Analysis on thermal debinding kinetics of iron-based powders by warm flow compaction
-
摘要: 采用流动温压工艺,以铁基粉末为原料、石蜡基聚合物为黏结剂成功制备出十字坯试样;在不同热脱脂速率下脱除聚合物黏结剂,利用热重分析(thermogravimetric analysis,TGA)法研究黏结剂在N2气氛下的热脱脂行为,采用微分法计算脱脂过程动力学相关参数,改进脱脂工艺;借助优化后的脱脂工艺对压坯进行脱脂,并在1300℃烧结获得烧结坯,对烧结坯的烧结收缩率、密度分布、微观组织进行研究。结果表明:聚合物黏结剂的脱除共有2个阶段,激活能为31.3~72.7 kJ·mol-1,指前因子为0.96×106~1.14×1010 min-1;脱脂第1阶段的激活能整体上均低于第2阶段的激活能,说明脱脂第1阶段中的低分子组元更易脱除,保证脱脂质量的关键因素是控制第1阶段的升温速率。Abstract: Cross-shaped parts were prepared by flow warm compaction using iron-based powders as raw material and paraffin wax-based polymer as binder, the polymer binder was removed at different debinding rates. The thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) was used to study the thermal debinding behavior of binder under N2 atmosphere, and the kinetic parameters were investigated by derivative thermogravimetric method. The parts prepared by the optimized debinding parameters were sintered at 1300℃, and the shrinkage, density distribution, and microstructures of the sintered parts were studied. Results show that, the thermal debinding processes can be divided into two stages, the activation energy and pre-exponential factor are ranging from 31.3 to 72.7 kJ·mol-1 and 0.96×106 to 1.14×1010 min-1, respectively. The activation energy of stage 1 is lower than that of stage 2, which means that it is easier to remove low molecular polymer binder in stage 1. The key factor of debinding quality is to control the heating rate of stage 1.
-
Keywords:
- warm flow compaction /
- iron-based powders /
- thermal debinding /
- debinding rate /
- kinetic
-
γ基钛铝合金具有高比强度、低密度等优点,在高温结构材料领域受到广泛关注[1–6]。但室温延展性差、高温抗氧化性能不足制约了其在高温结构领域的应用[7‒8],一般通过添加三元或四元合金元素来改善这两方面的不足。钛铝合金氧化膜为多层结构,由不同比例的氧化铝(Al2O3)和金红石(TiO2)非均匀混合物和金红石顶层所构成[9]。虽然这两种氧化物热力学稳定性相似,但Al2O3的生长速率慢于TiO2,而良好的抗氧化性取决于连续Al2O3的生成,因此,可以通过改变氧化层的特性来提高合金的抗氧化性。研究人员进行了大量合金化研究[10],比如在钛铝合金中添加Nb和Cr,虽然Nb和Cr的存在有助于促进连续致密的氧化层的形成,但也存在一些不足,固溶于基体合金中的Cr会降低基体中Al的含量,使合金的抗氧化性下降[11,12]。近年来,研究人员发现,添加微量稀土元素可以提高钛铝合金的高温抗氧化性,稀土元素的加入可以细化晶粒、净化基体、提高氧化膜的附着力,促进Al的选择性氧化[13]。Zhao等[14]研究了Y对Ti–45Al–8Nb在900 ℃高温抗氧化性能的影响,Y的添加降低了氧化膜的厚度并且有效改善了氧化膜与基体的结合力。
稀土元素对改善钛铝合金高温抗氧化性能的研究越来越多,但稀土镱(Yb)、铈(Ce)对钛铝合金高温抗氧化性能的影响和作用机制还鲜有报道。放电等离子烧结技术(spark plasma sintering,SPS)具有升温速度快、烧结时间短、烧结合金相对密度高等优点[15‒16],本文采用放电等离子烧结制备添加微量Yb、Ce元素的Ti–45Al合金,系统研究了在800 ℃时钛铝合金的高温氧化行为以及Yb、Ce元素对钛铝合金抗氧化性能的影响。
1. 实验材料及方法
实验原料为高纯钛粉、铝粉、原子数分数为0.3%的Yb2O3粉末和原子数分数为0.3%的CeO2粉末。将原料粉末在行星球磨机中进行混合球磨,球磨介质为不锈钢球,球料比为3:1,以300 r·min‒1的转速球磨6 h。对球磨得到的粉末进行放电等离子烧结,烧结温度为1100 ℃,压力为30 MPa,保压时间5 min,随炉冷却后得到所需烧结合金。将制备的合金线切割成8 mm×3 mm的圆柱形试样,根据所含元素不同,制备3种合金试样,编号为1#、2#、3#,各试样化学成分见表1。逐次用400~2000目的碳化硅水砂纸磨至光滑,使用乙醇溶液超声波清洗10 min后吹干。高温氧化实验前将所制备的合金试样放入60 ℃烘箱烘干30 min,所用坩埚在850 ℃高温电阻炉中干燥,每30 min称重一次。当坩埚的重量没有进一步变化时,将氧化样品放入坩埚中。静态高温氧化实验在高温电阻炉(KSS-1400郑州)中进行,氧化温度为 800 ℃,样品的加热和冷却速率为4 ℃·min‒1。氧化时间分别为5、10、25、50、100 h,每一氧化时间设置3个样品进行测试,以验证数据的重复性。样品取出后在空气中冷却至室温,用电子天平(精确度0.1 mg)进行称量得到氧化质量增重,进一步得到氧化动力学曲线。
表 1 实验制备试样的化学成分(原子数分数)及相对密度Table 1. Chemical compositions (atomic fraction) and relative density of the samples% 试样编号 化学成分 相对密度 1# Ti–45Al 98.2 2# Ti–45Al–0.3Yb2O3 99.5 3# Ti–45Al–0.3CeO2 93.4 使用阿基米德排水法测量合金试样的相对密度,结果见表1。采用X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction,XRD;D8岛津高级衍射仪)分析合金试样和氧化产物的物相组成。利用扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM;Zeiss Gemini 300显微镜)观察合金试样和氧化实验后氧化层的表面及截面显微形貌。通过金相显微镜观察钛铝合金的金相组织。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 钛铝合金氧化前的组织分析
图1为放电等离子烧结钛铝合金的X射线衍射图谱,图2为合金的显微形貌和金相组织。由图1可知,合金的主要组成相为α2-Ti3Al相和γ-TiAl相。从显微照片可以看出,3种合金的晶粒均为等轴晶,显微组织是由α2+γ片层晶团与等轴γ晶粒混合构成的双态组织。Ti–45Al–0.3Yb2O3/CeO2合金中的稀土元素弥散分布于晶界,达到细化晶粒,强化组织的效果。此外,加入稀土Yb后,合金中的孔洞明显减少,而加入稀土Ce的钛铝合金中的孔洞明显增多,这也是Ti–45Al–0.3CeO2相对密度降低的原因。
图3为放电等离子烧结钛铝合金的电子背散射衍射形貌(electron back-scattered diffraction,EBSD)及合金晶粒尺寸分布。由图3可知,加入稀土元素Yb或Ce使得合金晶粒尺寸得到细化。经统计,Ti‒45Al、Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3和Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2三种合金的平均晶粒尺寸分别为28.46 μm、11.35 μm、13.83 μm,显然,在Ti‒45Al中添加稀土元素,尤其是稀土元素Yb的添加,使得晶粒明显细化。
![]() 图 3 钛铝合金电子背散射衍射形貌和晶粒分布:(a)Ti‒45Al EBSD;(b)Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3 EBSD;(c)Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2 EBSD;(d)Ti‒45Al晶粒分布;(e)Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3晶粒分布;(f)Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2晶粒分布Figure 3. EBSD and grain size distribution of TiAl alloys: (a) Ti‒45Al EBSD; (b) Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3 EBSD; (c) Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2 EBSD; (d) Ti‒45Al grain size distribution; (e) Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3 grain size distribution; (f) Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2 grain size distribution
图 3 钛铝合金电子背散射衍射形貌和晶粒分布:(a)Ti‒45Al EBSD;(b)Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3 EBSD;(c)Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2 EBSD;(d)Ti‒45Al晶粒分布;(e)Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3晶粒分布;(f)Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2晶粒分布Figure 3. EBSD and grain size distribution of TiAl alloys: (a) Ti‒45Al EBSD; (b) Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3 EBSD; (c) Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2 EBSD; (d) Ti‒45Al grain size distribution; (e) Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3 grain size distribution; (f) Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2 grain size distribution2.2 氧化动力学分析
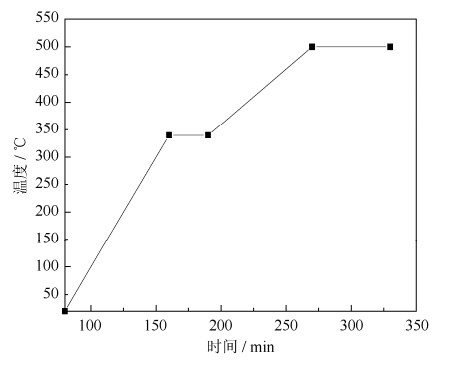
图4为Ti‒45Al、Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3和Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2合金在800 ℃等温氧化100 h的单位面积质量变化和氧化速率。由图4可知,在总时间为100 h的高温氧化过程中,单位面积质量变化呈现出抛物线规律,氧化速率先升高后降低。氧化初期,氧化速率较高,但在氧化时间不断增加的过程中,3种合金的氧化速率都不断降低最后慢慢平稳,这说明在100 h时,钛铝合金的氧化过程已经趋于稳态氧化。氧化时间到达100 h之后,3种合金总增重分别为14.63 g·m‒2、7.02 g·m‒2、8.19 g·m‒2。在抗氧化性能级别评定方面,Ti‒45Al达到2级抗氧化级别,Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3和Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2合金均达到1级完全抗氧化级别。在整个氧化过程中,Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3和Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2合金的质量变化始终小于Ti‒45Al合金。样品的质量变化曲线近似于抛物线规律,说明氧化反应属于扩散控制。一般认为,金属或合金的高温氧化动力学是由阳离子或阴离子通过氧化膜扩散控制的[17‒18]。抛物线定律定义如式(1)所示。
$$ \left( {{\Delta m / S}} \right)_{}^2 = {K_{\text{p}}}t + C $$ (1) 式中:Δm是样品质量变化,g;S是面积,m2;Kp是抛物线速率常数,g2·m‒4·h‒1;t是氧化时间,h;C为常数[18]。
通过质量变化的平方作为时间的函数来分析样品在800 ℃氧化时的氧化动力学,如图5所示,其中R2是拟合系数,表示统计模型与数据结果的吻合程度。R2越大表示拟合结果与数据越一致。Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3在800 ℃时的氧化速率常数Kp最低,为0.54 g2·m‒4·h‒1。
通过图4和图5观察到,钛铝合金在氧化过程中并不完全符合抛物线定律,而是在一定时间内(0~100 h)遵守抛物线定律。众所周知,抛物线定律是基于理想条件下氧化膜或氧化物/金属界面不存在缺陷的假设。事实上,在连续氧化过程中,氧化膜中可能会形成许多孔隙或裂纹,这会导致氧化动力学的偏差[19]。
2.3 氧化产物分析
图6为3种钛铝合金800 ℃高温氧化50 h后得到的氧化产物X射线衍射图谱。由图可知,Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3和Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2两种合金在高温氧化50 h后氧化产物相同,均为TiO2与Al2O3。图谱中并没有发现稀土衍射峰,这可能是由于稀土元素添加量较少。在800 ℃氧化50 h后,3种合金的主要氧化产物均为TiO2。
图7为3种合金在800 ℃高温下氧化100 h后的表面形貌。3种合金表面覆盖着不同尺寸的TiO2颗粒,TiO2颗粒皆具有粗晶柱状晶体的共同特征,而Al2O3颗粒为细晶且形状不规则。Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3表面形貌的特征是在较细的富Al氧化物鳞片上分布着一些特殊的小丘。图7中的高倍显微照片显示了小丘的细节,在添加稀土的条件下,由于Ti离子在Yb和Al氧化物中的溶解度有限,在丘顶形成了钛氧化物。此外,Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3表面氧化皮无明显脱落,Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2表面氧化皮有少量脱落,而Ti‒45Al合金等温氧化100 h后表面氧化皮发生了大面积脱落。3种氧化膜表面皆形成了TiO2型尖晶石,而Yb的添加明显抑制了氧化膜的生长,其表面氧化膜基本由突起的TiO2组成,还未形成一层完整的氧化膜。Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2和Ti‒45Al合金表面TiO2已经生长成为完整的一层,并且由于第二层混合氧化物疏松而发生不同程度的脱落。
为了进一步了解氧化物的结构,采用扫描电镜观察氧化试样截面形貌并进行能谱(energy disperse spectroscope,EDS)分析,结果如图8所示。由图可知,氧化皮为典型的层状结构。Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3氧化膜无明显脱落,平均厚度约为7 μm;Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2表面氧化膜部分脱落,厚度约为12 μm;Ti‒45Al表面氧化膜大面积脱落,脱落后氧化膜厚度约为3 μm。如图8(a)所示,氧化膜开裂脱落后只剩下部分内部混合氧化物层。氧化皮的开裂主要发生在内部混合氧化层中,从而导致外层氧化皮的脱落。添加稀土元素钛铝合金生成的氧化物比Ti‒45Al的氧化物细得多,外层密实、无裂缝,混合内层结构疏松,这可能是多孔层在冷却过程中发生氧化膜剥离的原因。在添加稀土元素的合金中,形成更连续的Al2O3层,氧化膜中不存在较厚的混合氧化层。
研究表明,钛铝合金的氧化大致可分为4个阶段:第1阶段生成TiO2;第2阶段生成Al2O3层以及富Ti层;第3阶段生成TiO2层以及富Al层;第4阶段生成Al2O3层[20]。阶段1的氧化受界面反应控制,阶段2和阶段3的氧化受离子通过氧化膜扩散控制。TiO2/Al2O3混合层的生长主要受氧气向内扩散控制,而TiO2混合层的生长主要受Ti离子向外扩散控制。本文实验材料Ti‒45Al中Ti含量比Al高,Ti活性比Al高,因此在高温氧化时会首先生成TiO2。然而,Ti‒45Al为双相组织,在合金表面Al、Ti的活性以及分布是变化的,难以形成连续大面积的TiO2氧化层。因为氧化速度比较慢,生成TiO2后导致基体一侧的氧化层富Al贫Ti现象相对较弱,最终生成了Al2O3和TiO2混合层,Ti和Al交替并互相促进地发生氧化,氧化层不断向基体方向生长。结合X射线衍射图谱可知,本文中3种合金的氧化层形成过程基本按照此4个阶段的顺序形成。
3. 结论
(1)采用放电等离子烧结制备3种TiAl合金试样,样品的相对密度最高达到99%,实现致密化。
(2)3种TiAl合金在高温空气中保温100 h的氧化动力学曲线均服从抛物线规律,在800 ℃空气中氧化100 h后,Ti‒45Al、Ti‒45Al‒0.3Yb2O3和Ti‒45Al‒0.3CeO2三种合金的质量增重分别为14.63 g·m‒2、7.02 g·m‒2、8.19 g·m‒2,稀土元素Yb或Ce的加入提高了TiAl合金在800 ℃的抗高温氧化性能。
(3)从氧化膜外表面到基体分别由TiO2层、Al2O3+TiO2混合层组成,添加Yb的钛铝合金氧化物尺寸更为细小,结构更为致密,稀土的添加促进了Al的选择性氧化,降低了氧化膜的生长速率,从而提高了TiAl合金的高温抗氧化性。
-
表 1 实验用金属粉末的成分与粒度
Table 1 Composition and particle sizes of the raw powders
粉末 粒度/μm 质量分数/% 水雾化铁粉 ≤147 78.5 羟基铁粉 5 20.0 还原钼粉 ≤75 0.5 石墨粉 ≤75 1.0 表 2 黏结剂组元热解温度和成分
Table 2 Thermal characteristic and composition of binder components
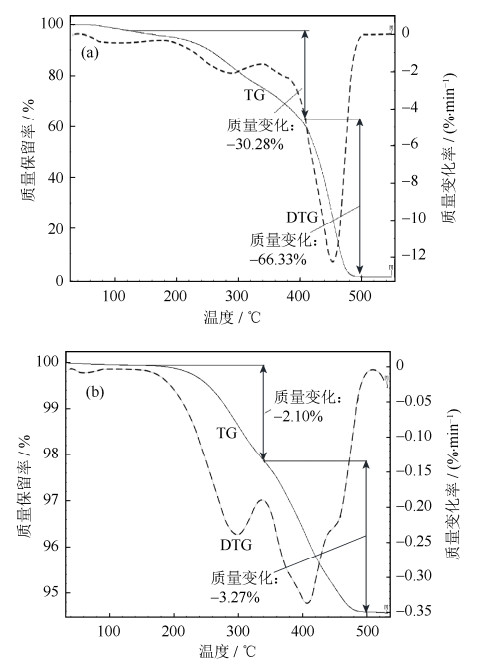
组元 熔点/ ℃ 热分解温度/ ℃ 质量分数/ % 聚酰胺(PA) 170.6 316.6~500.5 65.0 聚乙烯蜡(PE) 113.1 192.3~480.9 17.5 普通石蜡(PW) 64.7 180.1~307.0 17.5 表 3 生坯脱脂过程动力学参数
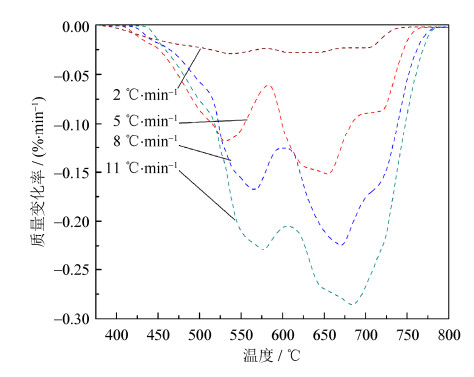
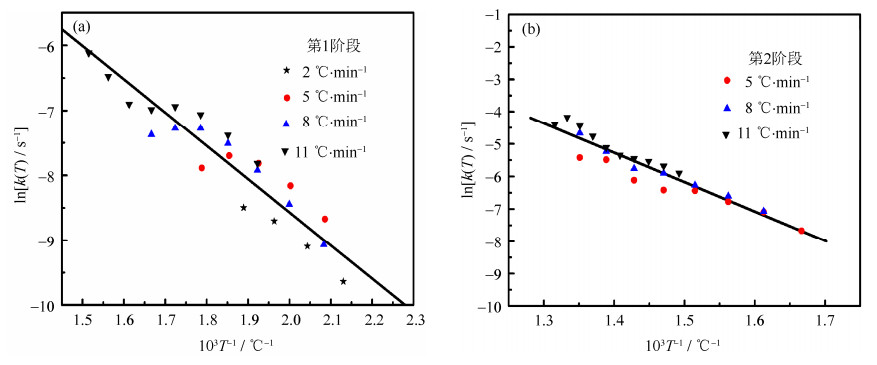
Table 3 Kinetic parameters of green compact with diffeent heating rates
热解阶段 升温速率,β/(℃·min-1) 激活能,Ea/(kJ·mol-1) 指前因子,A / min-1 拟合系数,r2 第1阶段(低温阶段) 2 44.3 5.82×106 0.9954 5 31.3 0.96×106 0.9970 8 34.8 3.23×106 0.9916 11 31.6 1.94×106 0.9954 第2阶段(高温阶段) 5 56.3 1.45×108 0.9914 8 70.2 4.65×109 0.9937 11 72.7 1.14×1010 0.9938 表 4 生坯密度、烧结坯密度和烧结收缩率
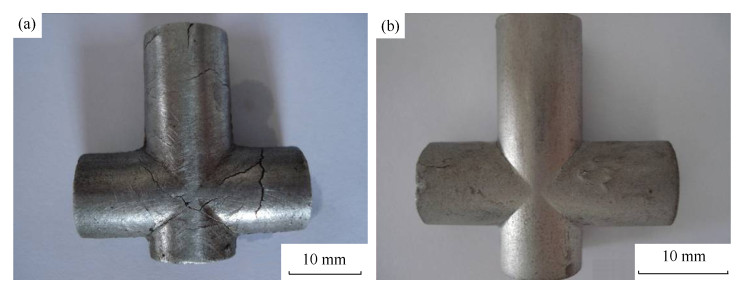
Table 4 Green density, sintered part density, and sintered part shrinkages
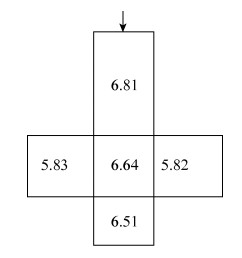
生坯密度/ (g·cm-3) 烧结密度/ (g·cm-3) 烧结收缩率/% 轴向方向 轴向直径 横向方向 横向直径 5.971 6.720 -5.83 -0.27 -6.10 -0.31 -
[1] Sokolowski P, Milbrath A, Vitti D, et al. Industrial performance of a new lubricant for manufacturing PM gears. Met Powder Rep, 2016, 71(3): 180 DOI: 10.1016/j.mprp.2015.12.002
[2] 肖志瑜, 柯美元, 李元元等. 温压工艺最新进展—流动温压技术. 粉末冶金工业, 2002, 12(5): 28 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2002.05.005 Xiao Z Y, Ke M Y, Li Y Y, et al. New development of warm compaction—Warm flow compaction. Powder Metall Ind, 2002, 12(5): 28 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2002.05.005
[3] St-Laurent S, Thomas Y, Azzi L. 粉末冶金零件需要的高性能润滑剂. 粉末冶金技术, 2014, 32(3): 226 http://pmt.ustb.edu.cn/article/id/fmyjjs201403013 St-Laurent S, Thomas Y, Azzi L. High performance lubricants for demanding pm applications. Powder Metall Technol, 2014, 32(3): 226 http://pmt.ustb.edu.cn/article/id/fmyjjs201403013
[4] St-Laurent S, Chagnon F. 用温压制造高密度材料的关键参数. 粉末冶金工业, 2012, 22(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYG201201002.htm St-Laurent S, Chagnon F. Key parameters for warm compaction of high density materials. Powder Metall Ind, 2012, 22(1): 1 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FMYG201201002.htm
[5] 肖志瑜, 张菊红, 邵明, 等. 金属粉末流动温压成形的特点及其技术问题分析. 中国机械工程, 2005, 16(3): 257 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2005.03.020 Xiao Z Y, Zhang J H, Shao M, et al. Characteristics of warm flow compaction forming of metallic powder and its technological problem analysis. China Mech Eng, 2005, 16(3): 257 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2005.03.020
[6] 刘长洋, 季根顺, 孟军虎. 超细316不锈钢粉末注射成形的脱脂工艺. 材料科学与工程学报, 2013, 31(3): 451 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLKX201303028.htm Liu C Y, Ji G S, Meng J H. Debinding process of superfine 316L stainless steel powder preform fabricated by injection molding. J Mater Sci Eng, 2013, 31(3): 451 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CLKX201303028.htm
[7] 赵利刚, 李益民. MIM热脱脂初始阶段行为研究. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2002, 7(3): 175 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2002.03.003 Zhao L G, Li Y M. Thermal debinding behavior of the initial stage in MIM. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2002, 7(3): 175 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2002.03.003
[8] 周时宇, 蔡一湘, 罗铁钢, 等. 钛注射成形用催化脱脂型喂料的制备与性能研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2015, 33(2): 95 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.02.003 Zhou S Y, Cai Y X, Luo T G, et al. Research on preparation and properties of catalytic debinding feedstock for titanium metal injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2015, 33(2): 95 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2015.02.003
[9] 李永, 王兴庆, 韩义林. 粉末注射成形石蜡基成形剂的脱除工艺. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2011, 16(1): 150 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.01.025 Li Y, Wang X Q, Han Y L. Technique of debinding wax-based binder for powder injection molding. Mater Sci Eng Powder Metall, 2011, 16(1): 150 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2011.01.025
[10] 陈慧, 敬小龙, 刘兵, 等. 304不锈钢粉末注射成形研究. 粉末冶金技术, 2016, 34(6): 440 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.06.008 Chen H, Ji X L, Liu B, et al. Catalytic debinding for 304L powder injection molding. Powder Metall Technol, 2016, 34(6): 440 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3784.2016.06.008
[11] 郑军君, 倪东惠, 胡昌旭, 等. 流动温压成形"十"字形零件及其烧结工艺的研究. 粉末冶金工业, 2010, 20(1): 32 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2010.01.006 Zheng J J, Ni D H, Hu C X, et al. A Study on fabrication and sintering process of cross-shaped part formed by warm flow compaction. Powder Metall Ind, 2010, 20(1): 32 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6543.2010.01.006
[12] Rath J, Staudinger G. Cracking reactions of tar from pyrolysis of spruce wood. Fuel, 2001, 80(10): 1379 DOI: 10.1016/S0016-2361(01)00016-3
[13] Enneti R K, Shivashankar T S, Park S J, et al. Master debinding curves for solvent extraction of binders in powder injection molding. Powder Technol, 2012, 228: 14 DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2012.04.027
[14] Jee C S Y, Guo Z X, Stoliarov S I, et al. Experimental and molecular dynamics studies of the thermal decomposition of a polyisobutylene binder. Acta Mater, 2006, 54: 4803 DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2006.06.014
[15] Alshehri S M, Al-Fawaz A, Ahamad T. Thermal kinetic parameters and evolved gas analysis (TG-FTIR-MS) for thiourea-formaldehyde based polymer metal complexes. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis, 2013, 101: 215 DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2013.01.004
[16] 袁海英, 贾成厂, 张新新, 等. 凝胶注模制备的铝铜胚体脱脂过程及动力学. 工程科学学报, 2016, 38(1): 102 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201601014.htm Yuan H Y, Jia C C, Zhang X X, et al. Thermal degradation mechanism and kinetics of aluminum-copper green bodies prepared by gelcasting. Chin J Eng, 2016, 38(1): 102 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKD201601014.htm
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王哲昊,吕绪明. 等离子喷涂技术在工程陶瓷涂层制备中的应用现状及展望. 材料导报. 2024(11): 52-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈开旺,张鹏林,李树旺,牛显明,胡春莲. 莫来石粉末化学镀镍和涂层的高温摩擦学性能. 材料研究学报. 2023(01): 39-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张一帆,王曲,王刚,刘鹏程,张琪,司瑶晨. 黏结剂种类对铝酸镧涂层材料性能的影响. 耐火材料. 2022(02): 123-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张志辉,李明. 316L钢表面超音速火焰喷涂Fe基粉末涂层显微结构及摩擦性能分析. 粉末冶金技术. 2022(04): 351-355+361 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 蔡浩,龚关,梁雅琪,仇秀梅,刘可. 莫来石在醇基铸造涂料中的试验研究. 中国新技术新产品. 2022(21): 26-28+145 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: