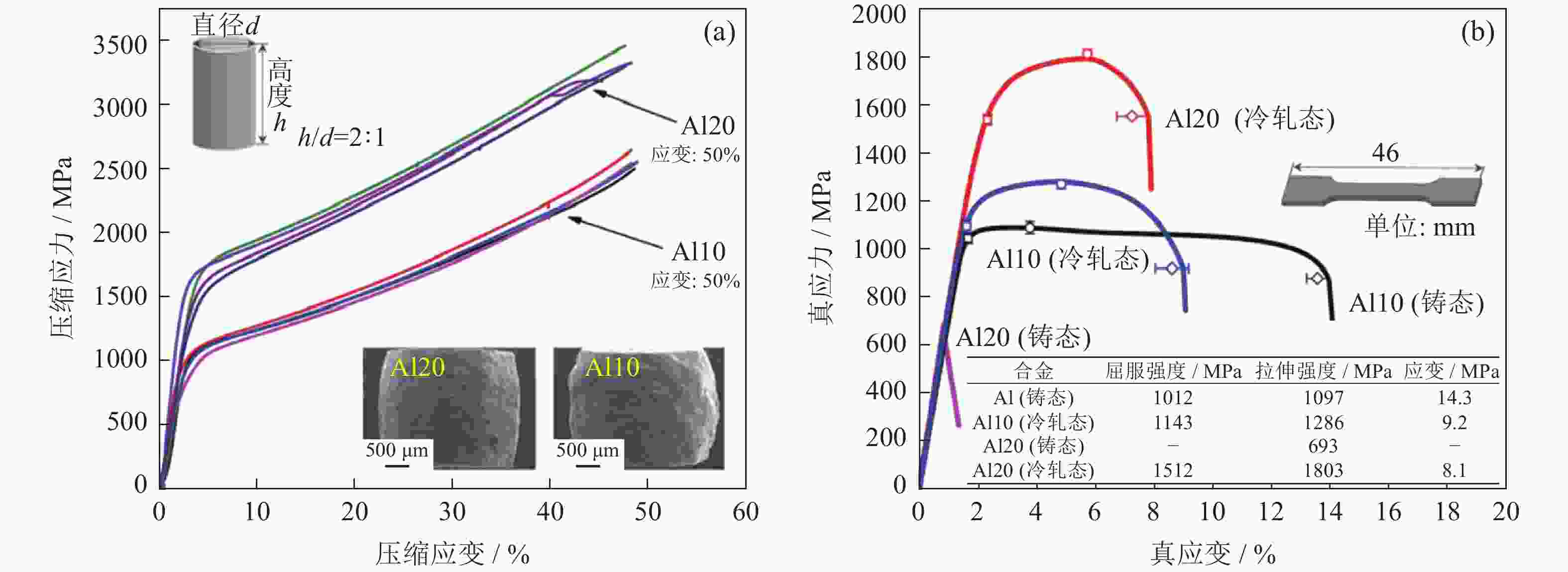
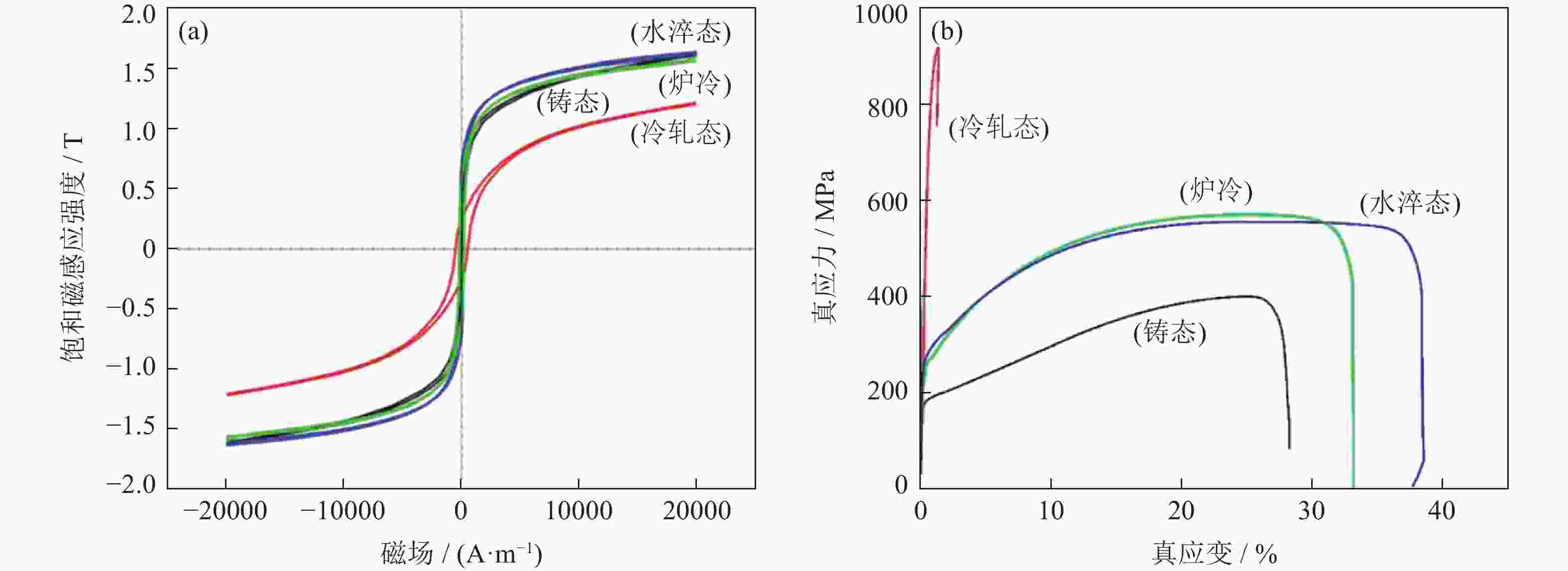
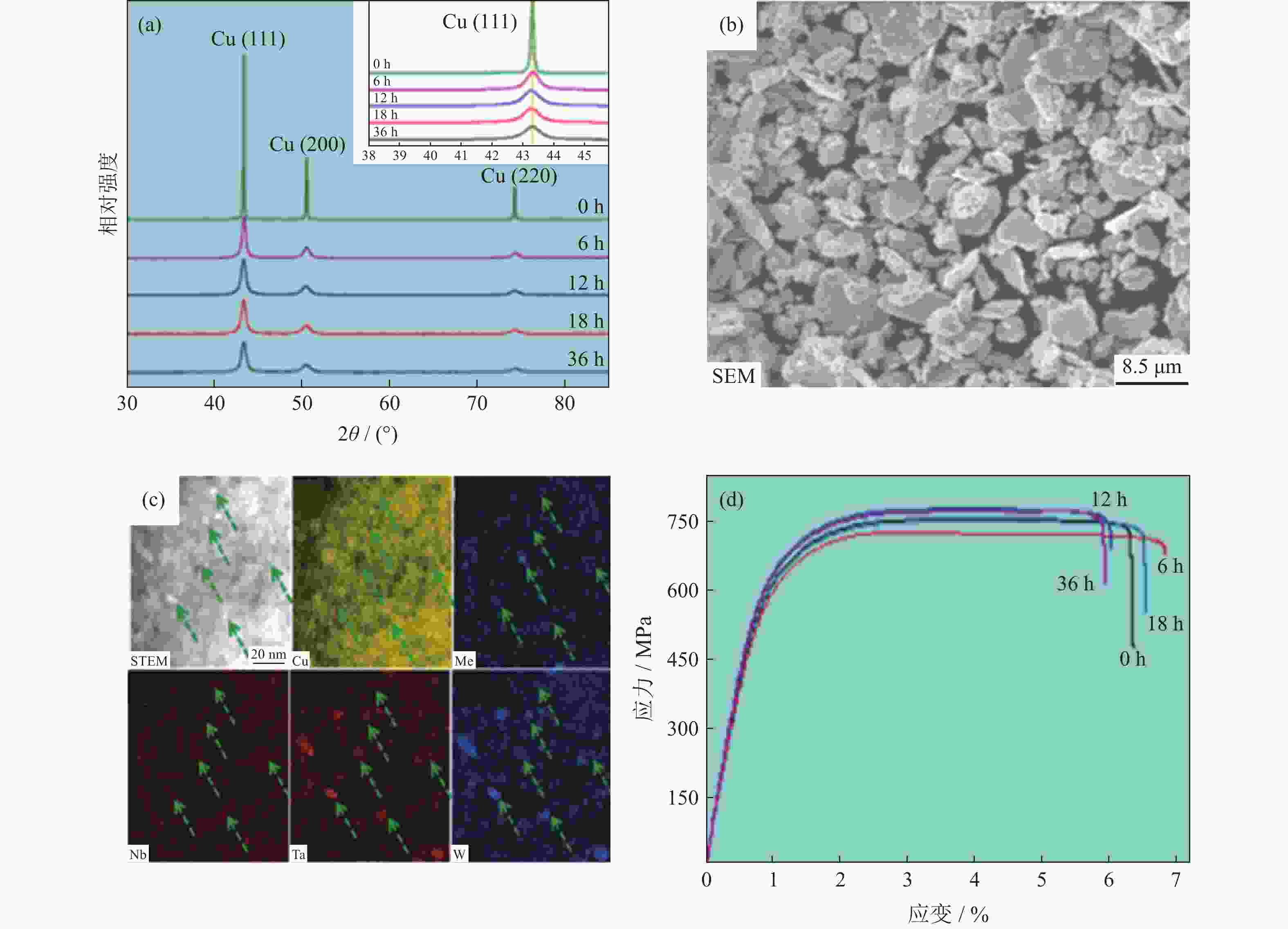
| [1] |
Tsai M H, Yeh J W. High-entropy alloys: a critical review. Mater Res Lett, 2014, 2(3): 107 doi: 10.1080/21663831.2014.912690
|
| [2] |
Ye Y F, Wang Q, Lu J, et al. High-entropy alloy: challenges and prospects. Mater Today, 2016, 19(6): 349 doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2015.11.026
|
| [3] |
Zhang Y, Zuo T T, Tang Z, et al. Microstructures and properties of high-entropy alloys. Prog Mater Sci, 2014, 61: 1 doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2013.10.001
|
| [4] |
Zhang W R, Liaw P K, Zhang Y. Science and technology in high-entropy alloys. Sci China Mater, 2018, 61(1): 2 doi: 10.1007/s40843-017-9195-8
|
| [5] |
Lu Y P, Dong Y, Guo S, et al. A promising new class of high-temperature alloys: eutectic high-entropy alloys. Sci Rep, 2014, 4: 6200
|
| [6] |
Lu Y P, Gao X Z, Jiang L, et al. Directly cast bulk eutectic and near-eutectic high entropy alloys with balanced strength and ductility in a wide temperature range. Acta Mater, 2017, 124: 143 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.11.016
|
| [7] |
Anand Sekhar R, Samal S, Nayan N, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Ti–Al–Ni–Co–Fe based high entropy alloys prepared by powder metallurgy route. J Alloys Compd, 2019, 787: 123 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.02.083
|
| [8] |
Pan J Y, Dai T, Lu T, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Nb25Mo25Ta25W25 and Ti8Nb23Mo23Ta23W23 high entropy alloys prepared by mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. Mater Sci Eng A, 2018, 738: 362 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.09.089
|
| [9] |
Tang Z, Senkov O N, Parish C M, et al. Tensile ductility of an AlCoCrFeNi multi-phase high-entropy alloy through hot isostatic pressing (HIP) and homogenization. Mater Sci Eng A, 2015, 647: 229 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.08.078
|
| [10] |
Chen S Y, Tong Y, Liaw P K. Additive manufacturing of high-entropy alloys: a review. Entropy (Basel), 2018, 20(12): 937 doi: 10.3390/e20120937
|
| [11] |
Luo S C, Zhao C Y, Su Y, et al. Selective laser melting of dual phase AlCrCuFeNix high entropy alloys: formability, heterogeneous microstructures and deformation mechanisms. Addit Manuf, 2020, 31: 100925
|
| [12] |
Wang Y, Li R D, Niu P D, et al. Microstructures and properties of equimolar AlCoCrCuFeNi high-entropy alloy additively manufactured by selective laser melting. Intermetallics, 2020, 120: 106746 doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2020.106746
|
| [13] |
Dhanaraj P S, Rathinasuriyan C. Optimization of fiber laser welding parameters for high strength aluminium alloy AA7075-T6. Mater Today Proc, 2021, 52: 283
|
| [14] |
Zhang Q H, Li J G, Jiang K, et al. Gradient structure induced simultaneous enhancement of strength and ductility in AZ31 Mg alloy with twin-twin interactions. J Magnesium Alloys, 2021, 10: 014
|
| [15] |
Li Z M, Pradeep K G, Deng Y, et al. Metastable high-entropy dual-phase alloys overcome the strength-ductility trade-off. Nature, 2016, 534(7606): 227 doi: 10.1038/nature17981
|
| [16] |
Lei Z F, Liu X J, Wu Y, et al. Enhanced strength and ductility in a high-entropy alloy via ordered oxygen complexes. Nature, 2018, 563(7732): 546 doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0685-y
|
| [17] |
Pan Q S, Zhang L X, Feng R, et al. Gradient-cell-structured high-entropy alloy with exceptional strength and ductility. Science, 2021, 374(6570): 984 doi: 10.1126/science.abj8114
|
| [18] |
Shi P J, Li R G, Li Y, et al. Hierarchical crack buffering triples ductility in eutectic herringbone high-entropy alloys. Science, 2021, 373(6557): 912 doi: 10.1126/science.abf6986
|
| [19] |
Yan X H, Liaw P K, Zhang Y. Ultrastrong and ductile BCC high-entropy alloys with low-density via dislocation regulation and nanoprecipitates. J Mater Sci Technol, 2022, 110: 109 doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2021.08.034
|
| [20] |
Chaudhary V, Mantri S A, Ramanujan R V, et al. Additive manufacturing of magnetic materials. Prog Mater Sci, 2020, 114: 100688 doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2020.100688
|
| [21] |
Zhang Y, Zuo T T, Cheng Y Q, et al. High-entropy alloys with high saturation magnetization, electrical resistivity and malleability. Sci Rep, 2013, 3(1): 1
|
| [22] |
Zuo T T, Gao M C, Ouyang L Z, et al. Tailoring magnetic behavior of CoFeMnNix (x=Al, Cr, Ga, and Sn) high entropy alloys by metal doping. Acta Mater, 2017, 130: 10 doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2017.03.013
|
| [23] |
Zhang Y, Zhang M, Li D Y, et al. Compositional design of soft magnetic high entropy alloys by minimizing magnetostriction coefficient in (Fe0.3Co0. 5Ni0. 2)100−x(Al1/3Si2/3)x system. Metals, 2019, 9(3): 382 doi: 10.3390/met9030382
|
| [24] |
Han L L, Rao Z Y, Souza Filho I R, et al. Ultrastrong and ductile soft magnetic high-entropy alloys via coherent ordered nanoprecipitates. Adv Mater, 2021, 33(37): 2102139 doi: 10.1002/adma.202102139
|
| [25] |
Kim H, Ahn J H, Han S Z, et al. Microstructural characterization of cold-drawn Cu–Ni–Si alloy having high strength and high conductivity. J Alloys Compd, 2020, 832: 155059 doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.155059
|
| [26] |
Sun C F, Guo Y C, Yang Z, et al. Microstructurally stable nanocomposite WTaMoNb/Cu prepared by mechanical alloying and hot pressing sintering. Mater Lett, 2022, 306: 130894 doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130894
|
| [27] |
Li Y S, Zhang Y. Light-weight and flexible high entropy alloys // High Entropy Alloys. London:IntechOpen Limited, 2019: 1
|
| [28] |
Li Y S, Liaw P K, Zhang Y. Microstructures and properties of the low-density Al15Zr40Ti28Nb12M(Cr, Mo, Si)5 high-entropy alloys. Metals, 2022, 12(3): 496 doi: 10.3390/met12030496
|
| [29] |
Li R X, Zheng R, Wu Y, et al. Mechanical behaviors and precipitation transformation of the lightweight high-Zn-content Al–Zn–Li–Mg–Cu alloy. Mater Sci Eng:A, 2021, 802: 140637 doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.140637
|
| [30] |
Shao L, Zhang T, Li L, et al. A low-cost lightweight entropic alloy with high strength. J Mater Eng Perform, 2018, 27(12): 6648 doi: 10.1007/s11665-018-3720-0
|



 下载:
下载: